Detention ponds [德国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Felix Witing
- 编辑者: Michael Strauch, Mona Pauer
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Rückhaltebecken
technologies_6265 - 德国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Schürz Christoph
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ)
德国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) - 德国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Detention ponds are artificially excavated basins that collect stormwater runoff and eroded sediment from the upstream catchment. The water stored in these ponds is slowly released into a water body or it infiltrates into the groundwater – or both. Their primary functions are flood control, erosion control and water quality improvement.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
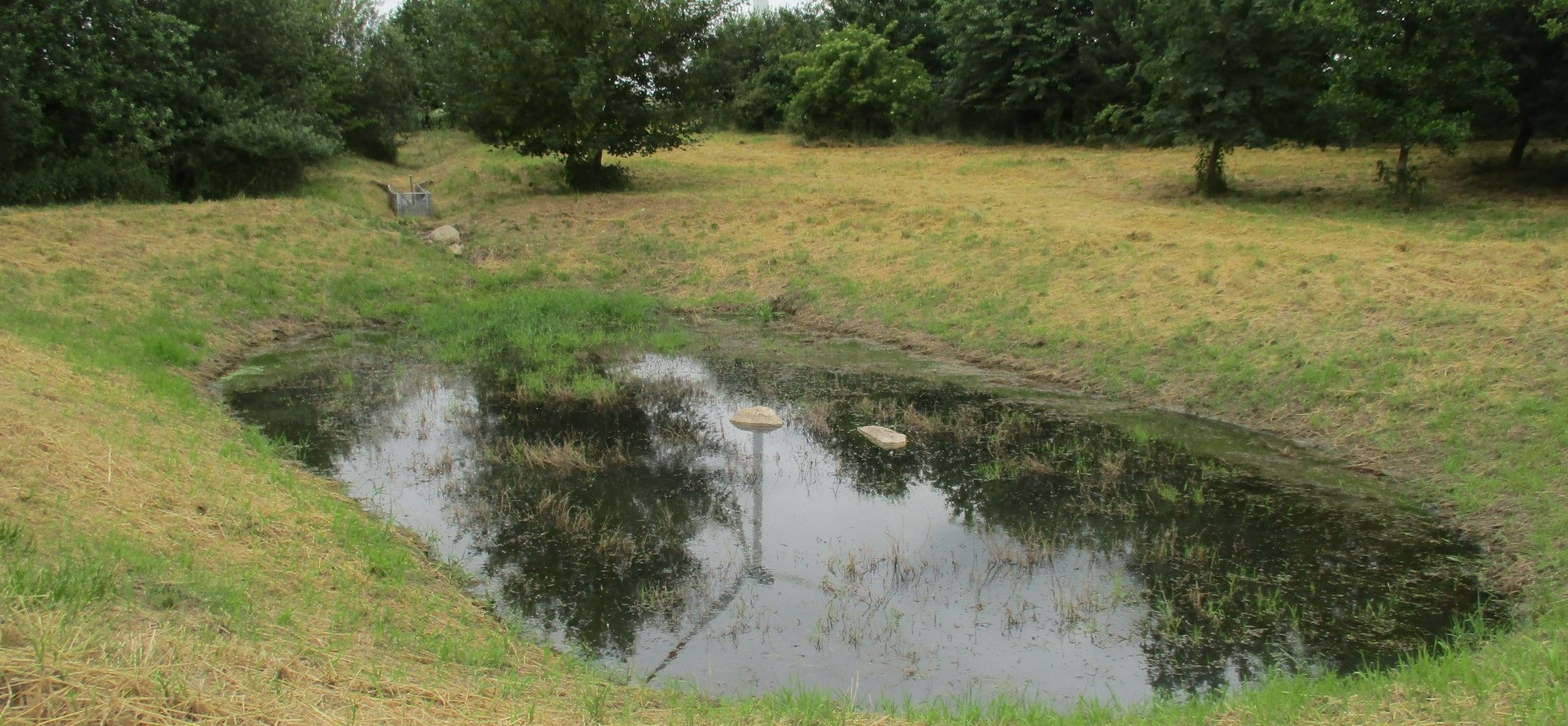
This documentation focuses on a detention basin constructed to hold surface runoff at the lowest point of an agricultural catchment. A well-designed detention pond is an effective flood control and landscape management measure. It stores surface runoff and releases it through controlled flow, infiltration, or evaporation (or a combination), and reduces nutrient inputs to the adjacent water body by filtering out sediment and nutrients through particle deposition, or nutrient uptake by plants. On average, water treatment in a detention pond can remove about 50-60% of suspended solids, 30-35% of total phosphorus and total nitrogen, and 25-65% of metals. Ponds also provide habitat for terrestrial, riparian and aquatic species. In addition to their ecological impact, they have an aesthetic and cultural value to society, for example, as a demonstration of effective sustainable water management.
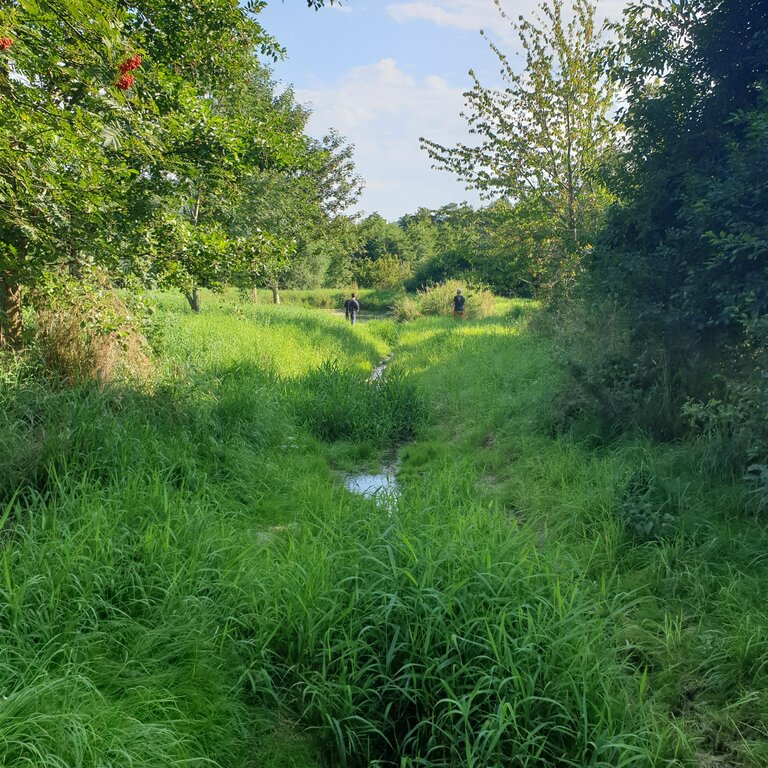
The detention basin described here was constructed by excavating a new depression and ditch system. It consists of a 450 m long inlet channel, a 250 m² pond, and an overflow channel that diverts excess water downstream to the nearest river (Schwarzer Schöps). However, there are no outlet structures for draining water that is captured in the pond (apart from the overflow). All the collected water seeps into the ground and soil particles settle. As a general rule, the size of such a pond should be 3-7% of the upstream catchment and should be able to hold at least the precipitation of a 1 in 30 year rainfall event. However, as the infiltration of the collected water is rather slow, the efficiency is reduced for successive events and overflowing is common. The depth should be between 1.2 m and 2.0 m. A deeper pond can lead to stratification and anoxic conditions, while a shallower pond may cause algal blooms and high biological activity in the summer. Water stored in the pond should remain for at least 20 days to ensure biological treatment.
The construction of the detention pond in this documentation was initiated as a compensation and replacement measure for the construction of a new road in 2016. Accordingly, the road construction authority, the landscape conservation association and a farmer were involved in the implementation.
As usual with such measures there are drawbacks as well as positive impact for landowners. The measure consumes a lot of land, which automatically results in yield losses. It is expensive to build and not easy to construct - and requires the help of an engineering firm while also being time-consuming to maintain. Maintenance is required to sustain the benefits of the technology. For a pond such as that documented here, the following maintenance activities are necessary: during the first three years, maintenance includes mowing the surrounding green area and the dried out pond and channel three times per year. After the fourth year, maintenance includes (a) an annual function check, (b) a check for pest infestation every two years, and (c) suppression of excess woody growth every eight to ten years. Twice a year (mid-June and late August), the grass around the pond and in the intake channel is mowed and the clippings are removed. Shrubs and woody plants are maintained, especially by pruning woody plants (every 8 to 10 years) and coppicing sections of shrubs (every 10 to 15 years). In the long term, it may be necessary to remove the deposited sediments in order to maintain the retention capacity.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
德国
区域/州/省:
Saxony
有关地点的进一步说明:
Reichenbach
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
- Compensation measure
注释(项目类型等):
The construction of the detention pond was initiated as a compensation measure for the construction for the road construction project "S70 OU Reichenbach 2. BA".
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 降低灾害风险
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

其它
具体说明:
extensively farmed grassland
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
- 减少基于生态系统的灾害风险
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
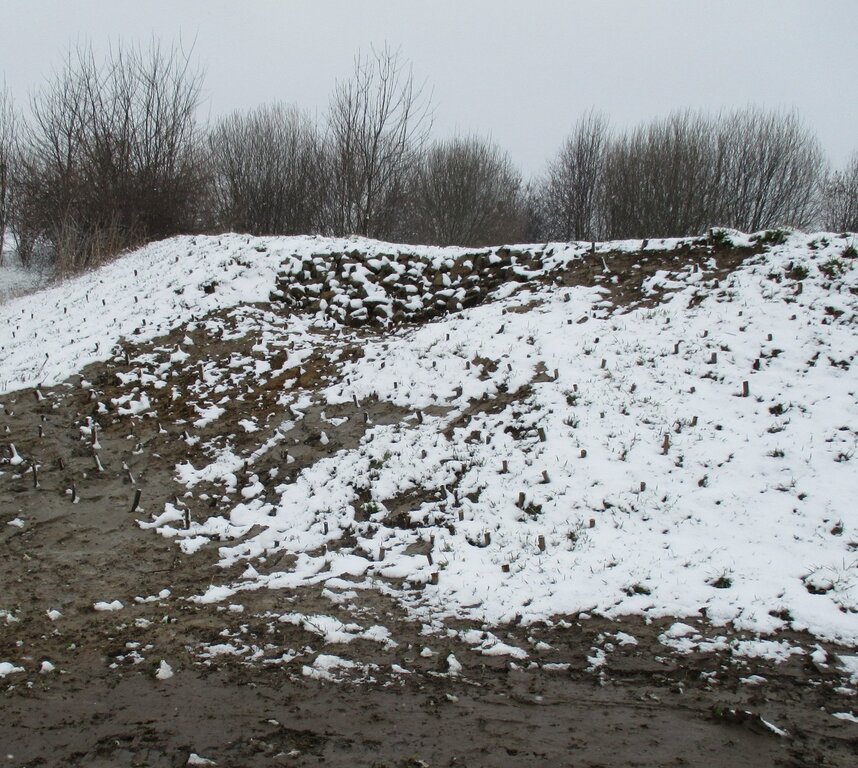
Securing dam stability by willow sticks.
作者:
LISt Gesellschaft für Verkehrswesen und ingenieurtechnische Dienstleistungen mbH, Bereich Kompensationsmaßnahmenmanagement
日期:
29/02/2016
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
A detention pond (in genreral) consists of a sediment forebay (pretreatment system), a permanent pool that is intended to remain wet throughout the year (but may dry out), a temporary storage pond for flood attenuation, and a shallow zone or aquatic bench along the edge of the permanent pool to support wetland planting that provides ecological and safety benefits. It should be wedge-shaped with a length to width ratio of between 3:1 and 5:1. The side slope shouldn’t be steeper than 1:3 for public safety and maintenance access.
作者:
Hunt et al. (2020)
日期:
20/02/2020
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Detention pond (as documented here)
指定单位面积(如相关):
225 m², ca. 337,5 m³ (water depth of 1,5m)
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
€
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.91
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
18.70 € per hour
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | remove topsoil | |
| 2. | profile water body according to site plan (Standing water 1.5 m deep, ditch 0.5-1.5m deep) | |
| 3. | installing of inlet channel | |
| 4. | installing erosion protection on embankments | |
| 5. | cover the topsoil / terrain profiling | |
| 6. | planting of shrubs & aquatic plants along the shoreline | |
| 7. | ditch connection to Schwarzer-Schöps | |
| 8. | reprofiling ditches (90m) | |
| 9. | desilting of drainage ditch to Schwarzer-Schöps | |
| 10. | subsequent installation of a spillway (beak structure: 'Schnabelbauwerk') and willow sticks as an erosion control measure for the ditch connection to Schwarzer-Schöps. |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
25250.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The costs were covered by the road construction authority (compensation measure for the construction of a new road)
注释:
based on estimated average costs (nwrm.eu)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | completion and development maintenance (mowing of the green area and the water-free water body) | first three years: three times per year |
| 2. | functional check | after the fourth year: every year |
| 3. | check for pest infestation | after the fourth year : every other year |
| 4. | check to suppress unwanted woody growth | after the fourth year: every 8 to 10 years |
| 5. | grass around the pond and in the intake channel is mowed and the clippings are removed | after the fourth year: twice a year (mid-June and late August) |
| 6. | pruning woody plants | every 8 to 10 years |
| 7. | putting sections of shrubs on stock | every 10 to 15 years |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
618.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The costs are covered by the road construction authority (compensation measure for the construction of a new road)
注释:
estimated average costs (nwrm.eu)
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
From the government perspective: A budget must be set aside annually for necessary maintenance to ensure functional efficiency.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Average annual rainfall in mm: 750.82 mm/a
Name of the meteorological station: https://whh-kliwes.de/mapview
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Length of growing period (LGP): 209 days
(https://www.umwelt.sachsen.de/dauer-der-vegetationsperiode-30631.html)
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Luvisol (German soil classification system: Parabraunerde)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
- 员工(公司、政府)
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
The technology was not built and is not maintained by a land user, but by a public authority (road construction authority).
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
not on agricultural inputs, but establishment and maintenance consume a lot of money.
工作量
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
注释/具体说明:
Improved water quality of subsequent river Schwarzer-Schöps.
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Soil moisture next to the retention pond increased due to infiltration.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
More plant diversity compared to normal farmed grassland.
动物多样性
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
The assessment is based on expert judgements. It is not based on on-site measurements.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
地下水/河流污染
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
The assessment is based on the expertise of the compilers and not on measurements in the case study.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 非常好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 热浪 | 好 |
注释:
In past summers there was little or no water left in the pond.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常消极
长期回报:
消极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| temporary water-bearing habitat |
| biotopic network |
| buffer effect |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| effective flood control and landscape management measure |
| Stores surface runoff, slows it down, and releases it incrementally through controlled runoff, infiltration, or evaporation. Reduces nutrient inputs to adjacent water bodies. |
| aesthetic and cultural value for the society |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Danger of siltation and succession if not maintained regularly and professionally. | |
| Difficult maintenance due to inaccessible terrain. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Consumes a lot of land, which means a loss of yield. | |
| expensive to build and not easy to construct | |
| requires the help of an engineering firm | |
| time-consuming to maintain |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
14/09/2021
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Hunt et al. (2020): Plant Selection for Infiltrating Wet Ponds in North Carolina
URL:
https://content.ces.ncsu.edu/plant-selection-for-infiltrating-wet-ponds-in-north-carolina
标题/说明:
nwrm.eu: Individual NWRM, retention pond
URL:
http://nwrm.eu/index.php/measure/retention-ponds
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块