Mulching and drip irrigation for banana [阿曼]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Daniel Danano Dale
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_1143 - 阿曼
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - 意大利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Mulch and drip irrigated banana commercial farm.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
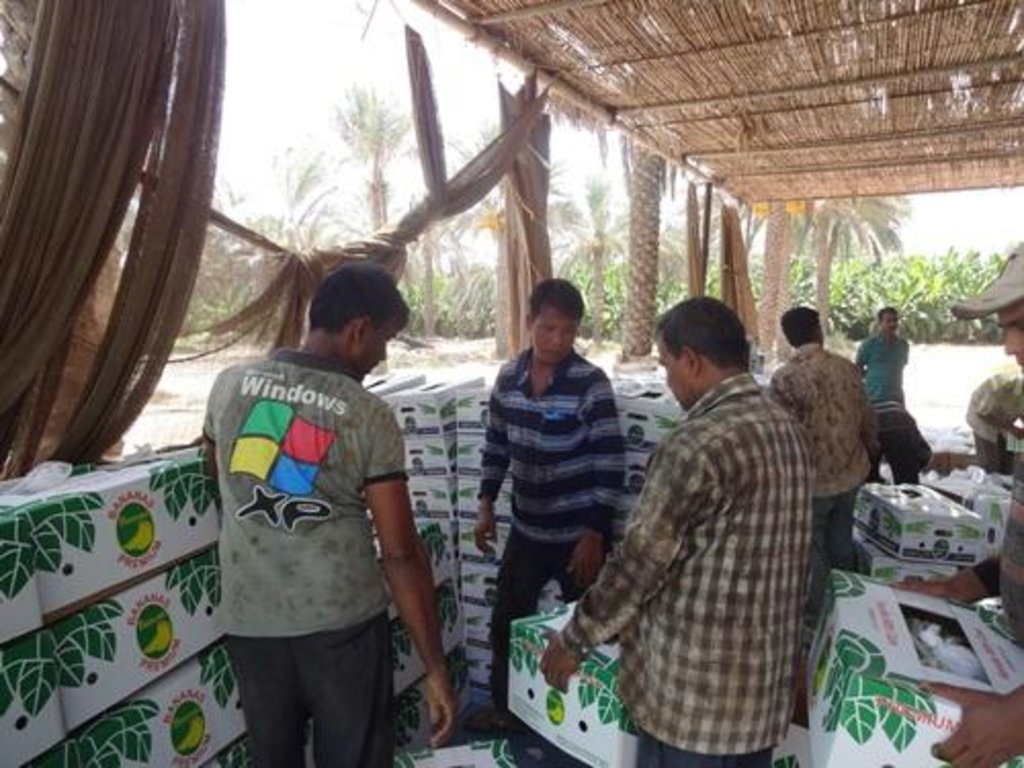
Banana is planted for commercial purposes on a medium sized farm in Elbatinah, Oman It is planted in a well prepared land, where ridges and furrows are made by machinery and manual labour. Seedlings are raised from tissue cultures that are imported. Before the seedlings are planted in the field the land is pulverized and watered. It is fertilized by combination of organic and inorganic fertilizers before seedlings are planted. After planting the seedlings get water through babblers from the pipes network. Water is delivered from a center, where soil nutrients are injected. Harvest takes place twice a year. Old banana plants are removed and chopped to be incorporated in the soils
The harvested banana is sold both in domestic market and mostly exported to neighboring countries. The most dominant variety cultivated is Cavendish. Hired labor coming from other countries are involved in most of the farm activities. Some are permanent workers, while most are temporary laborers who come and go depending on availability of seasonal jobs.
Purpose of the Technology: Managing land to control salinity of soils that impede normal growth and affect productivity of banana plants which produce banana for market.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The land is cleared first from weeds and dead plants using machinery. Mostly scrapers and cleaning machinery are used to remove dead banana plants and weeds. Following this the scraped material is incorporated into the soil or removed away. Then the land is harrowed and pulverized well before banana seedlings are planted. Tissue culture is imported from other countries and transplanted in plastic houses before planted out in the field. While planting the young seedlings are spaced at a given interval between plants and rows.
Natural / human environment: The farm is situated in one of the agricultural potential areas in the country. The land is nearly level to level. Some leveling is required wherever there is need to level. Land users in the surroundings include small holders, some with medium size farms and also there are large scale farms. The current farm where the documentation has been undertaken is among the top medium sized farms.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿曼
区域/州/省:
Al Batinah
有关地点的进一步说明:
Almusina
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
60.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 60 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180; Second longest growing period in days: 180
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): bacterial wilt diseases, shortage of water, fertility decline
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): diseases, shortage of water, fertility decline
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

其它
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, early planting, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), rotations / fallows, breaking compacted topsoil, furrows (drainage, irrigation), deep tillage / double digging
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, aligned: -linear, scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, droughts, land tenure
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), change in temperature, change of seasonal rainfall, population pressure, labour availability, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing)
Better crop cover
Material/ species: land mulch covered
Early planting
Material/ species: planting done in early october
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: banana with mango
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: organic manure
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: Urea, NPK
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: gypsum
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: fallows
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: G : grass
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Trees/ shrubs species: banana
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mango
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0-2%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 0-1%
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting banana suckers | October-November |
| 2. | weeding and cultivation, mulching | November-February |
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | irrigation | |
| 2. | mulching | |
| 3. | soil amendments / applying gypsum | |
| 4. | replanting banana suckers | |
| 5. | thinning and replanting | Nov-Jan |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Machinery/ tools: tractors, scarpers, pumps,
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Soil and the residue to be removed from the ground during
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: Coastal plains
Slopes on average: Nearly level to level slopes
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is very high
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 合作社
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: mostly men are farm laborers
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
30% of the land users are rich.
45% of the land users are average wealthy.
25% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 公司
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The farm is commercial and gets good return from the investment. Banana is at local market outlets and exported as well.The farm has skilled laborers to perform activities
生态影响
水循环/径流
蒸发
土壤
养分循环/补给
盐度
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
use of modern techniques of soil salinity control such as use of gypsum How can they be sustained / enhanced? mixing of various salinity level water from wells and making it moderate to e distributed through central pumping network |
|
use of high yielding variety of bananna How can they be sustained / enhanced? start to develop own tissue culture |
|
seedling / saplings preparation from tissue culture How can they be sustained / enhanced? producing quality saplings for transplanting out in the field |
|
use of organic fertilizers in combination with inorganic fertilizers, soil moisture conservation techniques and management of soil nutrient recycling How can they be sustained / enhanced? monitor salinity level of organic fertilizers |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块