Small Scale Irrigation System for Pasture Production [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: PRISCILLA VIVIAN KYOSABA
- 编辑者: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- 审查者: Nicole Harari, Udo Höggel
Okushukerera ebinyansi byente amazzi
technologies_3434 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Mugisa Edward
0791465941
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
22/01/2018
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
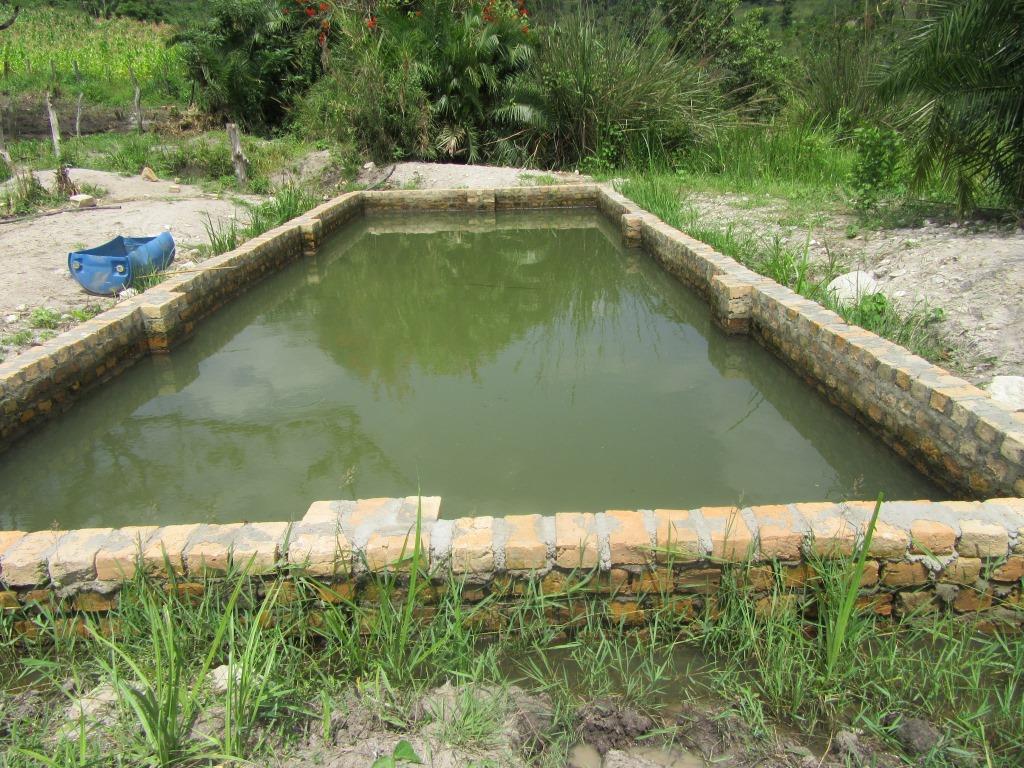
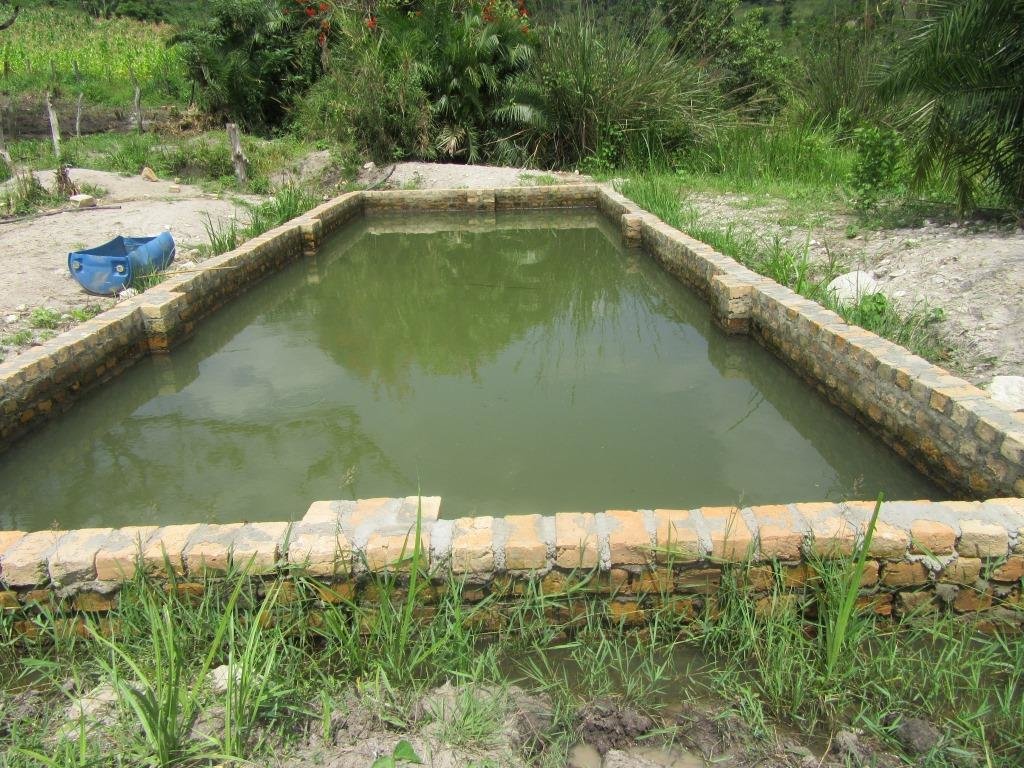
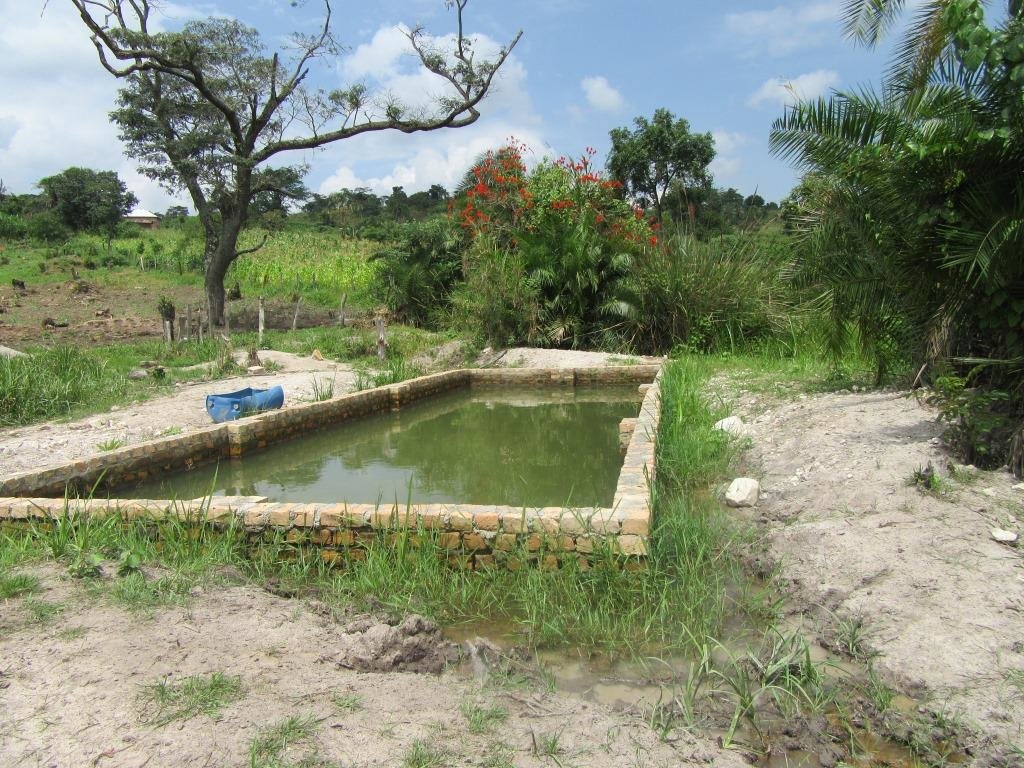
Small scale irrigation system for pasture production. This is practiced by a farmer who effectively utilized a swamp by constructing a relatively small water reservoir for watering pastures during dry season to ensure continuous pasture production all year around.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Small scale irrigation system for pasture production is the artificial supply of water to areas for agricultural use; in this case water is supplied to pasture land. It’s practiced by a cattle farmer in Kyegwemera Village Kyegegwa District in western Uganda who effectively utilized the swamp by constructing a relatively small water reservoir for watering pastures during the dry season to ensure continuous pasture production all year round.
This irrigation project was initiated and partially financed by the local government and is used as training ground for the various farmer groups interested in adoption of the technology; as technical guidance in popularizing farmer-managed smallholder irrigation systems. Also training of district staff members and other stakeholders in irrigation technology, the sustainable utilization and management of wetlands. More so, the monitoring and evaluation progress in irrigation activities in liaison with district specialists also increases development of this technology and its adoption in the district.
With support from local government, the farmer was able to construct the irrigation site to boost pasture production for his 9 dairy cattle grazed on the farm. The irrigation water reservoir has a size of 25 feet long by 10 feet wide of his total land area of 22 acres. The water reservoir has a holding capacity of approx. 25.000 liters.
This system has a small pump with the capacity of 25000 litres/h and is able to irrigate up to 5 hectares. The motorized pump is used to pump water from the swamp into an open water reservoir which is later pumped or supplied to the pastures. The water is also used for drinking for the animals.
From the irrigated fields, fodder yields are stable and reliable to meet production targets hence reduced fluctuations in year-to-year yields and reduced pasture failure during drought. With this system yields from irrigated pastures are expected to increase up to two to three (2-3) time’s higher hence increased pasture yield. In addition, irrigation enhances continuous cultivation due to available irrigation equipment like pumps and other ancillary equipment.
Establishment of the irrigation system cost two million seven hundred seventy thousand shillings only (2,770,000=); for reservoir construction labor, spade, bricks, sand, clay, fuel, servicing frequent pump breakdown, construction cement, water proof cement and generator. The system is simple to install and easy to use. The small-scale irrigation project addresses problems that have been caused by both severe and recurring drought and increasing desertification. However, majority of farmers are illiterate and lack basic knowledge of water requirements, irrigation scheduling, skills in maintaining and operating the pumps. This affects yields, as crops are either over or under-irrigated, leading to wastage of the little available water. Erosion is also a serious problem during the rainy season in addition to continuous cultivation and reduced fertility issues.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
A video for small scale irrigation system
日期:
22/01/2018
位置:
Kyagemerwa Village, Kyegeggwa District
摄影师的名字:
Aine Amon
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Western Region
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kyegegwa District
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2016
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The district local government partially funded the construction of the system to serve as a demo site for the other farmers in the area.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Grazing land
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 湿地保护/管理
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 不适用
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
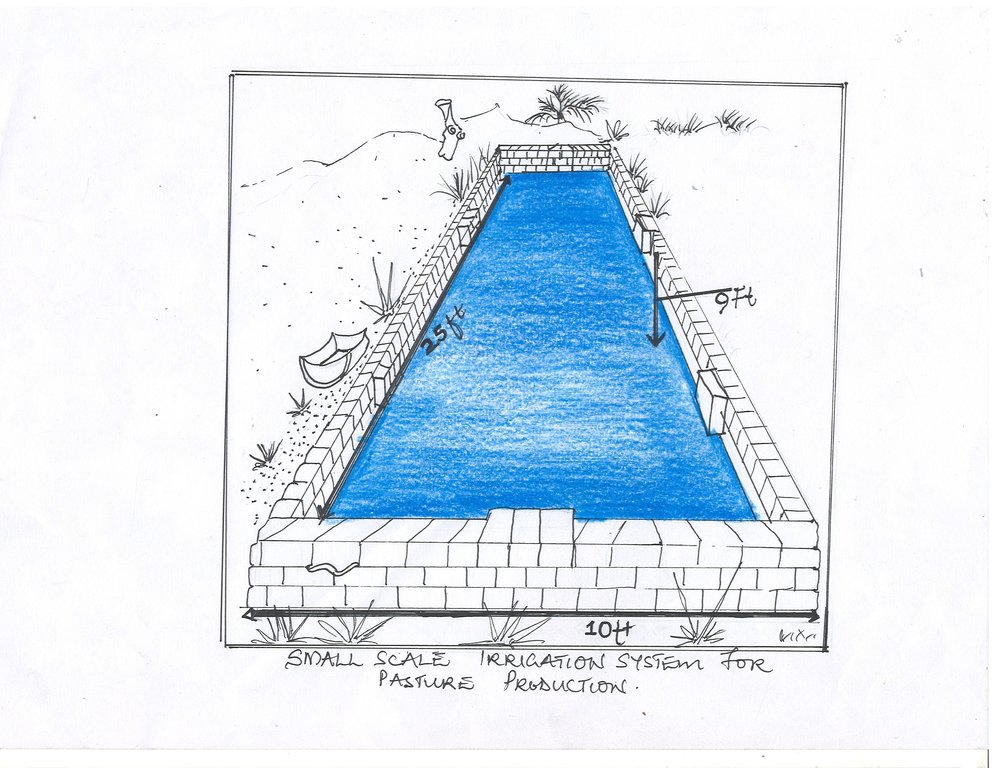
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Reservoir size is length 25 feet, width 10 feet.
Depth can be between 3 feet and 9 feet, depending on the water requirement.
Lateral gradient of structure is flat.
Space between structure and plants is 2 meters.
Capacity of the dam is approximately 25.000 liters (at 3 feet depth).
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Uganda shillings
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3650.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
10000
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing the area | 管理 | Once |
| 2. | Pumping the water | 管理 | Once |
| 3. | Constructing the reservior | 结构性的 | Once |
| 4. | Acquiring a motorized pump | 管理 | Once |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果可能,按下表分列技术建立费用,并列明各项投入和每项投入的费用。如果您无法分解成本,给出建立该技术的总成本估算。:
2770000.0
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labor | Person-days | 5.0 | 200000.0 | 1000000.0 | 50.0 |
| 设备 | Hoes | Piece | 2.0 | 10000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Spade | Piece | 2.0 | 10000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Motorized pump | Piece | 1.0 | 350000.0 | 350000.0 | 50.0 |
| 施工材料 | Bricks | Pieces | 3000.0 | 150.0 | 450000.0 | 50.0 |
| 施工材料 | Sand | Tone | 1.0 | 160000.0 | 160000.0 | 50.0 |
| 施工材料 | Clay | Tone | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Construction cement | bags | 10.0 | 32000.0 | 320000.0 | 50.0 |
| 施工材料 | Water proof cement | bags | 10.0 | 40000.0 | 400000.0 | 50.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2770000.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Kyegegwa District local government
注释:
The system was partially financed by the local government
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning the reservoir | 管理 | Daily |
| 2. | Treating the water | 管理 | Daily |
| 3. | Servicing the motorized pump | 管理 | Monthly |
| 4. | Buying fuel | 管理 | Daily |
注释:
The water is cleaned to prevent blockage of the water pipes and because sometimes the farmer gives it to the cows to drink.
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果可能,按下表分解技术维护费用,并列明各项投入和每项投入的费用。如果您无法分解成本,给出维护该技术的总成本估算。:
1246000.0
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labor | Person-days | 1.0 | 1000000.0 | 1000000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Servicing motorized pump | Piece | 3.0 | 50000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Fuel | Liters | 32.0 | 3000.0 | 96000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1246000.0 | |||||
注释:
Maintenance cost estimated on yearly basis
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
表面上
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
With an increase in pasture yields, this will also boost dairy production.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常消极
长期回报:
轻度消极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Continuous pasture production |
| Steady water supply all through the seasons |
| Increase in pasture yields |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Quite a good innovation |
| Natural resource utilisation |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Establishment is quite expensive | Government Agricultural bodies should take part in supporting farmers to help farmers establish such systems even for other crops other than pastures |
| Maintenance is relatively expensive |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Apart from the environmental risks; large-scale irrigation projects are also costly, not only in terms of capital expenditure, but also in terms of recurrent expenditures for the operation and maintenance of such systems. Such costs pose tremendous difficulties for the sustainability of irrigation schemes. Furthermore, the introduction of irrigation can also lead to inequities in the social context. | |
| Irrigation tends to increase land prices, which may lead to marginal farmers being bought out and landless tenants displaced. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
One (1) person in this case the land user
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Irrigation Techniques for Small-scale Farmers, Martin Smith, Giovanni Muñoz and Javier Sanz Alvarez, FAO 2014, ISBN 978-92-5-108326
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Internet
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
The Advantages of Small Scale Irrigation Schemes
URL:
http://publications.iwmi.org/pdf/H010663.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块