Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Julie Zähringer
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1453 - 塔吉克斯坦
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: March 21, 2017 (inactive)
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: July 23, 2017 (inactive)
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: Aug. 14, 2019 (inactive)
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kyrgyzstan Mountain Societies Development Support Programme, Aga Khan Development Network (MSDSP KG) - 吉尔吉斯斯坦有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Tree nurseries are established to test and identify varieties of tree species that are tolerant to climate change in the region.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
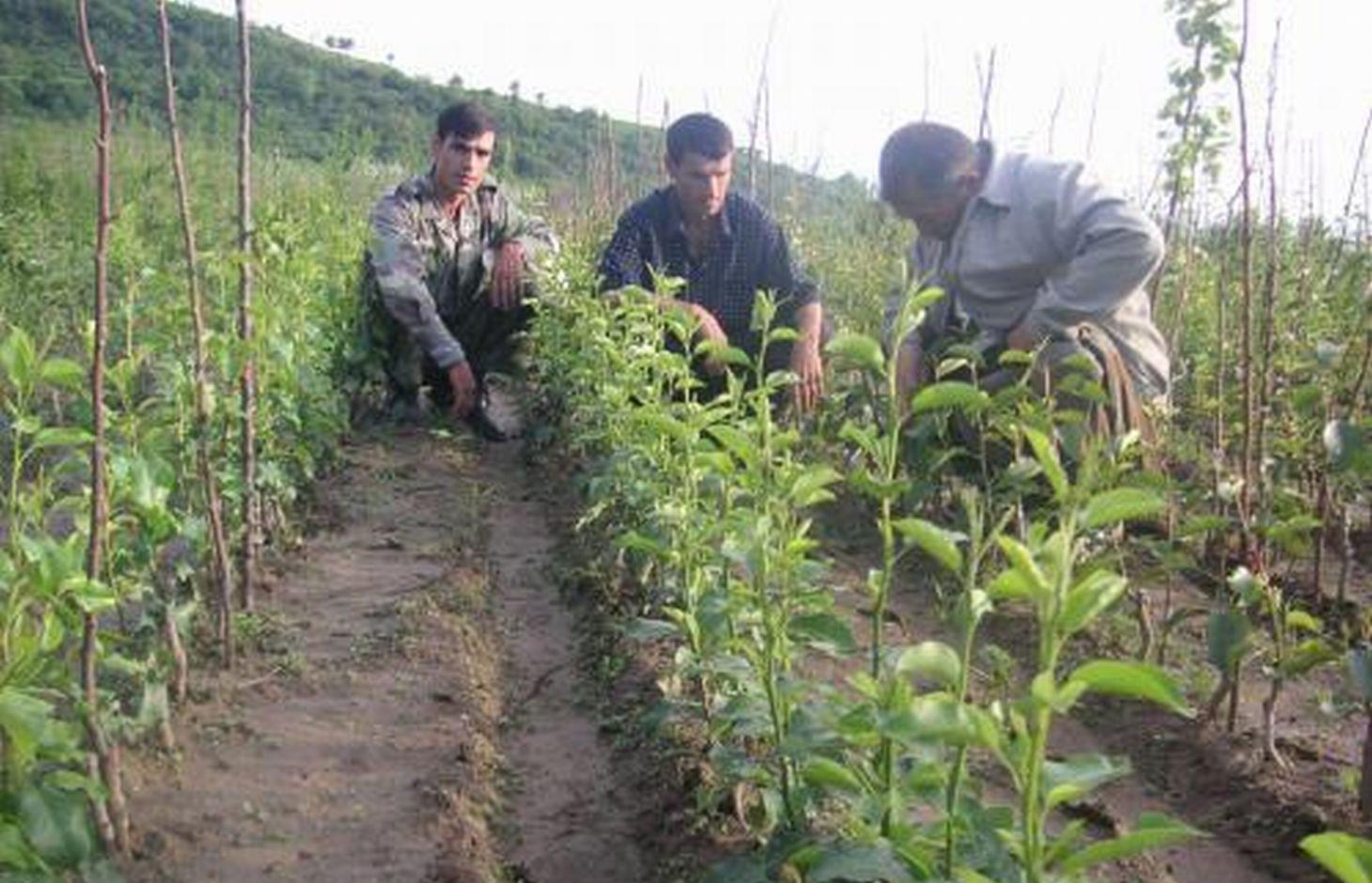
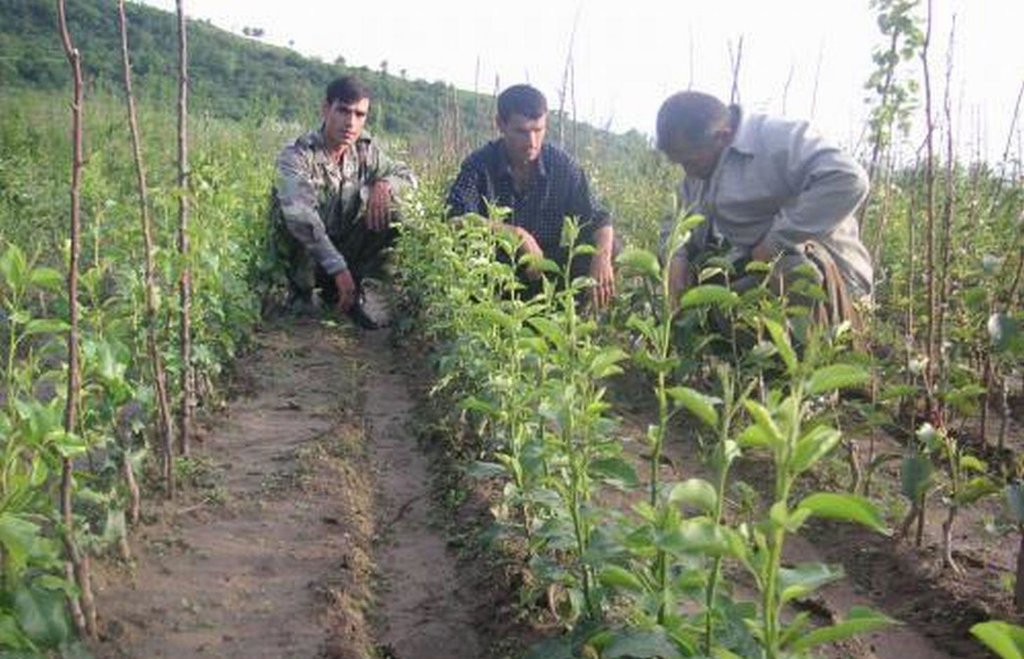
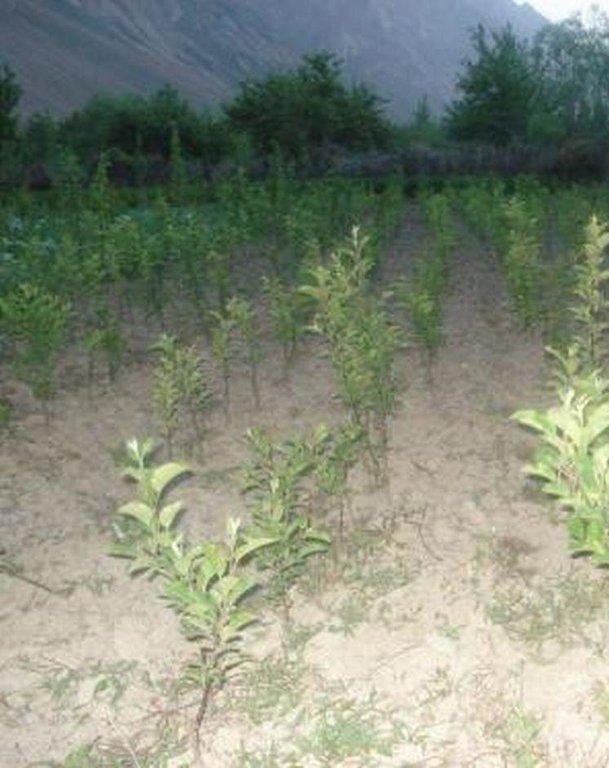
In 1995-96 the first tree nursery was established in the Vanj valley with support from the Mountain Societies Development Support Programme (MSDSP) of the Aga Khan Foundation. During Soviet times there were no tree nurseries in this region and seedlings had to be brought in from outside. Only the Pamir Biological Institute (PBI) was able to obtain seedlings for research purposes. A nursery of about 0.1 ha was established by one farmer on his own land. Tree species grown in the nursery include apple, peach, apricot, walnut, cherry and pear.
Purpose of the Technology: The main goal of the project was to make varieties of tree species adapted to different climatic conditions in GBAO locally available. The seedlings are used for other MSDSP projects, such as orchards for soil stabilisation, and are also purchased by private land users for their own land. In addition, the land user was taught how to establish a business by selling seedlings to other land users. There is a strong need for quality tree seedlings in the whole region and even people from as far away as Ishkhashim (7 hour journey by car) travel to Vanj valley to purchase seedlings from this nursery. The economic benefit for the land user is very high as during one year he can make more than 18,000 TJS (4000 USD) of profit from selling seedlings while the investments in fertilisers are comparably small.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The steps necessary for the establishment of a tree nursery are the following: (1) a suitable plot of flat land is chosen by the farmer, (2) the plot is fenced with dead branches to protect it from roaming animals, (3) in March, the farmer prepares several wooden boxes filled with humid soil in which he distributes 10 kg of seeds of different tree species and varieties. Those boxes have to be irrigated for a month while the seeds are germinating, (4) in April, the nursery plot is ploughed along the contour using animal traction and 1 ton of organic manure, 20 kg of phosphor and 2.5 kg of nitrogen is mixed with the soil, (5) seedlings are planted linearly along the contour with small irrigation ditches running parallel to the planting lines. These ditches were automatically established through the ploughing process, (6) two more times during the first season another 3 kg of nitrogen are applied. In the second year the grafting process is started and in the third year the farmer starts selling the seedlings. The farmer therefore splits up the nursery plot in three parts so that he can always have newly planted seedlings at the same time with second-year seedlings for grafting and third-year seedlings for selling
Natural / human environment: The technology was adopted by two other farmers from the village who had successfully applied to MSDSP for financial support for seeds and fertilisers. Many other farmers from neighbouring villages are interested. The bridge that is currently being built to allow for more trade between Afghanistan and Tajikistan might open further market opportunities for the land user. Furthermore this type of experience is being widely replicated in other districts and supported by MSDSP.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Tajikistan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Vanj
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
1995, through MSDP project
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 核果(桃、杏、樱桃、李子等)
- 树坚果(巴西坚果、开心果、核桃、杏仁等)
- 仁果类(苹果、梨子、柑橘等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 90Longest growing period from month to month: March-May
注释:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): reduction of vegetation cover, erosion of slope areas, decline of soil fertility,
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
注释:
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats
Main causes of degradation: soil management, deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), overgrazing
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature, change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, floods, droughts, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (avalanches, mud flows), population pressure, poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 3000 / 0.1 ha
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Trees/ shrubs species: apple, peach, apricot, walnut, cherries, pear
Change of land use practices / intensity level: from cropland to tree nursery
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Somoni
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
4.5
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.50
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select a place with enough water and good soil fertility on flat land for establishment of nursery | |
| 2. | Fencing with dead branches | |
| 3. | Ploughing and distribution of fertilisers | March-April |
| 4. | Plant seeds in box with humid soil and irrigate | March |
| 5. | After one month transfer seedlings to planting lines | March-April |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Fencing with dead branches | Persons/day | 80.0 | 20.0 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Ploughing and distribution of fertilisers | Persons/day | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Plant seeds in box with humid soil and irrigate | Persons/day | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Transfer seedlings to planting lines | Persons/day | 28.0 | 20.0 | 560.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | kg | 10.0 | 5.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | kg | 30.0 | 3.0 | 90.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2370.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 526.67 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | during first year |
| 2. | Apply nitrogen fertiliser twice more during the growing season | during the growing season |
| 3. | Grafting | second year |
| 4. | None | None |
| 5. | None |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Apply nitrogen fertiliser | Persons/day | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Weeding | Persons/day | 28.0 | 20.0 | 560.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Grafting | Persons/day | 28.0 | 20.0 | 560.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | kg | 6.0 | 3.0 | 18.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1158.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 257.33 | |||||
注释:
The costs were calculated for a nursery of 0.1 ha.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most determinate factors affecting the costs are for labour, although in the documented example, labour was provided voluntarily by the family of the land user. Costs for labour are estimates for a situation in which labour had to be paid in Tajikistan.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
500.00
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 1800 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Off-farm income specification: teacher
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
The land belongs to the state but the land user has a certificate.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Nursery established on cropland
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
The economic benefit for the land user is very high as during one year he can make more than 18,000 TJS (4000 USD) of profit from selling seedlings while the investments in fertilisers are comparably small.
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Availability of fruits
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
More fruits provide a more balanced diet with more vitamins
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
Aesthetic value of trees
SLM/土地退化知识
Livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Higher income from selling the tree seedlings, about 3,000 USD per year, allowing people to provide better education for their children and better access to healthcare
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
注释/具体说明:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
植物多样性
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
其它生态影响
Hazard towards adverse events
注释/具体说明:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Increased income and benefit start after three years when seedlings can be sold.
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
3 households
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: people from other villages in the valley contacted MSDSP because they would like to adopt the technology (however, they would need financial or material support).
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The technology is very important to the whole of the GBAO region as nurseries were not available during Soviet times and all tree seedlings were brought from outside How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improved access for farmers of interesting tree varieties that they can reproduce in their nurseries |
|
Creation of business opportunities. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Experience sharing between farmers from outside GBAO |
|
Through the spreading of this technology there will be more seedlings available to all interested households How can they be sustained / enhanced? Establishment of farmer field schools to disseminate the positive experiences of this technology and to increase the number of nurseries |
|
Varieties of trees that are adapted to local climate can be more easily obtained How can they be sustained / enhanced? Access to other new varieties should be improved |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| It is quite a complicated process that requires some expertise; the farmer needs to know about planting technologies, grafting and market opportunities etc. | Farmer to farmer dissemination of knowledge could be facilitated through the establishment of farmer field schools. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块