Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Michael Herger
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Brigitte Zimmermann, Donia Mühlematter
technologies_2092 - 肯尼亚
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Sept. 4, 2019 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Feb. 22, 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: July 11, 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Sept. 3, 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Oct. 4, 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Nov. 2, 2021 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Feb. 1, 2018 (inactive)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Leresi Patrick
+254721153572
ilngwesi@nrt-kenya.org
Il Ngwesi Group Ranch
Mukogodo Division, Laikipia North District, PO Box 263, 1042 Timau, Kenya
肯尼亚
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
22/01/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Yes and no, only time will tell here. Grazing principles and management (with partly applied Holistic Managment) of Il Ngwesi Group Ranch are said to be exemplary for group ranches in the area. In evaluation processes since the introduction of the new principles and also in reports, they were rated as "best practice". Land recovery is according to these reports in full swing. However, in the field the picture looks partially different. The land is in large areas (still) heavily degraded. Data suggests that vegetation and soil is in a rather bad condition - many erosion features characterize the land. Nevertheless, according to land users, land coverage has significantly improved since the introduction of the new technologies.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
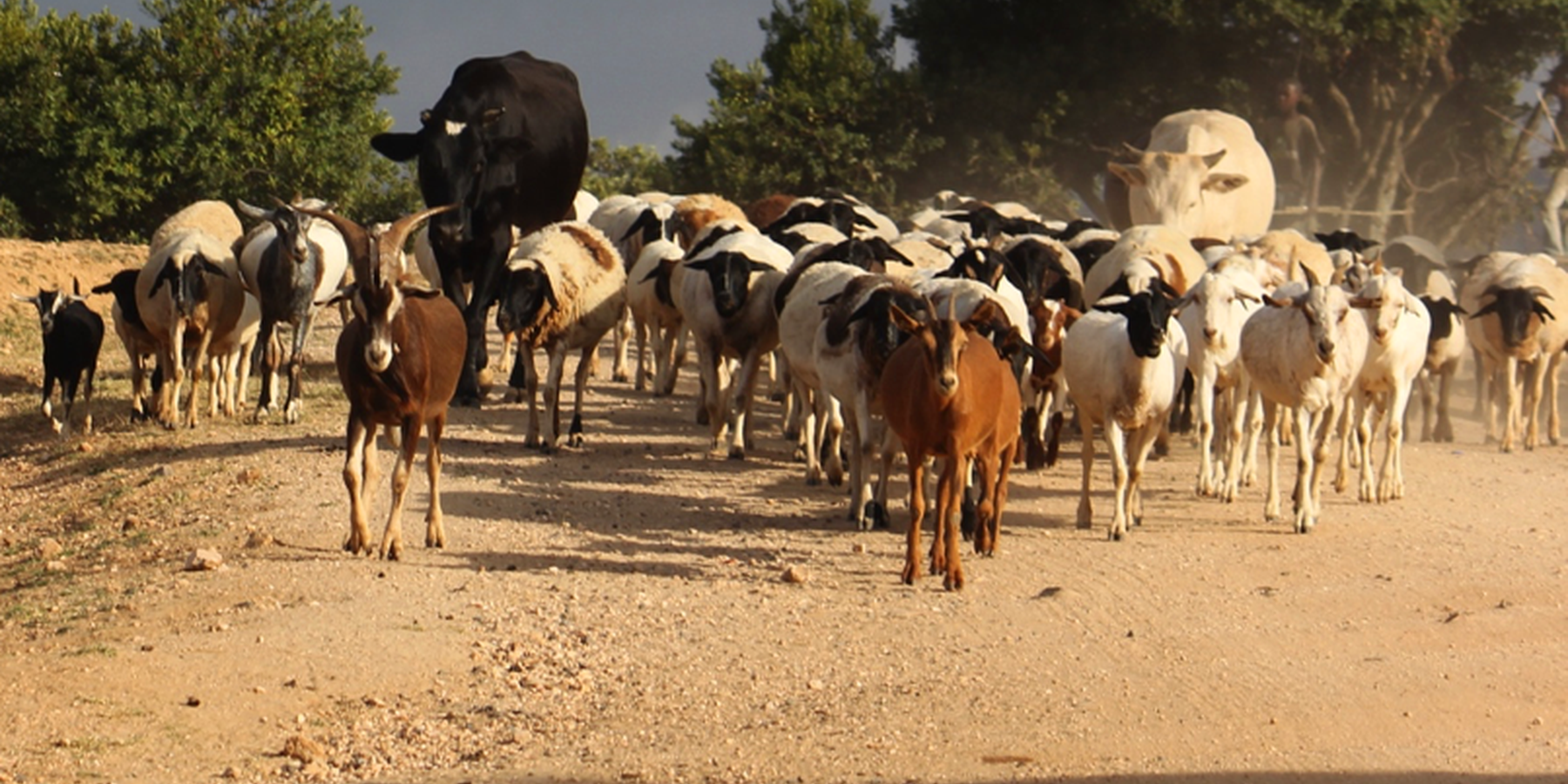
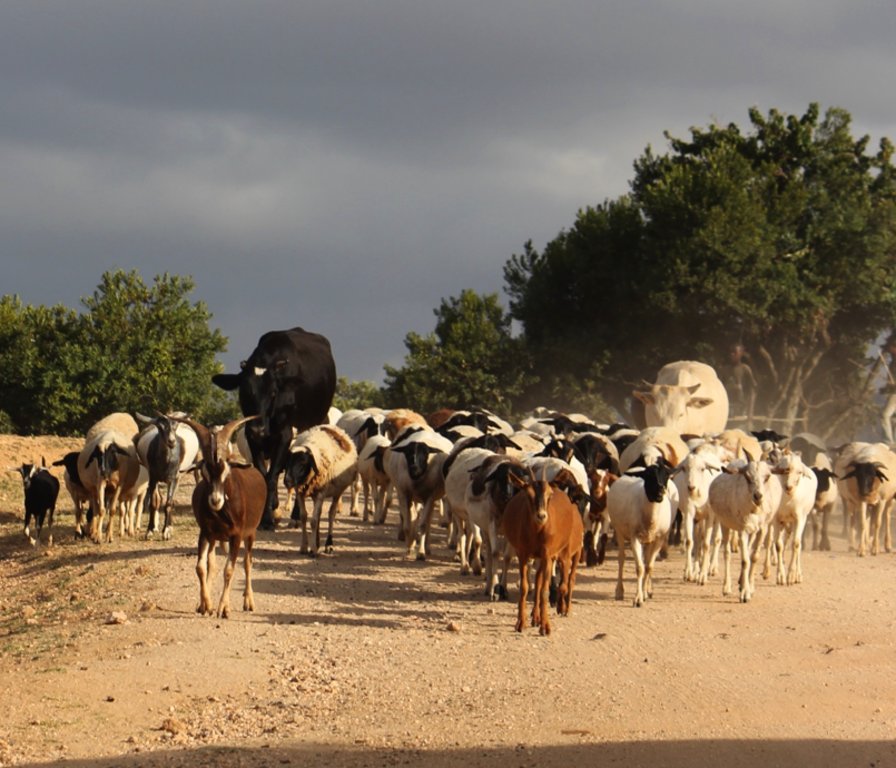
A group ranch belonging to the Masai (traditionally, nomad pastoralists) has applied "Holistic Management" grazing principles. The principles consist of separate, planned grazing in villages during the rains, then “bunching” and moving of all animals in herds during the dry season. Denuded land is recovered by a "Boma” technology: i.e. strategic corralling of animals overnight, and reseeding.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
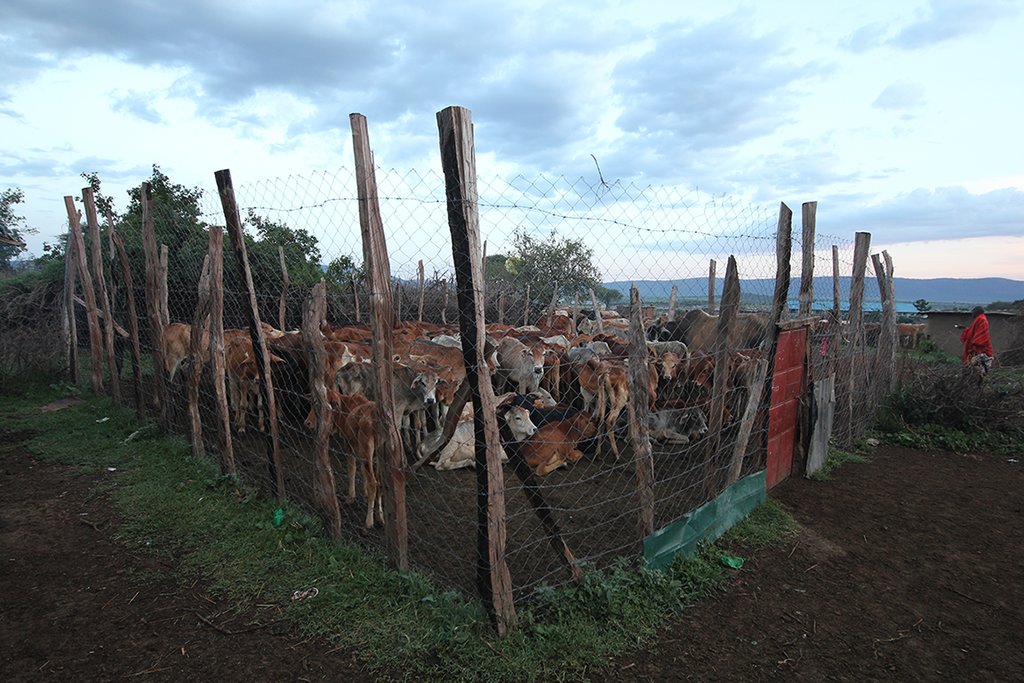
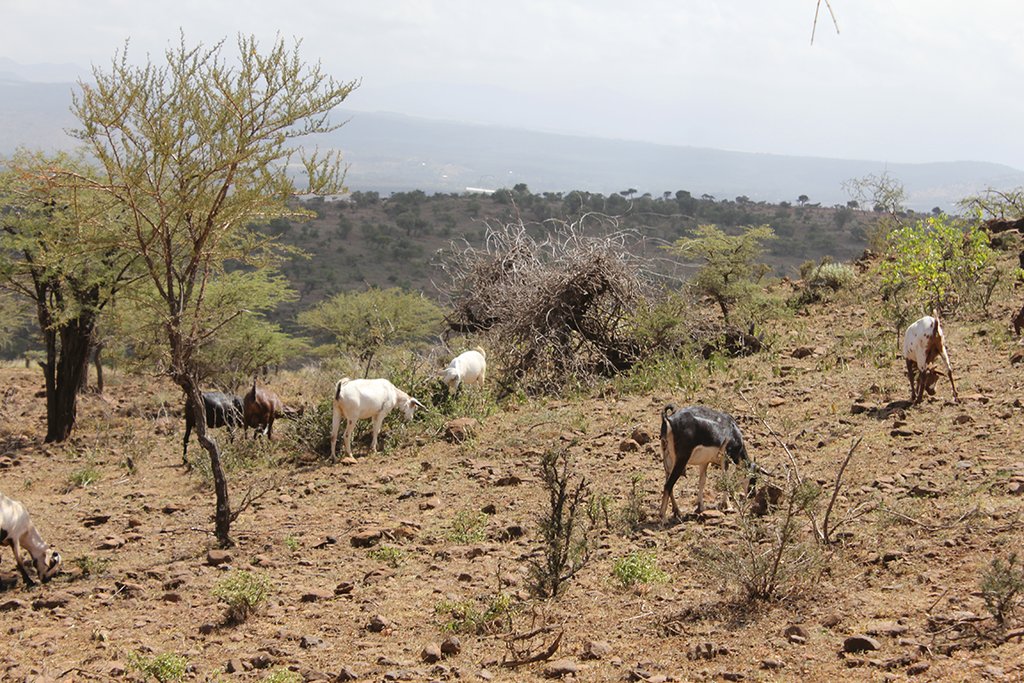
On Il Ngwesi Masai Group Ranch, livestock production management is a combination of traditional livestock keeping and holistic grazing management principles which were introduced in 2007. Livestock production at Il Ngwesi is for subsistence and sales - and has very high cultural significance. 80% of the land is used for conservation, where wildlife and their habitat are protected. The vision is to integrate community development and sustainable environmental management. Holistic Management (HM) was originally conceived by Allan Savory (1988), and is promoted by the Laikipia Wildlife Forum. It integrates decision-making, planning, and livestock keeping. On the land, this means bunching of all livestock close together (in order to act as a "plough" and break the soil to allow seeds, nutrients, and water to infiltrate) resulting in better plant growth. By moving the animals together from block to block, HM aims at managing high numbers of livestock while restoring degraded land. Instead of individual livestock-owning families herding and trekking their own animals, consolidated herds are now managed and moved together, and overseen by herders and supervisors. This allows intensive grazing in restricted areas while resting the remaining land - instead of continuous open grazing. However, Holistic Management principles are still a matter of controversy. While advocates of these management principles do not limit herd sizes, opponents see the root cause of degradation exactly in too high stocking rates. Criticism is plentiful and reviews of the method state that there are no peer-reviewed studies that prove that Holistic Management is superior to conventional grazing systems in outcomes (Carter et al. 2014, Briske et al. 2014).The group ranch land consists of a settlement and a conservation area. The conservation area is further subdivided into a small core zone, measuring 500 hectares and a larger buffer zone of 6,000 hectares. Within this buffer zone, pastoralists are permitted to graze livestock during the dry season.Besides these two main grazing areas in their group ranch, they use additional grazing areas outside their territory such as pasture in forests. In one forest - Mukogodo - they have settled officially; in Ngare Ngare and on Mount Kenya, on the other hand, it is more of an informal agreement. In Il Ngwesi, HM principles are very strictly applied in the conservation area; elsewhere only partly or not at all. During the movements to the forest glades and Mount Kenya, HM principles are maintained as far as possible. This documentation describes the combined grazing management system. During the rains, the grazing system is largely by traditional management: animals remain in and around villages managed individually by households. During the dry season, all livestock are bunched together and managed as one herd.During the wet season, grazing at Il Ngwesi Group Ranch is organized by elders within their seven villages. HM principles are only partly applied. During the dry season, once all the grazing land is eaten, livestock are bunched together and managed by a few herders and overseers. The block system rotation starts. To seek new pasture and water, cattle and smallstock are led to forest glades, and then to the Il Ngwesi conservation area. As soon as the forest pasture is gone, they move on to the conservation area. Usually, this movement of livestock to forests and conservation area starts in February; then they return to the villages in April; and then back to the forests and conservation area until the next rains in November. Whilst the livestock are bunched together, large bomas (corrals in Kiswahili) are constructed for overnight enclosure. Bomas are sited on bare land where dung accumulation and crust breaking by hooves helps rehabilitate land. Every year the boma sites are shifted slightly according to a plan. The total area that can be restored per year is almost 1% of the area of Il Ngwesi.
2.3 技术照片
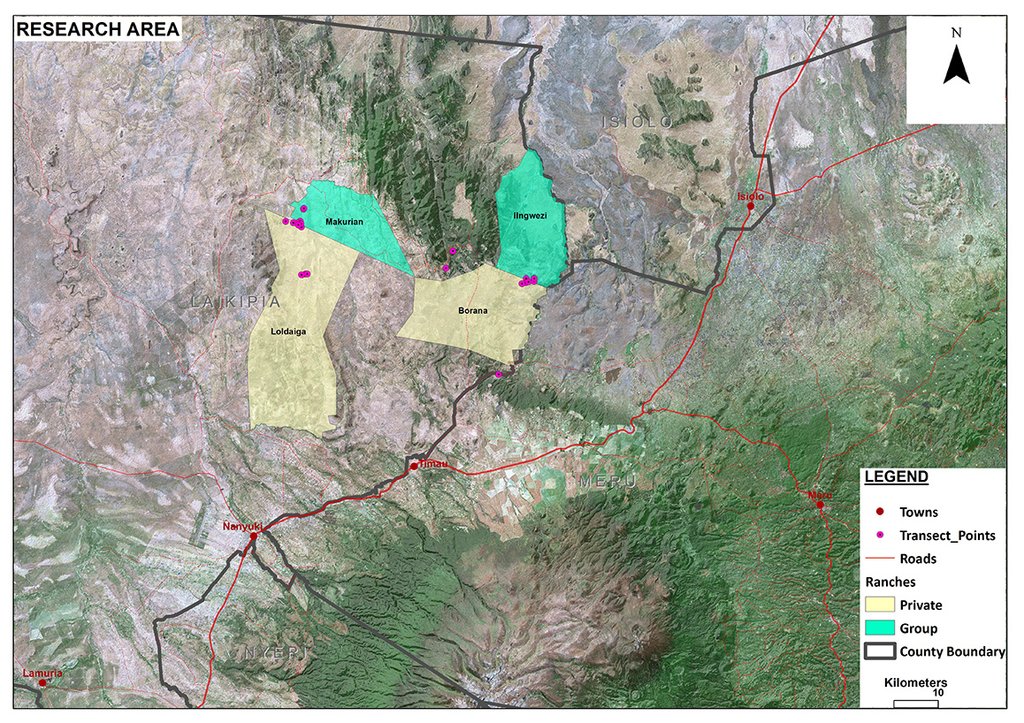
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Laikipia
有关地点的进一步说明:
Mukogodo Divison
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2007
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Holistic Management approach by Allan Savory.
In Laikipia, it was introduced by Richard Hartfield, Laikipia Wildlife Forum and funded by Laikipia Wildlife Forum (LWF), Lewa Conservancy and Northern Rangeland Trust (NRT) (approximately 50% of all additional costs of Il Ngwesi since the implementation were covered by funding). Agreement with elders was reached first, then the community was trained.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧场:
- 半游牧/游牧
主要动物种类及产品:
Livestock: Cattle, goats, sheep, donkeys, camels
Meat and milk production (also blood) and as a bank/ value asset. Mainly subsistence and local production.
Livestock: 4’800 TLU; Stocking rate: 3.3 ha/TLU (calculated with the total affected land by livestock: 157km2)
Pressure on land including wildlife: 3.3 ha/TLU (stays the same, calculated with wildlife biomass density estimated by Georgiadis et al. 2007).
Livestock numbers:
Lower Il Ngwesi: 4000 cattle, 20'000 shoats, 50 donkeys, 100 camels.
Sanga: 700 cattle, 2000 shoats, 20 donkeys.
Mukogodo: 1500 cattle, 5000 shoats, 20 donkeys
Livestock fluctuations (per year): -10% sales, -5% loss due to drought/diseases, -5% slaughtered,
+30% natural breeding, new purchase and deaths are mutually offsetting.
Steers are for fattening on private ranches and during droughts other livestock can be moved to private ranches (up to 3000).
Wildlife: elephant, antelope/ gazelle (like gerenuk, impala, Thomson's gazelle, dik-dik), hares, predators and more.

定居点、基础设施
- 定居点、建筑物
注释:
Villages, bomas, manyattas.
8'000 inhabitans.
Lodge for Tourism.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Short rains in November and December. Long rains in April and May. Rains from (October) November to December are usually better in this area. Rainfalls with strong local variations and changing regimes.
牲畜密度(如相关):
4’800 TLU; Stocking rate: 3.3 ha/TLU. Pressure on land: 3.3 ha/TLU
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
Il Ngwesi has an area size of 87 km2. However, the total affected land by livestock is 157km2. The technology is also applied on other ranches (mainly private ranches, see the documentation for neighboring "Borana") in Mukogodo division.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M4:活动时间安排的重大变化
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pi:覆土

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
注释:
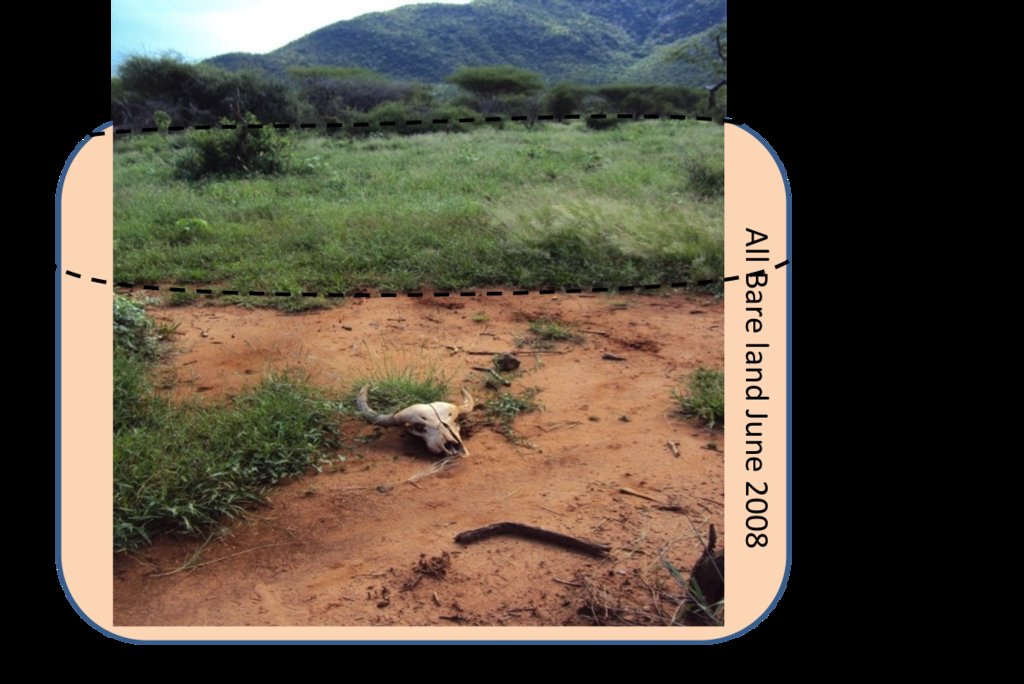
Across the grasslands and rangelands an increase in bare land and bush has been a clear trend all over Laikipia for many years, both on community-owned lands and private ranches. Major identified ecological problems (partly) caused by livestock production are: bare ground, low contents of soil organic carbon and plant-available nutrients, soil erosion (sealing, crusting, rills and gullies, water flow patterns, sheet erosion, pedestals), poor soil properties, undesirable species, and (increasing) woody and invasive species. However, Il Ngwesi is not affected by the invasive species Opuntia stricta. For more information on rangeland health see Herger (2018). The technology aims at improving vegetation cover of the land and thereby reducing further degradation and restoring degraded land.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
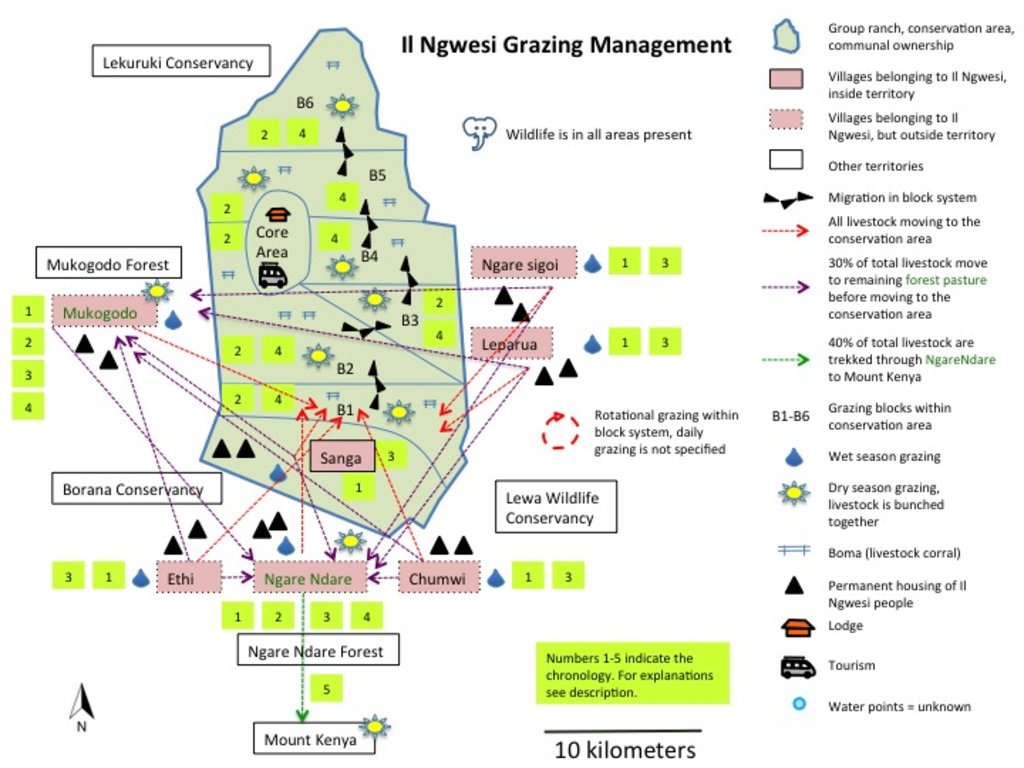
Grazing map of Il Ngwesi in Mukogodo Division
Grazing Principles:
- Rotational, planned grazing
- Bunching
- Resting periods for pasture
- Bomas for bare patches (night corrals)
Value Chain:
• Natural Breeding/buying (Ranches & individually)
• Grazing
o Settlement area (in red, during the wet season, until pasture is gone, organised by elders, bunching of all animals as soon as it gets dry)
o Mukogodo Forest / Ngare Ndare Forest (30% of total livestock, remainder to conservation area for grazing directly)
o Conservation area (6 blocks)
o Mukogodo Forest/Ngare Ndare Forest/Mount Kenya (Ngare Ndare Forest as corridor to Mount Kenya, about 40% of total livestock goes to Mount Kenya)
• Need-driven sales to local butcheries/NRT/Ranches
Il Ngwesi Masai also started to buy land outside their Group Ranch.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Herders, animals treatment. For the whole area affected by livestock (157 km2)
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
USD 2.5
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Training of elders and community by project leaders | 管理 | |
| 2. | Grazing planning for bunched animals (livestock from all households) | 管理 | |
| 3. | Hiring herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | 管理 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Costs for establishment unknown |
注释:
Trainings were funded by NRT, LWF and Lewa Conservancy. No figures on this.
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | 管理 | |
| 2. | Animal treatments (vaccination, spraying, injections) | 农业学的 | |
| 3. | Planning activites | 管理 | |
| 4. | Boma Management (mainly movement of Bomas) | 管理 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Herders, watchmen | Person-days | 250.0 | 540.0 | 135000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Supervisors | Person-days | 3.0 | 720.0 | 2160.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Planning activities, management | Person-days | 20.0 | 1500.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Livestock-owning families (for wet season, no wages paid, livelihood) | Person-days | 8000.0 | 300.0 | 2400000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Boma Movement | |||||
| 其它 | Animals treatments (spraying against ticks) | Per livestock unit | 5000.0 | 5.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Injections, vaccine | Per livestock unit | 5000.0 | 3.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 2607160.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Overall additional costs since introduction of new technology are estimated at 20% higher than before. 50% are covered by project funding (LWF, NRT, Lewa Conservancy).
注释:
Costs per unit are multiplied by days.
According to the interviewed manager, total costs are only USD 18'000 (without herders). However, the listing of all costs results in much higher total costs. Total animal treatment costs for Makurian Group Ranch in comparison are USD 428'000 (labor USD 380'000, animal treatment USD 48'000, without livestock-owning families).
Also, people living in the area (population of 8'000 inhabitants) are involved in livestock keeping and are included here in calcuations as labor (for 3 months, wet season, 10% of total population).
Cost/benefit is currently negative for livestock keeping. Income due to livestock sales is roughly estimated USD 340'000 (price for cattle on average USD 400 per unit, sales around 500 p.a., price for goats and sheep each USD 40 per unit, sales around 2'000 p.a., slaughtered units (for subsistence use) cattle: 50, shoats: 1'000 - detailed figures available Herger 2018).
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
- Managing of one big herd, many supervisors needed.
- Movement of bomas.
- Livestock-owning families (although they obviously don't receive any salary): this is simultaneously their livelihood and used for subsistence. But once all their livestock is bunched in a big herd, they lose their nutritional source (milk, blood) and livelihood (sometimes they keep back a few units for this reason).
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
497.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Rainfall gauge Borana HQ average from 2013-2016 (neighboring ranch). Strong local (and temporal) variation, changing rainfall regimes. Il Ngwesi is generally drier than Borana. Grazing areas are on different altitudes with different rainfall amounts. While Il Ngwesi Sanga (as one of the villages) is at almost 1700 m a.s.l. with similar rainfall like Borana HQ, Il Ngwesi Conservation area is at 1220 m a.s.l. with significantly lower precipitation (no rainfall gauge). Grazing glades in Mukgodo Forest are at 1850 m a.s.l. and in Ngare Ndare Forest at almost 2100 m a.s.l. (no rainfall measurements available, higher rainfall amounts) and varying heights with much higher precipitation on Mount Kenya (no defined areas).
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Rainfall gauge Borana HQ
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Hilly areas (e.g. Sanga village) and flat areas in lower altitude (conservation area).
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Red and brown sandy soils. Black cotton soil. Luvisol, Regosol, Vertisol.
SOC 1.1-1.4 %
pH: 6.3
Clay: 12%
Silt: 53%
Sand: 35%
More information in Herger (2018).
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Few springs, Ngare Ndare river, no boreholes. Source is Mount Kenya.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Grassed acacia bushland. Bare land up to 70% during the dry season. Loss of (native) vegetation. Invasive species coming in. Dominant grasses: Eragrostis species, Cynadon species, Hyparrhenia species, Kelenger species. Dominant shrubs: Solyneum inconum, Ipomea hildebranditi, Lyceum europaeum, Barleria acuthodies. Dominant trees: Acacia tortilis, Acacia mellifera, Acacia nilotica, Acacia etbaica, Boscia angustifolia. Detailed list of all species (also wildlife) available (see Herger 2018).
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 半游牧的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Masai people. 8'000 Masai living in Il Ngwesi. Traditional lifestyle. Livestock with very high cultural value. About 10% subsistence use, 90% is sold for local and national markets (mainly local).
Very little agriculture; tourism (award-winning eco-lodge in conservation area); people start to diversify. Schooling of children has a high importance today (e.g. smallstock is sold for school fees). Children and young warriors are traditionally herders, however, it is shifting towards hiring herders and sending children to school.
Have been historically "squeezed" from all sides into smaller areas for livestock keeping. Future of pastoralism is in question.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Applies for one household. Herders on the other hand trek livestock over an area of more than 10'000 ha.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
土地管理
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
家畜用水的可用性
收入和成本
工作量
注释/具体说明:
20-30% above normal (supervision, watchmen, moving big bomas). Previously, every household managed their livestock individually.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
土地使用权/用水权
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
External! Better land cover attracts invaders (Invasion from northern tribes), envy
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
Poorest livestock-owning families are better off now since their livestock are also bunched together with all the others. For instance, before they couldn't afford to trek their 5 cows to Mount Kenya for pasture, now their livestock are trekked with all the others - all have the same opportunities. Other households are complaining about this since they can't decide on their own anymore where they want to bring their livestock for grazing.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
Less runoff, more water stored in the soil.
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
植物多样性
外来入侵物种
注释/具体说明:
Il Ngwesi is not affected by the huge invasion of the exotic cactus, Opuntia stricta. However, there are some other invasives like Lantana in the area, but not as problematic as Opuntia. According to land users, native vegetation cover has improved, which results in fewer invasive species.
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
More stored in the soil. According to the land users, no measurements conducted.
有关影响评估的意见:
All listed impacts are as perceived by land users according to Patrick Leseri, Conservation Manager. In his opinion, vegetation cover has thanks to the new technologies improved. Planning activities significantly increased and therefore also socio-economic and ecological conditions improved. Results from a rangeland health assessment (only ecological conditions) show on the other hand partly heavily degraded ecological conditions (poor soil and vegetation, erosions features, inability of producing annual grasses after rains etc) (Herger 2018). Land users and experts are aware that the ecological conditions of this Group Ranch are still far from optimal, but do see good progress and exemplary management as well as slightly better conditions than on other Group Ranches.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 其他渐变气候 | Greater variation of seasonal rainfall, higher intensity of rainfall events, change in rainfall regimes in general (see Schmocker 2013 and Imfeld 2016). | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 热浪 | 好 |
注释:
Improved rangeland health, better internal organization, and cooperations make them less vulnerable to climate change impacts.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 10-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 气候变化/极端气候
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Masai people have changed their livestock composition towards owning more smallstock (goats and sheep) than cattle. Goats are tolerant of drought, and as browsers, they don't need any grass. Also, they can be turned into money much quicker than a cow in times of need and because of their more rapid reproductive cycle. They can also recover number more quickly after livestock losses through drought.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Proper utilisation of pasture – controlled usage/grazing. |
| Land recovery (more cover, more water, more fodder, less erosion). |
| Carrying capacity increased. |
| Traditional knowledge is still used. |
| More dialogue in community: brings everyone in the community together – they have a common point – everyone has the same interest. |
| Improving breeds is easier (because all are bunched together). |
| Easy vaccination of all livestock at once. |
| Approving cultural lifestyle of Masai: the higher the livestock numbers – the better for the land. |
| Better for disadvantaged community members: for instance for those who could not afford to move their livestock to Mt Kenya on their own before. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The listed advantages from Patrick Leseri, the land user, are for the most part shared share with the compiler's view. Improved planning of livestock production with planned grazing and long resting periods, improved dialogue in the community, and the named advantages of a big herd (like easy vaccination etc) are important advantages. Regarding Holistic Management (HM) principles, there remains uncertainty about land recovery. On the one hand, it is generally questionable to state as in HM: “the more animals the better” (as long as they are managed properly they can even recover degraded land), which seems dangerous in areas with such high livestock numbers and cultural value of livestock keeping - without scientific proof of the principles in similar ecological conditions. We have witnessed rather poor condition of the land, and the much-vaunted good land was difficult to find. Favourable descriptions might also be related to funding of the project. Results from a rangeland health assessment show (partly) heavily degraded ecological conditions (bare ground, poor soil and vegetation, erosion features, partly an inability of producing perennial and annual grasses after rains etc) (see Herger 2018). However, an evaluation of change over time is impossible to assess. Further monitoring is necessary. Land users and experts are aware that the ecological conditions of this Group Ranch are still far from optimal, but do see good progress and exemplary management as well as slightly better conditions than on other Group Ranches. However, the efforts towards good management and a sense of community was not difficult to notice. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Higher costs. Above 20% more than normal costs. Northern Rangeland Trust (NRT), Laikipia Wildlife Forum and Lewa conservancy as main funders for applying holisitc management principles. Since 2007, they covered about 50% of all costs.. | |
| More labour intensive. 20-30% above normal (supervision, watchmen, moving big bomas). | |
| Challenge to bring people together (and their livestock) and agree on a joint management. | |
| Some families still prefer to manage their livestock on their own and make their own decisions. There are no individual decisions anymore: principles apply to everyone. | |
| Breeding can also be a problem – those with good genetic material (better livestock) may lose and those with poor may win by mixing. | |
| Conflicts among animals; bulls fight a lot. No separation of heifers, cows, steers and bulls. | |
| Management of high numbers of big herds is a challenge. | |
| Diseases are easily transmitted. | |
| Once livestock is collected to big herds, individual families lose their nutritional basis (milk, blood). However, some also keep a few livestock units back. | |
| Sometimes trees are cut for bomas. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
4 field visits with included "rangeland health assessment" in different parts of Il Ngwesi (mostly in Sanga village though) where I could see the condition of the land as well as several other visits of the area.
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Several meetings with the grazing coordinator, conservation manager, chief, elders, and other resource people of Il Ngwesi over half a year.
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
Truman Young
Dan Rubenstein
Dino Martins
John Letai
Samali Letai
Peter Hetz
Dominic Maringa
Joseph Putunoi
Patrick Ekodere
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Scientific papers, LWF reports etc.
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Herger, M.B. (2018). Environmental Impacts of Red Meat Production. MSc Thesis. University of Bern.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
University of Bern
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Modeling Seasonal and Annual Precipitation using long-term Climate Records and Topography. Master’s Thesis. Noemi Imfeld (2016).
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
University of Bern
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Savory, A (1988). Holistic Resource Management. Gilmour Publishing, Harare, Zimbabwe
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Online
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
•Carter, J., Jones, A., O’Brien, M., Ratner, J., Wuerthner, G. (2014). Holistic Management: Misinformation on the Science of Grazed Ecosystems.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
International Journal of Biodiversity.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
•Briske, D.D., Ash, A.J., Derner, J.D., Huntsinger, L. (2014). Commentary: A critical assessment of the policy endorsement for holistic management. Agricultural Systems 125:50-53.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块