SUNN HEMP AS A SOIL AMENDMENT AND FOR MITIGATION OF SALINITY [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Laksamee Mettpranee
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_7274 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Siangsunthia Mana
泰国
Compiler:
co-compiler:
Raksasarp Pithcanun
Land Development Department
泰国
co-compiler:
reviewer:
reviewer:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - 泰国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Centre of Excellence for Soil Research in Asia (CESRA)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

EXTENSION OF SUNN HEMP AS A SOIL AMENDMENT … [泰国]
An outreach programme aims to educate farmers about the benefits of ploughing rice stubble into the soil and incorporating green manure crops such as sunn hemp - as well as other sustainable practices. Groups of farmers are formed, and they are assisted by various organisations including the Land Development Department …
- 编制者: Laksamee Mettpranee
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
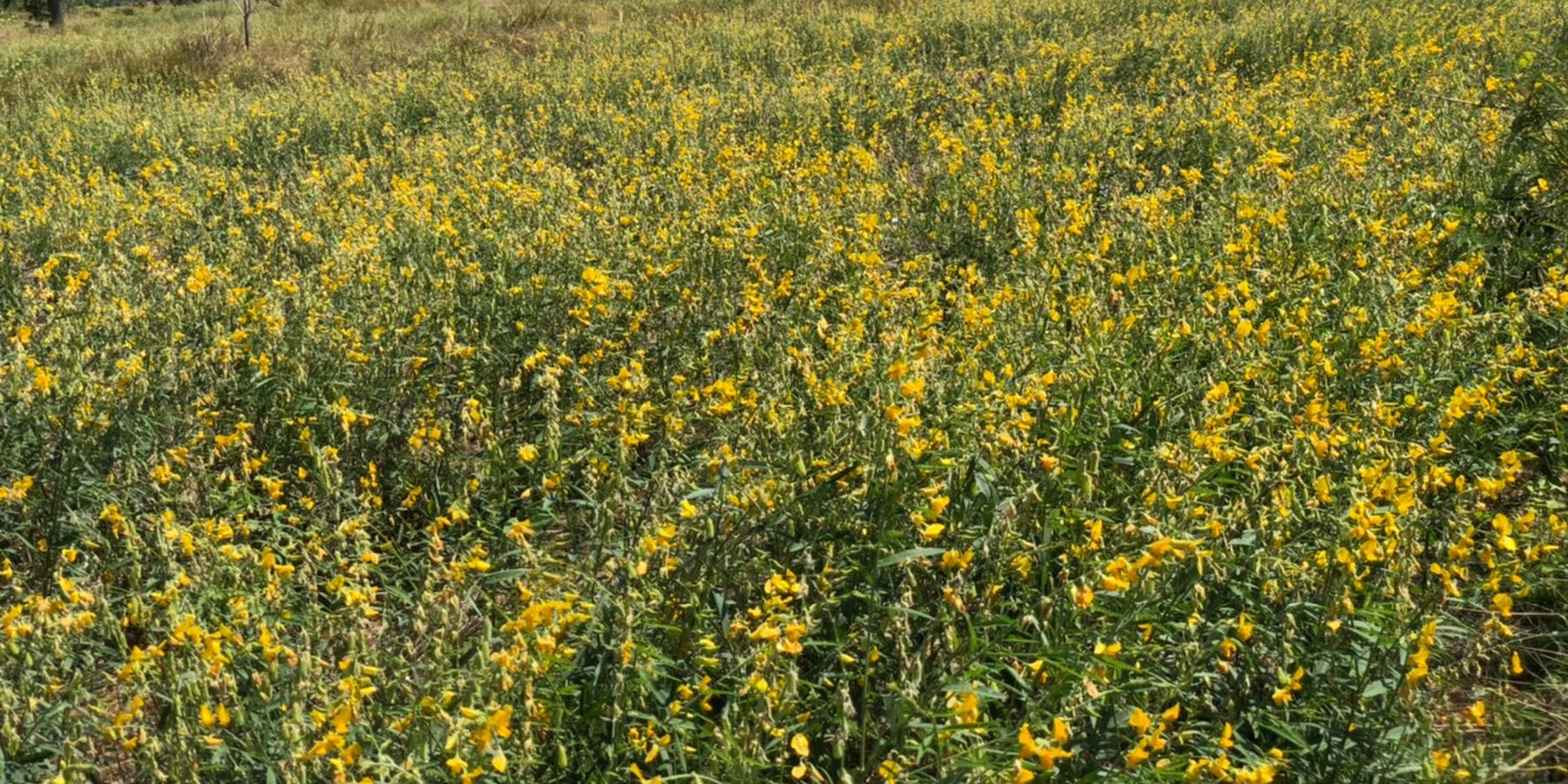
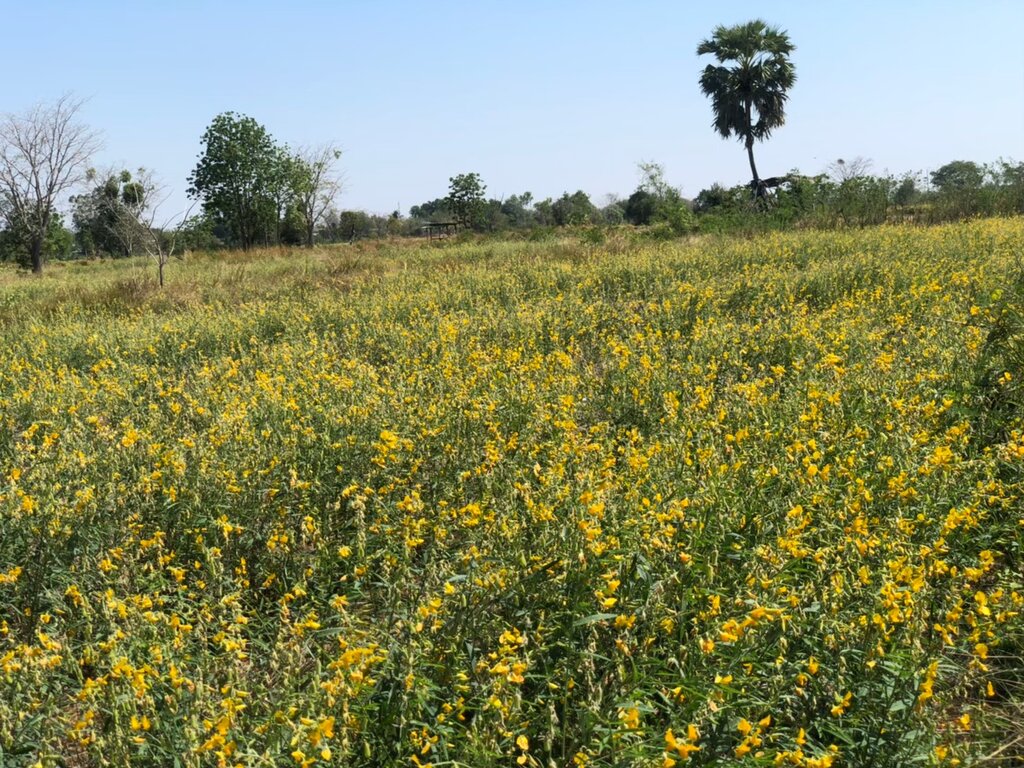
Sunn hemp (Crotalaria juncea) has been promoted by the Land Development Department as a green manure plant with the objectives of increasing soil organic matter, improving soil fertility and reducing salinity levels.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The Northeast of Thailand has the largest area dedicated to rice production in the country. However, the average yield per hectare remains low. Here, rice production heavily depends on rainfall, but distribution is inconsistent. Additionally, soil fertility is low, with a rapid decline in soil organic matter (SOM). Another significant threat to productivity in this area is salinity, with 17% of the rice production area affected.
The Land Development Department (LDD) of the Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives has promoted the use of soil amendments, such as green manure plants - including sunn hemp (Crotalaria juncea) - to enhance organic matter and restore soil fertility under saline conditions. Green manures are ploughed under, and incorporated into the soil to achieve their effect.
In the Non Thai district of Nakhon Ratchasima province, farmers face water shortages during the dry season, as the area lies outside the irrigation zone. Farmers, along with officers from the Land Development Department, have worked to increase SOM in degraded soils through knowledge transfer. Volunteer soil doctors and local farmers have adopted technologies that combine SOM improvement with soil and water conservation measures.
One notable example is Mr. Mana Siangsuthia: since 1997, he has collaborated with LDD officers, receiving beneficial microorganisms (PD microorganisms), green manure plants, vetiver grass, and water resources for his paddy fields. He has implemented LDD guidelines to develop his 1.12 hectare rice plot. Previously, this land was unproductive due to soil degradation caused by long-term monoculture of industrial crops and excessive use of synthetic fertilizers.
Fermented bio-extracts from banana shoots and chemical fertilizers were applied according to recommended guidelines. In 2004, rice yields averaged 1,125–1,550 kg/ha. Continuous implementation of these practices raised yields to 2,500 kg/ha by 2011. Over 16 years, using sunn hemp as a soil amendment significantly improved soil aggregate stability and reduced salinity. This success led to a shift towards natural agriculture practices in 2013, where chemical fertilizers were no longer used.
Farmers in the area now employ weather observation techniques and efficient water management strategies during dry spells. Green manure plants are sown every two years, complemented by the cultivation of salt-tolerant rice varieties, which also exhibit drought and pest resistance. These practices have resulted in rice yields of 3,125–3,750 kg/ha.
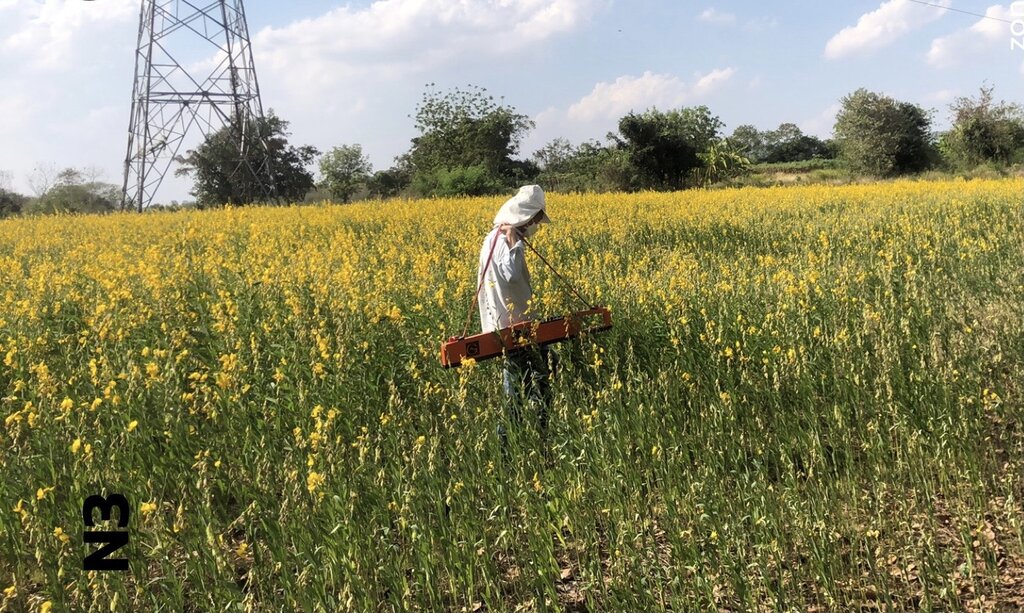
After rice harvesting, rice straw and stubble are ploughed in together with banana shoot PD 2 bio-extract. After approximately 2 weeks of decomposition, sunn hemp is sown at the rate of 31.25 kg/ha. When sunn hemp reaches 120 days, its seeds are collected. Then sunn hemp stems of around 1.2 meters height are ploughed in order to obtain more biomass.
Water conservation remains a focus in the cultivation area. During the rainy season, excess rainwater is stored for use during dry periods. Additionally, farmers employ techniques to wash salt from the soil surface into drainage channels. Water quality is enhanced using fermented bio-extracts, ensuring adequate water for dry-season cultivation.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
Nakhonratchasima
有关地点的进一步说明:
Moo 5, Ban Kok Phrom, Non Thai sub-district, Non Thai district
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
11200.0
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
1999
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology arises from land users’ innovation and is supported by external interventions and government agencies that acknowledge the value of technology to the community by providing resources, funding and supporting research and development.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
- sunhemp - rice
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Rice and sunn hemp
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
- sunhemp-rice
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
Rainfed lowland rice can be supported by small ponds for irrigation.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
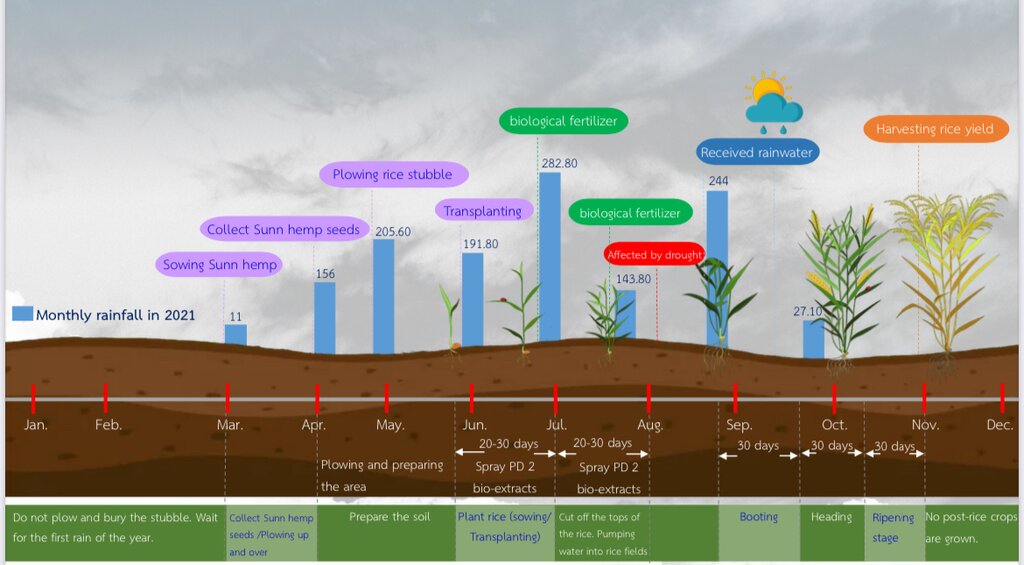
Above shows irrigation ponds associated with rice production. Below is the annual planting calendar where sunn hemp is used.
作者:
Wanaporn polsang
日期:
02/08/2020
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Methods of planting Crotalaria juncea (sunn hemp) to be used as a green manure plant in areas with saline soil are as follows:
1. The period of planting is during February to April whereby planting is conducted in between after harvesting rice yields so that Crotalaria juncea ( Sunn hemp) can thrive and give out high biomass.
2. Plough and ferment rice stubble together with using PD 2 bio-extracts to create bacterial process in the soil accelerating decomposition taking about 2 weeks. Then, sunn hemp is sown at the rate of 31.25 kg/ha in the soil with appropriate moisture throughout the plot in order to bring about regular germination.
3. Plowing up and over to cover sunn hemp stubble at the age of 120 days after collecting seeds of sunn hemp whereby the stem of sunn hemp is at the average of more than 1.2 meters resulting in obtaining more biomass. After that, during the period of preparing the area for planting rice, rice can be sowed in May or when there is enough amount of water.
4. When the seeds are kept to be used in the following season, the seed coat of sunn hemp is used as material incorporated with soil to make compost for soil amendment in growing vegetables.
作者:
Wanaporn polsang
日期:
02/08/2020
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1.12 ha
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
1 ha=6.25 rai
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
34.0
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting is conducted in between after harvesting rice yields so that Crotalaria juncea ( Sunn hemp) can thrive and give out high biomass. | February-April |
| 2. | Plough and ferment rice stubble together with using PD 2 bio-extracts to create bacterial process in the soil accelerating decomposition taking about 2 weeks. Then, sunn hemp is sowed at the rate of 31.25 kg/ha in the soil with appropriate moisture throughout the plot in order to bring about regular germination. | February-April |
| 3. | Ploughing up and over to cover sunn hemp stubble at the age of 120 days after collecting seeds of sunn hemp whereby the stem of sunn hemp is at the average of more than 1.2 meters resulting in obtaining more biomass. After that, during the period of preparing the area for planting rice, rice can be sowed in May or when there is enough amount of water. | May-August |
| 4. | When the seeds are kept to be used in the following season, the seed coat of sunn hemp is used as material incorporated with soil to make compost for soil amendment in growing vegetables. | May-August |
注释:
Ban Kok Phrom Village, Non Thai sub-district, Non Thai district, Nakhon Ratchasima province
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Plow to prepare plots | Time | 1.0 | 14.71 | 14.71 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Sow rice | Time | 1.0 | 17.65 | 17.65 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Pump water | Time | 2.0 | 58.82 | 117.64 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Harvest yield | Time | 1.0 | 183.82 | 183.82 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Rice seeds | Kilogram | 8.0 | 0.53 | 4.24 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Weight | Liter | 40.0 | 0.29 | 11.6 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Green Manure | Kilogram | 5.0 | 0.68 | 3.4 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Oil costs for farm truck | Time | 1.0 | 58.82 | 58.82 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 411.88 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 12.11 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The Land Development Department does not provide financial support but instead supports agricultural production inputs, such as green manure seeds and raw materials for compost production.
注释:
Calculation of costs and expenses
Expenses are calculated per areas using technology (Unit of size and area: 1.12 ha)
The currency used to calculate expenses with the unit as Baht
Exchange rate (to US. dollars) 1 US. Dollars = 34.0 Baht
Average wage in hiring labor per day is 8.82 USD
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
1. Labour costs
2. Fuel costs
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
表面上
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
是
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
Being areas with saline soils with salt stain on the soil surface, yields per hectare
SLM之后的数量:
Soil properties become better, the quantity of products increases
作物质量
SLM之前的数量:
Yields per hectare are low.
SLM之后的数量:
The plants receive nutrients and the soil quality improves resulting in better product quality.
土地管理
SLM之前的数量:
Factors and soil amendment materials are used continuously every year.
SLM之后的数量:
Good soil properties make soil management for cultivation become easier.
注释/具体说明:
Using a questionnaire
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
SLM之前的数量:
Rainwater is used for conducting agricultural farming.
SLM之后的数量:
Water resources in the paddy field
灌溉用水的质量
SLM之前的数量:
Affected by salt water
SLM之后的数量:
Water qualities are improved by using fermented bio-extracts.
注释/具体说明:
Salt meter
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
A large quantity of factors and soil amendment materials were used
SLM之后的数量:
Materials easily found in the area such as fermented extracts, green manure are used.
注释/具体说明:
Using a quetionnaire
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
Low productivity
SLM之后的数量:
Received higher quantity of rice products
注释/具体说明:
Using a quetionnaire
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
Yields not enough for consumption in the household
SLM之后的数量:
Having the quantity of rice products for household consumption enough throughout the year accounting for 700 kg./year
注释/具体说明:
Using a quetionnaire
健康状况
SLM之前的数量:
--
SLM之后的数量:
Conducting natural farming by avoiding fertilizer and chemical application
注释/具体说明:
Using a questionnaire
社区机构
SLM之前的数量:
Study how to solve proStudy how to solve problems by themselvesblems by themselves
SLM之后的数量:
Building interaction of farmers groups in the area based on consulting and mutual problem solving
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
There is no knowledge propagation.
SLM之后的数量:
Farmers in the adjacent plot accept the technology and implement methods of soil management in their own areas.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
SLM之前的数量:
The soil is arid with flaky salt on the soil surface.
SLM之后的数量:
There has been accumulation of organic matter and mulch keeps moistures and reduces water evaporation in the soil.
注释/具体说明:
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
养分循环/补给
SLM之前的数量:
--
SLM之后的数量:
Nutrients increase due to planting different crops such as sunn hemp and plowing up and over rice stubble.
注释/具体说明:
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
盐度
SLM之前的数量:
Moisture in the soil was low. The soil was characterized by having flaky salt appearing on the soil surface.
SLM之后的数量:
Salinity measured from the soil surface decreased. Organic matter and the number of microbes accumulating in the soil increased.
注释/具体说明:
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
土壤有机物/地下C
SLM之前的数量:
--
SLM之后的数量:
Organic matter from plowing up and over to cover rice stubble, green manure plants
注释/具体说明:
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
SLM之前的数量:
--
SLM之后的数量:
Plant varieties which can be planted and grow in the area more such as rice, sunn hemp
注释/具体说明:
Observation
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
SLM之前的数量:
Small-scale water resources
SLM之后的数量:
Expansion of digging ponds resulting in more areas of water storage
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 热浪 | 适度 |
| 干旱 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
The land users are responsible for covering the costs themselves. The Land Development Department provides support by supplying green manure seeds to demonstrate and test whether growing green manure crops can effectively improve saline soil.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Farmers manage soil and water use integrated farming methods, leading to additional income opportunities |
| Farmers in the area are committed to overcoming challenges and limitation related to soil, water, and environmental conditions |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Support for forming farmer groups in the area to exchange knowledge on soil management for increasing crop yields and addressing local farming issues, as well as developin professions for community farmers. This includes promotiong the production of safe |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Quality problems of Sunn hemp seeds result in low germination rates. | Land Development Department officials inspect the quality of seeds before they are distributed to farmers. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
8
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
5
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Sustainable soil management practices in Asia
URL:
https://e-library.ldd.go.th/library/Ebook/bib10906.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

EXTENSION OF SUNN HEMP AS A SOIL AMENDMENT … [泰国]
An outreach programme aims to educate farmers about the benefits of ploughing rice stubble into the soil and incorporating green manure crops such as sunn hemp - as well as other sustainable practices. Groups of farmers are formed, and they are assisted by various organisations including the Land Development Department …
- 编制者: Laksamee Mettpranee
模块
无模块