Permanent grassland on peaty and eroded soils [爱沙尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Endla Reintam
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
Püsirohumaa turvas- ja erodeeritud muldadel
technologies_3113 - 爱沙尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
土地使用者:
Selge Are
Hummuli Agro
爱沙尼亚
researcher:
Penu Priit
Agricultural Research Centre
爱沙尼亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
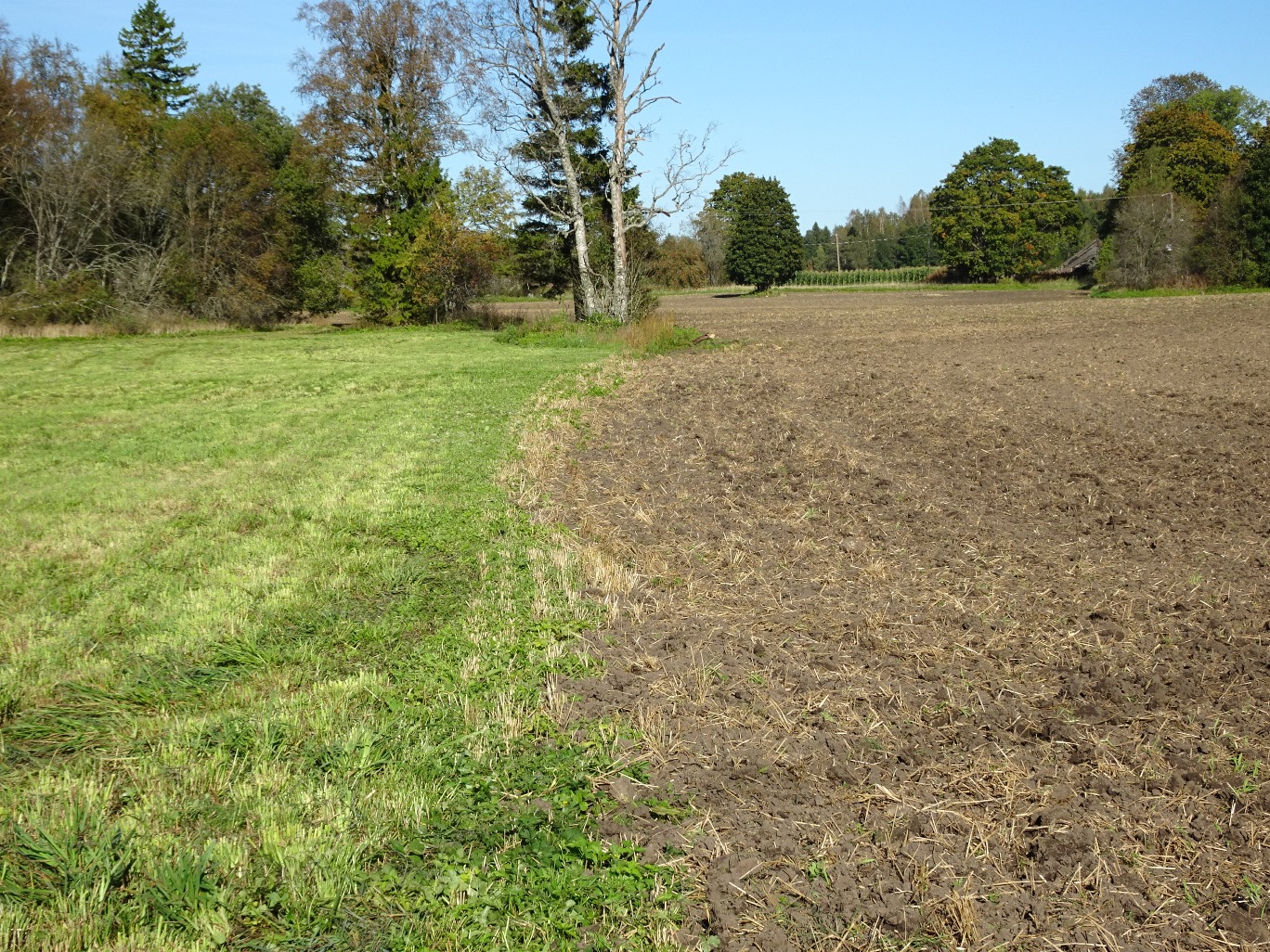
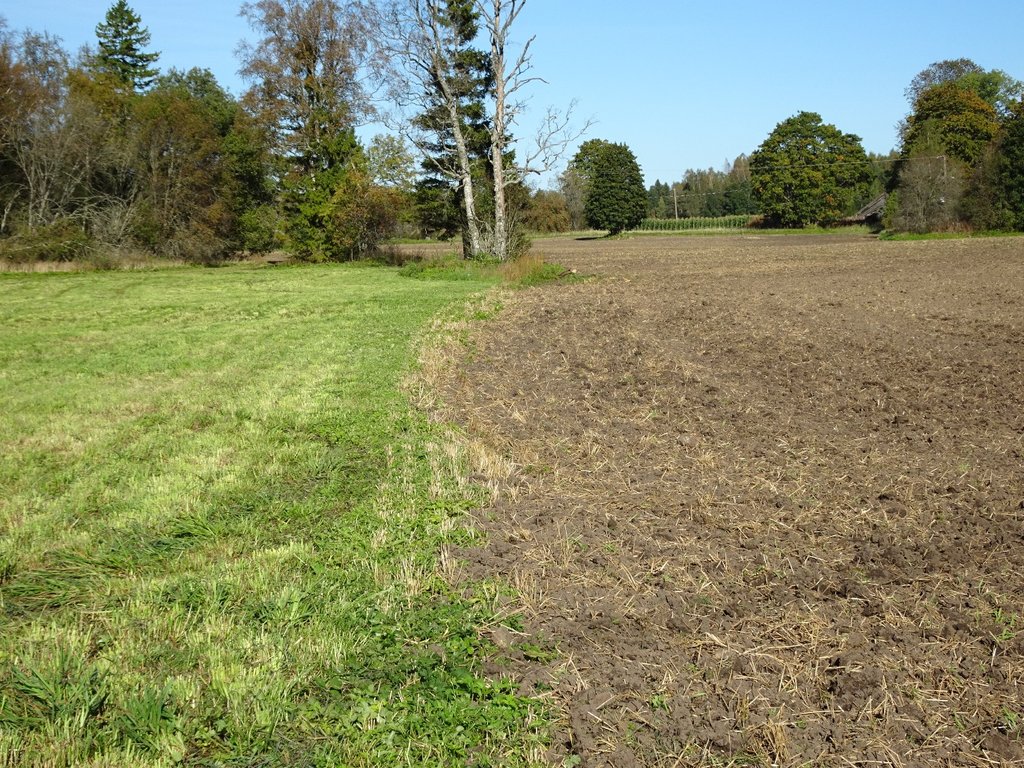
A permanent plant cover is maintained or established to protect soil against erosion or peat decomposition.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
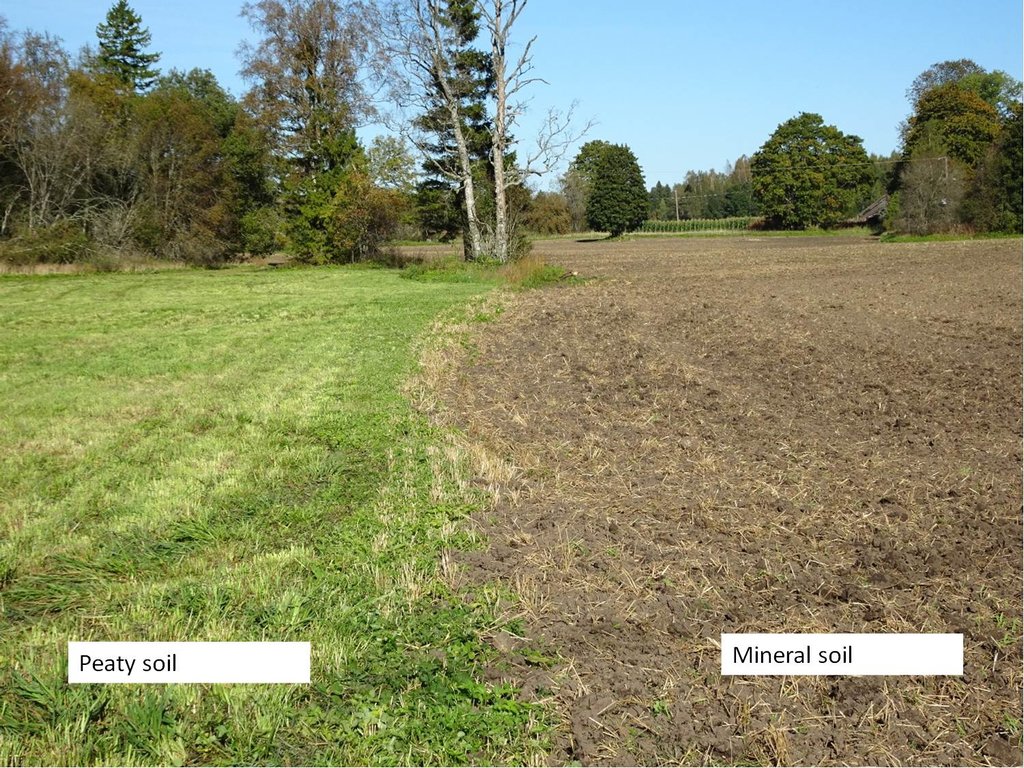
The technology is applied in sub-humid climate with an average of 696 mm of precipitations per year, from which more comes from July to October and less in March and April. Average annual temperature is +4 C, length of the growing period is 180-195 days. The territory is mostly flat to slopes of 6-10%. Average altitude from the sea level is 50 m. About half of the Estonian territory is above 50 m and half is below it. Soils are from very shallow (less than 0.1 m) inthe north to very deep (> 120m ) in the south. Soil cover is very variable. The peat cover of peatlands varies from 0.3 m to more than 10 m from well decomposed to poorly decomposed peat. On hilly areas the soils are medium textured with low (< 1%) organic matter in topsoil. Groundwater in near the surface in peatlands and deep in hilly areas. Biodiversity of these areas is medium. Market orientation of production system is mixed and off-farm income less than 10%. Relative level of wealth is average from individual households to cooperatives. Soil management is mechanized. Land belongs to land users but is leased also in case of bigger farms (over 1000 ha).
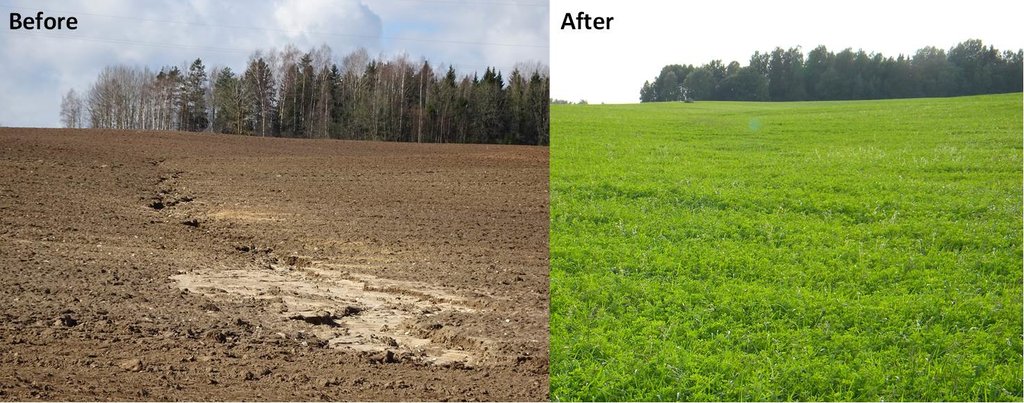
In the agricultural land the area will be excluded from intensive tillage by establishing a permanent plant cover, mainly with grass. The aim is to protect the slopes over 10% against erosion and peaty soils from further intensive decomposition of organic matter and with that the reduction of CO2 emission. The farmers should maintain permanent plant cover in the areas mentioned, or establish permanent plant cover. Renewing of the grassland is allowed from the top (without ploughing) once in a 5 year period. Government pays support of 50 EUR/ha if the area is bigger than 0.3 ha. The technology reduces intensively tilled area and thus the possibility to grow cash crops and/or reduces the yield from grassland. On the other hand it allows to still use wet areas for agriculture (i.e. fodder production).
The rules of the technology are fixed with the Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014-2020 under activity "Support for regional soil protection" (https://www.agri.ee/et/eesmargid-tegevused/eesti-maaelu-arengukava-mak-2014-2020) related to the reguation of the European Parliment and of the Council 1305/2013, article 28. The regulation is relevant more to the South-Estonia in case to reduce erosion, as the landscape is more hilly there. The exclusion of peatlands from agricultural use is relevant more in West-Estonia where the share of peatlands of the total area is the highest. However, it can be applied in whole Estonia if the area of peatland is bigger than 0.3 ha.
2.3 技术照片
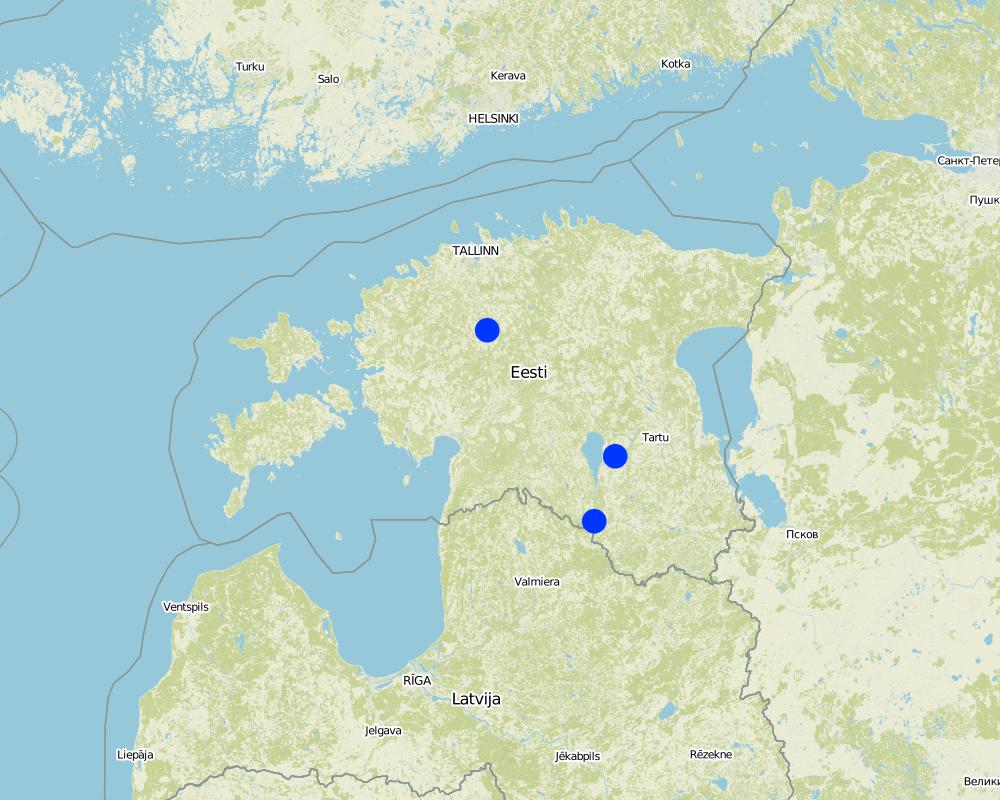
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
爱沙尼亚
区域/州/省:
One site at Rapla, second at Tartu, third at Valga (erosion)
有关地点的进一步说明:
One site: Rapla county, Pae; second site Tartu county, Annikoru, third site Valga county, Hummuli
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
To get the governmental support the area should be larger than 0.3 ha. Othervise the size is not important, depending on the area covered by hilly area or wet soils in the landscape.
In 2016 it was 10554 ha Histosols and only 40 ha of eroded soils covered with this technology in Estonia. This area excludes grasslands on another soil types. On specific sites: in Rapla county in Pae the size of the field is ca 3.2 ha, at Tartu county, Annikoru 2.8 ha.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
- Governmental tool
注释(项目类型等):
The tool is a part of Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014–2020 for soil fertility.
The survey was done by the Soil Survey Bureau of the Estonian Agricultural Research Centre (http://pmk.agri.ee/). The results presented here are partly from this survey and from the work done by the project iSQAPER.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 燕麦
- 谷类 - 黑麦
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豌豆
- 油料作物 - 向日葵、菜籽、其他
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
- wheat
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
For the cereals one harvest per year, for grasslands 1-4 cuts per year. For hay 1 cut, for silage 2-4 cuts depending on the year

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 经营牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- 牛 - 奶制品
- 牛 - 非奶牛牛肉
- 绵羊
产品和服务:
- 肉类
- 奶类
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
注释:
Usually before the implementation of the technology the land was intensively tilled and used for annual crop plantation. After implementation the grasslands can be used for cutting and grazing.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
On Histosols the groundwater is close to the surface.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A3:土壤表面处理

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
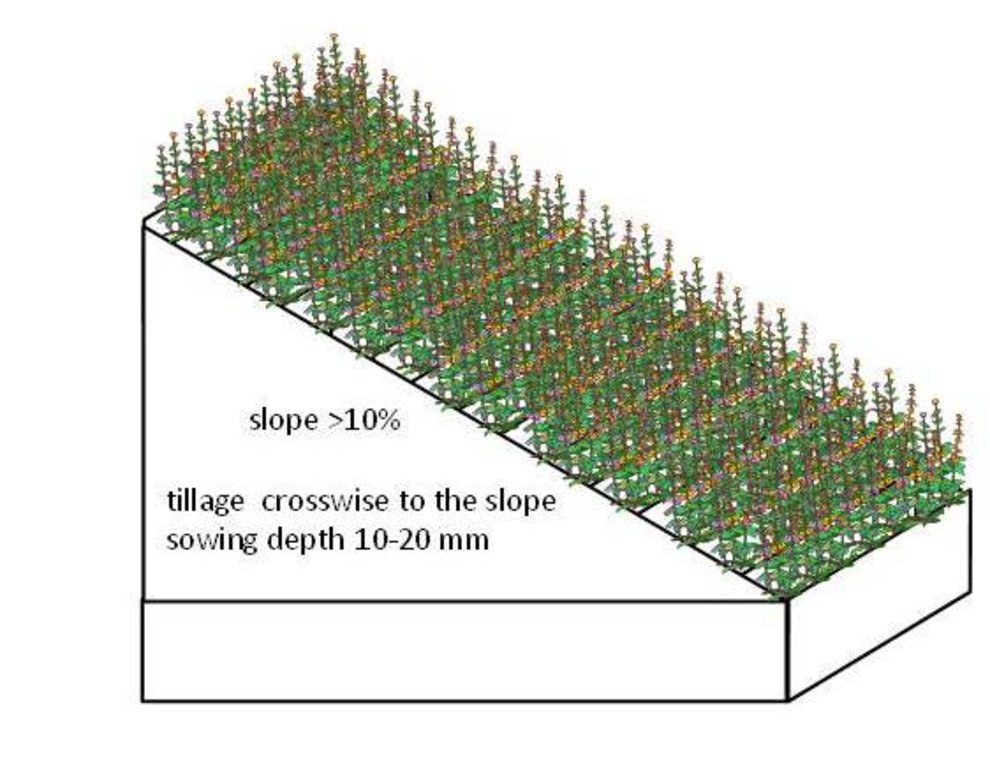
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The requirements to create a permanent grassland depends on soil type.
Species mixture suitable for the permanent grassland on wet soils (Histosols): Bromus sitchensis 30%, Phalaris arundinacea 45%, Phleum pratense 20%, Poa pratensis 5%. Sowing rate 20 kg/ha.
For the drier areas (eroded soils) the next mixture is suitable: Dactylis glomerata 65%, Phleum pratense 26%, Poa pratensis 9%. Sowing rate 23 kg/ha.
作者:
Endla Reintam
日期:
14/08/2017
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
per hectar
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
EUR
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
1.18
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
36-40 EUR/day + taxes
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage (ploughing, cultivation) | in spring |
| 2. | Collecting stones, slip (by demand) | in spring |
| 3. | Fertilization | in spring complex fertilizer |
| 4. | Sowing | in spring |
| 5. | Rolling | in spring |
| 6. | Cutting the weeds | during growth (summer) |
| 7. | Fertilization during growth period | after every cut of grass, if cutted grassland, N-fertilizer |
注释:
If renewing the grassland, there will be no ploughing, collecting the stones and sliping. Only chisel plowing and/or sowing with fertilization. If the grassland will be use for grazing, no need for fertilization during growth period.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Driver (machinery work) | person day | 0.5 | 36.0 | 18.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Equipment (machinery) cost on establishment year | year | 1.0 | 207.0 | 207.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | kg | 22.0 | 2.47 | 54.34 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Complex fertilizer | kg | 500.0 | 0.42 | 210.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Ammonium fertilizer | kg | 100.0 | 0.33 | 33.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 522.34 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 442.66 | |||||
注释:
For tillage and other operations it is calculated 14-18 EUR/ha.
If to hire equipment the labour costs should be included to the machinery costs - for cutted grassland 225 EUR/ha, for grazed grassland 162 EUR/ha
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting or grazing the grass | 1-4 times per vegetation period |
| 2. | Fertilization | in spring in the beginning of season and after every cut N-fertilizer, after each second year complex fertilizer |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Grasslands for cutting - machinery costs | year | 1.0 | 141.0 | 141.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Ammonium fertilizer | kg | 200.0 | 0.33 | 66.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Complex fertilizer | kg | 200.0 | 0.42 | 84.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Materials for hay making | year | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 306.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 259.32 | |||||
注释:
The governmental support to establish and to maintain the grassland is 50 EUR/ha.
If to use the land for the grazing, the machinery cost per year is 38 EUR/ha.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Fuel price.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
696.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Average 696 mm, almost equally spread over the year, more from July to October, less in March and April
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Tartu Tõravere
农业气候带
- 半湿润
LGP 180-195 days
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凸形情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Eutric Histosol, well decomposed peat, drained area.N 2.32%; C32.89%; C/N14.20%; P2,62 mg/100g; K 13.73 mg/100g; Ca 1762.32 mg/100g; Mg 166.98mg/100g
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Histosols biodiversity depends on the base saturation and level of groundwater (degree of drainage). Diversity is higher at higher pH and better drainage.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 合作社
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
注释:
There are also small-scale and medium-scale farms applying the technology. At Pae, the farm have 4900 ha of land, from which 1800 are grasslands, at Annikoru the farm have 2320 ha of land from which 390.5 ha are grasslands.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
- individual/open access
注释:
Groundwater belongs to the state. Smaller water bodies can be in individual use, larger are usually open access
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
The area will be excluded from crop production and it means no cash crops can be cultivated on this area. Instead of crops hay or silage is possible to sell.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
As it is not allowed to renew these grasslands intensively, the quantity of grass will drop. For short term clover+grasses mixture the average yield is 16 tons/ha per year, for long-term grass mixtures 5.2 tons/ha per year.
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Due to the change of species in the mixture, the protein level will drop. Instead of red clover grasses will be used in the mixture of long-term grasslands.
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Due to the changes in silage/hay quality (protein) there can be reduction of milk and meat production if the differences will not be covered with other fodder.
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
In case of crop orientation, there are new products to sell - grass, hay, silage, or grasslands to rent.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Depending on the farm it can be simplified or hindered. If focus was on crops, then new machinery is needed to manage grasslands (for cutting, hay or silage making).
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
As renewing of grassland is after every 5 years, there is no need to buy seeds every year, as well as pesticides and to till the soil.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Due to the reduction of the inputs costs, the income my increase. Also the government pays support 50 EUR/ha for the land under these measures.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Next to the yield (grass, silage, hay) the support from the government (50 EUR/ha)
工作量
注释/具体说明:
It may decrease due to no need of every year tillage and sowing and due to the change from 2 year short-term grasslands to the permanent grasslands. However, if not managed grasslands earlier it may increase the workload as cutting and collecting the grass is needed.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
More land under grasslands than under crops. Grasses are suitable for animals feeding, not for human direct consumption.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
If land was eroded before and soil was on the road, everybody can see the differences after establishment of the grasslands. It is not so severe in case of peatlands, however, less tractors will stuck in to the mud on rainy period.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
In case of erosion, no soil will be washed down to the hill as plant cover protects soil surface and increases infiltration. In case of peatlands, grass cover creates better structure and increases water infiltration thus decreases surface runoff during heavy rainfall.
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
Grass creates protection to the soil surface and raindrops can't destroy the soil structure any more. Also grass roots create better porosity and structure in the soil leading to better water drainage.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
The difference in soil moisture between mineral and organic soils under cereals and under grassland was ca 5% and 25%, respectively, in favour to the grasslands in autumn 2016.
土壤覆盖层
SLM之前的数量:
40%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
Under spring cereals soil is covered only 4-5 months per year, under grasses soil is covered 100% of the year.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
On the slopes depending o the crop and the amount of precipitations, the loss varied from 3 to 60 tons/ha, under permanent grass cover it is less than 0.05 tons/ha per year. Without every year tillage there is no intensive decomposition of the peat, as well as no wind erosion.
土壤堆积
注释/具体说明:
Under grasses we can increase the soil organic matter content by 0.35 t/ha in 5 year period in peatlands. In eroded soils we can increase 0.02% per year.
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
As plants protect soil surface, raindrops can't destroy the soil structure and there will be no crust formation
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
Under the grasslands the bulk density was lower by 0.1-0.2 g/cm3 compared to tilled soil.
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
As the intensive decomposition of the peat stops or there will not be any leaching by water, more nutrients remain in the soil. Also the permanent plant cover during the whole year stops nutrient leaching.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Under permanent grasslands the Corg increases by 0.35 t/ha per 5 year period.
酸度
注释/具体说明:
Without periodic liming the acidity of peatlands starts to increase. If no CaCO3 in mineral part, also pH of previously eroded soils starts to decrease slowly, as organic acids form during decomposition process.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Thanks to the permanent plant cover there is no period of the year without vegetation.
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
If previously the plant residues were mixed with the soil by tillage, now there will always some extent of plant mass be left above ground (5-10 cm), even if the most is removed for hay or silage.
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Long-term grassland includes at least 4 species in the mixture, short-term mixtures 2-3 species. However, compared with the cereals, the annual weeds will disappear and the diversity may decline.
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
There are more spiders, ants, beets.
有益物种
SLM之前的数量:
2 species of earthworms
SLM之后的数量:
3-4 species of earthworms
注释/具体说明:
Under grasslands were 1-2 more earthworm species than under tilled management. More spiders and ground beetles were found there compared to the tilled soil.
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
Grasslands create untilled patterns to the landscape.
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Grasses surpress many soil born crops diseases and pests, also annual and perennial weeds.
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
注释/具体说明:
Grass roots go to the deeper soil and they are not so sensitive to the drought.
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Under permanent grasslands reduced CO2 emission by 1.10 t/ha per year compared to the tilled areas.
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
If the grass will not be cutted before winter, the dry grass has the risk of higher landscape fires in the spring.
微气候
注释/具体说明:
The changes of soil temperature as well as moisture content are smaller under permanent grass cover than under tillage.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
All year plant cover helps to bind nutrients and stop their leaching from the soil. Higher amount of organic matter in the soil increases water holding capacity.
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
Organic peat particles are light and are easy subject of wind erosion in dry conditions by tillage. Permanent plant cover stops such kind of erosion
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
On hilly landscape no extra soil is flushed to neighbours fields. In case of peatlands no dust is carried around.
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
In case of erosion, no soil is carried by water or wind to the ditches and on the roads.
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
Under permanent grasslands reduced CO2 emission by 1.10 t/ha per year compared to the tilled areas.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 季节性温度 | 冬季 | 增加 | 适度 |
| 季节性温度 | 春季 | 增加 | 适度 |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 未知 | |
| 季雨量 | 冬季 | 增加 | 未知 |
| 季雨量 | 秋季 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 适度 |
| 局地雷暴 | 未知 |
| 局地雹灾 | 未知 |
| 局地雪暴 | 适度 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 寒潮 | 未知 |
| 极端冬季条件 | 适度 |
| 干旱 | 适度 |
| 陆地火灾 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 适度 |
| 风暴潮/沿海洪水 | 适度 |
| 滑坡 | 好 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
In 2016 two hundred four households got the governmental support, in total 10554 ha
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
Anyway, the use of Histosols and Gleysols is limited due to their properties and regular use of these soils is for grazing or grass cutting.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Better soil protection |
| Possibility to earn money in unsuitable soil conditions. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reduces soil erosion on hilly landscape |
| Reduces the decomposition of peat on Histosol |
| Reduces CO2 emission from agricultural land. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Loss of income | Governmental support (50 EUR/ha) |
| Problems with the grass (farms without animals) | Cooperation with neighbours, selling the hay for energy production |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Farmers don't want to use the technology | More effective lobbying |
| Wrong declaration of the land under the technology | Better advisory system and improvement of electronic databases |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
5 within iSQAPER project but more than 20 during another projects
- 与土地使用者的访谈
10 within iSQAPER project but more than 20 during another projects
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
8
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
04/06/2017
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Bender, A. (koostaja) 2006. Eritüübiliste rohumaade rajamine ja kasutamine. I. ja II. osa. Jõgeva
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Bender, A. 2010. Heintaimede sordiaretus ja seemnekasvatus. Jõgeva Sordiaretuse Instituut
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Older, H. 2011. Kohalikud söödad. Eesti Rohumaade Ühing.
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014–2020
URL:
https://www.agri.ee/en/objectives-activities/estonian-rural-development-plan-erdp-2014-2020
标题/说明:
Kattetulu arvestused taime- ja loomakasvatuses 2016. Koost: Marju Aamisepp, Helle Persitski. Maamajanduse infokeskus. 2017.
URL:
http://www.maainfo.ee/data/trykis/kattetulu/KATTETULU2016.pdf
标题/说明:
Statistics Estonia
URL:
https://www.stat.ee/en
标题/说明:
Eesti maaelu arengukava 2007-2013 2. telje ning Eesti maaelu arengukava 2014-2020 4. ja 5. prioriteedi püsihindamiseks 2016. aastal läbiviidud uuringute aruanne. Põllumajandusuuringute keskus. Saku 2016.
URL:
http://pmk.agri.ee/mak/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/09/aruanne_uuringud_2015.pdf
标题/说明:
Eesti tuleviku kliimastsenaariumid aastani 2100
URL:
https://www.envir.ee/sites/default/files/kliimastsenaariumid_kaur_aruanne_ver190815.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块