Rooftop rainwater harvesting system [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Madhav Dhakal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
Akase paani sankalan pranali - Nepali
technologies_1497 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: Water Harvesting – Guidelines to Good Practice (Water Harvesting)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
20/10/2006
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
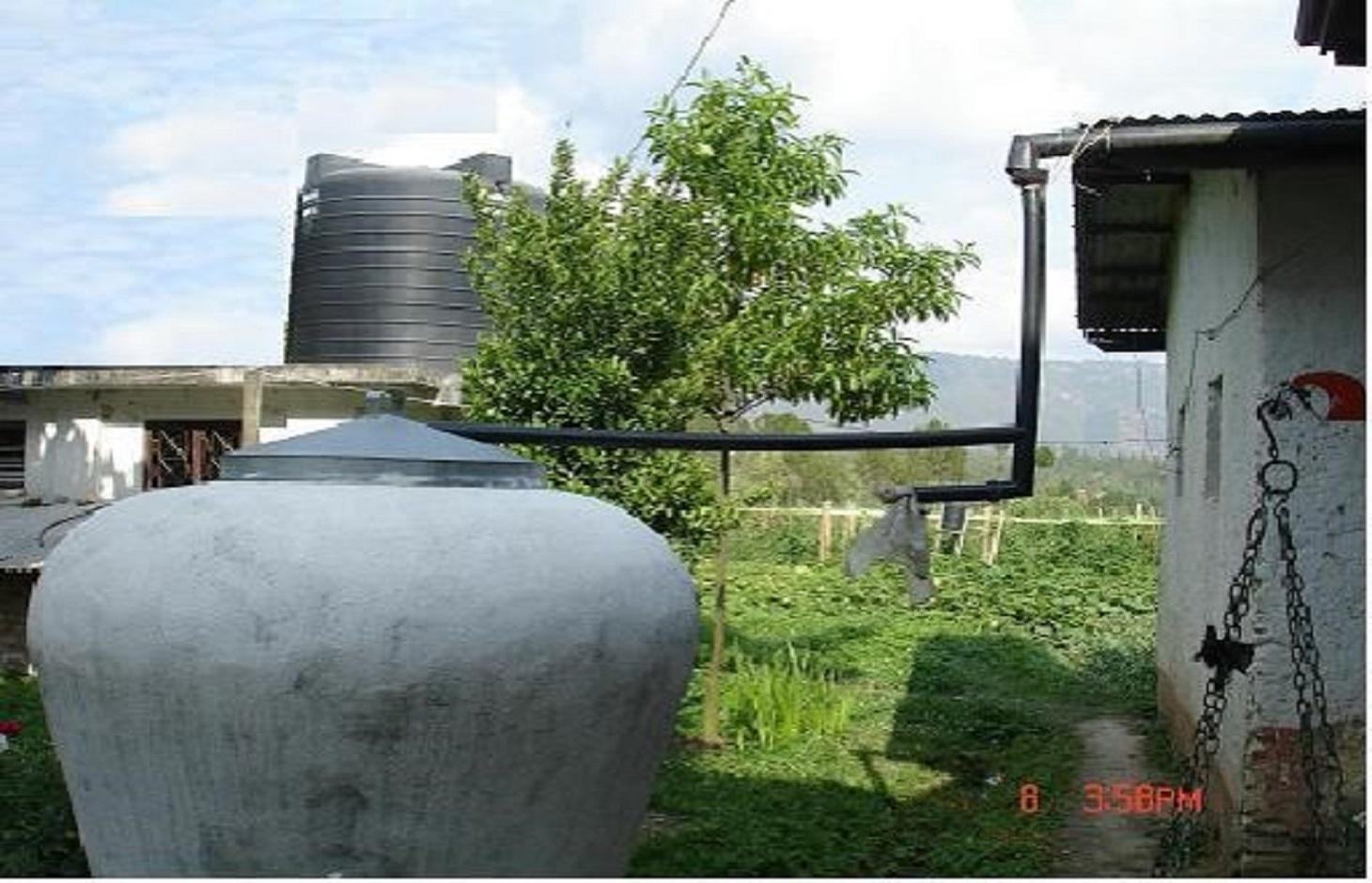
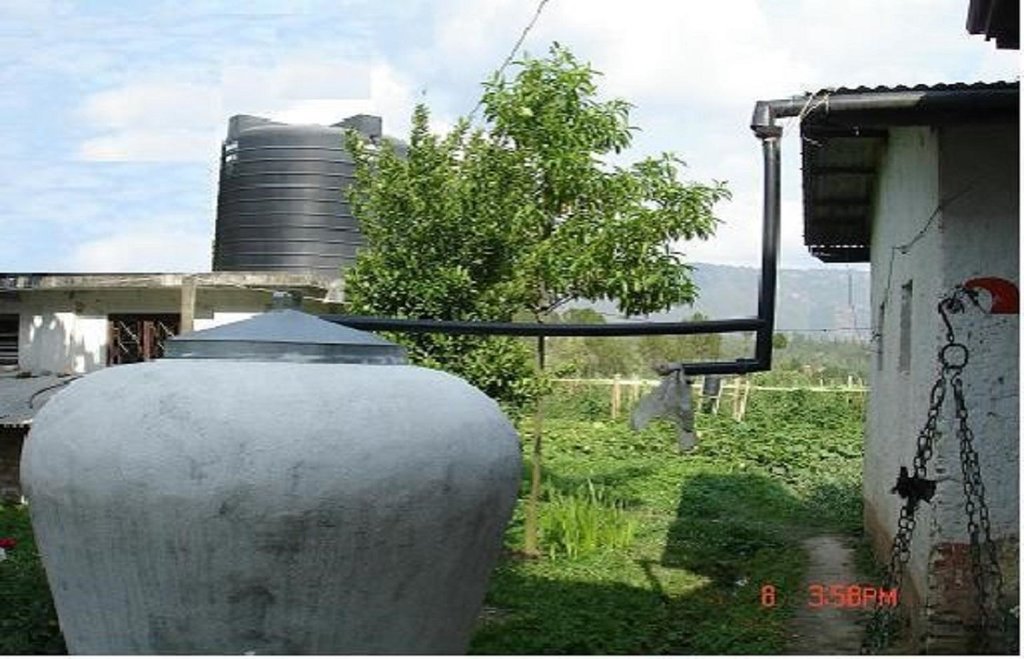
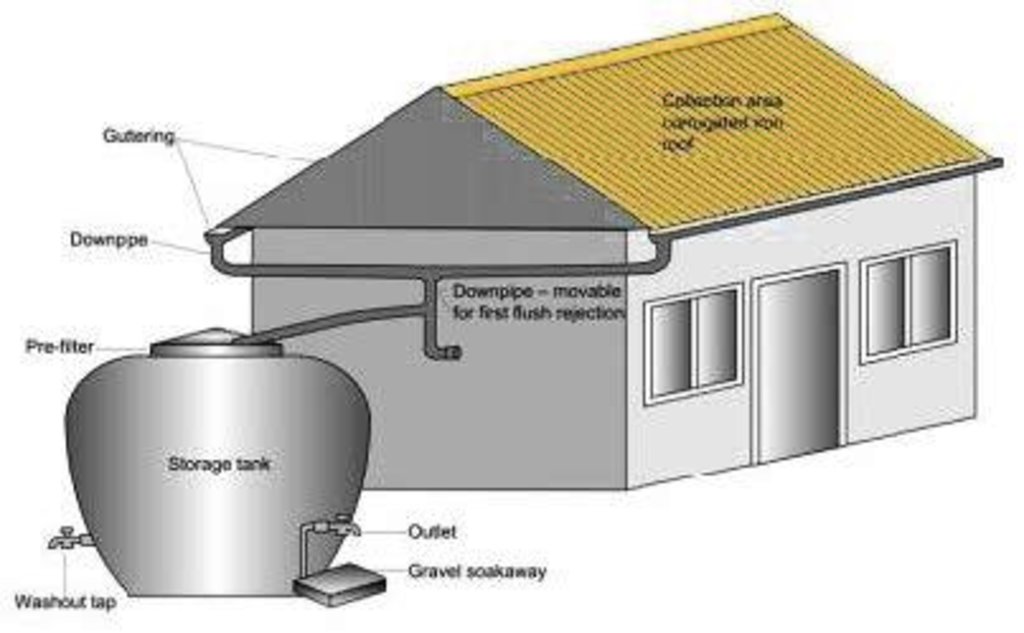
A water harvesting system in which rain falling on a roof is led through connecting pipes into a ferro-cement water collecting jar.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Many households in Nepal’s midhills suffer from water shortages during the pronounced dry season. The technology described here - harvesting roofwater during times of heavy rainfall for later use - is a promising way of improving people’s access to water for household use, especially for households with no or only limited access to spring or stream water. The technology has yet to be extensively adopted in Nepal’s midhills.
Purpose of the Technology: The technology was introduced in the Jhikhu Khola watershed to demonstrate an alternative source of water for domestic use (mainly drinking water). This technology is appropriate for scattered rural households in mountaineous areas. The harvesting system consists of a catchment roof, conveyance pipes, and a storage jar. The pipes include a gutter system made from longitudinally split polythene pipe which has a flushing system that allows the system to be periodically flushed clean.
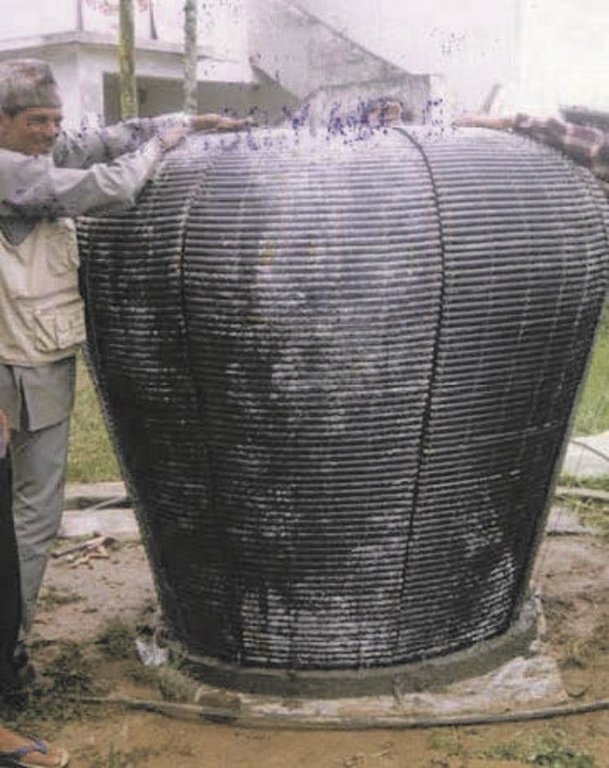
The collected water enters a 500 or 2000 litre capacity ferro-cement jar made using a mould (see photo). A preconstructed mould made from iron rods and polythene pipes is installed on a concrete base plate. Metal wires are extended from the base plate over the main mould to the top. Chicken mesh is then wrapped over the mould and tied securely with thin wire. A cement coating is applied over the metal structure. The jar is finished with three coatings of cement and the opening is covered with a fine nylon mesh to filter out undesired coarse matter. A tin lid is placed over the top.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A tap is fixed about 20 cm above the ground. This height allows for water to be collected in the typical 15 litre local water vessels (gagri) and avoids collection of too much water in bigger vessels as well as minimising the dead storage of water (Nakarmi et al. 2003). Trained masons can easily install the entire system. Provided all the materials and the mould are available, the entire system can be put together in about a week. The main maintenance task is to keep the roof clean, especially after long dry periods. This is done using the gutter pipe flushing system in which the first dirty water from the roof is diverted away from the jar.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
区域/州/省:
Kharelthok, Sathighar, Panchkhal, Hokse and Patalekhet VDCs of the Jhikhu Khola watershed
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kavrepalanchowk district
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Water harvesting is an ancient practice, the system used in the Jhikhu Khola watershed came from Thailand, so the technology is often called 'Thai jar". In Nepal, the Rural Water Supply and Sanitation Support Programme (RWSSSP), which is jointly funded by the Government of Finland and His Majesties Government of Nepal, introduced it in the water deficit districts of western Nepal (Arghakhanchi, Gulmi, Kapilvastu, Nawalparasi, Palpa, Parbat, and Rupandehi).
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- Access to water
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

定居点、基础设施
- 定居点、建筑物
注释:
courtyard
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Inadequate water supply during the late winter and pre-monsoon months and sediment contamination during the wet season. The discharge from traditional water sources like dug-out ponds, springs, seepage ‘holes’, shallow wells and streamlets becomes limited soon after the end of the monsoon.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Many settlements are located on ridge tops and most water sources are located below making it difficult to provide water to households through networks of pipes. Women and girls often face hardship in carrying the water uphill, especially during the monsoon when trails are slippery.
Constraints of settlement / urban
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
每年的生长季节数:
- 3
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
Roof rainwater harvesting jars were demonstrated mostly in the villages located at the watershed divides, hilltops, and elevated terraces where communities face chronic water shortage particularly during the dry period.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

物理性土壤退化
- Pw:水浸
注释:
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
A water harvesting system with roof catchment, connecting pipes and storage tank.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Structural measure: Dam/ pan/ pond
Material: Concrete
Structural measure: Jar
Structural measure: Gutter
Structural measure: pipes
Construction material (other): Cement
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Rooftop rainwater harvesting system
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.10
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construct the concrete base plate with the help of base moluld | 结构性的 | 1st day of a week |
| 2. | Curing work | 结构性的 | 2nd to 7th days of a week |
| 3. | Final checking and metal cap putting over the top of the jar | 结构性的 | 7th day of a week |
| 4. | First coat of cement | 结构性的 | 2nd day of a week |
| 5. | Gutter and pipe fitting; including flush pipe | 结构性的 | 4th day of a week |
| 6. | Inner coat of cement | 结构性的 | 6th day of a week |
| 7. | Main mould installation with the help of metal wires, wrapping of chicken mesh | 结构性的 | 2nd day of a week |
| 8. | Removal of mould | 结构性的 | 6th day of a week |
| 9. | Second coat of cement | 结构性的 | 3rd day of a week |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Construction of rooftop rainwater harvesting system | Persons/unit | 19.5 | 2.1 | 40.95 | 25.0 |
| 施工材料 | Cement | unit | 1.0 | 23.6 | 23.6 | |
| 施工材料 | Sand and aggregate | unit | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Chicken wire mesh | unit | 1.0 | 20.9 | 20.9 | |
| 施工材料 | Metal jar cover | unit | 1.0 | 5.5 | 5.5 | |
| 施工材料 | Plastic sheet/mosquito screen | unit | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| 施工材料 | Polyethylene, pipes, reducer | unit | 1.0 | 23.7 | 23.7 | |
| 施工材料 | Nail, clamps, pipe elbow etc. | unit | 1.0 | 3.6 | 3.6 | |
| 施工材料 | Brass tap. socket, seal tap | unit | 1.0 | 3.5 | 3.5 | |
| 其它 | Paint | unit | 1.0 | 2.1 | 2.1 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 126.75 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.25 month(s)
Materials: cement (kg) 23.6 materials sand,aggregate (m3) 1.4 100 materials chicken wire mesh (m) 17.5 materials Iron wire (kg) 3.3 materials metal jar cover (no) 5.5 materials mosquito screen (m) 0.5 materials plastic sheet (m) 1 materials binding wire (kg) 0.1 materials snowcem paint (kg) 1.4 materials enamail paint (litre) 0.7 materials 90 mm HDP pipe (m) 10.3 materials 63 mm HDP pipe (m) 6.2 materials 40 mm HDP pipe (m) 6.8 materials reducer (no) 0.4 materials plain and roofing nails (kg) 0.2 materials metal clamp (no) 1.4 materials elbow, tee,end cap (no) 2.1 materials brass tap with latches (no) 2.1 materials 0 .5*10 inch GI nipple(no) 0.2 materials 1*10 inch GI nipple(no) 0.2 materials 1inch end cap (no) 0.7 materials GI socket (no) 0.2 materials thread seal tap (no) 0.1 Additional info Q 3.1.1.4: - less chance of disputes over turns to fetch water - medium General comments: Water harvesting is an ancient practice. The system used in the Jhikhu Khola watershed comes from Thailand, so the technology is often called ‘Thai jar’. In Nepal, the Rural Water Supply and Sanitation Support Programme (RWSSSP) introduced it in the water deficit districts of western Nepal.
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning the jar | 结构性的 | dry months/one or twice in a year |
| 2. | Flushing contaminated water | 结构性的 | After a long dry spell/whenever required |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cleaning the system | Persons/unit | 7.0 | 2.1 | 14.7 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 14.7 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: hacksaw, steel scissors, hammer, pliers, wrench, trowel, steel pan bucket, and jug
Per unit cost of structure. The above mentioned cost is for unit water harvesting system. It can not be converted into hectare basis. It was estimated in 2006.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The mould and tools were provided by the project and can be used to install many water harvesting systems. Therefore, the cost of tools are not included here. Material costs fluctuate from time to time. The transport costs will vary according to the remoteness of the site. During 1999/2000, the cost of a system varied from US$80 to US$120, of which land users contributed about US$40 by providing the unskilled labour and locally available materials like sand and fine aggregates (calculated at an exchange rate of US$1 = NRs 73).
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Also valley floors
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water quality (untreated): More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
15% of the land users are rich and own 35% of the land.
35% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
50% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land (as ranked by the land users).
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
by the house to accommodate the water jar
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
in dry seasons
harvested water can be used during busy periods ( field preparation, vegetable planting, rice harvesting, and festivals).
收入和成本
工作量
SLM之前的数量:
1 hour
SLM之后的数量:
5 minutes
注释/具体说明:
greatly reduced time needed to fetch water
reduced women's workload i.e. per day water fetching time reduced from about 12 hours to about 1 hour ( for the households having ~10 family members).
其它社会经济效应
Water is available near the house
注释/具体说明:
A house hold having 10 family member require about 12 gagree ( 1 gagree is equivalent to15 litre)
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
together with adopters, other potential local adopters have started discussing options
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
through training, demonstration, and knowledge sharing
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Improved heath condition due to clean water availability
Sanitation
注释/具体说明:
more water avilable forwashing leading to improved health
Risk of injury from carrying water along slippery and steep tracks
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
a little portion of rainfall traped directly from the roof and collected at the courtyard
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
reduced eroded materials from the courtyard.
availability of water for neighbours during scarce period
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Although the initial investment is high, the users immediately get more water. The high cost of installing the system means that the short term benefits are slightly negative.
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
46 households in an area of 1 - 10 sq km (200 - 500 persons/sq km)
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 10-50%
注释:
74% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
34 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
26% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
12 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The number of households applying the technology is increasing without further incentives being provided.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The stored water can be kept for use in emergencies such as to prepare food for guests during busy times like rice planting and harvesting, and during festivals. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Share experiences to extend adoption of the technology |
|
Harvested water is tastier due to being cooler compared to the water collected in the polythene tank. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Laboratory analysis of the harvested rainwater in different time period, i.e. from 1st month of harvest to 12th month could help to know the quality status. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Harvested rainwater has saved almost one workday per day per family due to reduced water fetching time in this case referring to the rainy season, however water will generally be used during the dry season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Publicise the economic benefits of the technology through experience sharing programmes. |
|
Women are responsible for fetching water and so the technology reduces their workloads. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Implement a larger scale programme to promote the technology. |
|
The jars are more durable than plastic tanks. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Carry out regular maintenance to keep systems in good working order. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The technology is expensive for poor households. | External support is needed for poor households to afford this system. |
| The height of the tap is very low which makes it inconvenient to collect water in the gagree. | It was designed to use collected water efficiently, the tap height can be raised, which means that the dead storage is increased, i.e. more water is unavailable for use. |
| There are chances of the jar’s base plate subsiding due to lack of compactness of foundation. | The area of base plate should be made more compact. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| 2,000 litre capacity jars barely meet the dry season needs of a household. | Larger sized jars or more than one jar need to be built to meet most household’s requirements. |
| Microbiological contamination (total and faecal coliform bacteria) and levels of phosphate above the EC maximum were found in a number of the jars caused by bird droppings and dust particles from the roof. | Regularly clean catchment roofs and treat water before drinking by boiling or chlorinating. Rainwater has a low mineral content which can be harmful for the human body, if taken in large quantities (due to reverse osmosis process). |
| This technology is not suitable for temple roofs because such roofs are usually home to large numbers of pigeons, and their excreta will contaminate rainwater that falls there. | Avoid badly contaminated catchments. |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Sharma, C. (2001) Socioeconomic IndicativeImpact Assessment and Benchmark Study on Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting, Kabhrepalanchok District, Nepal, a report submitted to ICIMOD, Kathmandu, Nepal
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ICIMOD
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
ICIMOD (2000) Water Harvesting Manual, unpublished manual prepared for PARDYP Project, ICIMOD
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ICIMOD
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ICIMOD
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Lessons Learned from the People and Resource Dynamics Project , PARDYP/ICIMOD. 2006.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ICIMOD
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Nakarmi, G.; Merz, J.; Dhakal, M. (2003) ‘Harvesting Roof Water for Livelihood Improvement: A Case Studyof the Yarsha Khola Watershed, Eastern Nepal’. In News Bulletin of Nepal Geological Society, 20: 83-87
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Nakarmi, G.; Merz, J. (2001) Harvesting Rain Water for Sustainable Water Supplies to Rural Households in the Yarsha Khola Watershed, a report submitted to Kirchgemeinde Zuoz, Switzerland and ICIMOD, Kathmandu, Nepal
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ICIMOD
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块