Homestead Development [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sewalem Salele
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Tatenda Lemann
Yegaro zuriya temere den
technologies_4138 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Debebe Agmassu
Abagerima Kebele Association
埃塞俄比亚
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Carbon Benefits Project (CBP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Water and Land Resource Centre Project (WLRC)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Agriculture - Amhara Nation Regional State - Bahir Dar (amhboard) - 埃塞俄比亚有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Water and Land Resource Centre (WLRC) - 埃塞俄比亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
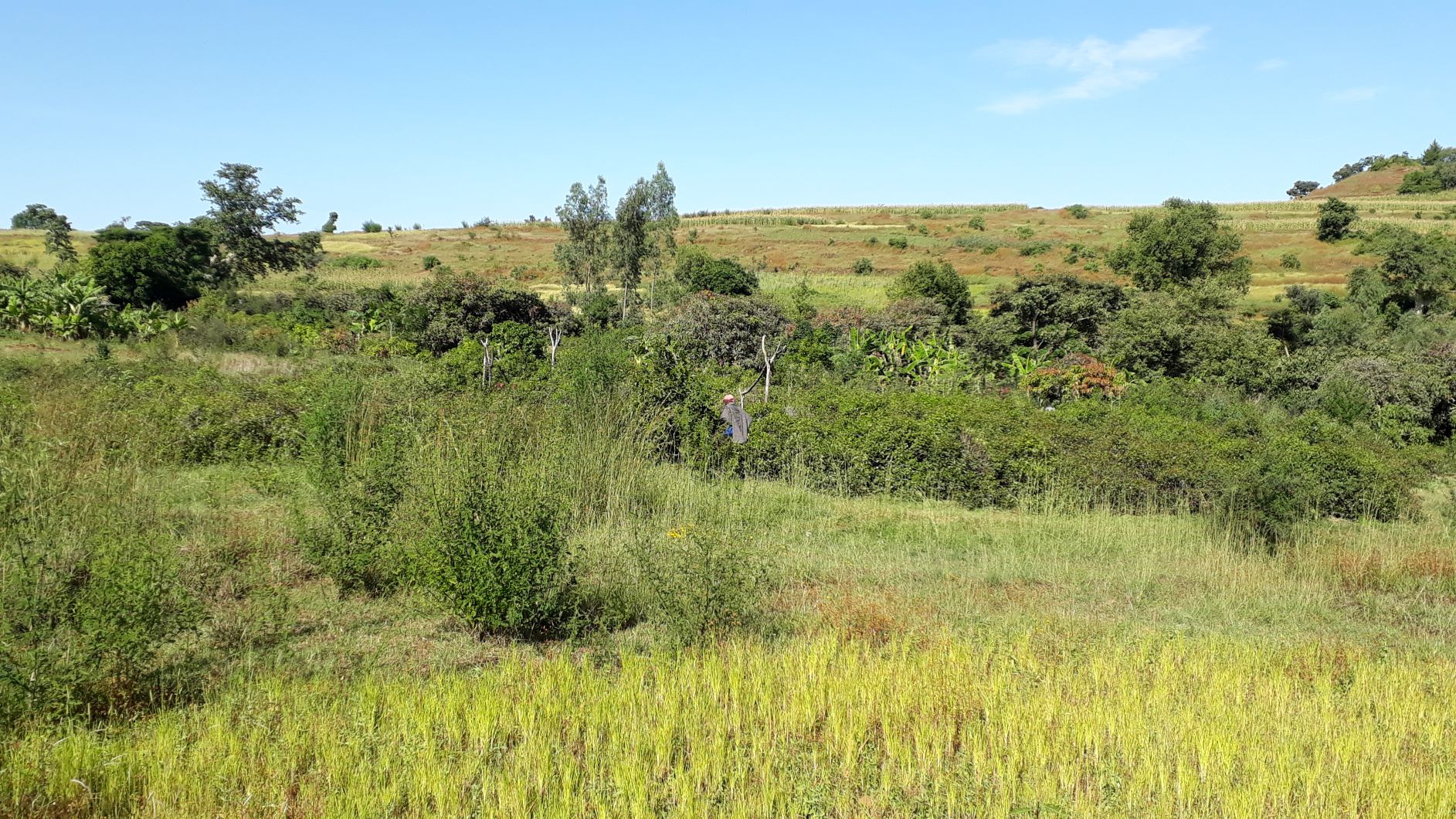
Homestead development is a diverse, dynamic and interesting horticultural area; it appears as an agroforestry plot in a cultivated landscape surrounding it, and it is more productive than single cropping, since harvesting is continuous over a great portion of the growing season and beyond.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
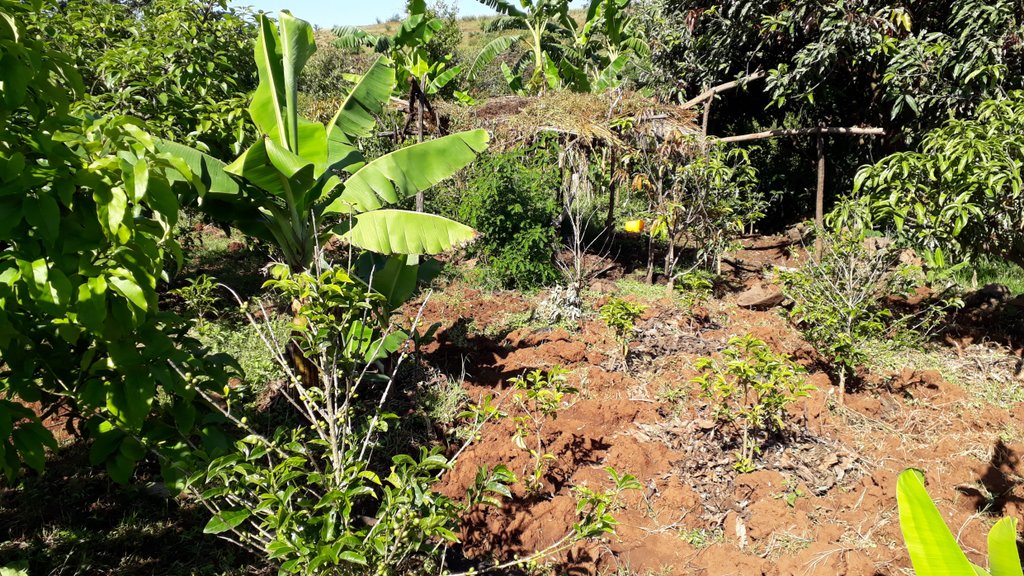
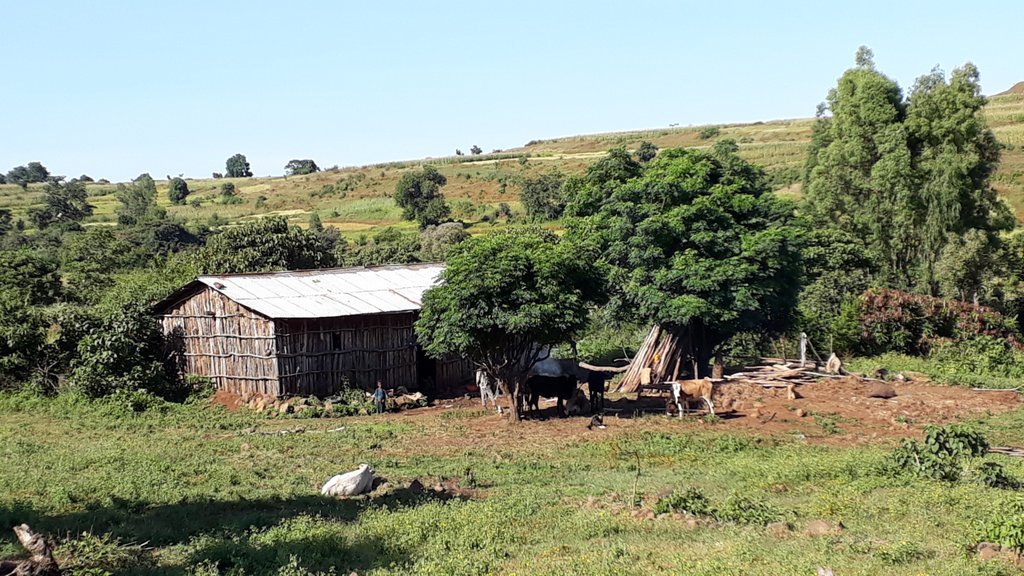
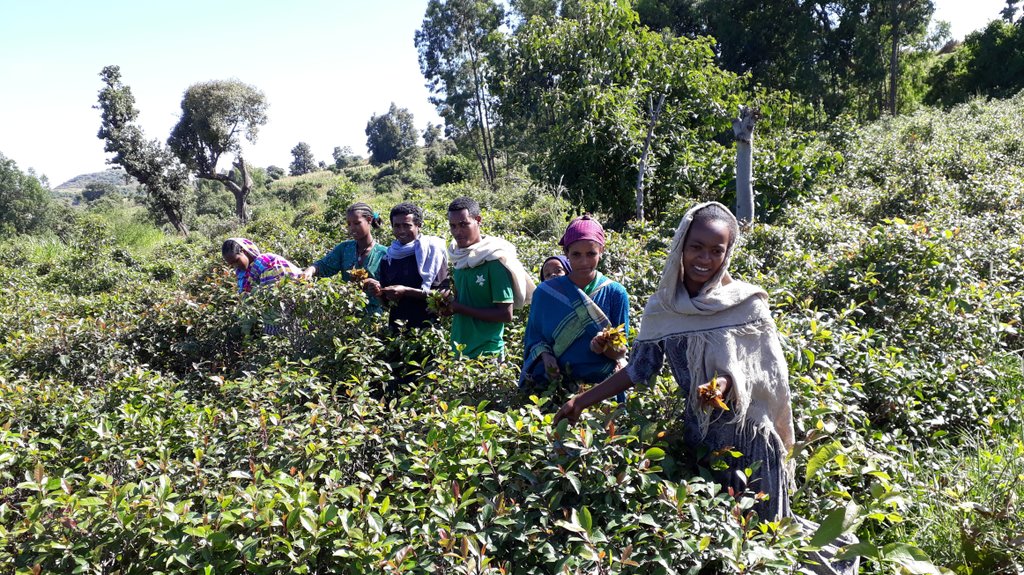
1. Homestead development is a horticultural area, usually around a homestead, and consisting of trees (mango, avocado), bushes (citrus fruits, coffee, gesho (hops), chat, banana), while ground crops (vegetables, maize) are grown at the same time and on the same parcel of land.
2. The technology applies the principle of intercropping, i.e. two or more plant species are grown in close proximity, providing multiple outputs and yields, while combined applications and shared inputs are possible.
3. Economically, homestead development helps to reduce poverty through increased production, improved human nutrition through diverse species. It also reduces deforestation and pressure on wood land by providing fuelwood.
4. In order to make the land suitable for homestead development, market-oriented seeds or seedlings must be available, thus a nursery for seedling provision. farm equipment, adequate water (hand-dug well), and sufficient work power are preconditions.
5. Homestead development as a technology is both economic and environmental, as the agroforestry setup also serves for conservation of natural resources.
6. Land users like additional outputs from their small plots of land, including the variety of fruits and vegetables, the recreational area around their homes, and the availability of water in hand-dug wells that are needed for irrigation.
7. Nevertheless, land are aware that homestead development gardens need continuous follow-up and management, as well as intensive labour inputs.
2.3 技术照片
关于照片的一般说明:
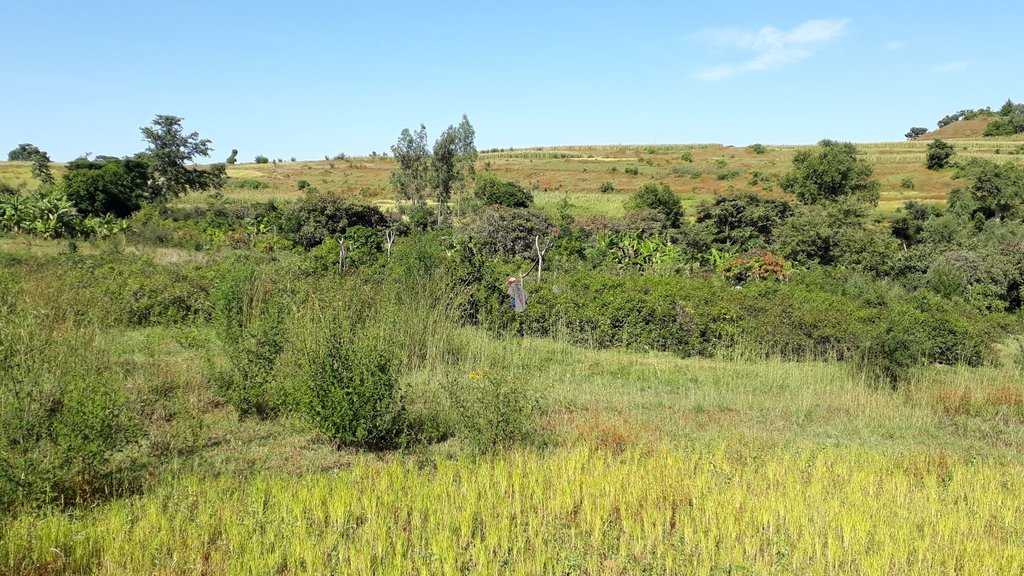
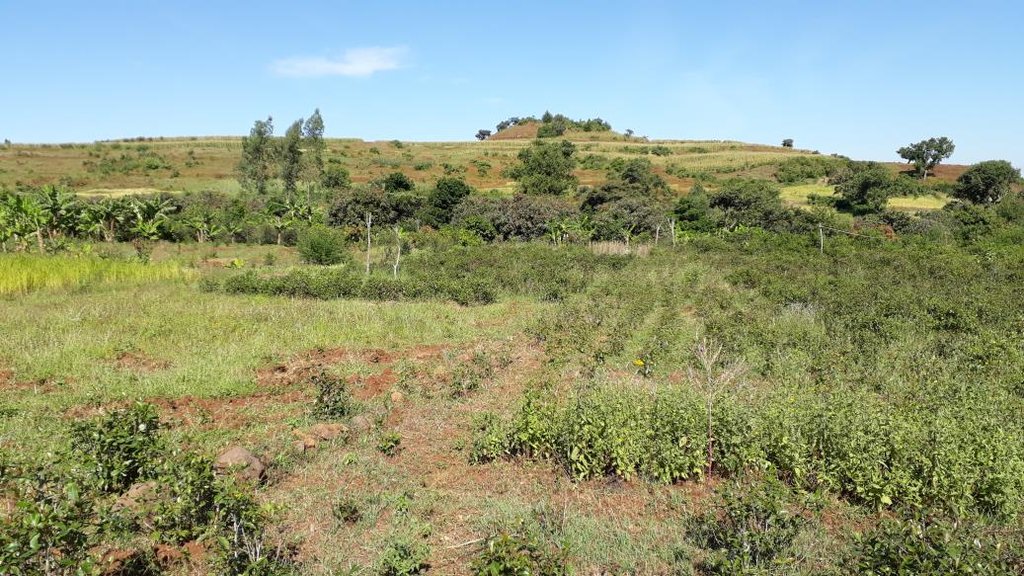
The photos were all taken during field work on 24 October 2018, while several technologies were assessed by different compilers. In the Abagerima area a full watershed was developed in 2013 by the Water and Land Resource Centre, Addis Ababa University and Centre for Development and Environment (CDE), University of Bern, funded by Swiss Development Cooperation and its Ethiopian partners.
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
Amhara Regional State
有关地点的进一步说明:
Abagerima Watershed, Laguna Village near Bahir Dar, the regional capital of Amhara Region, Ethiopia
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2013
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 燕麦
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
年作制度:
玉米/高粱/谷子与豆类间作
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 鳄梨
- 柑橘属
- 咖啡,采树荫栽培
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
- Gesho (hops), Chat
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Two or more plant species are grown in close proximity, providing multiple outputs and yields, while combined applications and shared inputs are possible
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
varying

森林/林地
- 植树造林
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 混交品种
- Sesbania Sesban; Vernonia amygdalina
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 常绿
产品和服务:
- 薪材
- 放牧/啃牧
注释:
Previous to the homestead development, the area was used for keeping livestock near the house, with some eucalyptus tees planted for construction and fuel wood. If the homestead garden is larger, it was previously also used for cultivating crops, and as grazing area.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- Teff
年作制度:
休耕 - 小麦/大麦/燕麦/旱稻
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
maze /sorghum/millet inter-cropped with legume
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Consecutive (rotational) cropping with occasional fallow

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 经营牧场
动物类型:
- 牛 - 奶制品
- 牛 - 非乳制品工作
- 马
- 骡子和驴
- 绵羊
是否实行作物与牲畜的综合管理?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Livestock is used as ploughing animals, donkesy and horses as carryin animals, sheep and goats for meat.
产品和服务:
- 肉类
- 交通工具/役畜
注释:
The homestead area was transformed from the above land uses to horticulture, while the 'old' land use system prevails in the surrounding area.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
For irrigation small hand-dug wells are constructed, up to a depth of about 5 metres, while the water level is usually quite near the surface during the rainy season.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 家庭花园
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
- V4:更换或清除外来/入侵物种

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降

水质恶化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
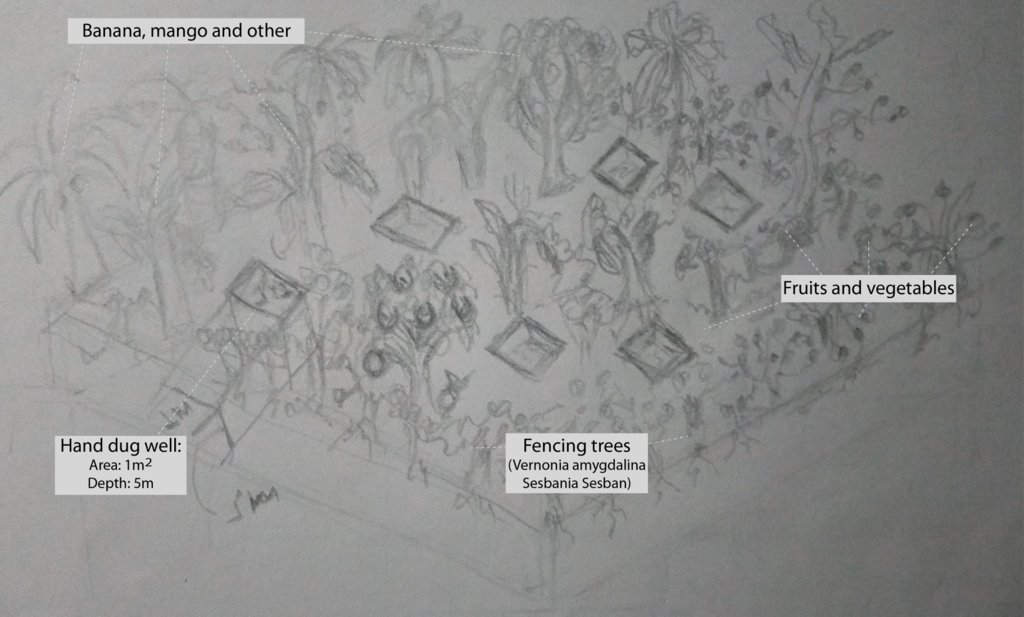
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The slope gradient of the Homestead Development area is less than 3%, and trees, bushes and garden products are planted very close to each other, so that passing through becomes difficult in places.
作者:
Sewalem Salele
日期:
24/10/2018
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
0.81 hectares
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
Other homestead development areas can be larger, the largest in Abagerima Watershed being 2.3 ha.
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
1.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | preparation of shallow wells | during dry season (to get deepest ground water) |
| 2. | improved fruit, vegetable and fodder seed(ling)s | during seed(ling) planting time |
| 3. | establishment of nursery site in the garden | after crop harvesting |
| 4. | preparation of the farm for plantation | after harvesting annual crop |
| 5. | planting of seedlings | July to August during main rainy season |
| 6. | continuous follow up and management practice performed | throughout the year |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | shallow well preparation (3 wells) | person-days | 27.0 | 5.0 | 135.0 | 70.0 |
| 劳动力 | farm preparation (first year) | person-days | 12.0 | 5.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | farming tools (first year) | pieces | 6.0 | 4.0 | 24.0 | 60.0 |
| 植物材料 | improved seed(ling)s | kg | 5.0 | 3.0 | 15.0 | 50.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | compost (first year) | m3 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | pesticides (first year) | litre | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | stones (first year) | m3 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 298.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 298.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Remaining costs were covered by the Agricultural Office
注释:
The labor cost for garden work is more expensive because it is difficult, strenuous, intensive and the working hours are longer.
The costs are mostly covered by the owner.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | shallow well maintenance | once a year |
| 2. | farm preparation (expansion) | throughout year |
| 3. | weeding and plowing | throughout the year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | shallow well maintenance | person-days | 5.0 | 5.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | farm preparation | person-days | 11.0 | 5.0 | 55.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | weeding and plowing | person-days | 15.0 | 5.0 | 75.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | improved seed(ling)s | kg | 2.0 | 4.0 | 8.0 | 50.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | compost | m3 | 7.0 | 5.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | pesticides | litre | 2.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 204.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 204.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Remaining costs were covered by the Agricultural Office
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Inflation rate fluctuations
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
One rainy season between April and October, with a peak in July and August and occasional rains also in the dry season.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Abagerima meteorological station
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
A major source of pollution are sediments resulting from soil erosion on cultivated land, and excess runoff from overgrazed areas.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Rent in and rent out in cultural norms
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 个人
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
Yezota (ownership right)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
作物质量
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
木材生产
森林/林地质量
非木材林业生产
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
能源生产
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
经济差异
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
土地使用权/用水权
文化机会
娱乐机会
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
注释/具体说明:
This may worsen when more homestead development areas are established around homes
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
This includes evapotranspiration
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
酸度
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
外来入侵物种
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
滑坡/泥石流
干旱影响
飓风、暴雨的影响
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
风速
微气候
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 非常好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 冬季 | 增加 | 非常好 |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 非常好 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 非常好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 非常好 |
| 局地雷暴 | 非常好 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 非常好 |
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 非常好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It helps fulfilling home consumption needs without incurring additional cost. |
| The water availability for irrigation has increased due to hand-dug wells. |
| It helps income diversification (from different fruits, vegetables and other crops such as chat) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increase of water table due to soil and water conservation on the land above the technology. |
| Creation of a conducive environment for the area. |
| Improvement of soil and water conservation practices. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| labor intensive, need continuous follow-up | use of family labour (female and children) |
| lack of research output to get more production from small parcel of land | improve link between farmers and researchers |
| lack of modern market linkages | create a market linkage before harvesting time |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| General lack of special attention for small scale farmers | Government should improve extension system for innovative small scale farmers |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Observations were performed in the area, and pictures taken
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Interviews were held with land users
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
Interviews were held with SLM expertes at Kebele level
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Secondary data like rainfall and temperature was taken from a station within the Abagerima Watershed
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
24/10/2018
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
primary data
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
obtained from land users
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Homestead development
7.4 一般注释
The questionnaire is transparent and easy to understand even for a first-time user.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块