African market gardens [塞内加尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Julie Zähringer
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
technologies_944 - 塞内加尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Dov Pasternak
International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT)
尼日尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: SLM in Practice - Guidelines and Best Practices for Sub-Saharan Africa (SLM in Practice)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ICRISAT International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) - 尼日尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The African Market Garden (AMG) is a horticultural production system based on low-pressure drip irrigation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
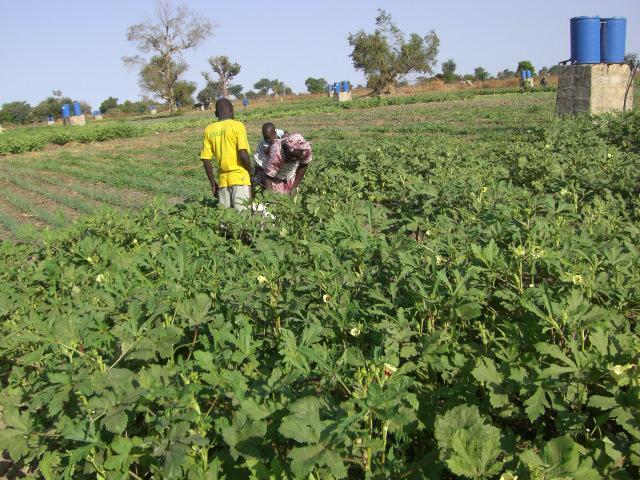
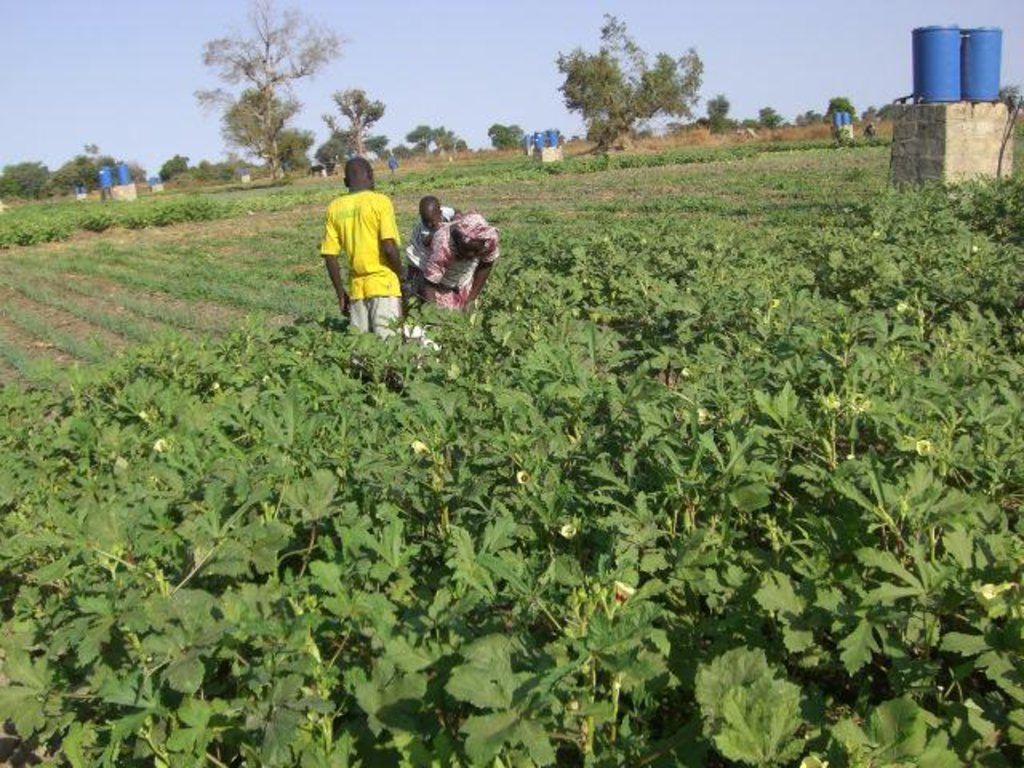
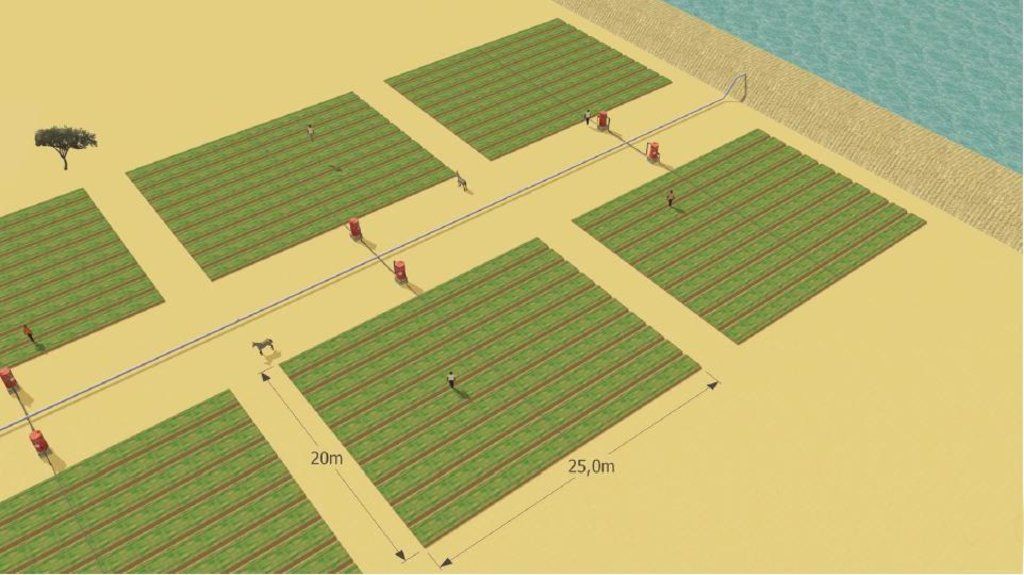
According to the level of experience, market orientation or social structure of the land users, four different AMG models have been developed. This case study focuses on the “Cluster System” which is suitable for an organized group of independent vegetable producers sharing a common water delivery system. From a central source, water is distributed through a pipe network to a cluster of plots. Each farmer operates a 1,000 m2 unit, and each is equipped with an elevated 200 litre barrel and a standard irrigation kit, including a tap, filter and thick-tube drip laterals. Minimal size of an AMG unit should be 500 m2. Affordable high-quality material is used and the design and operation is simple. The barrel also serves as a fertilizer tank. A float ensures a constant pressure head. Water supply is calculated by the time needed for delivery of the daily water dosage, or through the use of water dosing valves. Producers have individual control of water use. Since the AMG requires only 1 meter pressure for operation, it can draw on low-capacity renewable energy sources such as elevated dams, solar pumps or reservoirs. To supply an area of 50,000 m2 with 8 mm/day in the hot season a 400 m3-reservoir is required. The crops are planted on elevated beds. Water mixed with urea as fertilizer is applied daily. Drip irrigation improves growing conditions for crops while at the same time saving labor, water and other inputs. AMG is promoted as a holistic management package, integrating all aspects of production, post-harvest and marketing in one system. This includes the use of improved vegetable varieties, improved crop husbandry, integrated pest management, as well as improved storage, processing and marketing of products, and improved access to inputs.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The following establishment activities are connected to this technology: 1. Build concrete reservoir. 2. Drill borehole (110 mm diameter; 12 m deep, hand drilled). 3. Install motor pump and tubes to connect well with reservoir. 4. Install drip kit with tap, filter and drip laterals (8-16 mm in diameter). 5. Establish a fence to protect the garden.
For maintenance the following activities are required: 1. Prepare elevated beds with a basic dressing of 4 kg/m2 manure and 0.1 kg/m2 NPK fertilizer biannually. 2.Add urea to irrigation water (concentration: 50-100 ppm N). 3. Operate water supply system.
Natural / human environment: AMG is spreading fast in Senegal and Burkina Faso. Up-scaling of AMG in dry West Africa will depend on access to technology, inputs, knowledge and organization, and a conducive institutional environment.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塞内加尔
有关地点的进一步说明:
Ngoyé Ndioffogor and Mbassis Tadadem
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: AMG is suitable for urban/peri¬urban areas where producers have access to credit, markets, technical support
Strong organisation in groups is important for the maintenance of the system and for access to training/backstopping
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 收割后的措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A7:其它

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Cluster system with several AMG plots connected to a central water source - in this case a small elevated dam
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water spreading
Agronomic measure: drip irrigation
作者:
ICRISAT, Niamey, Niger
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Get inputs |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Tools | Unit | 1.0 | 65.0 | 65.0 | |
| 设备 | Drip system | Unit | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | |
| 设备 | Oil drum | Unit | 1.0 | 56.0 | 56.0 | |
| 设备 | Well/borehole | Unit | 1.0 | 16.0 | 16.0 | |
| 设备 | Motor pump | Unit | 1.0 | 34.0 | 34.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Fence | Unit | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| 施工材料 | PVC connections | Unit | 1.0 | 79.0 | 79.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 575.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 575.0 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prepare elevated beds with a basic dressing of 4 kg/m2 manure and 0.1 kg/m2 NPK fertilizer biannually | biannually |
| 2. | Add urea to irrigation water (concentration: 50-100 ppm N) | |
| 3. | Operate water supply system |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | Unit | 1.0 | 510.0 | 510.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 510.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 510.0 | |||||
注释:
A unit corresponds to the area irrigated by one producer (=500 m2). Establishment costs include labour inputs (2 US$ per person-day). Annual maintenance costs include labour, fuel and agricultural inputs (e.g. fertilizer, seeds; based on ICRISAT recommended rates). For a 1000m2-unit prices are doubled (except for tools and fence)
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Effective application of fertilizer with the water
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Due to doubled profits from vegetable production (compared to traditional irrigation methods)
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Reduced workload: total workload for AMG is 11.5 man-days compared to 30 man-days in traditional irrigation system (allows people to engage in other activities or education)
其它社会经济效应
Production cost
注释/具体说明:
Costs for drip irrigated gardens are 50% lower than for traditional irrigated gardens due to savings in labour, water and consequently in fuel
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Improved organisation (farmer associations, user groups)
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Improved knowledge on irrigation techniques /horticulture
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
Water availability / reduced pressure on water resources
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Effective use of water due to accurate and equal distribution of water at optimal rates
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Payback period is only 6 months. Net income per farmer after all deduction is about US$ 1,000 per year. The profitability of the AMG is around double that of vegetable gardens irrigated with traditional methods
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: AMG is spreading fast in Senegal and Burkina Faso. Cost reduction (e.g. alternative energy sources), collective action and intensive training / back¬stopping are very important provisions for successful adoption. Adoption trend: Up-scaling of AMG in dry West Africa will depend on access to technology, inputs, knowledge and organization, and a conducive institutional environment.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| AMG is a holistic management package, integrating all aspects of production, post-harvest and marketing in one system |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Irrigated vegetable production is a capital intensive undertaking | sharing infrastructure, land and water through producer groups can cut investment costs by 60% per unit area. Set-up and operation costs further decrease if producer groups can use communally owned infrastructure and/or alternative energy sources (e.g. elevated dams, solar pumps, artesian well). |
| The AMG system is not suitable for farmers with limited access to knowledge, marketing and services | improve access to markets and training programs (for extensionists and farmers); guarantee technical assistance during 2-3 years; target the system to educated producers who make a living out of vegetable production. Set up AMG service and demonstration centres offering credit, farm inputs, marketing support, training and technical advice. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Woltering L., D. Pasternak and J. Ndjeunga. 2009. The African Market Garden: Development of an Integrated Horticultural Production System for Smallholder Producers in West Africa – Draft Submitted to Irrigation and Drainage 21-10-2009
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
ICRISAT. 2009. The African Market Garden - Advanced Horticulture for the Poor (Flyer)
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块