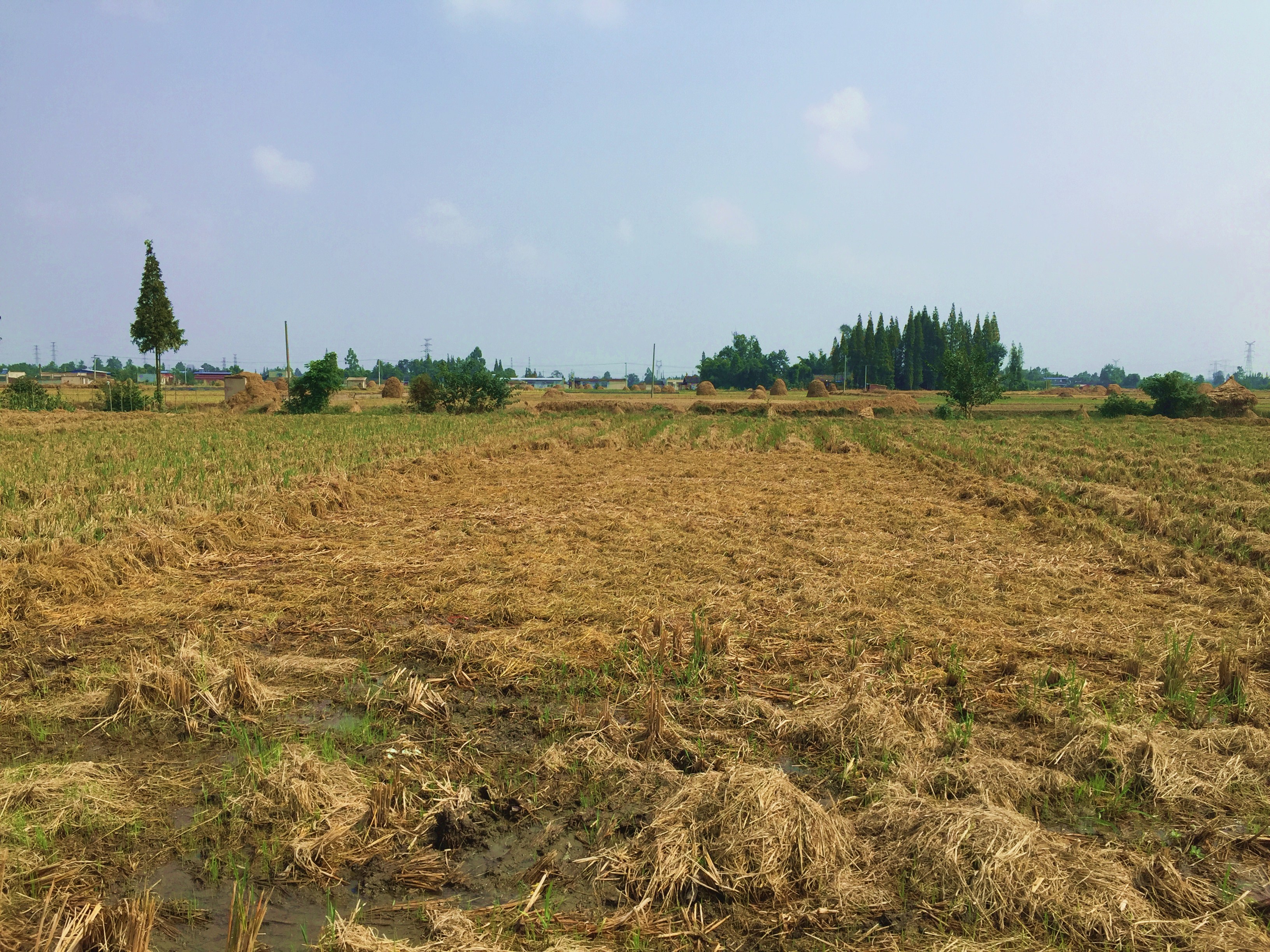
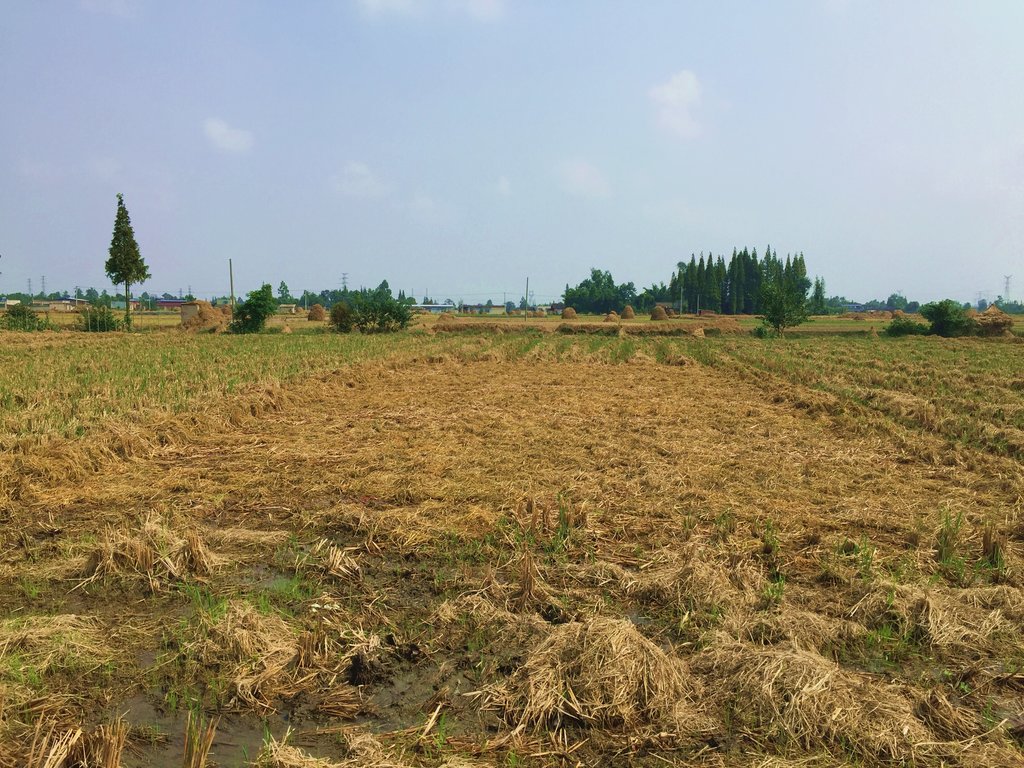
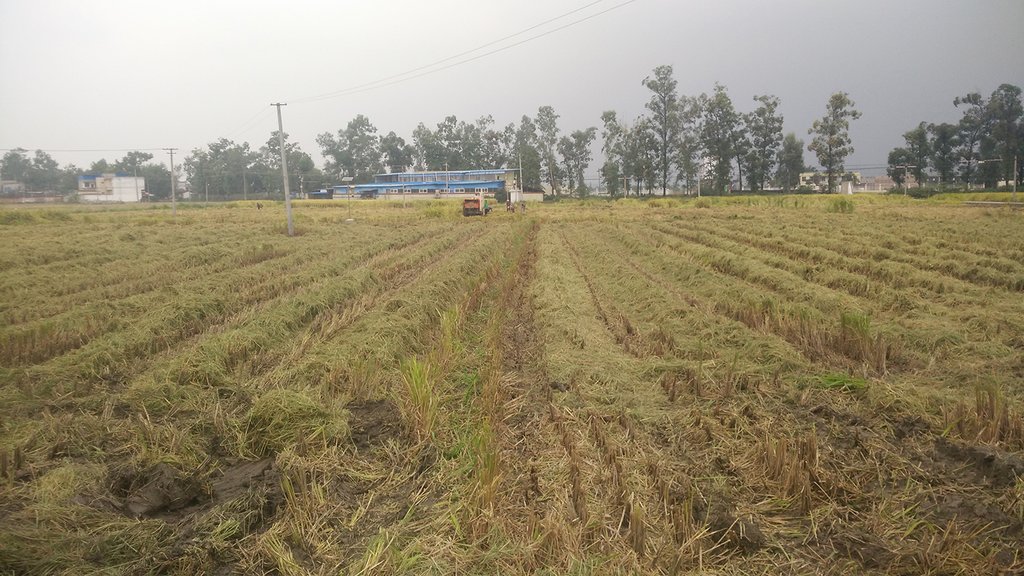
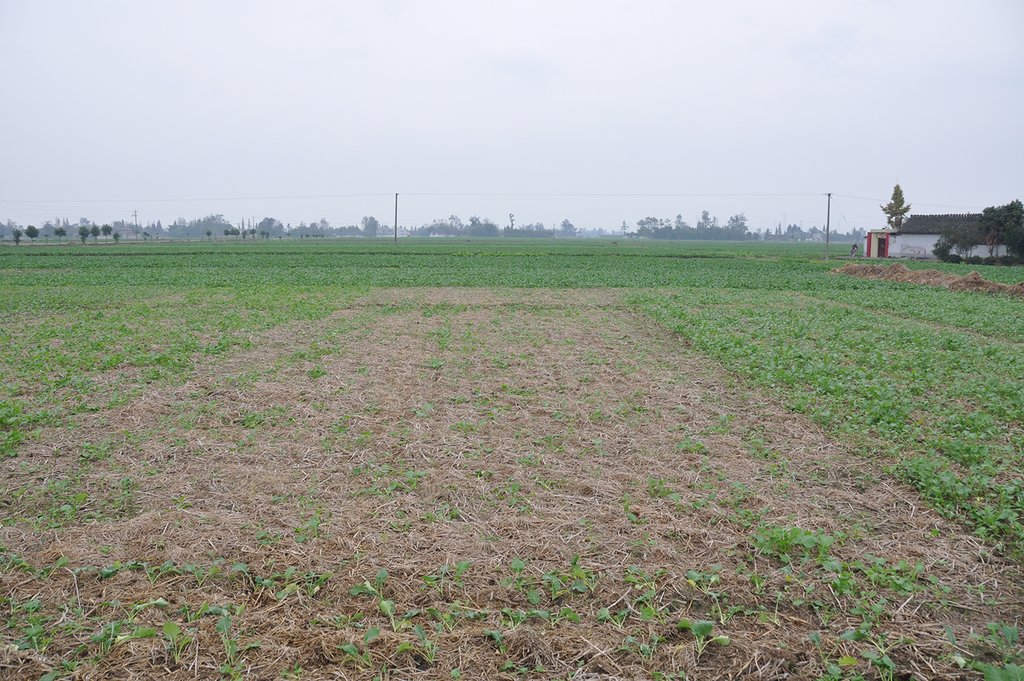
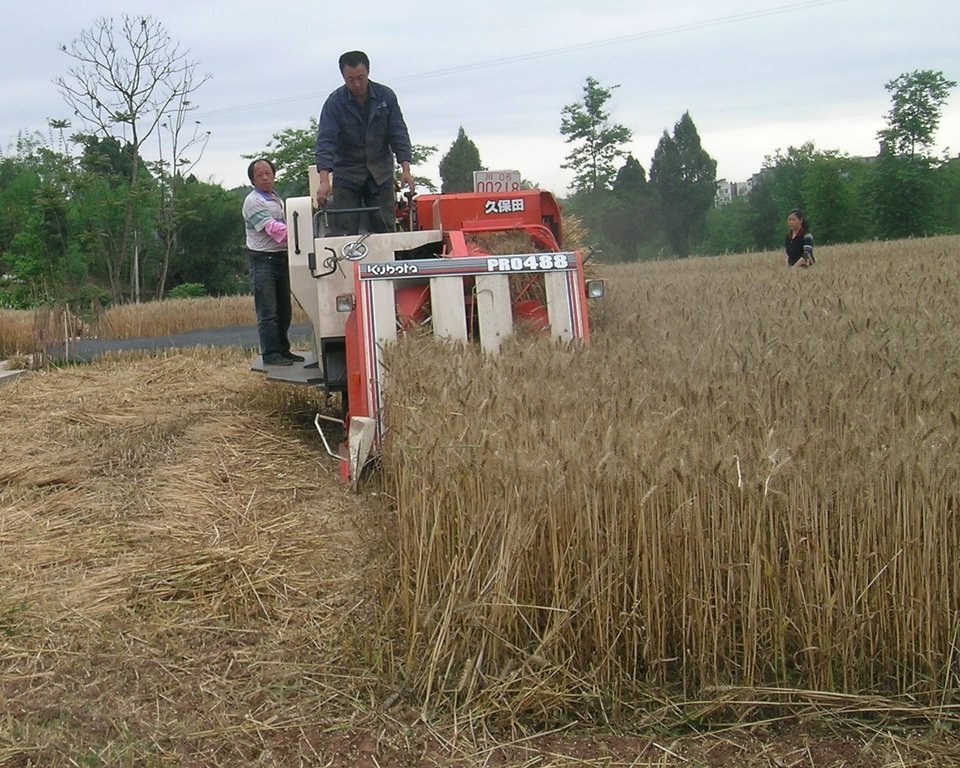
Straw residues left on field after harvest and no tillage [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Song Guo
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Gudrun Schwilch, Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
No tillage planting
technologies_3239 - 中国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Hongzhu Fan
Soil and Fertilizer Institute of the Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences
中国
土地使用者:
Wu Shengde
中国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
‒ Soil and Fertilizer Institute of the Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences (SFI) - 中国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Method of this agricultual technology the rice straw will be left on the field after mechanized harvesting. Succession crop, such as rape, wheat or potato, were seeded directly under no tillage condition. Both measures aim at better soil regeneration and soil conditions for agriculture and subsequently increased yield and less soil degradation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The SLM practice (straw mulching and no tillage) is applied in the Chengdu Plain Paddy Soil. The Chengdu plain has mild climate and abundant rainfall. It belongs to the warm humid subtropical Pacific monsoon climate zone.The main types of soil in the Chengdu plain are paddy soil and purple soil.The total land resources of the Chengdu plain are 1331800 hectares, and the per capita land resources are about 0.1044 hectares per person. In 2010, the total amount of cultivated land in the Chengdu plain was 478069 hectares, accounting for 35.90% of the area of the plain, accounting for 42.36% of the total area of agricultural land in the region, and the per capita arable land area was only about 0.0375 hectares. The Chengdu Plain is an important grain production base in Sichuan. Rice field-upland field rotation (rice - wheat, rice - rapeseed) is an important agricultural system.
On the case study area, the N, P and K fertilizers were applied as urea, calcium superphosphate and potassium chloride at the rates of 120-150 kg N ha-1, 75-120 kg P2O5 ha-1,and 75-120 kg K2O ha-1, during every crop. During crop season, the rate of 60% of N, 100% of P, and 50% of K fertilizers were applied as base fertilizer, while remaining 40% of N and 50% of K were used as top dressing fertilizer. The main measures of this SLM is rice straw or wheat straw mulching while havesting (leaving the straw after havest scattered on the field). Crops were harvested by a combine harvester (Kuotian combine harvester, model PR0488), then straw and stubble of crops were left at size of less than 20 cm in the field. The seeding of succession crop such as wheat and oil seed rape is done by a direct seeding machine. The land users are working eighter with a contractor or they use their own machines and labour force. The purposes of this technology were to increase production and improve soil fertility. Although plough layer can become shallow by long-term no tillage cultivation, more and more land users like this technology because it promises increased grain yield, reduction of fertilizers (and subsequently cost), and it improves soil physical, chemical and biological properties of soil. Thus, it is expected that the measures of this SLM-Technology ends up in improved soil moisture, higher diversity of soil life and finally soil fertility .
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
Basin plain, Chengdu, Sichuan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Guanhan City, Wenjiang District, Chongzhou City
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
注释:
This long-term straw mulch experiment was started in the 2005. This site is situated in subtropical monsoon region with anverage annual temperature of about 16.3℃, 281 days frost free. Annual precipitation is about 890mm.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
The current case study bases only on a test area within the scope of the iSQAPER Project. A long-term straw mulch and fertilization experiment was initiated in 2005 at Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences Soil and Fertilizer Research Institute’s Guanghan agricultural experiment station in Sichuan province, southwest China. Thus, effects of long-term fertilization and straw much on crop yields, soil physical and chemical properties under rice-rapeseed rotation were assessed in a paddy soil
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 油料作物 - 向日葵、菜籽、其他
- wheat, rice
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Method of this agricultual technology the rice straw will be left on the field after mechanized harvesting. Succession crop, such as rape, wheat or potato, were seeded directly under no tillage condition.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 轮作制度(轮作、休耕、轮垦)
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pk:熟化和结壳
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The SLM practice (straw mulching while harvesting and no tillage) is applied in the Chengdu Plain paddy soil. The main measures of this SLM method is straw mulching while harvesting and no tillage. Crops are harvested by machine (actually in this case study by Kuotian combine harvester/model was PR0488), and then straw and stubble were left at size of less than 20 cm on the soil surface. The N, P and K fertilizers to the succession crop were applied in form of urea, calcium superphosphate and potassium chloride at the rates of 120-150 kg N ha-1, 75-120 kg P2O5 ha-1, and 75-120 kg K2O ha-1. Rates of 60% of N, 100% of P and 50% of K fertilizers were applied as base fertilizers, while the remaining 40% of N and 50% of K were used as top dressing fertilizers. After previous crop harvest of rice the succession crop as for example wheat, oil rape, maize will be seeded directly under no tillage condition.
作者:
Hongzhu Fan
日期:
30/10/2017
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 hectare
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Renminbi (RMB)
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
6.6
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
120 RMB per day
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | mechanized harvesting | August or September |
| 2. | spreading the straw residues after havest on the field | after harvest of crops |
| 3. | fertilization | October |
| 4. | no tillage and direct seeding | October |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | All reccurent labour (above) is done within the familiy* | person-day | 0.5 | 120.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | harvester (machine from contractor without labour force)* | ha | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Direct seeding machine (from contractor without labour force)* | ha | 1.0 | 1800.0 | 1800.0 | |
| 植物材料 | seed (weat, rape) | kg | 120.0 | 2.0 | 240.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | urea | kg | 280.0 | 3.0 | 840.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | calcuim superphosphate | kg | 810.0 | 1.0 | 810.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | potassium chloride | kg | 200.0 | 3.5 | 700.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 7450.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1128.79 | |||||
注释:
*The labour (for harvesting, fertilizering and seeding ) is unpaid when those were done by farm familiy.
But in China, there is no contractor to do all work (for harvesting, fertilizing and seeding). If all works done by a contractor, farms will give up planting crops. Usually, a contractor provide machine to farm, but no labor. Farm members engaged in agricultural production will do most of the work by themselves in order to save cost.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Most of important factor affecting the costs of this technology is the type of machine used for harvest. (E.g. cost is high by the mini combine harvester because of the low efficiency).
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil type is alluvial soil, PH is 5.5, SOC 31.3g/kg, N 2.02g/kg,P 1.04g/kg, K 7.69g/kg, available nitrogen 189.7mg/kg, available phosphorus 12.6mg/kg, ammonium acetate extractable potassium95.5mg/kg.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
In China, land ownership belongs to the state, but land use rights belong to farm. In other words, farm can decide to plant rice, wheat, or fruit tree in the land, but the farm cannot sell this land.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
14.9 t ha-1*
SLM之后的数量:
15.5 t ha-1*
注释/具体说明:
* yield for rape
Wheat yield were 6.3 t ha-1 before SLM and 6.7 t ha-1 after SLM, respectively. Rice yield were 8.6 t ha-1 before SLM and 8.8 t ha-1 after SLM, respectively.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
No tillage is an important way to reduce cost by machine plough field. Less fertilizing work and amount of fertilizers by leaving straw on field (straw contains a large amount of C, N, P, and K)
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
Straw mulching can decreased demand for irrigation water, because water can be keep in the straw, and straw mulching on the soil also can reduced evaporation of water.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
No tillage is an important way to reduce cost by machine plough field. Less fertilizing work and amount of fertilizers by straw return compared with no straw mulching (straw contains a large number of C, N, P and K. Therefore agricultural inputs can be reduced.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Do to better yield and reduction of costs.
工作量
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Increased knowledge on the benefits of straw mulching by the land users.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Due to straw mulching, because the water can be kept in the straw and soil evaporation can be reduced to improved oil cover.
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Due to the mulching by straw, the soil remain covered practically the whole year round.
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
Without ploughing the soil crusting can occur at long term use of the technology (findings from a long-term straw mulch and fertilization experiment was initiated in 2005 at Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences Soil and Fertilizer Research Institute’s Guanghan agricultural experiment station in Sichuan province)
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
Without ploughing the soil gets more compact at long term use of the technology (findings from a long-term straw mulch and fertilization experiment was initiated in 2005 at Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences Soil and Fertilizer Research Institute’s Guanghan agricultural experiment station in Sichuan province)
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Due to mulching by rice straw (crop residues)
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Due to mulching by rice straw (crop residues)
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Due to mulching by rice straw (crop residues), soil life has increased.
有益物种
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Traditional burning of rice straw on the fields has been reduced, as straw is needed for mulching. Subsequently the C can be bound within the soil and will not be emitted into the air in form of CO2.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
Traditional burning of rice straw on the fields has been reduced, as straw is needed for mulching. Subsequently the C can be bound within the soil and will not be emitted into the air in form of CO2.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| This technology can improve the yield |
| It can save labour by leaving straw on the field |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Straw mulching can increase the soil carbon input, and improve the soil quantity. |
| This technology can reduce land degradation. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Soil structure was deteriorated by no tillage cultivation. | tillage |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Soil hardening occured, and also a thin impervious layer was built at the soil surface | It could be good to plough up the soil after an interval of 5 years |
| Obstruction of rainwater infiltration | |
| Soil plough layer becomes shallow |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 与土地使用者的访谈
94 people
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
20/09/2016
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Composition of Wheat Rhizosphere Antagonistic Bacteria and Wheat Sharp Eyespot as Affected by Rice Straw Mulching. CHEN Huai-Gu, CAO Qi-Guang, XIONG Gui-Lin, LI Wei, ZHANG Ai-Xiang, YU Han-Shou and WANG Jin-Sheng.2010.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ScienceDirect. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Effects of pre-sowing irrigation and straw mulching on the grain yieldand water use efficiency of summer maize in the North China Plain. Zhenxing Yan, Chao Gao, Yujie Ren, Rui Zong, Yuzhao Ma, Quanqi Li. 2017
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ScienceDirect. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Effects of snow cover plus straw mulching on microorganisms in paddy soil during winter.Hao Zhanga,b, Jie Tanga, Shuang Liang.2017
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ScienceDirect. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Effects of Non-flooded Cultivation with Straw Mulching on Rice Agronomic Traits and Water Use Efficiency. QIN Jiang-tao , HU Feng , LI Hui-xin , WANG Yi-ping , HUANG Fa-quan , HUANG Hua-xiang.2006
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ScienceDirect. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Growth Characteristics and Yield of Late-Season Rice under No-tillageand Non-flooded Cultivation with Straw Mulching. WANG Dong, LI Hui-xin, QIN Jiang-tao, LI Da-ming, HU Feng.2010
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ScienceDirect. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Impact of tillage practices on soil bacterial diversity and composition under the tobacco-rice rotation in China. Yanping Lei, Yongliang Xiao, Lifeng Li,Chaoqiang Jiang, Chaolong Zu, Tian Li, and Hui Cao.2017
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ScienceDirect. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Nutrient Decomposition Rate and Sugarcane Yield as Influenced by Mung Bean Intercropping and Crop Residue Recycling Tie-Guang He,Li-Rong Su,Yang-Rui Li,Tian-Ming Su2 Fang Qin,Qin Li.2017
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ScienceDirect. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Process rates of nitrogen cycle in uppermost topsoil after harvesting in no-tilled and ploughed agricultural clay soil. Merjo Laine . Tobias Ru¨ tting . Laura Alakukku . Ansa Paloja¨rvi . Rauni Stro¨mmer.2017
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ScienceDirect. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Research on the effect of straw mulching on the soil moisture by field experiment in the piedmont plain of the Taihang Mountains. LI Man, ZHANG Wei, HE Yu-jiang, WANG Gui-ling.2017
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ScienceDirect. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Rice–wheat cropping system: tillage, mulch, and nitrogen effects on soil carbon sequestration and crop productivity Keshav R. Adhikari,Khem R. Dahal,Zueng-Sang Chen,Yih-Chi Tan,Jihn-Sung Lai.2017
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ScienceDirect. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Soil Carbon Sequestration and Crop Yields in Rice–Wheat and Sugarcane–Ratoon–Wheat Cropping Systems Through Crop Residue Management and Inoculation of Trichoderma viride in Subtropical India.S. K. Shukla,Swaha Shee,S. K. Maity,S. Solomon,S. K. Awasthi,Asha Gaur,A. D. Pathak,V. P. Jaiswal.2017
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ScienceDirect. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
成都平原麦稻双免耕秸秆还田技术模式.汤永禄 , 黄钢, 郑家国, 李朝苏,邓先和,付书明.2008
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.cnki.net/. No
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Influence of straw mulching with no-till on soil nutrients and carbon pool management index.CHEN Shang-hong, ZHU Zhong-lin, LIU Ding-hui, SHU Li , WANG Chang-quan.2008
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.cnki.net/. No
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Effects of pre-sowing irrigation and straw mulching on the grain yieldand water use efficiency of summer maize in the North China Plain.
URL:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2017.02.017
标题/说明:
Effects of snow cover plus straw mulching on microorganisms in paddy soil during winter
URL:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.05.023
标题/说明:
Growth Characteristics and Yield of Late-Season Rice under No-tillageand Non-flooded Cultivation with Straw Mulching
URL:
DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6308(08)60117-1
标题/说明:
Impact of tillage practices on soil bacterial diversity and composition under the tobacco-rice rotation in China
URL:
DOI 10.1007/s12275-017-6242-9
标题/说明:
Nutrient Decomposition Rate and Sugarcane Yield as Influenced by Mung Bean Intercropping and Crop Residue Recycling
URL:
DOI 10.1007/s12355-017-0548-0
标题/说明:
Process rates of nitrogen cycle in uppermost topsoil after harvesting in no-tilled and ploughed agricultural clay soil
URL:
DOI 10.1007/s10705-017-9825-2
标题/说明:
Rice–wheat cropping system: tillage, mulch, and nitrogen effects on soil carbon sequestration and crop productivity
URL:
DOI 10.1007/s10333-015-0511-1
标题/说明:
Soil Carbon Sequestration and Crop Yields in Rice–Wheat and Sugarcane–Ratoon–Wheat Cropping Systems Through Crop Residue Management and Inoculation of Trichoderma viride in Subtropical
URL:
DOI 10.1007/s12355-016-0470-x
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块