Organic-Based System of Rice Intensification (SRI) [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1302 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Dinamling Djolly Ma
DA-BSWM
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Raquid Jemar G.
DA-BSWM
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Manguerra Jose D.
DA-BSWM
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Ventigan Filipina Z.
DA-BSWM
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Poliquit Juanito F.
VSU
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Rapis Thelma
DA-8
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Garcia Pastor
VSU
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Visayas State University (VSU) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Agriculture-Region VIII (DA-8) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Intensifying the irrigated rice production while at the same time reducing farm inputs including seeds, fertilizer, and water.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
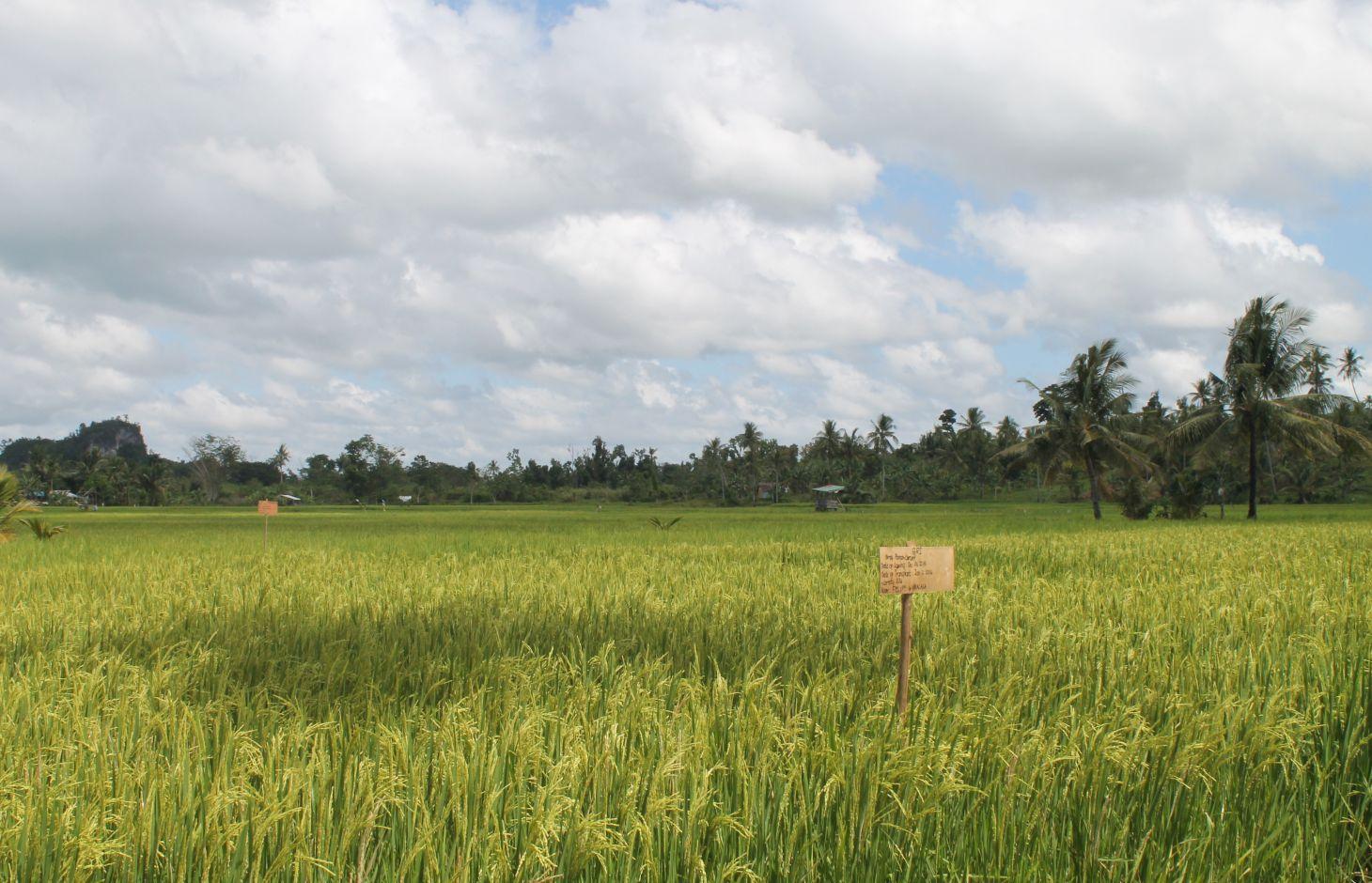
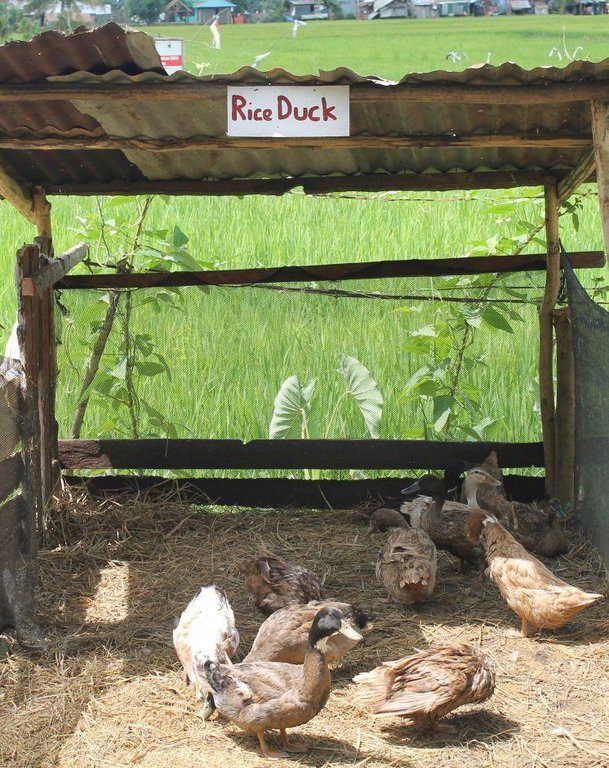
The Organic-based system of rice intensification modifies the usual rice farming system in terms of seedling condition, planting distance, irrigation time and water requirement, and with the incorporation of organic fertilization scheme. Furthermore, integration of rice duck is carried out. This makes the farming system reduce its farm inputs leading to a lower production cost. With the utilization of organic fertilizers and natural concoctions, soil fertility and soil structure is improved. It was also observed that rice grown under SRI can tolerate strong winds. This type of rice production management is currently part of the Caritas Foundation’s project, a non-government organization, called Sustainable Learning Agricultural Farm which promotes diversified-integrated organic farming systems. With this, other practices (i.e. rice-duck farming) are being integrated in some SRI areas. Integration of ducks helps in the weeding since it eats weeds as well as harmful insects. In addition, its droplets/manure served as organic fertilizer in the rice field.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology is to promote better soil management as well as more efficient water management.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Under SRI, the following practices were implemented: In the land preparation stage, 25cm x 25cm plant spacing is made using the man-made implement.
Intermittent irrigation is applied up to the panicle initiation stage with the following irrigation schedule: (1) 3 days after transplanting, (2) 9 days after transplanting, (3) 14 days after transplanting, and (4) 19 days after transplanting. The field is irrigated up to 5-cm water depth level per schedule.
Fertilizer application includes compost and natural organic concoctions. This is applied on different crop stages.
Natural / human environment: The existing project sites are located in Samar experiencing Type IV climate wherein rainfall is more or less evenly distributed throughout the year. Most of the farmer practitioners of this technology belongs to the small scale and average type of land user.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Marabut, Samar
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- rice
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil fertility deterioration, water-use management
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): soil fertility deterioration
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- Crop intesification
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

管理措施
- M4:活动时间安排的重大变化
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Ca:酸化

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ca: acidification, Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Main causes of degradation: soil management (dependency on chemical fertilizers), population pressure
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
System of rice intensification for lowland rice growing.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: compost, natural concoctions
Major change in timing of activities: irrigation schedule
作者:
Patricio A. Yambot, Bureau of Soils and Water Management
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
6.6666
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of rice seeds | - |
| 2. | Duck raising | - |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物材料 | Rice seeds rice seeds | kg | 24.0 | 0.7779 | 18.67 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Ducks | animal | 80.0 | 2.22225 | 177.78 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 196.45 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 196.45 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | clearing | before land preparation |
| 2. | organic fertilizer application | after clearing |
| 3. | first plowing | 10 days after clearing |
| 4. | second plowing | 8-10 days after first plowing |
| 5. | transplanting | 18-25 days after first plowing |
| 6. | weeding | 15 days after transplanting |
| 7. | fertilizer application (compost) | after weeding |
| 8. | weeding | 9-10 days after 1st weeding |
| 9. | spraying of natural concoctions | at the start of pannicle iniation unitl 2 weeks up to flowering |
| 10. | harvesting |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | clearing | Person/day | 8.0 | 11.1125 | 88.9 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Fertilizer Application/Plowing/weeding | Person/day | 10.0 | 6.6666 | 66.67 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine | day | 4.0 | 33.3333 | 133.33 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Labour: Transplanting/Spraying/harvesting | Person/day | 26.0 | 2.22222 | 57.78 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | kg | 700.0 | 0.13334 | 93.34 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 440.02 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 440.02 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: tractor
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Level of mechanization: All were selected and perceived as equal important
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产故障风险
水资源可用性和质量
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
社区机构
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
蒸发
土壤
土壤压实
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
有益物种
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| strong winds | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
注释:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increase production yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Intensify their Sustainable Learning Agricultural Farm program |
| Improvement in crop growth and development |
| Soil fertility improvement |
| Ease on weed management |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Need for an adequate supply of organic inputs | Sustainable production of organic inputs through composting methods |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块