Small Earth Dams [赞比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: MAIMBO MALESU
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
technologies_1331 - 赞比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: Water Harvesting – Guidelines to Good Practice (Water Harvesting)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Water harvesting and storage structures to impound runoff generated from upstream catchment areas.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
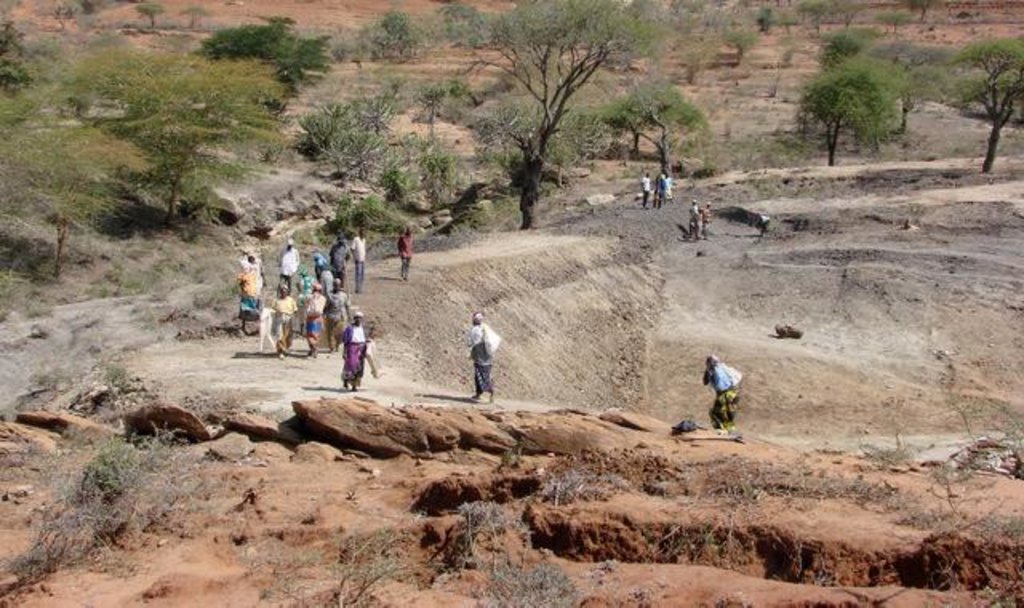
Small earth dams are water harvesting storage structures, constructed across narrow sections of valleys, to impound runoff generated from upstream catchment areas.
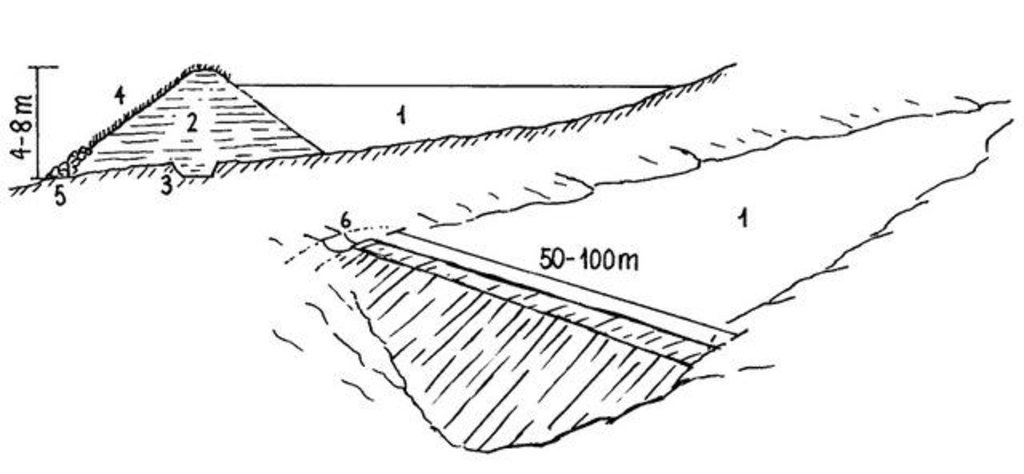
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Construction of the dam wall begins with excavation of a core trench along the length of the dam wall which is filled with clay and compacted to form a ‘central core’ that anchors the wall and prevents or minimizes seepage. The upstream and downstream embankments are also built using soil with a 20-30% clay content. During construction – either by human labour, animal draught or machine (bulldozer, compacter, grader etc.) – it is critical to ensure good compaction for stability of the wall. It is common to plant Kikuyu grass (Pennisetum clandestinum) to prevent erosion of the embankment. The dam is fenced with barbed wire to prevent livestock from eroding the wall. Typical length of the embankment is 50-100 m with water depth ranging 4-8 m. An emergency spillway (vegetated or a concrete shute) is provided on either, or both sides, of the wall for safe disposal of excess water above the full supply level. The dam water has a maximum throwback of 500 m, with a capacity ranging from 50,000 – 100,000 m3.
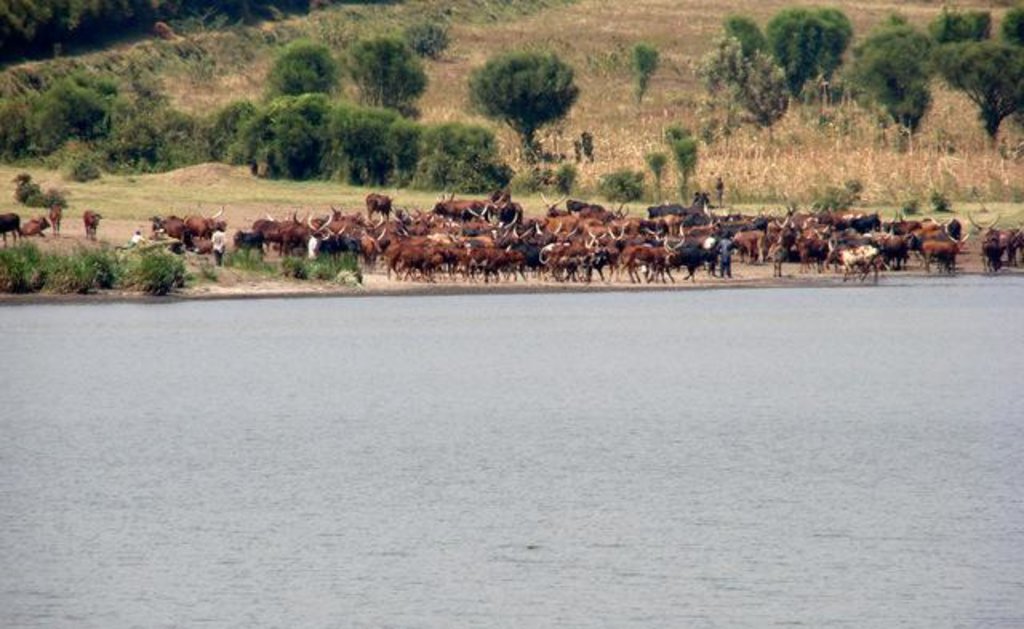
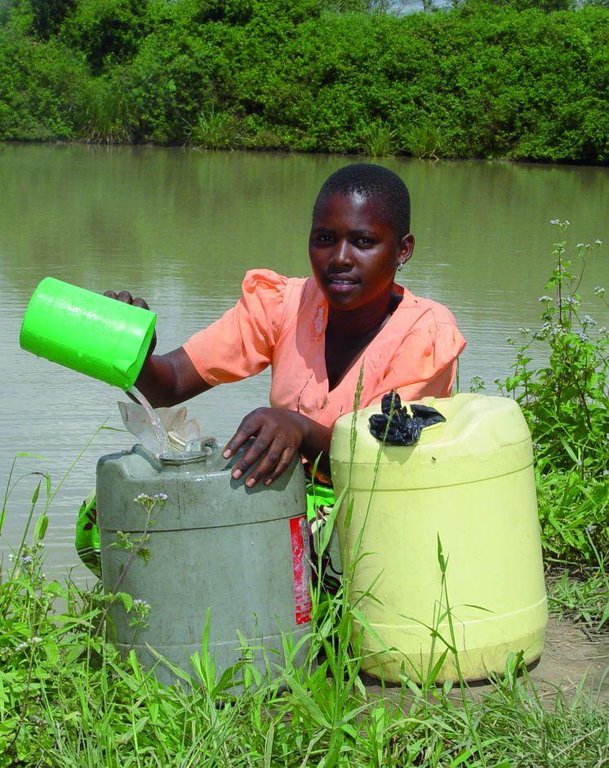
Natural / human environment: The dams are mainly used for domestic consumption, irrigation or for watering livestock. If the dams are located on communal lands, their establishment requires full consultation and involvement of the local community. The government provides technical and financial assistance for design, construction and management of these infrastructures. Community contribution includes land, labour and local resources. The community carries out periodic maintenance of the infrastructure – including vegetation management on embankment, desilting etc. – and of the catchment areas (through soil and water conservation practices).
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
赞比亚
区域/州/省:
Southern Province
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- Access to water
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): water degradation, soil erosion, low surface water availability
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Nov-April
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 集水
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
In the study area there are over 293 dams serving a cattle population of 1.1 million and human population of nearly 1 million people
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
注释:
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), floods
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Dimensions and main components of a small dam: (1) water body; (2) dam wall (with layers of compacted soil; side slopes 3:1); (3) central core ('key'); (4) grass cover; (5) stone apron; (6) spillway
Southern Province
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: Pennisetum clandestinum
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4.00
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50.00
Construction material (earth): 20-30% clay content
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 100000.00m3
Dimensions of spillways: 5.00m
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Dam
指定体积、长度等(如果相关):
10’000 m3 (44 m long; 8 m deep)
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site selection in consultation with community. | 管理 | |
| 2. | Dam survey and design: Topographical survey of dam area; using leveling equipment (dumpy level or theodolite); Determination of dam wall dimensions. | 管理 | |
| 3. | Dam wall construction: Excavate core trench (usually 4m wide; 2m deep). Excavate and transport clay-rich soil to the dam site. Construct core and embankments (slope angles 3:1). Continuously compact placed soil. | 结构性的 | |
| 4. | Construct lateral spillway(s), 5-30m wide (depending on the flood flow and the return slope). | 结构性的 | |
| 5. | Design and installation of irrigation and drainage infrastructure (in case of crop production). | 结构性的 | |
| 6. | Completion: plant kikuyu grass on dam embank-ment, spillway and irrigation canals and fence of; alternatively line with cement | 植物性的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Dam and spillway construction | unit | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 20.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | unit | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | 20.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | unit | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 20.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | unit | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 20.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Biocides | unit | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 20.0 |
| 施工材料 | Stone | unit | 1.0 | 15000.0 | 15000.0 | 20.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 50000.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Catchment conservation to minimise siltation of dam and irrigation infrastructure (continuous). | 结构性的 | |
| 2. | (Re-)planting grass on dam and irrigation infrastructure (annually, using hand hoes). | 结构性的 | |
| 3. | Desiliting of the dam (every 5-10 years): excavate and remove the silt deposited in the dam. | 结构性的 | |
| 4. | Cleaning of dam and irrigation infra-structure (annually): remove trees/ shrubs from dam / canals. If concrete lined: repair of any damages. | 结构性的 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Maintenance of dam | unit | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| 设备 | Tools | unit | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | unit | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Stone | unit | 1.0 | 1500.0 | 1500.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 4000.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: machinery, ox-ripper, hoe/pick, shovel
Establishment costs are calculated for a dam with an earthwork volume of 10’000 m3 (44 m long; 8 m deep; side slopes 3:1). 20% of costs are borne by the community (in-kind contribution: labour and local materials such as sand, stones). Construction machinery can include: tipper truck, bulldozer, motor scraper, compactor, tractor, grader
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
700.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Gentle (plains), moderate (plains), rolling (plains) and hilly (valleys)
Altitudinal zone: Also 1000-1500 m a.s.l., range from 300-1200 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- not titled
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
畜牧生产
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
娱乐机会
社区机构
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水的回收/收集
地下水位/含水层
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
下游洪水
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on adoption trend: Records of 1991 indicate at least 537 such dams exist in Zambia. In the study area there are over 293 dams serving a cattle population of 1.1 million and human population of nearly 1 million people.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Small earth dams allow for the diversification of income activities including tree nurseries, brick making, fish farming, raising ducks and geese and thus alleviate poverty improvement of access to markets will be crucial to support such income generating activities |
|
Saves people’s time by reducing the distance to fetch water for domestic use clear and equitable water use rights and agreements |
|
Reduced risk of crop failure by bridging prolonged dry periods and as such contribute to food security and climate change adaptation How can they be sustained / enhanced? combine with water saving cultivation practices such as mulching, pitting etc. |
|
Reduced damages from soil erosion and flooding by storing excessive runoff water How can they be sustained / enhanced? use an integrated watershed management approach to reduce flood and erosion risk |
|
Possibility for watering cattle near the village reduced soil compaction and erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? regulate access of cattle to avoid degradation around the water source and protect water source from pollution |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Dams are communally owned | requires strong organisation and commitment by community |
| Risk of siltation | de-silting and Catchment conservation is essential |
| Vulnerability to climate change | increase depth and design storage to last at least for two rainy seasons |
| Evaporation and seepage losses | maintain minimum design depth of 4 meters; if seepage is high: provide impervious material on the upstream embankment, i.e. clay or plastic lining if necessary |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Nissen-Petersen E. 2006. Water from small dams. A handbook for technicians, farmers and others on site investigations, designs, cost estimations, construction and maintenance of small earth dams
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Morris P. H. 1991. Statement of Policy: Progress Review of the Drought Relief Dam Cons/ruction Project, Southern Province. Part 1 — Main Report. Irrigation and Land Husbandry Branch, Department of Agriculture, Chôma
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Sichingabula H.M. 1997. Problems of sedimentation in small dams in Zambia. Human Impact on Erosion and Sedimentation (Proceedings of the Rabat Symposium, April 1997. IAHS Publ. no. 245, 1997
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
The Jesuit Centre for Theological Reflection. 2010. Social Conditions Programme.
URL:
http://www.mywage.org/zambia/main/minimum-wage/comparitive-minimum-wage
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块