The new theory of agriculture for mixed farming system [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Prapa Taranet
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
The royal new theory of agriculture
technologies_4146 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Singhophon Chaung
泰国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - 泰国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Allocating and managing small-scale farm areas to make it be able to use for agricultural production with the highest efficiency
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
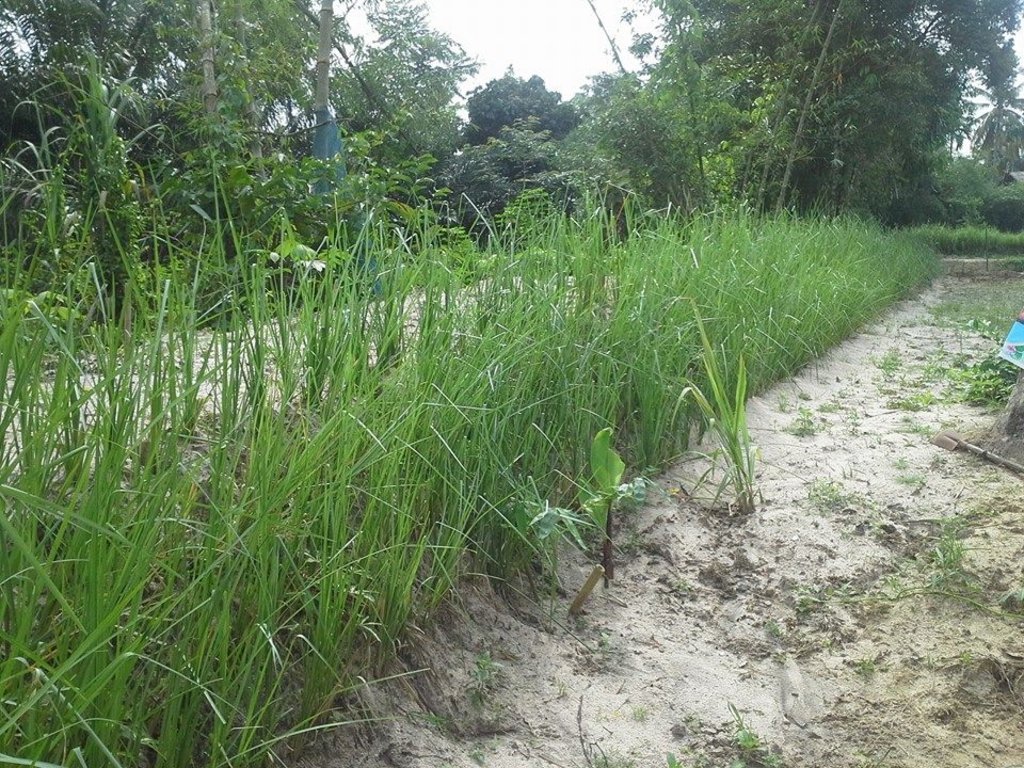
The new theory of agriculture is the application of mixed farming systems to poor farmers on small land holdings in Chang Sai sub-district, Phra Phrom district, Nakhon Si Thammarat province, Thailand. The most important concept of new theory farming is an efficient allocation of land to serve the different needs of farm households, including paddy fields, farm ponds for water and fishes, and cash crops, fruit trees, and trees for farm income, plus a residential area. It has a goal to solve the problem of shortage of land and water resources, which is a very important problem in Thailand, for making a living of smallholder farmers. Apart from the fact that the size of the area and water resources are the limit factors for farmers in this area, the land is also degraded causing by both natural and human activities. The area is classified as sand dunes with low to very low soil fertility where farmers mostly grew same plant species in the whole area during the rainy season of every year. This results in high risks in regard to a fluctuation of the amount of production and insufficient food crop production for household consumption. Therefore, land allocation for agriculture under the concept of the new theory agriculture can be the appropriate measure in making use of resources of small-scale areas for optimal benefits and increase incomes for a household. Nowadays, farmers in the adjacent area realized the benefits obtained from allocating the area, they formed a group of farmers in order to set up management, improve the use of their small-scale areas for optimal benefits.
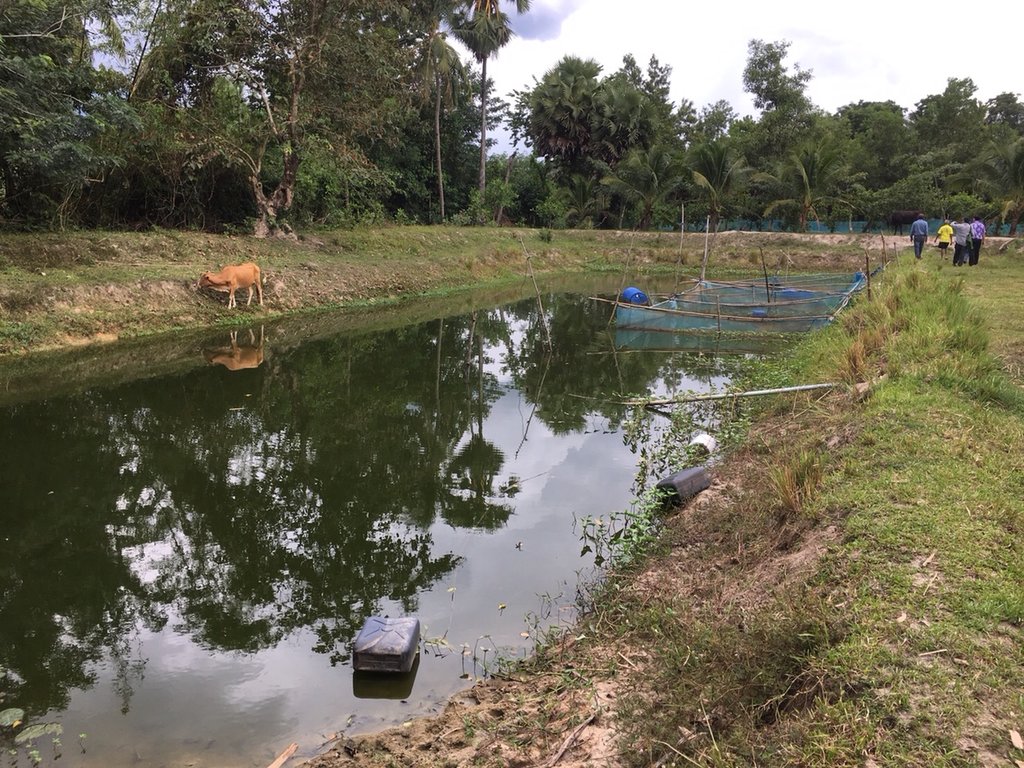
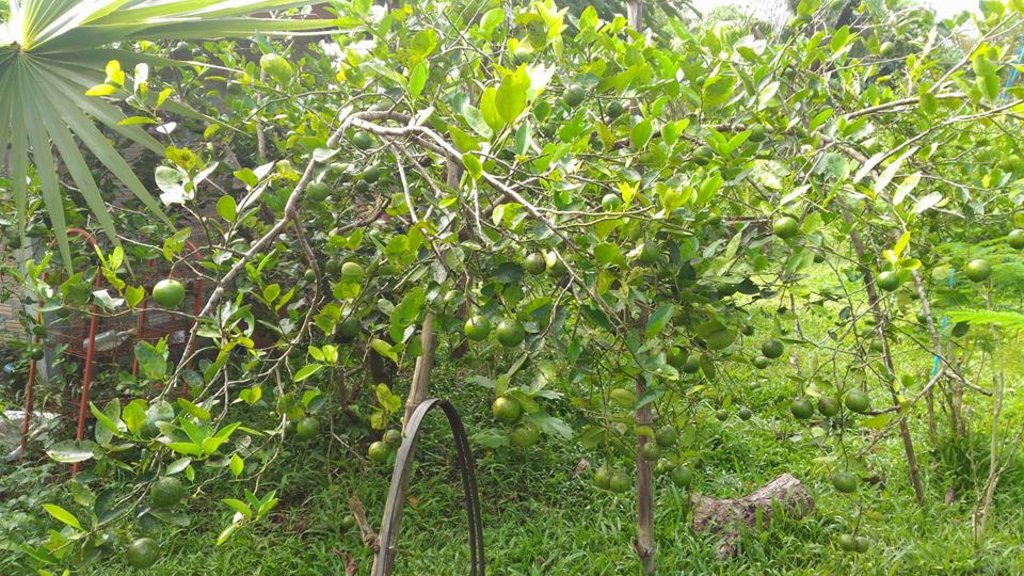
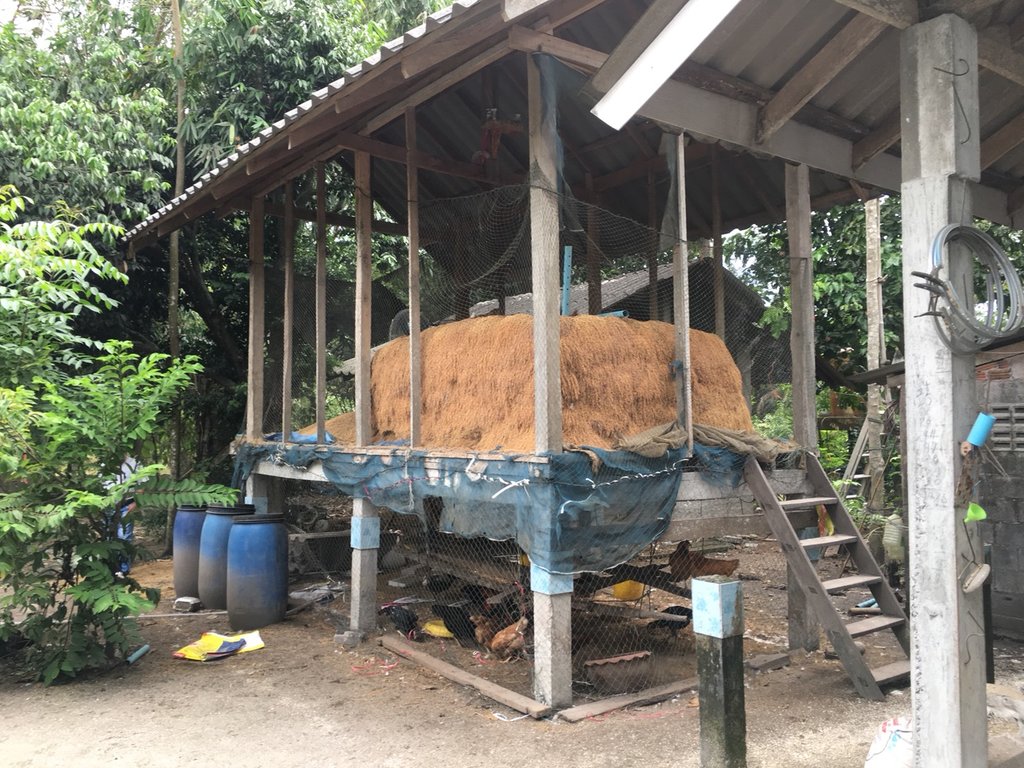
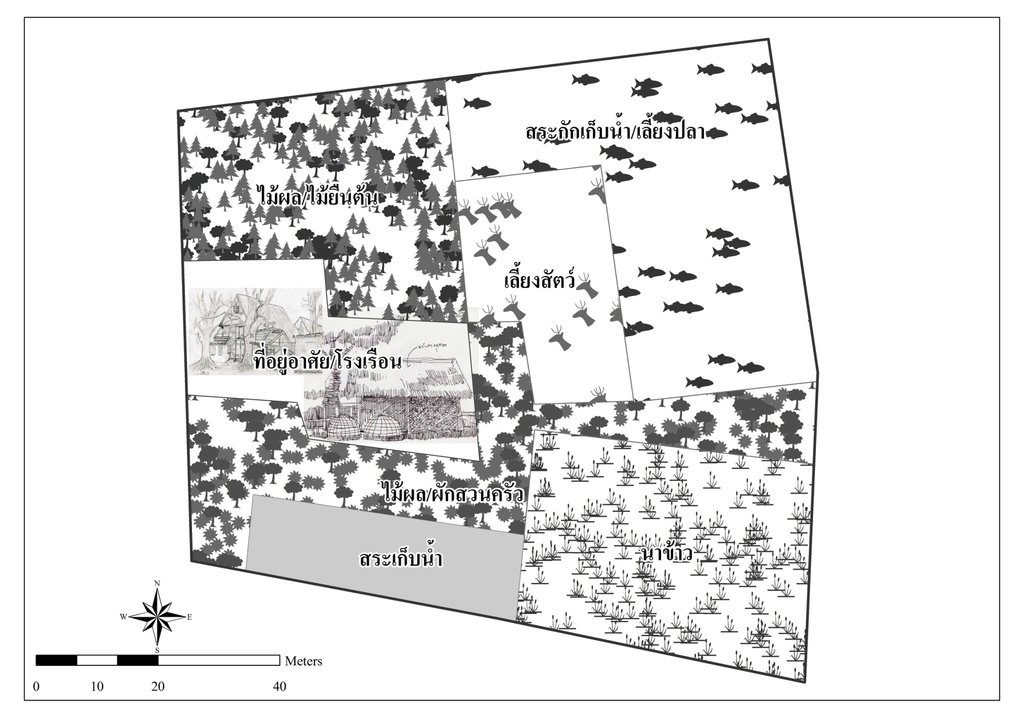
The new agricultural theory was initiated by His Majesty the Late King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand to provide help for farmers who had small-scale areas for agricultural purposes. For the land allocation, the land is divided into 4 parts. Part 1 is designated for a pond to store rainwater during the rainy season and to supply water to grow crops in the dry season as well as for raising aquatic animals (fishes, field crabs) and plants (such as morning glory, water mimosa, etc.). Part 2 is set aside for rice cultivation during the rainy season as a daily staple in households throughout the year sufficiently, which cut down on expenses and allow the farmers to be self-reliant. Part 3 is used for growing fruit and bearing trees, perennials, vegetables, field crops for daily consumption. If any surplus from consumption, it can be sold. Part 4 is used for dwelling, animal husbandry, roads and other structures (barn, straw, pile of compost, houses, mushroom nurseries, stalls, flowering-plants, ornamental plants, home-grown vegetables of backyard gardens). In any case, the proportion of the area in each section can be adjusted for either increase or decrease depending on the suitability of area conditions of each location and the necessity of farmers who make use of the area, but it is usually 30:30:30:10.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
Nakhon Si Thammarat province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Chang Sai sub-district, Phra Phrom district
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2010
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
This technology was initiated by His Majesty the Late King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand and disseminated to farmers by several departments under Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田

其它
具体说明:
Mixed farming system
注释:
cropland mixed with aquatic animals
注释:
Crops include rice, vegetable, limes, tropical fruits, and trees, while aquatic animals include a variety of fishes, field crabs.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 水稻(湿地)
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
- 家庭花园
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别

其它措施
具体说明:
Introduction of aquatic animal
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Land allocation according to new theory of agriculture in the area with the size of 5.3 rai of informants by dividing the land into 4 parts, first part is the ponds accounting for 1.5 rai (about 28% of the total area), second part is paddy field accounting for 1 rai (about 19% of the total area), third part is for growing fruit-bearing trees, home-grown vegetables, perennials accounting for 1.3 rai (about 25% of the total area) and last is for building construction for dwelling, animal husbandry and other constructions accounting for 1.5 rai ( about 28% of the total area).
作者:
Prapa Taranet
日期:
20/09/2018
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
5.3
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
6.5
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Baht
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
33.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
300 Baht
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pond construction | dry season |
| 2. | Labours | rainy season |
| 3. | Seeds | rainy season |
| 4. | Seedling | rainy season |
| 5. | Aqautic animals (fishes and field crabs) | rainy season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cultivation | days | 60.0 | 300.0 | 18000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hiring tractors for pond construction | ponds | 3.0 | 16000.0 | 48000.0 | 70.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | Kilogram | 300.0 | 10.0 | 3000.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | Plants | 100.0 | 50.0 | 5000.0 | 80.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost | Ton | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 50.0 |
| 施工材料 | Roof tiles | each | 240.0 | 60.0 | 14400.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Cement | bags | 8.0 | 100.0 | 800.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Sand and rocks | ton | 1.0 | 1650.0 | 1650.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Pillars | each | 12.0 | 100.0 | 1200.0 | |
| 其它 | Fishes and crabs | each | 2500.0 | 1.0 | 2500.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 97050.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 2940.91 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Government agencies
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Labours | throughout the year |
| 2. | Seeds | rainy season |
| 3. | Seedlings | rainy season |
| 4. | Aquatic animal | 9 months |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cultivation | days | 260.0 | 300.0 | 78000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Cultivation | days | 260.0 | 300.0 | 78000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost | ton | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 50.0 |
| 其它 | Fishes and crabs | each | 5000.0 | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 30.0 |
| 其它 | Feeding | month | 9.0 | 5000.0 | 45000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 208500.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 6318.18 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Government agencies support some inuts
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Water - if there is a lack of water during the dry season, some agricultural activities may not be practiced. This leads to a reduction of agricultural cost; however, this also leads to a reduction of a household income during that period.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
274.00
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Nakhon Si Thammarat meteorological station
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
The soil in this area is sandy soil, classified into Coated, isohyperthermic and Typic Quartzipsamments. The parent material is beach ridge or sand dune. The area condition is quite flat up to little undulating with the slope of 1.5%. The soil is very deep and well drained. Water permeability is fast but runoff on the soil surface occurs slowly. The soil reaction is very acidic to a little acidic (pH 5.0 - 6.5) throughout the soil profile. The soil fertility is low. Land use limitation is low fertility and a shortage of water.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
100
SLM之后的数量:
500
注释/具体说明:
Considering from rice production in 1 rai
作物质量
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
As farmer allocates the land to different types of crop, they can evaluate the suitable types of crops for the markets and climatic conditions
水资源可用性和质量
家畜用水的可用性
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Rainwater can be collected in the ponds and this could supply to cultivation during the dry season
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
The knowledge about SLM comes through the support of the government agencies
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Application of compost in the farm leads to an increase in soil organic matter
生物多样性:植被、动物
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
Earthworms, Birds, Bees, Cicada, and Varanus.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
Agrichemical products did not apply to the farmland, resulting in less soil contamination to environment
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 季节性温度 | 夏季 | 增加 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
Members in the community (about 50-60 households in the community) and parts of the outside community nearby show interest in this technology because they see that it can increase household incomes and start to implement it in their own areas. However, allocation of the land differs according to the area conditions and the needs of the owners themselves.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
The government provides some inputs for farmers who want to apply this technology to their farmland such as fishes and rice seeds. Then most farmers get some support before they start the activity on the farm.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 不断变化的市场
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Since organic markets get bigger in the areas, then some farmers produce their products without using agrichemical products. This allows farmers to improve the price for their products.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Water can be available even in the dry season since this technology includes the farm pond construction for rainwater storage. |
| Farmers should be able to grow enough rice for the whole year’s consumption. |
| Production planning can be done for the household consumption and supply to the market. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Allocation of the land into 4 parts according to the new theory of agriculture is considered an appropriate option for smallholder farmers who are having small farmland and water shortage. This is due to they can plan what crops, and when, to grow for each growing season based on climatic condition and market. Importantly, farmers learn how to plan the production that will be distributed to the market and for making a living. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| A lack of household labor results in some farmers adopted only part of technology where the efficiency of this technology may be lower than the adoption of full management. | Mose farmers hire labor or mechanical equipment to help them farming. although this increases the farming cost, it helps farmers to get their work done in time. |
| The cost of investment is rather high, especially for digging the pond. | Farmers ask the support from the government. While some farmers receive 80% help from the government, foundations, and the private sector for digging the ponds, others receive less support from the government. |
| Farmers have limited land for farming, to allocate the land to usual allocation as recommendation may not be suitable. | Farmers changed or improved the allocation ratio by themselves based on the land conditions, climatic condition, and the environment. For example, some farmers who have enough water sources in their areas, the size of the pond can be reduced to make room for other uses. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Due to the fact that managing the area with many activities may require more time to take action than monoculture farming, which cannot interest some farmers to practice. Furthermore, it may take time to make it worth the paid expenses due to complexity, little understanding, insufficient labor force, and more hiring may require. | The government needs to take action in the areas to provide more knowledge on this technology and find the solution to the problems. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
20/09/2018
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
New Theory of Agriculture, 2011, Office of the Royal Development Projects Board.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.rdpb.go.th/UploadNew/Documents/%E0%B8%97%E0%B8%A4%E0%B8%A9%E0%B8%8E%E0%B8%B5%E0%B9%83%E0%B8%AB%E0%B8%A1%E0%B9%88.pdf
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Implementation manual for new theory of agriculture, 2015, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www3.oae.go.th/rdpcc/images/filesdownload/SUFFICIENCY/9.9.pdf
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Sufficiency Economy & New Theory
URL:
http://www.chaipat.or.th/eng/concepts-theories/sufficiency-economy-new-theory.html
7.4 一般注释
The long-term impact on household income might change or improve if they practice this technology longer period than 8 years.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块