Check Dam [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Haiyan WEI
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Lan Sha Ba
technologies_1365 - 中国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Check Dam [中国]
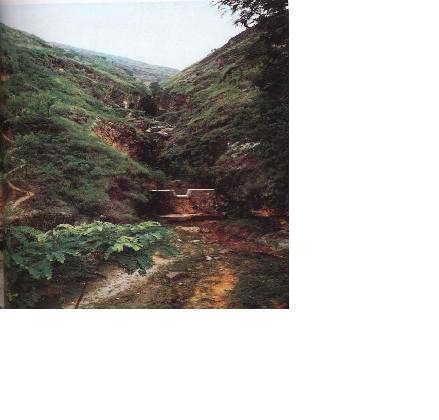
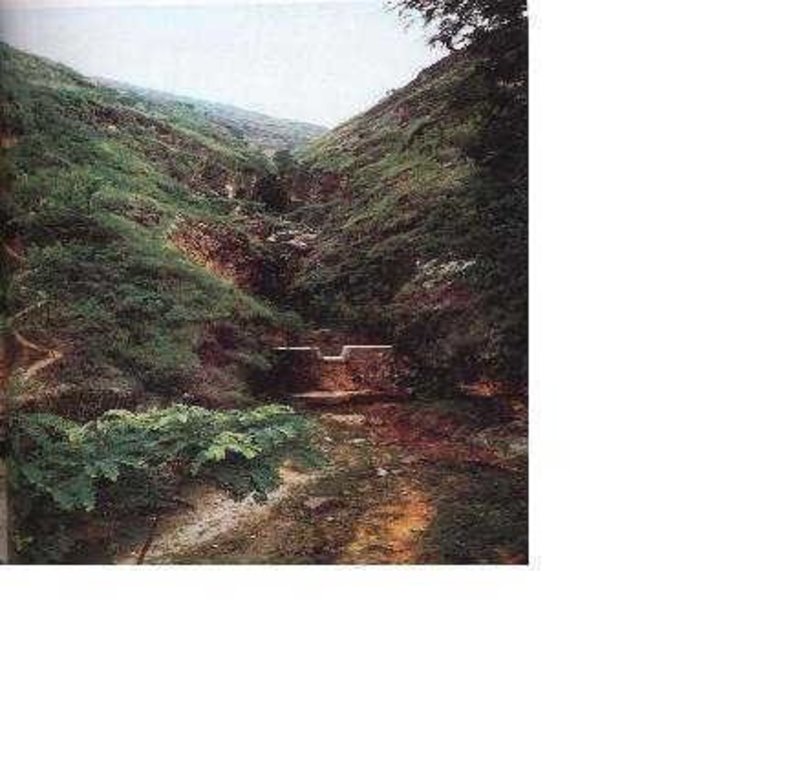
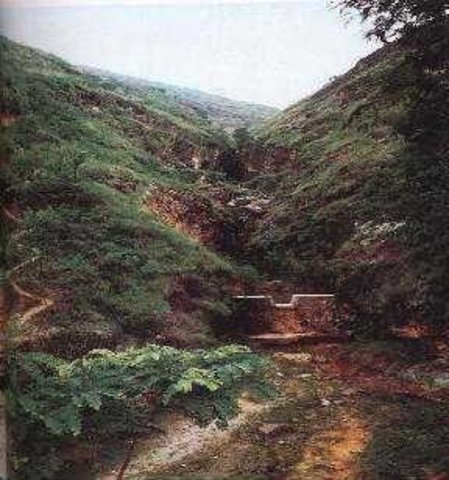
Check dam is a kind of sediment storage dam of 5m below and is built in channels to control the down cutting of channel bed.
- 编制者: Haiyan WEI
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Check dam refers to dam that constructed in the gullies or river ways and the height of the dam is often lower than 5m.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Check dams are built in the gully systems to harvest water and sediment. Usually many check dams are built in a gully or waterway to control the gully erosion. Check dams can be classified into "masonry dam", "check dam of earth", "check dam with willow" according to materials. Some strong masonry can last more than 10 years. As willow pegs in the "check dam with willow" can grow into timber after years.
Maintenance work should be done before rainy seasons every year so as to prevent the dam from destruction.
Following are the building procedures:
Masonry dam & check dam using earth:
1. Preparation---Removing grass, roots and surface soil; Digging a channel along an axis of a check dam in order to combine the dam and the bed firmly.
2. Construction---If a dam is planned to be made of earth, do scarification first, then adding earth (about 0.3m thick) and ramming it into 0.2m layer by layer. Building the dam with stones and/or rocks.
3. Base---If a bed of a gully consists of earth or sand, "base" should be built at the downstream feet of the dam. Length of the base should be twice as that of the dam and thickness should be 50-70cm.
4. Building a spillway at the top of the dam.
Check dam with willow:
1. Removing grass, roots and surface soil.
2. Cutting branches from willow; chopping the branches into pegs with the thick ends wedge.
3. Inserting the pegs into the ground.
4. Entwining wattles from willows around the pegs compactly.
5. Filling the space between two rows of pegs with stones, bricks, treetops etc. Making the stuff surface 10cm lower than the pegtop.
6. Combining the dam into a whole with iron chains.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
Shanxi, Beijing
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
145.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 145 km2.
As a traditional SWC technology, check dams have been used widely in China.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
Experiences from the local people's many SWC practice.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Sep

牧场

水道、水体、湿地
- 池塘、大坝
主要产品/服务:
Check Dam
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Serious gully erosion by water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gullies were widened and deepened greatly in the rainy season and crop land area is decreasing above the gully edges.
Constraints of urban land use
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
- reduce loss of cropland
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), poverty / wealth (Lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Description of Building Check Dam Procedures
Location: the Loess Plateau. Shanxi, Beijing
Date: 2000
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Construction material (earth): Loessial earth
Construction material (stone): if available
Construction material (wood): willow pegs
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 16%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 90%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:30
作者:
LIU Baoyuan, Beijing China
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
RMB Yuan
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
8.27
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation | |
| 2. | Construction | Before rainy season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 120 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | reparing after rainstorm. |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Length, width and height of check dams.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Sizes and materials of the check dams.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
580.00
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average also gentle, moderate and rolling
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land (No difference).
Off-farm income specification: The land users who made the check dams can own more "deposited land". Generally these deposited land is fertile and produces high yield.
Level of mechanization: animal traction: on steep slope
Level of mechanization: mechanized/motorized: plateau or gully flat.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
48
SLM之后的数量:
30
土壤
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
180
SLM之后的数量:
110
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
180 household are using the technology and represent 65 percent of the poeple living in the stated area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
55% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
150 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
30 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: In the past (planning economy)SWC activities are administrative action to call local land users to carry out, but nowadays in the market economic conditions, if no or little benefits obtained, land users would not like to do any more.
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
How to design the dry masonry dam in the Hanjiachuan watershed. Tianyuzhu, Wangzuliang. Beijing. Water conservation in Beijing.. 2000.3.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Consideration about the check dam design and application. Liu shunzong. Soil and water conservation in China.. 1990.6.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Special Planning of Soil and Water Conservation in Xinzhou Region, Shanxi Province. 1986-2000.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
The application of the Check dam with willow in controlling gully erosion.Tu xingwen. Soil and water conservation in China.. 1986.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Check Dam [中国]
Check dam is a kind of sediment storage dam of 5m below and is built in channels to control the down cutting of channel bed.
- 编制者: Haiyan WEI
模块
无模块