Pond Sand Filter (PSF) [孟加拉国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: John Brogan
- 编辑者: Md. Rahmatullah Faruque, Shahid Kamal
- 审查者: Nicole Harari, Hanspeter Liniger, Alexandra Gavilano
FILTER
technologies_550 - 孟加拉国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
22/08/2016
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
There is no land degradation as the PSF pond embankment is surrounded with vegetable products and serves as a source of water. This technology reduces water shortage during disasters like drought or coastal flood.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Pond Sand Filter (PSF) increases flood resilience, providing an alternative source of drinking water during disaster events
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
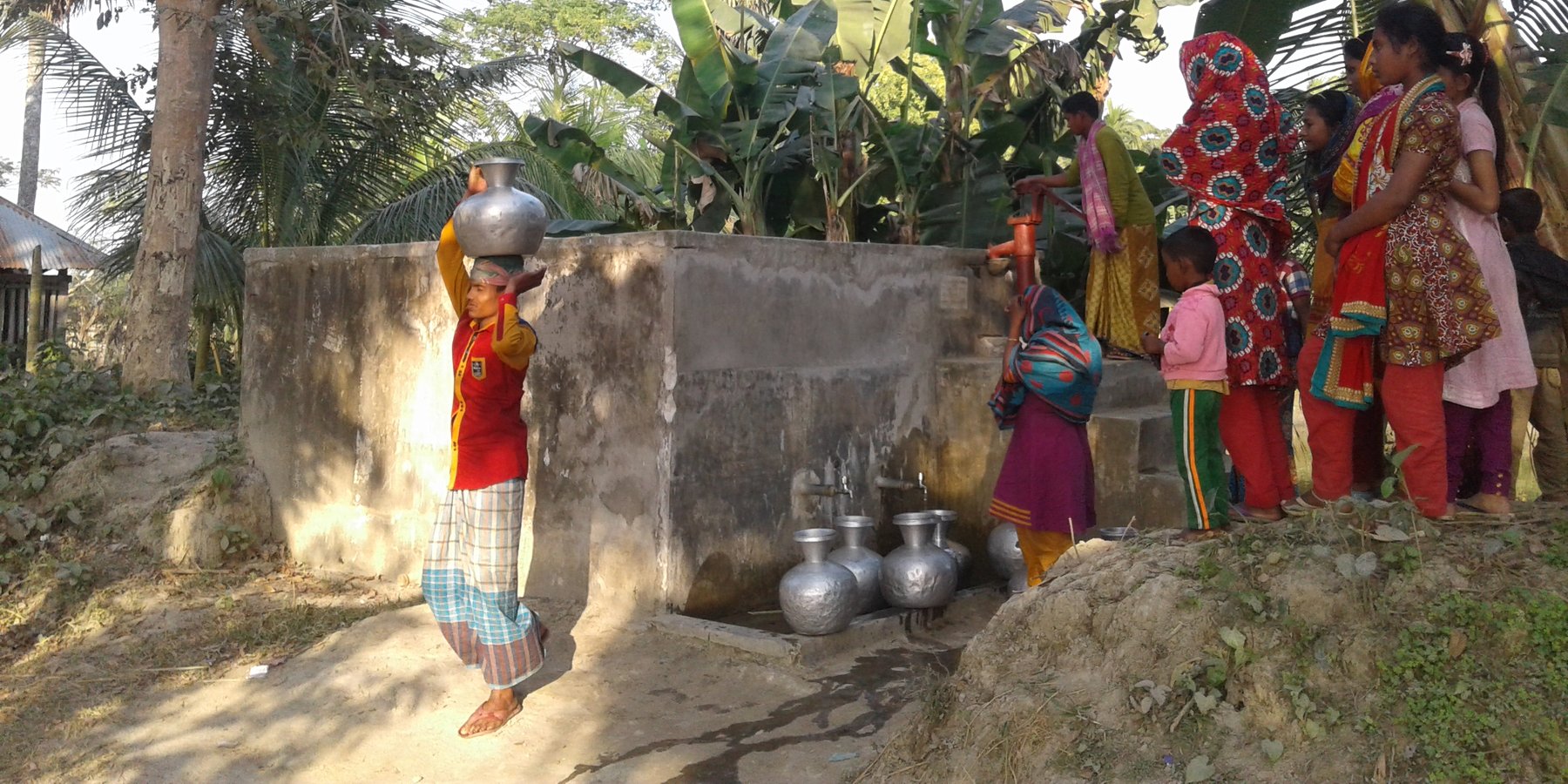
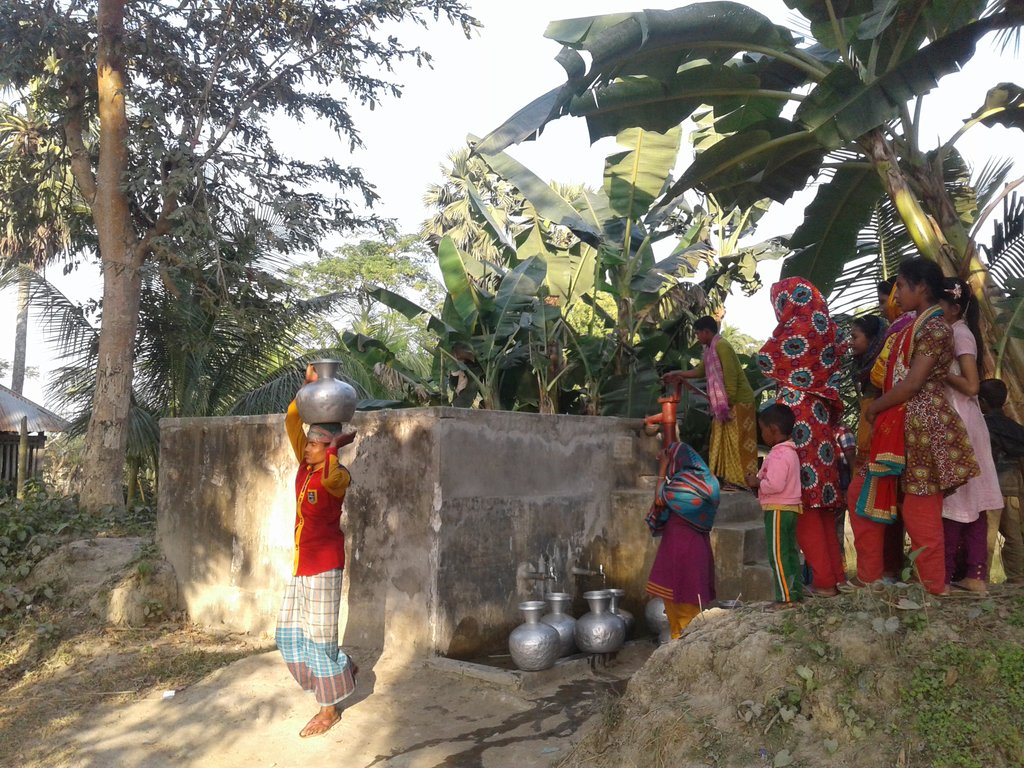
The technology is embedded in a natural environment. Necessary materials include cement, sand, brick, rods, pipes, etc. There are multiple purposes of the technology which filters pond water and supplies drinking water for consummation and cooking. To establish/maintain this technology, we need to form and build capacities of PSF committees, which operate and maintain the PSF, excavate the pond and raise the pond embankment, fence the PSF for protection, open a bank account for smooth operations and establish links with research-based organizations and local government authorities working on improved water management technology. The principal benefit of the technology is that households have access to drinking water close to their home. In addition, it enables cultivating vegetables on the embankment of PSF which can support a balanced nutrition and can generate additional income. There is no noticeable disagreement at community level about the technology because it provides a reliable and alternative source of drinking water especially during disaster event.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
孟加拉国
区域/州/省:
Patharghata, Barguna district in coastal region
有关地点的进一步说明:
Vill: Baratangra, Ward:4, Union: Patharghata Union Parishad
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2016
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

不毛之地
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 不适用
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
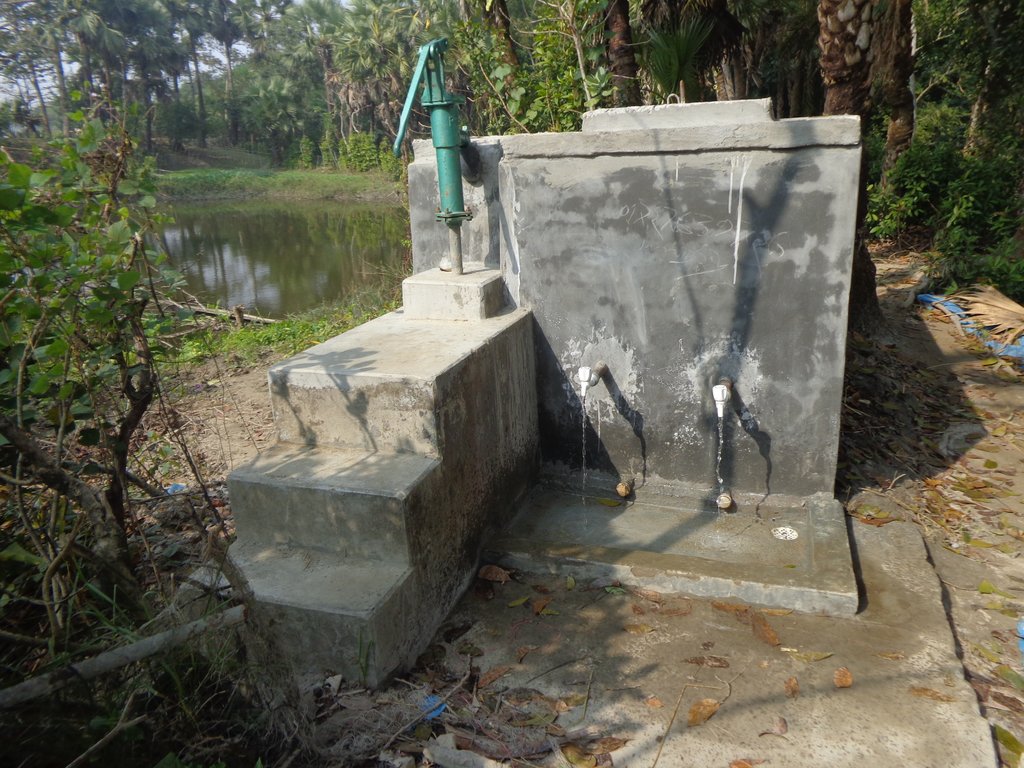
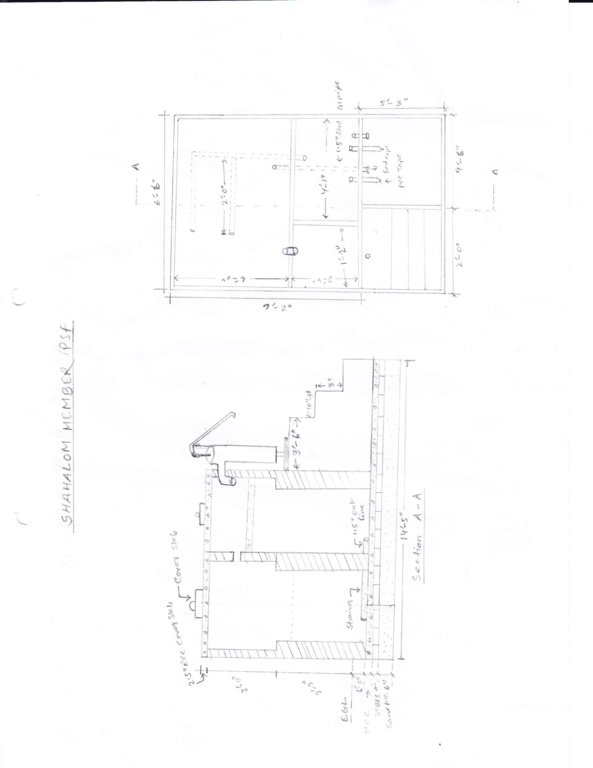
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Height-4 feet 2 inch, Length-14 feet 5 inch, Width-7 feet with 1.5 km vertical interval structure having 0.4 decimal catchment area. The capacity of PSF is 2500 liter water. The construction materials used in rebuilding PSF include brick, sand, brick chips, cement, GI Pipe, water tap and MS Rod.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Pond Sand Filter
指定体积、长度等(如果相关):
average 36.45 meter
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5 $ per day for each labor
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Community consultation for Committee Formation | 管理 | Before onset of rain |
| 2. | Fund raising initiative | 管理 | Before onset of rain |
| 3. | Approval from by Union Parishad | 管理 | Before onset of rain |
| 4. | Needs assessement | 管理 | Before onset of rain |
| 5. | Technician selection for reconstruction | 结构性的 | Before onset of rain |
| 6. | Contribution from PSF committee | 管理 | Before onset of rain |
| 7. | Contribution from Tdh | 管理 | Before onset of rain |
| 8. | Commencement of PSF reconstruction | 结构性的 | Before onset of rain |
| 9. | Excavating | 结构性的 | Before onset of rain |
| 10. | Pond fencing | 结构性的 | Before onset of rain |
| 11. | Pond embankment | 结构性的 | Before onset of rain |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Excavation work | days | 30.0 | 5.0 | 150.0 | 10.0 |
| 设备 | Repairing tools | 1 | 4.0 | 15.0 | 60.0 | |
| 设备 | Tubewell | 1 | 1.0 | 29.0 | 29.0 | 10.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | bleeching | 1 | 0.5 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | ||||||
| 施工材料 | ||||||
| 施工材料 | bricks | pieces | 15.0 | 1.5 | 22.5 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | sand | pieces/bags | 80.0 | 0.5 | 40.0 | 10.0 |
| 其它 | brickchips | pieces | 10.0 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| 其它 | MS rod | pieces | 30.0 | 1.0 | 30.0 | |
| 其它 | Cement | bag | 12.0 | 6.0 | 72.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 415.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The remaining costs bore by the project contribution. It's a mode of cost sharing and developing a culture of belongingness and sustainability.
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repairing | 其它措施 | Before onset of rains |
| 2. | Cleaning | 管理 | Before onset of rains |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | For cleaning | days | 4.0 | 14.0 | 56.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | bleeching powder | bag | 5.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 | |
| 施工材料 | sand | pieces/bags | 80.0 | 1.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Brick chips | pieces | 10.0 | 5.0 | 50.0 | |
| 其它 | Cement | bag | 6.0 | 12.0 | 72.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 268.0 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Comparatively, construction materials costs was reflected as expensive cost.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
www.discoverybangladesh.com
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
SLM之前的数量:
1
SLM之后的数量:
3
注释/具体说明:
The availability of water was very little before setting up such technology
收入和成本
经济差异
SLM之前的数量:
1
SLM之后的数量:
3
社会文化影响
健康状况
SLM之前的数量:
1
SLM之后的数量:
3
注释/具体说明:
Water borne diseases was in epidemic form before setting up PSF technology which was getting gradually decreased.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
SLM之前的数量:
1
SLM之后的数量:
3
注释/具体说明:
The usage of surface water has been promoted significantly as it contains acceptable level of iron.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 好 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 适度 |
注释:
PSF serves as disaster resilient Technology that can well cope with the effects of climate change.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 大于 50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The Technology is useful for supplying drinking water at household level and can meet the nutritional needs through cultivating medicinal plants and vegetables at the pond embankment |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The Technology is conducive for ensuring supply of water for drinking, cooking and irrigation purposes if the community is motivated and understand the impact of PSF when faced with water shortage during dry season and other disaster events. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Every six months, the PSF needs to be taken care of. This requires some maintenance costs that must be deposited every month for smooth operations. PSF DRR fencing is also necessary to protect PSF against animals. | Deposit monthly saving to incur the six monthly maintenance costs as well as create relationship with local research organization to improve the cost-effectiveness of the technology |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Six to seven
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
five
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块