Utilisation of invasive species biomass for charcoal production [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Beatrice Otieno
- 编辑者: Albrecht Ehrensperger, Christian Hergarten
- 审查者: Ross Shackleton
Utilisation of invasive species biomass for charcoal production
technologies_3475 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
R4D Woody Weeds有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
13/03/2018
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
注释:
The main objective of the technology was to minimize environmental pollution through environmentally friendly production processes, uphold preservation of threatened indigenous species by using invasive Prosopis juliflora as a feed stock thereby reducing its woody biomass as well as controlling its spread. However, it is reported that such extractions of the tree parts for charcoal production purposes enhances coppicing, facilitating further invasion. Although disputed by recent research work, the potentiality of control through utilization in managing Prosopis spread is still uncertain. However, there are chances that unless integrated by other management strategies involving active land restorative measures as documented in technologies 3444 and 3455, charcoal production may not sustainably control the spread of Prosopis juliflora.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Charcoal production from invasive Prosopis juliflora has several objectives. It has been promoted to control the spread and reduce the abundance of invasive Juliflora while generating income opportunities for poor rural households producing and selling charcoal. Wood pyrolysis is an efficient, environmentally friendly charcoal production technology through indirect heating of wood at high temperatures with the release of water vapor.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The use of invasive Prosopis wood for charcoal production is intended to control its spread, create space for agricultural or grazing activities and restore degraded land.
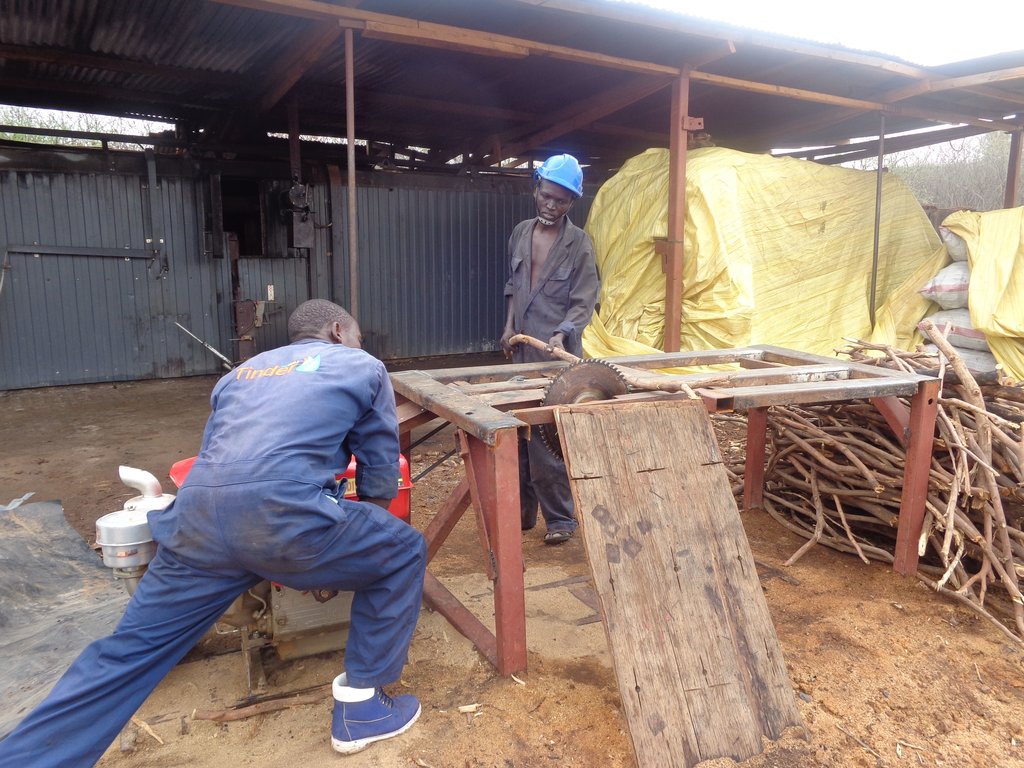
Tinder Eco fuels limited is a private company whose aim is to efficiently produce charcoal through modern, environmental friendly techniques using the ‘EURO’ line charcoal kilns. Approximately 60 tons of invasive Prosopis wood are collected weekly, ejecting an estimate of Ksh. 400,000 weekly income to the local community.
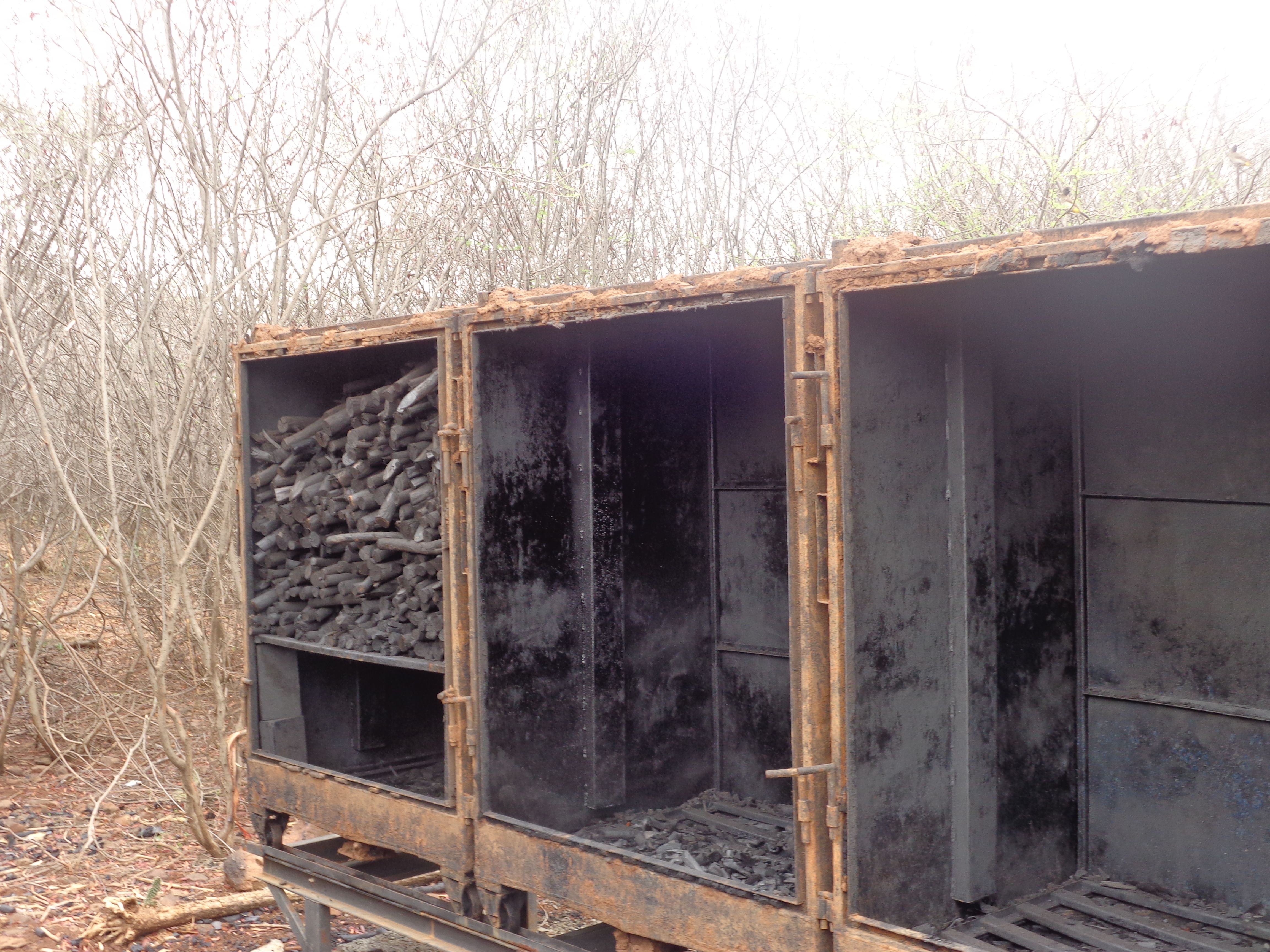
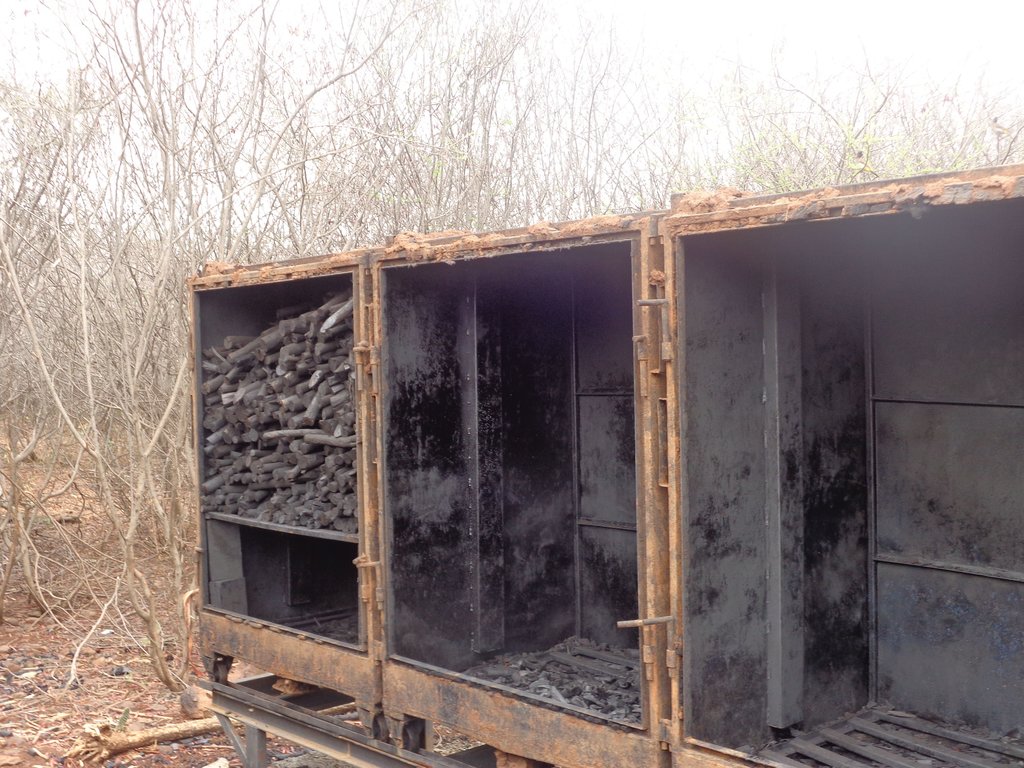
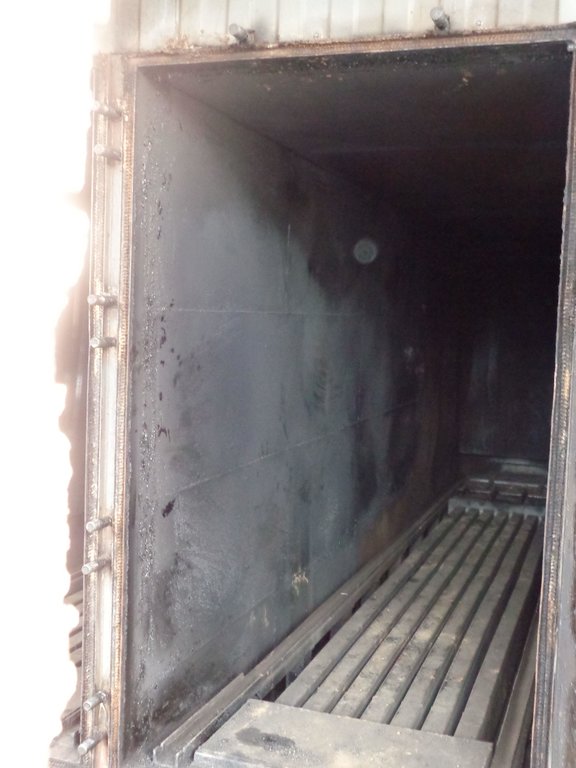
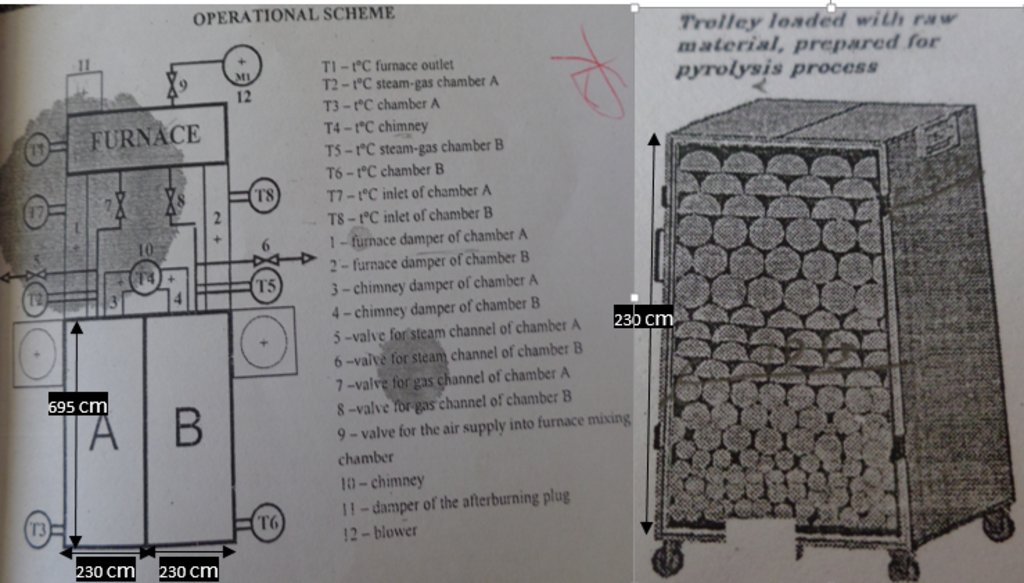
Prosopis, the only tree in Baringo permitted for charcoal production is cut by land users and dried for three days to lower its water content before being transported to the production firm. The trees are then weighed and cut into 15 cm lengths, a corresponding dimension of the loading and offloading trolleys. In the carbonizing chambers, the raw materials are subjected to indirect burning and consequent cooling by pyrolysis gas heated at 250 – 500 degree celcius, a process that takes 8-16 hours. Operations in the chambers are controlled and regulated by an assembly of sensors. Ready charcoal is offloaded into a winch which is covered and sealed by a sandy-clay mixture for further cooling to prevent combustion.
Land users prefer this technology to the traditional one as it is more efficient with a guaranteed income from the sale of Prosopis wood. The carbonization process is fine-tuned, minimizing smoke production and the number of point sources of pollution through household-based traditional charcoal production. A steady production process that is resilient to rainy seasons ensures market readiness and reduces price fluctuations. Clearing the land from invasive Prosopis increases the land's economic and ecological value and the provision of mutliple ecosystem services relevant for local people.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Baringo County
有关地点的进一步说明:
Marigat Sub-County
注释:
No precise location, rather indication of area where the technology is being implemented.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2015
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was established by a private company to transform traditional to a modern environmentally friendly charcoal production technique while advocating for the protection of indigenous tree species threatened by invasive Prosopis.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
- enhance provision of multiple ecosystem services
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:
- 选伐
- 清除枯木/剪枝
产品和服务:
- 薪材
注释:
The cleared lands, unless located within the irrigated farmlands where cultivation usually follows, are usually left idle allowing Prosopis to coppice and the harvesting cycle continues.
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
The challenge with charcoal production from prosopis is that without supporting measures and interventions, prosopis may not be reduced. Therefore it is very important to define a clear goal before implementing the technology. If complete eradication of prosopis is the goal, then charcoal production from prosopis can only be a technology to cover the transition from prosopis to e.g. agriculture or pasture.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
具体说明:
Prosopis is an evergreen tree and easily regenerates and becomes invasive without any human intervention. Cutting of stems or uprooting without a restorative measure in place facilitates their ability to coppice and re-germinate due to the resistant nature of their seeds.
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 天然和半天然森林管理
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 节能技术
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
While charcoal production is most efficiently achieved in a centrally located production facility, the woody material from invasive Prosopis typically originates from heavily invaded areas easily accessible and close to the prodcution facility. The size of the facility's catchment area typically depends on the level of invasion.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V3:植被的清理
- V4:更换或清除外来/入侵物种

管理措施
- M5:物种组成的控制/变化
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

生物性退化
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
If accompanying measures are put in place, then the technology can also contribute to restore and rehabilitate degraded land.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Charcoal production plant
指定体积、长度等(如果相关):
1
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
100.0
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction | 结构性的 | once during the plant establishment |
| 2. | Machine installation | 结构性的 | once during the plant establishment |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | machine installation (35% of machine cost) | Men | 14.0 | 50000.0 | 700000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | ‘EURO’ line charcoal kiln | a set | 1.0 | 2000000.0 | 2000000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | welding machine | unit | 1.0 | 22000.0 | 22000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | cutting disk | unit | 1.0 | 1800.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Operations' shade | building | 1.0 | 100000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | business operations permit | operations permit | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2843800.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transportation of wood from land users | 管理 | daily |
| 2. | Cutting of wood | 结构性的 | daily |
| 3. | Loading into carbonizers | 结构性的 | daily |
| 4. | Packing of ready charcoal | 结构性的 | daily |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Technical employees | monthly salary | 12.0 | 60000.0 | 720000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Casual workers | monthly salary | 3.0 | 20000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | wood | tonne | 3360.0 | 1200.0 | 4032000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | water | |||||
| 其它 | permit | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 | |
| 其它 | electicity | amperes | 180.0 | 267.0 | 48060.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | water | litres | 54000.0 | 0.8 | 43200.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 4923260.0 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Weather conditions may affect transportation of wood due to poor rural road condition
Power outages
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
671.00
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Average annual rainfall in mm: 671.0
Rainfall is characterized by seasonal and annual uctuations
The area is in a semi-arid zone with temperatures ranging
between 16 to 36 degrees, averagely 24.6 degrees, accompanied
by high evaporation rates of up to 6mm. It experiences an
average rainfall of 671 mm annually which are very erratic.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Marigat is heavily invaded by Prosopis which have out competed native vegetation and grasses, threatening biodiversity.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
作物质量
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
木材生产
森林/林地质量
注释/具体说明:
Coppicing of the cut trees slightly increases the woody biomass of Prosopis weed.
产品多样性
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Land management is simplified on condition that other restorative measures are incorporated
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
经济差异
工作量
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Charcoal production has led to the establishment of community-based charcoal production associations which regulate all transactions relating to charcoal production, marketing and sale.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Am initial directive restricting charcoal production to Prosopis trees enhanced the protection of indigenous trees , creating awareness on the need for their management.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
Although traditional charcoal production is widespread among the households in the community, the eco-friendly power generation technology has been adopted by only one private farm due to the initial high cost of acquiring machinery to carry out the operations
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Fast and efficient means of producing charcoal compared to traditional technologies as it produced 3 times the amount of charcoal from the same quantity of wood within 16 hours compared to 1 week. |
| Readily available raw materials at affordable price |
| A reliable source of income to the community members |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Environmentally friendly technology of utilizing Prosopis weed with reduced number of point sources for air pollution. |
| Improved community well-being through assured high income from the sale of Prosopis wood compared to their initial practice of tideous traditional charcoal burning and sale. |
| Potentiality in sustainably managing Prosopis / invasive species if integrated with other restorative land management strategies. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Poor roads and power shortages during rainy seasons hinders transportation of wood and charcoal production processes as reliance on a fuel generator increases production costs | Improving the road network |
| Corruption and associated assault by police during transportation of charcoal to the market. | Establishment of transparent and clear laws on legal requirements related to charcoal production activities |
| Unsteady regulatory and policy frameworks disrupting charcoal production |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Unsustainability in controlling invasive species | Integration with other land restoration measures to control re-invasion. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1
Tinder Eco-fuels Limited
- 与土地使用者的访谈
3
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Spatial Evolution of Prosopis Invasion and its Effects on LULC and Livelihoods in Baringo, Kenya. Mbaabu et al. 2019.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101217
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Experimental prosopis management practices and grassland restoration in three Eastern African countries. Eschen et al, 2023.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43170-023-00163-5
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Chapter 12. A REVIEW OF BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES FOR THE CONTROL OF INVASIVE PROSOPIS TREES
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Forthcoming (Schaffner et al. 2024)
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块