Mainstreaming river water to facilitate irrigation in Barind [孟加拉国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Jalal Uddin Md. Shoaib
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Udo Höggel, William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Sharmongla Sech Prokolpo.
technologies_5171 - 孟加拉国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Establishing National Land Use and Land Degradation Profile toward Mainstreaming SLM Practices in Sector Policies (ENALULDEP/SLM)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Environment (DoE) - 孟加拉国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
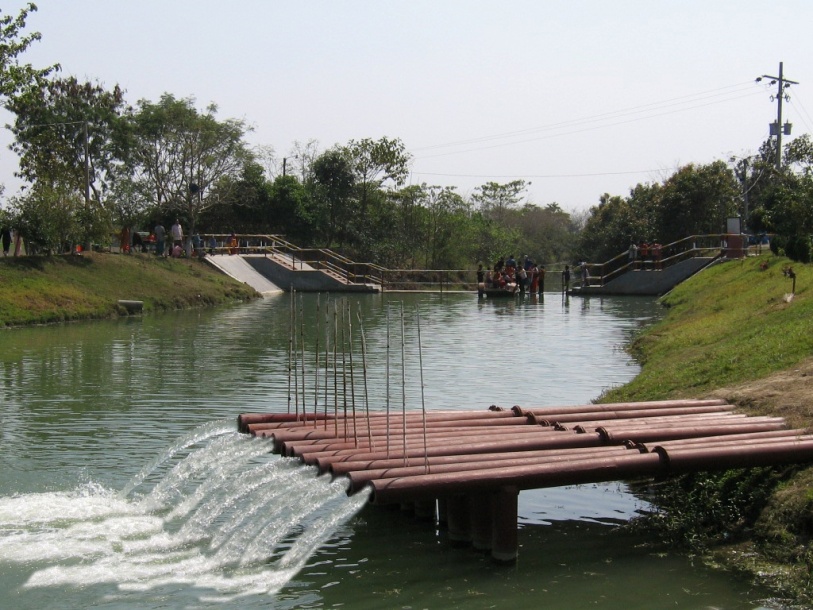
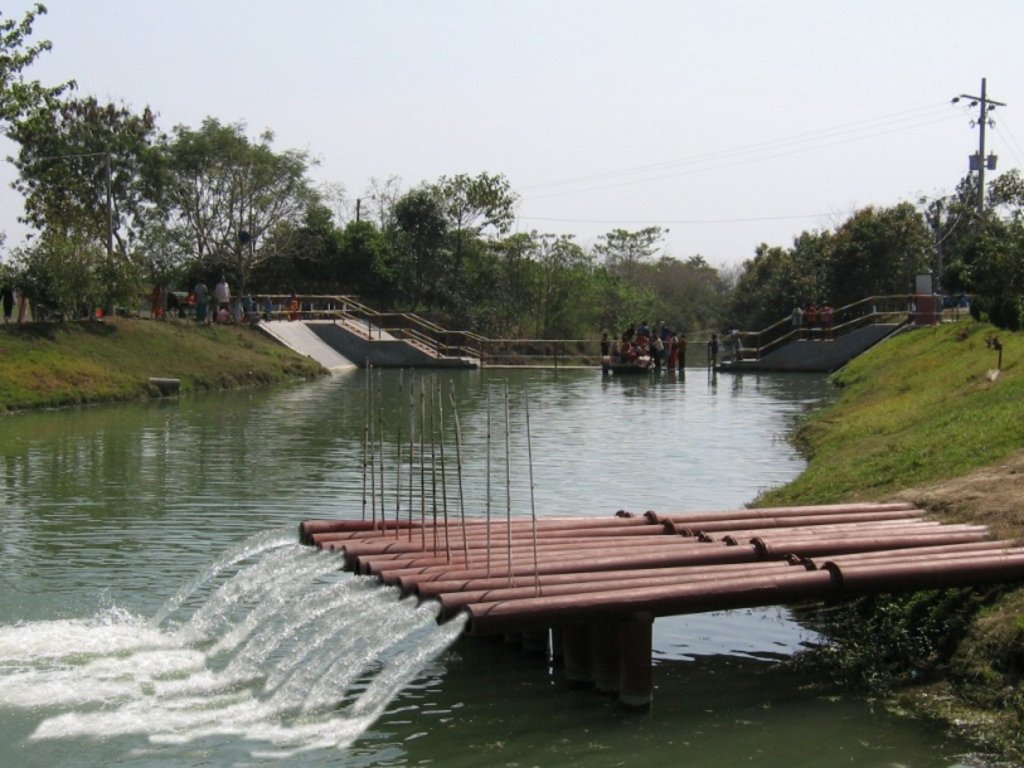
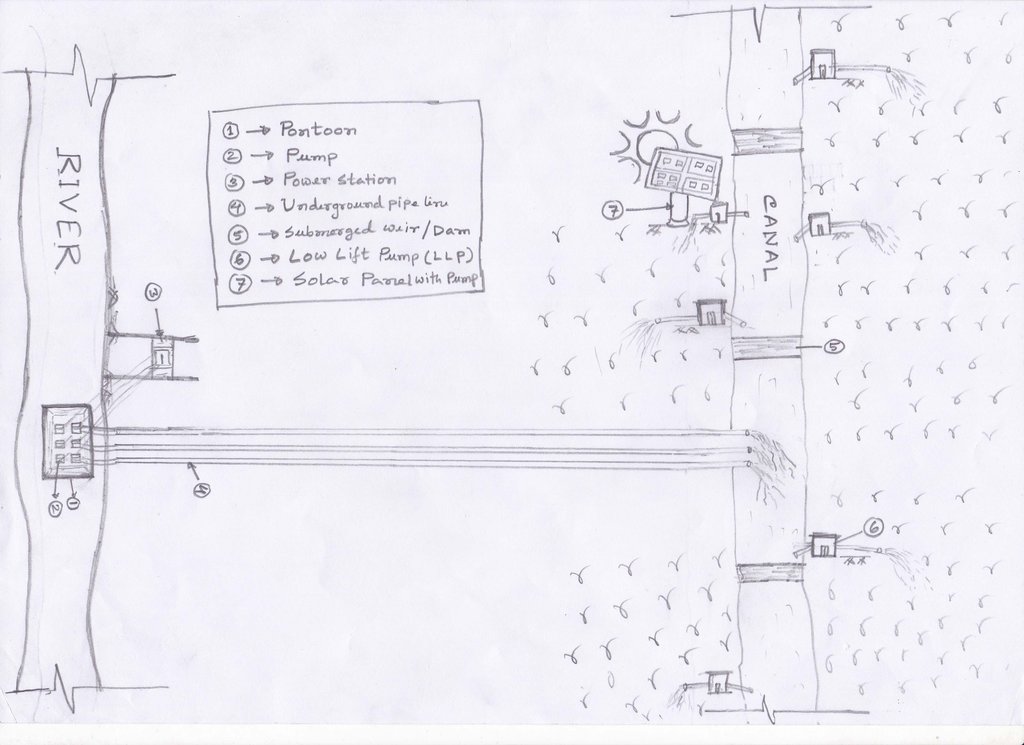
The technology promotes the lifting of river water by pump sets and conveys the water through buried pipelines to a canal. The conserved canal water is used for irrigation delivered by low lift pumps (LLP). Because water is held in the canal it revitalises the ecosystem along its length. Furthermore, using river water for irrigation avoids dangers associated with groundwater depletion.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
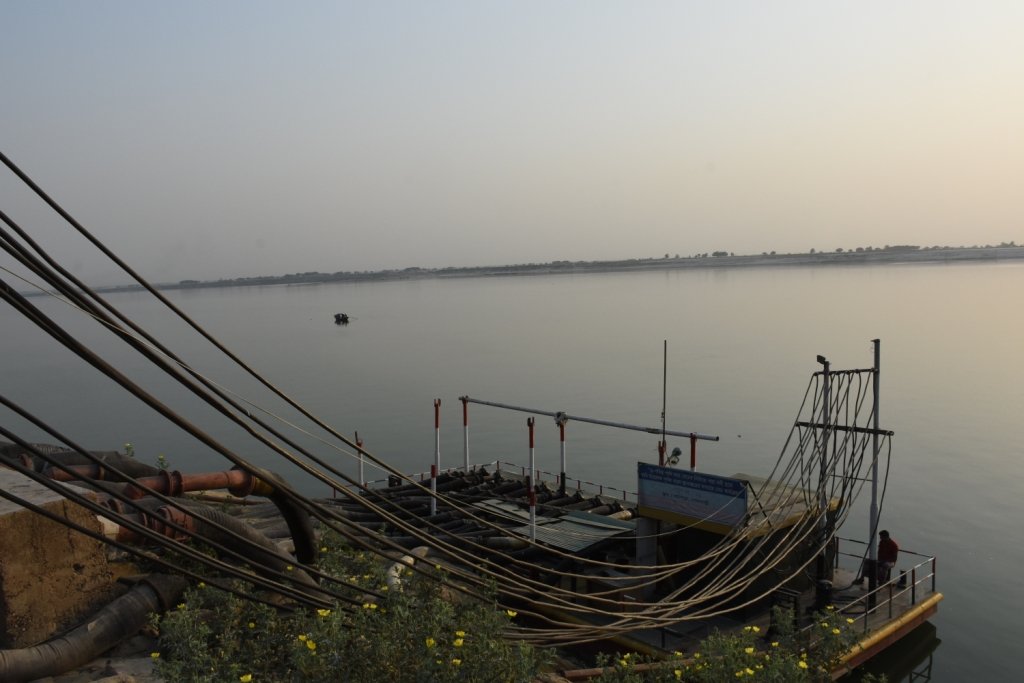
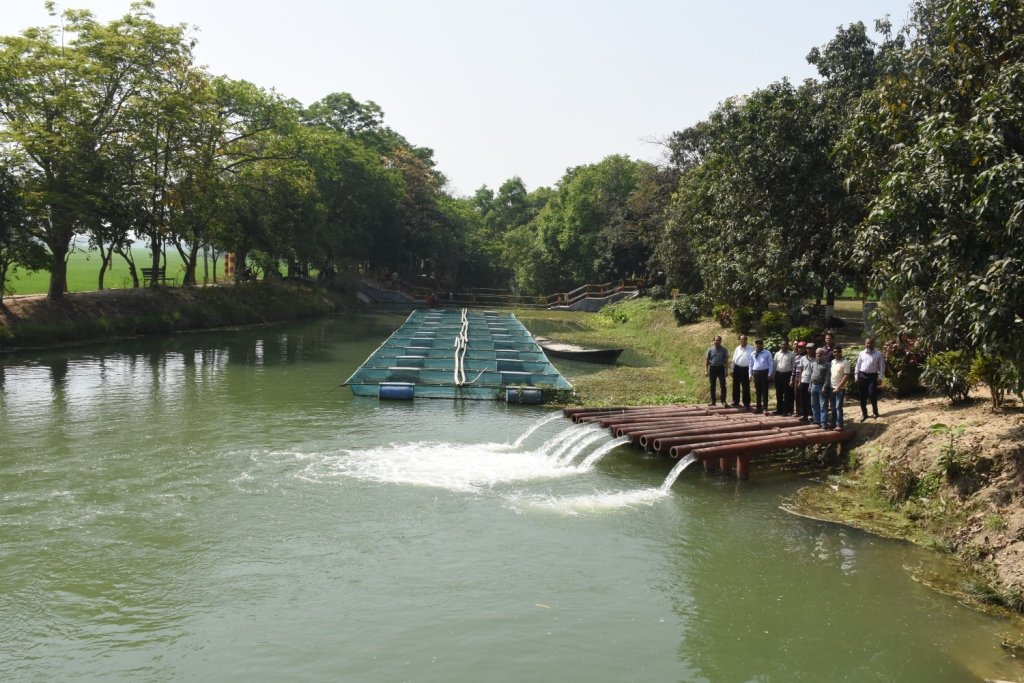
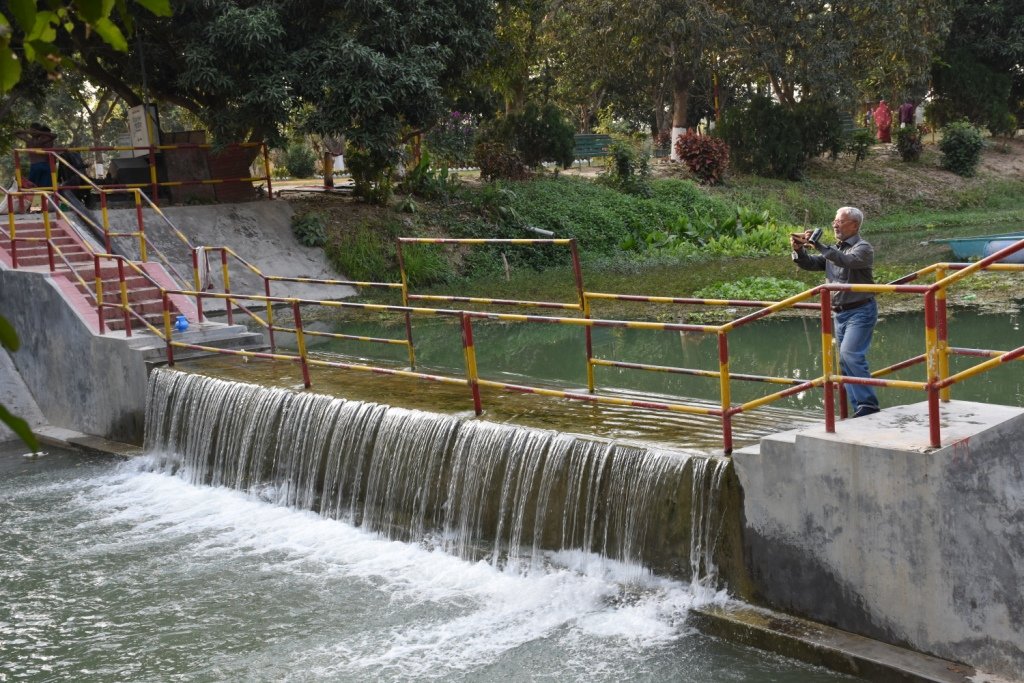
The project is sited at Sharmongla under Godagari Upazilla of Rajshahi district. The Sharmongla canal is located about 3.5 km away from the Padma river. Its total length is 29.0 km. Under this technology, water is lifted from the Padma river by pumps set on a pontoon. The lifted water is then discharged to a canal through underground pipelines. The water so discharged is lifted to the crop fields (delivery points) for irrigation. The elevation difference between the delivery points and the sourcing river is about 21 m. There are numbers of submerged weirs/dams constructed across the canal at different locations for conserving water: the water then helps regenerate the ecosystem along its banks and enriches the habitat.
Pontoon at a glance:
•Year of construction: 2004
•No. of centrifugal pumps at pontoon: 12
•Pump capacity: 50 m lifting height.
•Power of each pump: 60 HP
•Capacity of each pump: 2.5 cusec
•Total capacity of pump sets: 30 cusec
•Capacity of electric sub-station: 750 KW
•No. of discharge pipelines: 12
Sharmongla canal at a glance:
•Length of the canal: 29 km
•Average width of the canal: 15 m
•Average depth from ground level: 5 m
•No. of submerged weirs and dams within the canal: 14
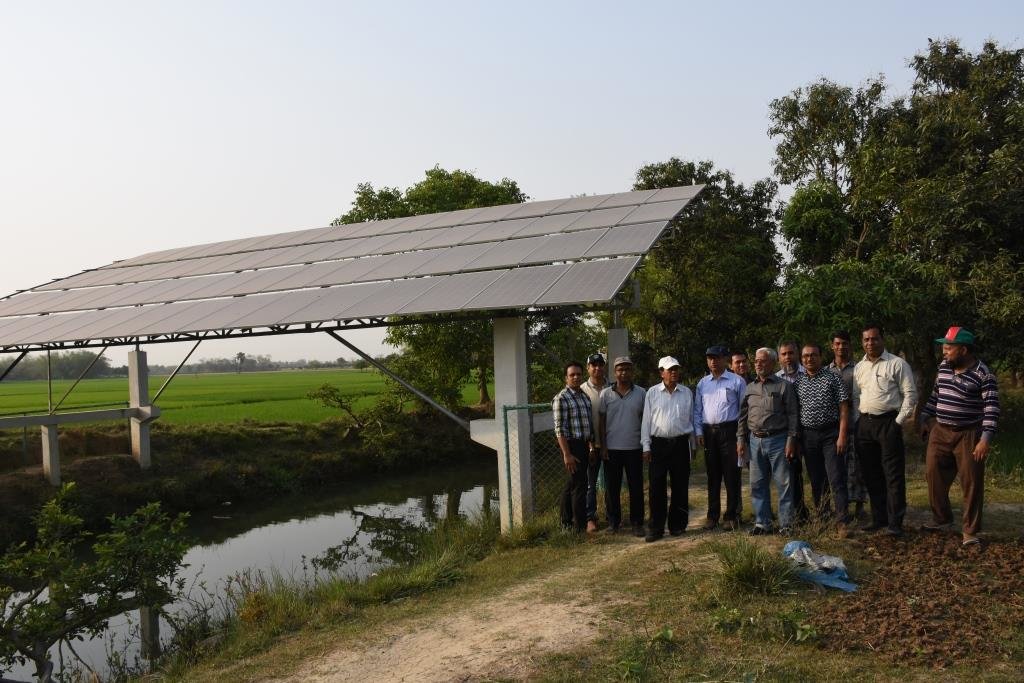
•No. of LLP (low lift pump): 27 electrified and 6 solar pumps
•Total irrigated area: 1850 ha
•Benefiting farmers: 5330
•Harvest yield of rice per year: 20,500 metric tonnes (approx.)
•Afforestation on the canal bank: 65,500 trees
Purposes/objectives of the technology:
•The main purpose of the said technology is to provide water for irrigation. This prevents abstracting of groundwater, which has adverse effects on the environment: therefore this system is environment friendly.
• Enhancing groundwater recharge thereby supports ecosystem function.
•The storing of river water in irrigation canals supports the enrichment of the habitat.
Approach for implementing the technology:
There was no irrigation facility for crop production in this drought-prone area. Government officials came to the locality, discussed with the local community, elites, as well as the farmers. Finally, the local community was convinced about the technology. Then the irrigation system could be implemented in the area. On seeing the success of the technology, the same has been replicated on approx. 9400 ha. in Barind area, benefitting approx. 32,200 farmers.
Maintenance of the technology:
In case of problems, the respective mechanic of that area informs the Assistant Engineer through the Sub-Assistant Engineer. Thus the problem is solved by their own initiative. It is also monitored by the Executive Engineer of the respective District, and finally by the Executive Director from the headquarters if needed.
Crop cultivation:
Due to the application of the technology, previously fallow land has come under cultivation/irrigation facilities, mono-cropped land has been converted into multi-cropped land. Different crops, like rice, wheat, maize, mustard, pulses, potato, tomato, spices and other vegetables are cultivated.
Farmers’ acceptance:
The technology has been well accepted by the farmers, as uncultivated land has been brought under cultivation and different crops are now being cultivated year-round.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
日期:
25/03/2019
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
孟加拉国
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The following project were providing the irrigation facilities in Barind region:
i) SEMP - Sustainable Environment Mgt. Project
ii) RWCP - Rain Water Conservation Project
iii) EIBA – Extension of Irrigation in Barind area through conservation water in canal
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
- Irrigated rice (Paddy
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
每年的生长季节数:
- 3
具体说明:
Rabi-Pre-Kharif- Kharif
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Mango with rice,
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Major crop rotation is Boro (winter rice) - Transplanted Aman, Minor crop rotations are Potato-Boro- Tasplanted Aman, Rabi crops (mainly vegetables)- Boro- Transplanted Aman
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Mango and rice
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备
- S10:节能措施

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
注释:
There are two stages of harvesting water.
1 - from river water, which is not going directly to the field
2- water reserved in canals and supplied to the field
Para S10 - refers to saving conventional electricity by using solar power for distribution of water to fields
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
- Hq:地下水水质下降
注释:
Barind was driest part of Bangladesh. It was enhanced when groundwater abstraction increased to support cropping by irrigation. The reduction of the groundwater table enhanced the dry out of dug wells, which supported domestic consumption. Hence, aridification was prominent in the area. It is reported that after the application of this technology, there are indications of recharging of the groundwater. Due to the increase in vegetation, the local temperature tends to be cooler than before.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
This technology helps reducing land degradation through using river water rather than groundwater for irrigation, thereby
preventing land degradation through increasing the vegetation cover on land.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
1. Pontoon: Length 55 ft, Width: 25 ft, Height: 4.50 ft
2. Centrifugal pump (12 nos)—each pump 60 HP,capacity-2.5 cusec, pump head: 50m
3. Electric power station capacity: 750 KW
4. Underground water distribution line (12 nos): Length of each line is 3.50 km
5. Length of water storage canal (Sharmangla canal): 29.0 km (average width 15.0 m and depth 5.0 m)
6. Nos of submerged weir/dam to reserve water in the canal: 14 nos
7. Nos of LLP (electrified) to lift water from the canal to crop field through buried pipeline : 27 nos
8. Nos of solar pump to lift water from the canal to crop field through buried pipeline: 06 nos
9. Nos of Prepaid meter for collecting irrigation charges (Revenue): 33 nos
10. Irrigated area: 1850 ha
11. Construction materials:
-Pontoon: A kind of platform that float on water made of Mild steel sheet, Stainless steel etc.
- Power station: Transformer, electric pole, wire etc.
- Distribution line: mild steel and PVC pipe
- Dam/Submerged weir: steel bar, cement, sand, brick, stone etc.
作者:
Sayed Zillul Bari
日期:
25/03/2019
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
1 Pontoon, Pumps, Pipes, weir construction etc
指定单位面积(如相关):
Pontoon (Length 55 ft, Width: 25 ft, Height: 4.50 ft) is a platform build on iron sheets, that can float on river, where pumps were set. The pipes for water delivery were of PVC. Water canal in this case compiler referred to canals of Barind which were ephemeral. Now water reserve for year round use.Piping system includes PVC pipe to convey water to the field, where a valve was set to control water disposal. There is a pipe of 12 inch dia to maintain water head through out the system.
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
BDT
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
85.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
800 BDT
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pontoon construction and installation on the river | 60 days |
| 2. | Pumps installation on the pontoon | 30 days |
| 3. | Construction of underground water distribution line | 70 days |
| 4. | Re-excavation of derelict canal | 120 days |
| 5. | Construction of submerged weir / dam | 180 days |
| 6. | LLP installation at the canal bank (27 nos) | 150 days |
| 7. | Solar pump installation (06 nos) | 45 days |
| 8. | Pre-paid meter installation at pump sites to collect irrigation charges (33 nos) | 30 days |
| 9. | Buried pipe line construction for irrigation at crop land sites | 120 days |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 施工材料 | Pontoon construction and installation on the river | 1 | 1.0 | 5000000.0 | 5000000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Construction of underground water distribution line | 1 | 1.0 | 27800000.0 | 27800000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Construction of submerged weir / dam | 1 | 14.0 | 1600000.0 | 22400000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Re-excavation of derelict canal | 1 | 1.0 | 29000000.0 | 29000000.0 | |
| 其它 | Pre-paid meter installation at pump sites to collect irrigation charges | 1 | 33.0 | 243000.0 | 8019000.0 | |
| 其它 | Solar pump installation | 1 | 6.0 | 2000000.0 | 12000000.0 | |
| 其它 | LLP installation at the canal bank (27 nos) | 1 | 8.0 | 2700000.0 | 21600000.0 | |
| 其它 | Pumps installation on the pontoon | 1 | 12.0 | 1833000.0 | 21996000.0 | |
| 其它 | Buried pipe line construction for irrigation at crop land sites | 1 | 1.0 | 23100000.0 | 23100000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 170915000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 2010764.71 | |||||
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
1439.02
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
none
注释:
Labor costs etc all included in construction, pipeline installation etc.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pontoon repair and maintenance | 1/5years |
| 2. | Pump repair and maintenance | As per requirement, 1/yr |
| 3. | Distribution line maintenance | As per requirement, 1/yr |
| 4. | Power station repair and maintenance | As per requirement, 1/yr |
| 5. | Submerged weir / dam repair and maintenance | 1/5yrs |
| 6. | LLP repair and maintenance | 2/yr or as and when necessary |
| 7. | Buried pipe line repair and maintenance | 1/6yrs, as and when necessary |
| 8. | Prepaid meter repair | 2-3/yr |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Prepaid meter repair | 1 | 0.2 | 100000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Buried pipe line repair and maintenance | 1 | 1.0 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| 其它 | Pontoon repair and maintenance | 1 | 1.0 | 500000.0 | 500000.0 | |
| 其它 | Pump repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| 其它 | Distribution line maintenance | 1 | 1.0 | 75000.0 | 75000.0 | |
| 其它 | Power station repair and maintenance | 1 | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | |
| 其它 | Submerged weir / dam repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1.0 | 200000.0 | 200000.0 | |
| 其它 | LLP repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 915000.05 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 10764.71 | |||||
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
11.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Land users share their participation in kinds and allowing installation of pipelines and other infrastructure
注释:
Land users were trained and they provided land for infrastructures. For example space for outlets and underground pipe installation. Practically they did not contribute any cash.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Pontoon construction, power supply and lining of the underground piping system.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1600.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Most of the rainfall events happen during May to October
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Agroecological region 26
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
High Barind tract, mainly dissected (Closely & Broadly) terrace, soil pH is acidic, low in Nitrogen content, low CEC
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Area is above flood level
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
注释:
Yes. The farmers of Barind are of wide range. The large farmers are basically absentee. Medium range farmers engage themselves in their land and in addition they rent land from large farmers. So there is complex ownership.
This was from field feedback.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 租赁
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
作物质量
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
生产故障风险
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
At present land users are used to grow high water demanding crops. For example Boro paddy and potato both crops require large volume of water and the irrigated area slowly increasing, that situation demand of irrigation water increasing.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
The supply of agricultural inputs increased and channelized through deploying dealers etc. Hence expenses relatively decreased
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
经济差异
注释/具体说明:
Basically in this area could be grouped in to two. One group has almost no land and previously they have to migrate beyond barind area as labor and they were poor. At present they have job (agri-labor or otherwise) in their area and become more solvent then past 90's. On other hand the second group cultivate the land of their own or leased, which they could not in 90's. They also in handicap because of poor crop and no option to cultivate in two seasons. Hence apparently both groups as of their status are in well shape. The peoples those who have no land for cultivation now can engage them in many other entrepreneurship (e.g. farm product marketing, livestock/poultry raring, carpentering, grocery, etc etc) emerged.
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
土地使用权/用水权
文化机会
娱乐机会
社区机构
国家机构
注释/具体说明:
Along with the Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) other national institutions like Department of Agricultural Extension, Livestock, Fisheries, Bangladesh Rural Development Board (BRDB), Financial institutions- Rajshahi Agricultural Development Bank and others (NGO) are operating more effectively in the Barind in multiple dimensions. In addition students from Rajshahi University also engaged in their research on various issues. BMDA also improving its capacity and skill to develop more effective approach for Barind area.
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
水的回收/收集
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
This comment was done comparing between conveying water by open drainage and through pipeline. Definitely there are almost no run-off from pipe line distribution. On the hand land users have to confirm their field bunds to protect run-off. Prepaid metering system also restricted land users not to allow excess water to over flow from their field. In-spite of that there may be small amount run-off, but the detachment of top soils is within tolerable limit and accumulate within field bunds.
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
注释/具体说明:
It is reported that ground water slowly recharged, As a results shallow tube wells are also working , which were about to abandoned before.
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Vegetation coverage increased,
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Increased land cover-Reduced drought
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
In 90's the lands were bare and in monsoon after heavy downpour a large amount of water going to downstream as run-off with detached top soil. At present land is covered, field bunds are strengthen, restrict run-off as a result soil loss decreased.
土壤堆积
注释/具体说明:
Field bunds enhance soil accumulation by limiting run-off water by field bunds/dykes.
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
Mechanized cultivation and usage of farm machinery however enhance soil compaction.
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
The area is above flood level
干旱影响
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Emission of carbon decreased as vegetation cover round the year increased.
微气候
注释/具体说明:
Reduced dusty wind, temperature cooler then before.
其它生态影响
The Barind was almost desert like before 90's. Its natural vegetation were almost extinct. Biodiversity both Species and habitat were low. At present it is improving spectacularly.
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
In all a desert like Barind tract become green now.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
Usage of surface water reduces groundwater abstraction and improves groundwater (GW) recharge
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
As the land cover has increased, that has a substantial impact on limiting polluted surface water to flow up to river.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 减少 | 非常好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 夏季 | 减少 | 非常好 |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 夏季 | 增加 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
It could rather to explain as the beneficiaries of the technology. Truly a single land user or a group of land user will not able to install this type of system for multiple reasons. There are two components of this technology, one is the government institution who provided the scope of using surface water for irrigation and the second one are the land user who use the scope or facilities of irrigation system Here about 1800 farmers are involved to use surface water as their irrigation source.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
Most of the farmers of the area who has land adopted surface water for irrigation instead of ground water abstraction.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 劳动力可用性(例如,由于迁移)
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
where there are no canal for water storage , local ponds are used to reserve the surface water to irrigate land surrounding the pods and obviously where river water could not be reached.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Ensured crop production through irrigation |
| Reduced ground water irrigation and decrease ground water depletion. |
| Increased work facility at project area |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improved socio-economic condition of beneficiaries |
| Increased ground water recharge |
| Increased fish cultivation and duck farming at the canal |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Scope of individual level implementation is very limited | Community approach will facilitate the SLM implementation etc. |
| Maintenance, distribution and regulation of water etc have no control of the beneficiaries | Capacity of the beneficiaries to be developed |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Source of lifting water points may be shifted in the long run | Efficiencies of irrigation water supply need more attention with demand and supply. |
| Weak linkage with beneficiaries | Integrated approach needed to include community and implementing agencies. |
| Crops with high water demand may not sustain in the long run | Appropriate crop and cropping patterns are to be adopted with crop zoning |
| Increasing cropping intensity leads to deficiency of soil nutrients | Monitoring of soil health essential for this region. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Three times with experts of this area
- 与土地使用者的访谈
20
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
10
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Consulted relevant project documents
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
25/03/2019
注释:
A long process was maintained from building capacity of the professionals to handle WOCAT tools, initial inventory with core experts and screening with local professionals, documentation in field and compiling data in the WOCAT format, which was again validated with large local groups of scientists, extension officials, local government, NGO, lead farmers etc.
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Project documents
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Available in BMDA
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Questionnaires on Tecnologies (QT)
URL:
www.wocat.net
标题/说明:
Sustainable land management (SLM)
URL:
https://knowledge.unccd.int/topics/sustainable-land-management-slm
标题/说明:
Achieving Land Degradation Neutrality at the country level
URL:
https://knowledge.unccd.int/topics/land-degradation-neutrality
7.4 一般注释
Excellent
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块