Establishment of improved orchards and vineyards [阿富汗]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Bettina Wolfgramm
- 编辑者: Roziya Kirgizbekova
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Bunyodi boghi va boghi anguri behbudyofta
technologies_669 - 阿富汗
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Mirza Bay Gholam Sakhi
Natural Resources Management Comittee (NRMC)
阿富汗
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Researcher:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar, Afghanistan (LIPT)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bern University of Applied Sciences, School of Agricultural, Forest and Food Sciences (HAFL) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
SLM practices documented in the frame of the Rustaq NRM study were established only recently (1-3 years ago). It is too early for a final judgment on the sustainability of these technologies within the human and natural environment of Chokar watershed.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Local and new varieties of fruits are planted on degraded land in accordance with improved management practices. The established orchards and vineyards serve double purpose of soil protection and income generation for the rural households. The alfalfa under the trees supports tree growth and is used for livestock fodder.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
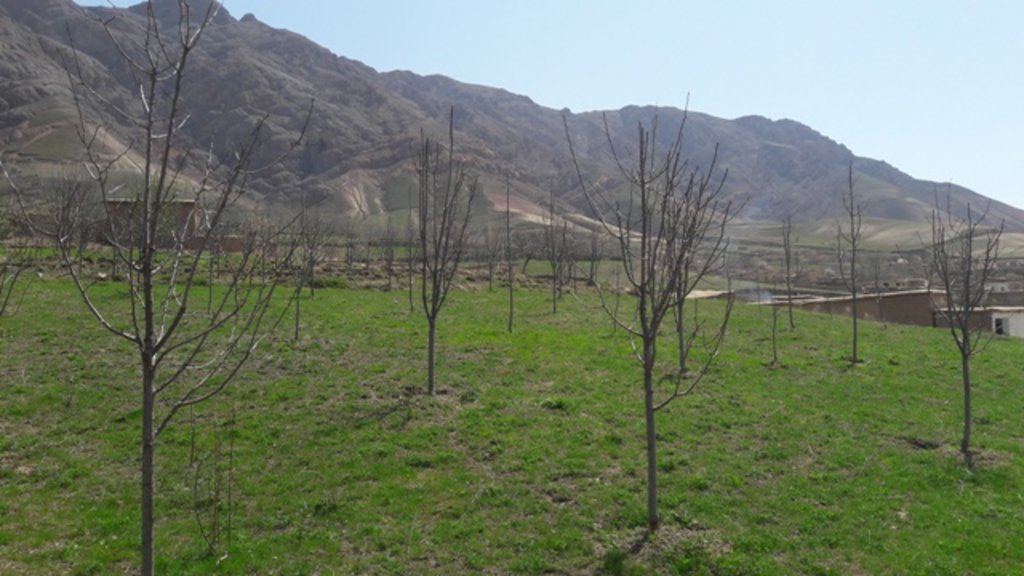
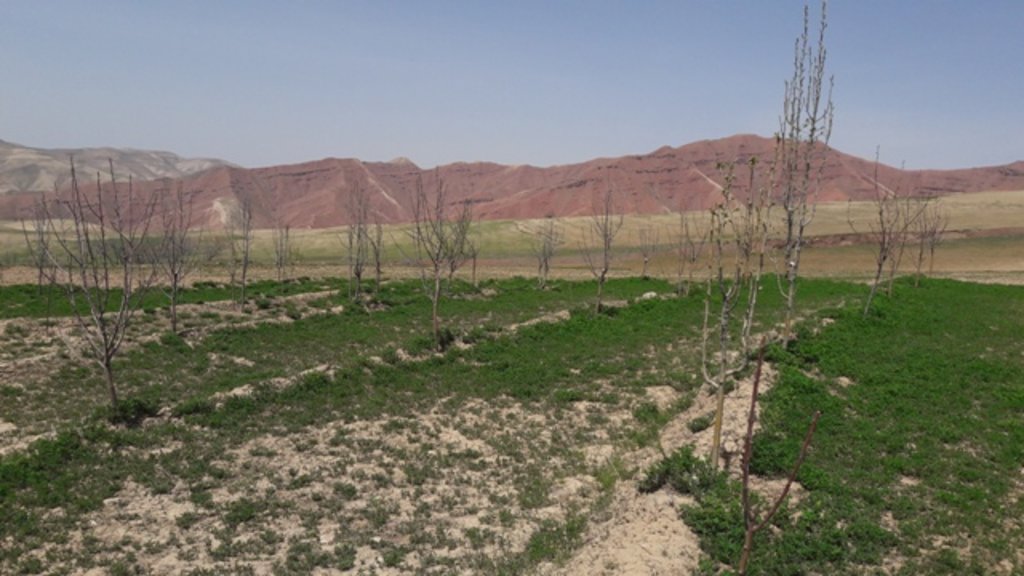
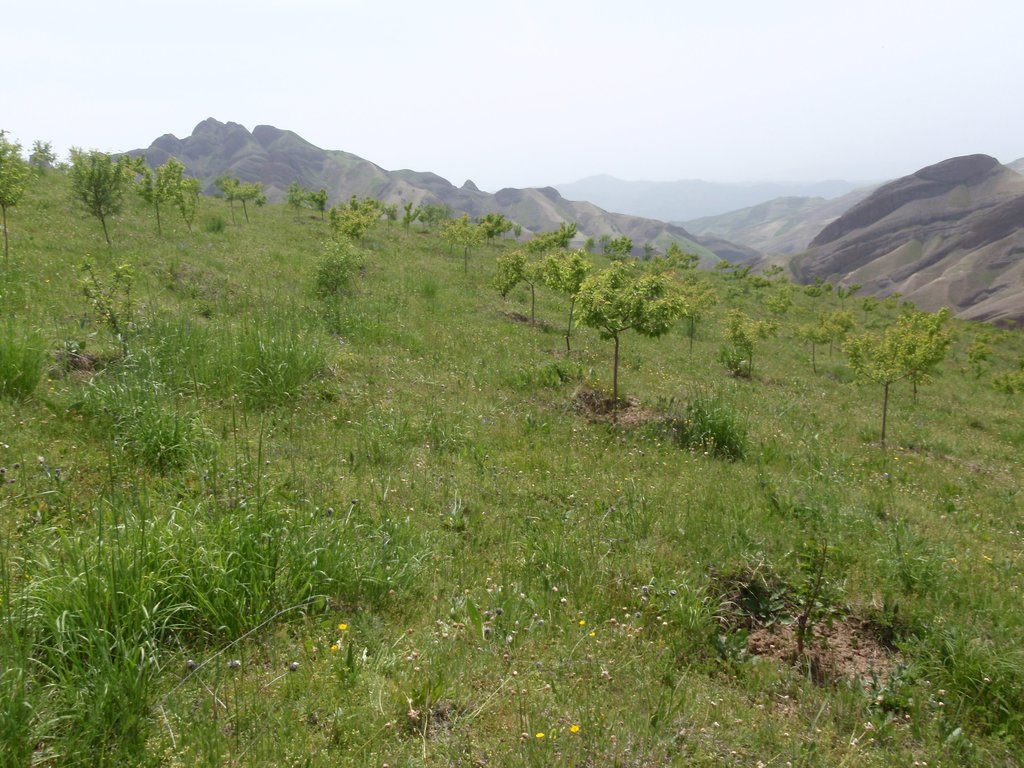
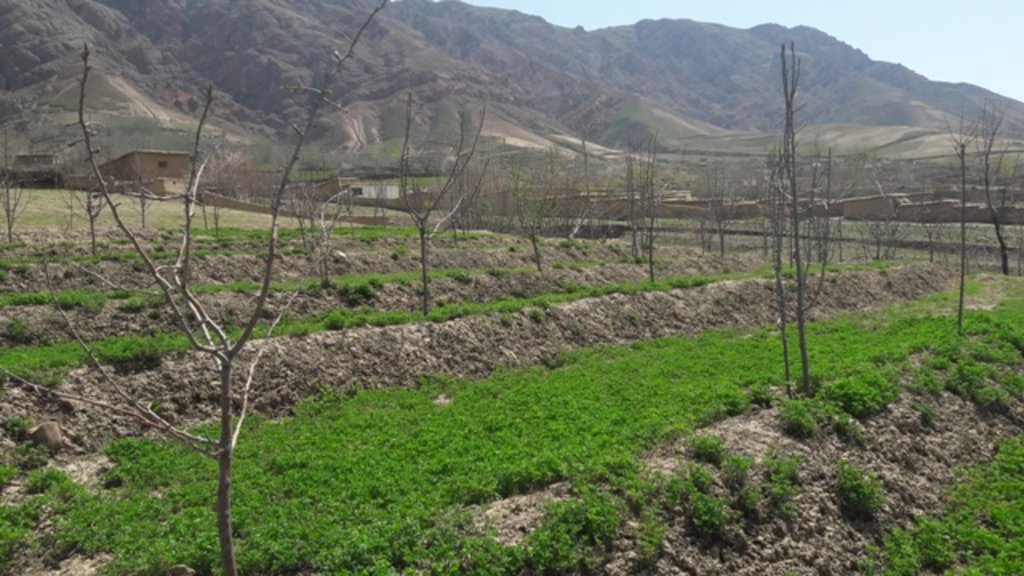
Project supported implementation of improved orchards and vineyards has taken place in the villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai, located in Chokar watershed of Rustaq District in Northern Afghanistan. The Chokar watershed is a mountainous area situated between 600 - 2,500 m above sea level. The climate is semi-arid with harsh and cold weather in winter and hot and dry summers. The annual precipitation in average years is 580mm. Land degradation affects all forms of land use and includes low vegetation cover, heavy top soil erosion from water, and poor soil fertility. Unsustainable agricultural practices, over-exploitation and high pressure on the natural resources are adversely impacting on the socio-economic well-being of local communities as well as contributing to the risk for being adversely affected by drought as well as landslides and flash foods triggered by heavy rainfall. The data used for the documentation of the technology is based on field research conducted in Chokar watershed, namely in the villages: Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai. These villages represent the upper, the middle and the lower zone of Chokar watershed, respectively. They differ considerably in access to services and infrastructure, but in general are poorly served. The communities depend on land resources for sustaining their livelihoods. In a good year with high yields, wheat-self-sufficiency lasts about 5 months. The three villages are home to ethnic Qarluq communities. Since 2012 the Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland has initiated a range of NRM interventions.
The rural population in Rustaq district of Afghanistan traditionally grows local varieties of apples, pears and grapes. Mostly it is subsistence farming with a small-scale local marketing. Shortage of irrigation water and lack of specific knowledge about horticultural and viticulture practices, negatively affects fruit yields. Apart of providing diverse fruits for consumption, orchards are also important for providing fodder for the livestock, retaining soil moisture and protecting the soil from erosion.
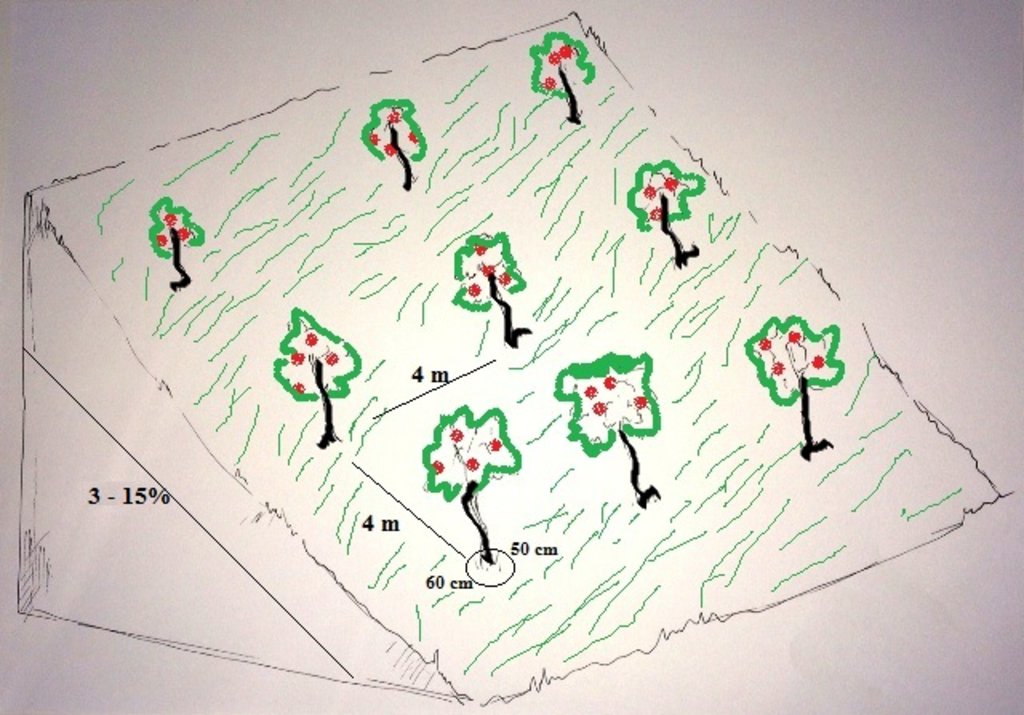
The local land users interested in the establishment of improved orchards and vineyards were mobilized through the Natural Resources Management Committees (NRMC) in Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai villages. In addition to the local varieties of pears, apples and grapes, new improved varieties were used for orchards and vineyards on 6.5 ha of degraded land. Such orchards were established inside or close to the villages on mountain slopes with gentle (3-5%) and moderate (6 -15%) steepness. Fruit trees are planted on locally identified dark and light soils, which correspond to moderately deep and loamy soil of medium soil fertility. Considering the medium quality of the soil, the first step of tree plantation is application of organic fertilizer. Afterwards, the plot is designed according to 4m x 4 m spacing between the trees. Under such parameters, on 1 jirib (0.2 ha) of land 125 fruit tree (apple or pear) seedlings are planted. The depth of the planting pits is 60 x 50 cm. The planted tree is watered and the lower trunk is covered with lime and water solution. Alfalfa is sown under the trees to serve as a fodder for the livestock. The orchards are irrigated mostly during summer once a week. In areas where there is shortage of irrigation water the trees are rainfed. Other maintenance activities include pest and disease control provided by a trained local specialist.
The new orchards only recently started giving fruits. The actual fruit yields are expected in 2017-2018. Expected higher yields of improved verities of pears, apples and grapes serves as a strong incentive for the local land users and their families to establish and maintain the orchards. Orchards are very demanding, but their reward is very promising in terms of improved harvest and more opportunities to sell the produce. Some land users have successful experience on their plots and already have fruits in their gardens and plan to enlarge their garden and plant more varieties of fruit trees, such as persimmons. Alfalfa which grows under the trees has important production value, particularly during the early years after the establishment phase, when the trees are too young to give fruits.
Female members of the households, which implemented orchards are also involved in establishing and maintaining orchards and vineyards. They take part in planting trees, watering, hay making and protecting the trees from livestock and people. Their contribution, plays an important part for the successful implementation of improved orchards and vineyards in Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿富汗
区域/州/省:
Takhar Province, Rustaq District
有关地点的进一步说明:
Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, Dashti Mirzai
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
This documentation is based on the experiences of SLM implementers from Sari Joy (8 plots), Jawaz Khana, (6 plots), and Dashti Mirzai (3 plots). Additionally insights were gained through interviews with both SLM implementers and observers from all three villages.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) supported by Swiss Development Cooperation (SDC) from 2012-17
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 饲料作物 - 苜蓿
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 饲料树木(朱缨花属、银合欢、前庭草等)
- 葡萄
- 仁果类(苹果、梨子、柑橘等)
- 树坚果(巴西坚果、开心果、核桃、杏仁等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1

牧场

森林/林地
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
注释:
About half of orchard plots are established on cropland.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
Often the trees are watered with supplementary irrigation, from irrigation channels, or fetching the water in buckets.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
注释:
Many land users establish a fence around their orchards to protect the trees from animal and the fruits from theft.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Orchards are established on mountain slopes with gentle (3-5%) and moderate (6-10%) steepness. Considering the medium soil fertility, the first step of tree plantation is application of organic fertilizer. Afterwards, the plot is designed according to 4m x 4 m spacing between rows and trees. Under such parameters, on 1 jirib (0.2 ha) of land 125 fruit tree (apple or pear) seedlings are planted. The depth of the planting pits is 60 x 50 cm. The planted tree is watered and the lower trunk is covered with lime and water solution. Alfalfa is sown under the trees for livestock fodder.
作者:
Aslam Qadamov; Roziya Kirgizbekova
日期:
03/04/2017
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 ha
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
67.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.2-5.3 USD per day
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of the area for orchard (Men) | Fall |
| 2. | Applicatoin of manure (Men) | Fall/Winter |
| 3. | Design of tree spacing in the orchard assisted by project staff (Men) | End of winter |
| 4. | Digging pits for planting (Men/Women) | Spring |
| 5. | Planting of fruit trees (Men/Women) | Spring |
| 6. | Sowing of alfalfa under the trees (Men/Women) | Spring |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Application of manure | person-day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | 83.0 |
| 劳动力 | Design of tree spacing | person-day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | |
| 劳动力 | Digging pits for planting | person-day | 15.0 | 5.3 | 79.5 | 83.0 |
| 劳动力 | Planting trees, sowing alfalfa and watering | person-day | 10.0 | 5.3 | 53.0 | 83.0 |
| 设备 | Meter | piece | 1.0 | 2.25 | 2.25 | |
| 设备 | Rope | Meter | 500.0 | 0.07 | 35.0 | |
| 设备 | Shovel | piece | 2.0 | 3.8 | 7.6 | |
| 设备 | Pick axe | piece | 1.0 | 2.25 | 2.25 | |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings (apple/pear) | piece | 625.0 | 0.75 | 468.75 | |
| 植物材料 | Alfalfa seeds | kg | 17.5 | 0.42 | 7.35 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | DAP | Kg | 250.0 | 0.9 | 225.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Urea | Kg | 250.0 | 0.45 | 112.5 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Animal manure | ton | 10.0 | 60.0 | 600.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Pesticide | cc | 500.0 | 0.9 | 450.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Lime | Kg | 25.0 | 1.5 | 37.5 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2133.7 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 31.85 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland
注释:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.2- 0.4 ha or 1- 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering of the trees (Men/Women) | 2 times/month/Summer |
| 2. | Weeding (Women) | |
| 3. | Pruning (Men) | |
| 4. | Lime application (Men) | |
| 5. | Hay making (Men/Women) | |
| 6. | Harvesting fruits (Men/Women) |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Irrigation | person day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Weeding | person day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Pruning | person day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Lime application | person day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Scissors for pruning | piece | 2.0 | 9.0 | 18.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Lime | Kg | 25.0 | 1.5 | 37.5 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 161.5 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 2.41 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des Hommes (Tdh) Switzerland
注释:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.2- 0.4 ha or 1- 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Due to the remoteness of the villages where the Technology has been implemented, all the inputs for establishment, such as agricultural equipment, plant material, fertilizers, etc., are purchased in Rustaq town. The expenses for traveling and delivering the inputs affect the establishment costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
580.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Average annual percipitation for the area was calculated with 580 mm, with minimums in dry years (2000 and 2001) of 270 mm and maximums in wet years (2009/2010) of 830 mm. The absolut maximum rainfall was calculated for 1986 with 1024 mm. The data series covers the time from 1979 to 2014.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR), http://rda.ucar.edu/pub/cfsr.html
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Derived from the publicly available dataset on length of growing period (LGP) (Fischer 2009 / IIASA-FAO). Internet link: http://tiles.arcgis.com/tiles/P8Cok4qAP1sTVE59/arcgis/rest/services/Length_of_growing_period/MapServer
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Local land users differentiate between the following soil types where orchards and vineyards are established:
- Light soil: moderately deep; texture medium; medium, low organic matter
- Dark soil: moderately deep; texture medium, medium; medium organic matter
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Floods occur mainly during the rainy seasons in spring and autumn. Availability of surface water differs for the three study villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, and Dashti Mirzai. Sari Joy has sources and good surface water availability. Jawaz Khana has poor water availability as water has to be fetched from a lower laying stream. Dashti Mirzai has good water availability also from an irrigation channel.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The land users in the area where the Technology is applied belong to the Uzbek ethnic minority group Qarluq.
Although the men are generally the main land users, however, women and children also take active part in the related work. The functions of men and women are clearly distinguished within the Afghan society. At the same time within the family this division of work and functions also results in men and women working hand-in-hand. An improvement of the family’s livelihood situation is expected to positively affect all family members. While, it is recognized that the involvement of women is key in order to secure basic human rights for everyone, to achieve good governance, sustainable development, and to efficiently contribute to poverty reduction (SDC 2004), it is also clear that a context sensitive approach is of high importance.
Women in rural Afghanistan are involved in many production and income generating activities that contribute to the overall household income, however, very few women own resources such as land and livestock, and their income generating options are fewer in comparison to that of men.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
Those who own land and use water for irrigation are obliged to pay for the water. The payment is made both in kind and in cash to the Mirob - the person in charge of distributing water in the community. The amount of the payment varies from village to village.
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
The local and new improved varieties of fruit trees planted and managed sustainably give better fruit yields. Enhanced fruit production is also due to proper and timely control of pests and disease.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
The grass (alfalfa and sainfoin), which is planted under the fruit trees is used as fodder for livestock.
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Indirect contribution to animal production is achieved through availability of more fodder for the livestock from the grass in the orchards. Animals also feed on the tree leaves in autumn.
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
Production of wood is limited. Fuel wood is made from seasonal pruning of the trees.
非木材林业生产
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
Multiple varieties of fruit trees are grown, also through grafting techniques.
生产区域
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
The new practice of establishing orchards and vineyards ensures better yields. New variety of fruits such as apples, pears, almonds and grapes improve the diversity of household's production and consumption. The households have better opportunity to earn more from selling their fresh and dried fruits on the local market.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Land users learned new methods of planting trees according to the soil conditions and water availability. They were trained with such skills as grafting, pruning, pest and disease control and were introduced to improved verities of fruit trees.
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
Female headed households are not included. Technology is implemented on private land, therefore people without land are excluded. However, they have they opportunity to earn income as a hired worker for the SLM implementers.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
土壤
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Improved vegetation cover resulting from the tree plantations and the grass.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
缓冲/过滤能力
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
These comments apply to 6.1 and 6.2:
- Socio-economic impacts: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the benefits from orchards and vineyards. They were asked to indicate production increase of crops; fodder; animals; wood; non-wood forest products; increase in product diversity; or production area. The most important increase they rated with 3, the second most with 2, others with 1 point. Averages of the points given by all implementers of orchards are reflected here.
- Similarly for the "ecological impacts" and on "off-site impacts": Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the on-site and off-site impacts of orchards and vineyards on water; soil; and vegetation. They were asked to indicate the strength of impacts with three, two or one points. Averages of the points given by the orchard implementers are reflected here.
- Socio-cultural impacts: This section is answered by the scientists, based on information collected during focus group discussions, and interviews conducted with persons from the 3 villages where the LIPT project implemented the SLM practices.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 非常好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
注释:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: SLM implementers were asked to jointly discuss and rate how much the SLM technology reduced the lands vulnerability to drought and local rainstorms. Only vulnerability to the most prevalent climate extremes (drought and local rainstorms) was discussed. SLM technologies were rated as reducing vulnerability poorly, well, or very well. The average points reflected here are from multi-criteria matrixes compiled in three villages where the SLM technology had been implemented.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: During the FGD with SLM implementers, a multi-criteria matrix was elaborated, and different SLM practices were rated. In the frame of this exercise, SLM implementers were asked to jointly discuss and rate short term (1-3 years) and long-term (10 years) returns of the SLM practice. As the SLM technology was only implemented 1-2 years ago, it is too early to compare benefits to maintenance costs. Farmers have little experience so far on the actual benefits of the SLM technology. The ratings are mostly based on expected benefits and not on actual benefits.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
6.5 ha
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
Individual SLM implementers were asked whether they received support for implementing the Technology. Each indicated the type of support he received from the proposed options: "Full Support 100%, Some Support, No Support 0%". 18% have adopted the technology without receiving support.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
其它(具体说明):
protection
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Some of the land users built a wall around their orchard. The wall made from locally available clay material, protects the trees and the grass from animal and people intrusion.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The land users have high expectations about the benefits of the improved practices to grow fruit trees. They see the benefit of growing different types of fruits. Expectations are high about increased fruit yields and increased opportunities to sell more fresh and dried fruits and nuts on the local market. Fruits and nuts sell very well and can generate higher incomes for the households. |
| The ecological benefits of the orchards in protecting the soil from heavy rains is valued by the land users. The villagers mark improved vegetation cover as their villages are becoming greener with the fruit trees and the alfalfa in the orchards. |
| It is appreciated by the land users that they were introduced and provided with new varieties of fruits. They were also trained on planting and maintaining orchards and vineyards in accordance with local conditions and using such techniques as grafting, pruning, mulching, protection from pests and diseases, etc. |
| The orchards not only give fruits, but also are the source of fuel wood, which is made from pruning the trees. Considering that many households keep livestock, the grass under the trees and tree leaves are used to feed the livestock. In return livestock manure is used as organic fertilizer for the trees. |
| Some land users having seen the positive outcome of their work, are interested in enlarging their orchards. Others are ready to support those who want to plant fruit trees by sharing tree saplings or seedlings with them. |
| Women share the expectations of earning more money for their household through growing more fruits and selling them on the local market. In Dashti Mirzai and Jawaz Khana women are particularly excited over their grape, which still need some time to give yields. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Better management practices in growing fruit trees will benefit the land user and the land through strengthening soil resistance to heavy rainfall and prevent erosion. Over the period of few more years the trees and undergrowth grass will significantly enhance infiltration and moisture retention in the soil, which in turn increase the vegetation cover and halt the degradation process. |
| The SLM knowledge obtained through project training is disseminating inside and beyond the villages, along with exchange of seedlings from new varieties of fruit trees. In addition to that, land users are aware of pest and disease control and have access to these services through trained specialist. |
| Households do not have to rely only on wheat and legumes, but are able to diversify their agricultural production even more. The expected opportunity to sell more fruits and nuts has the potential to increase households income. This in turn will enable the family to secure their food supply for longer periods. |
| Female family members' participation is one of the key elements for sustaining orchards and vineyards. Women highly value the importance of their work in orchards and the benefit it provides to their households. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Lack of irrigation water is a crucial issue, especially in Jawaz Khana, which makes it very difficult for the land users to maintain their orchards. | Rehabilitate the Yakhdons. Yakhdon is a local storage method for collecting snow water in winter to be used for drinking and irrigation in spring and summer. One Yakhdon can provide water for up to six months. Several of these Yakhdons are destroyed and their rehabilitation would provide better access to water for Jawaz Khana. |
| The young trees are sensitive to droughts and need to be watered regularly to ensure that they survive. | |
| Establishment of orchards requires hard work and sufficient money from the land user to buy seedlings and in some cases to build a wall around the orchard or build an irrigation canal. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The establishment of orchards is reported as one of the most labour-intensive SLM practice for both men and women. Working in orchards increases the burden of women in addition to their household chores. | |
| Technical knowledge on planting and maintaining fruit trees and grapes is required to ensure tree survival, good productivity and protection from pests and diseases. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Focus group discussions (FGD) were organized by CDE team to collect information from SLM implementers. Total of 17 land users who have implemented terraces participated in the FGDs held in the three villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai.
Interviews were conducted by the HAFL team to collect information from persons representing all the three study villages. Very detailed interviews were conducted with 41 persons interested in orchard implementation, of which 14 persons are from households that already have implemented orchards.
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
Close collaboration took place during the compilation of this material with the technical staff of the LIPT project in Rustaq.
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Information provided in the reports of the LIPT project in Rustaq served as an initial source of information during the preparatory phase and also solidifying the description of the technology and area of implementation. Other background papers on Afghanistan were referred to for general information on agriculture and natural resource management in Afghanistan.
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
27/10/2016
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Guidelines for Focus Group Discussions
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Methods section of the Rustaq NRM study
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块