Smallstock Manure Production [多哥]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Julie Zähringer
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano
Houré bow
technologies_955 - 多哥
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
20/08/2007
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Smallstock manure production technology is an easy and efficient method to produce organic fertilizer for the conservation and improvement of soil fertility.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
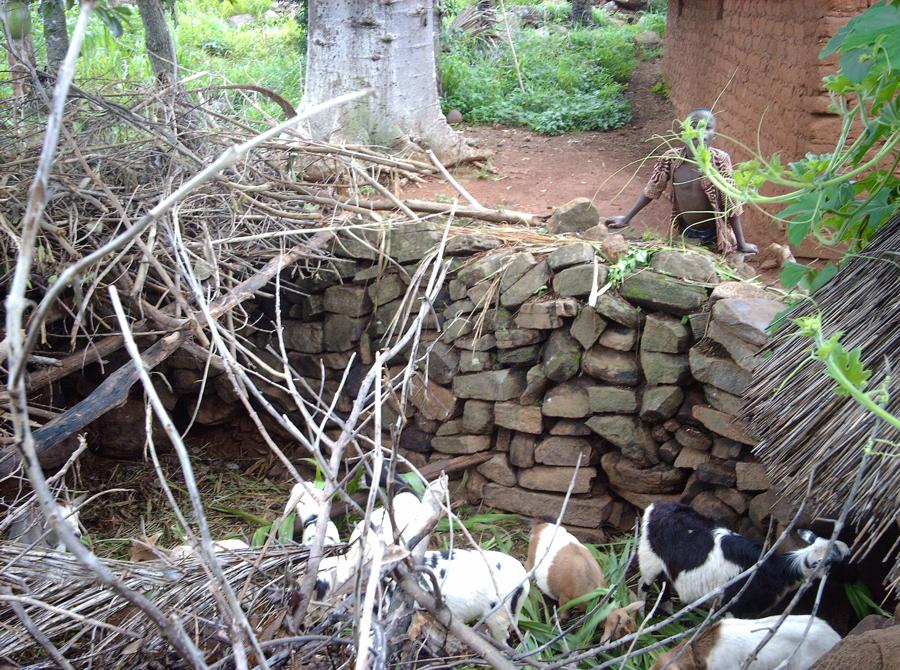
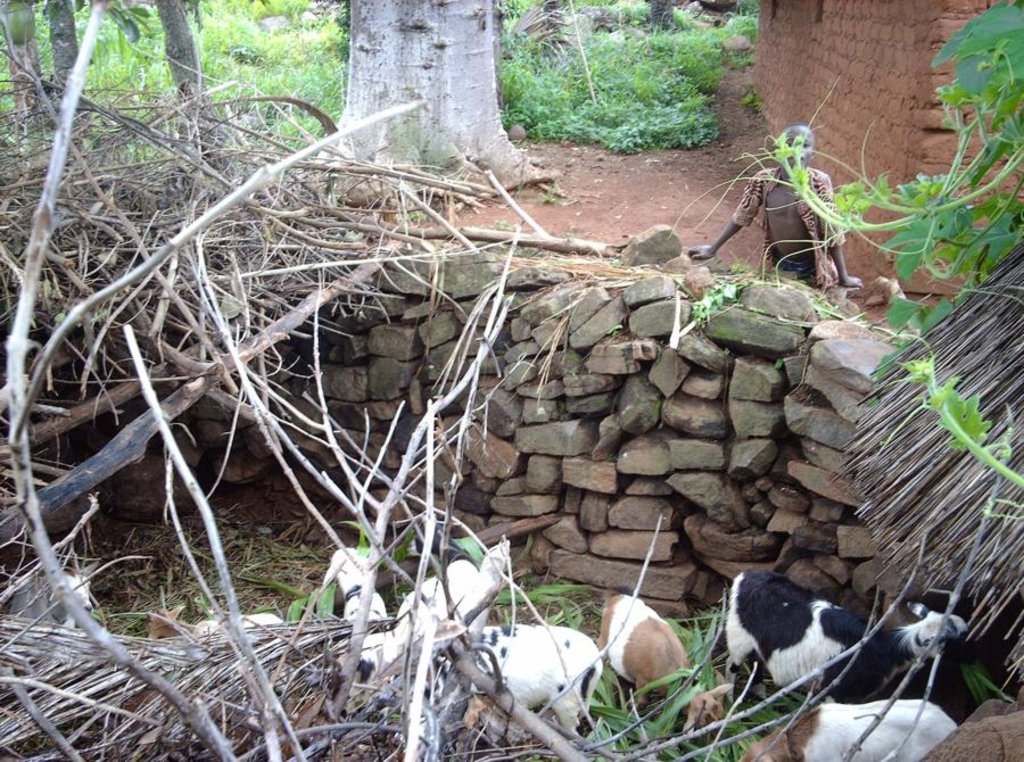
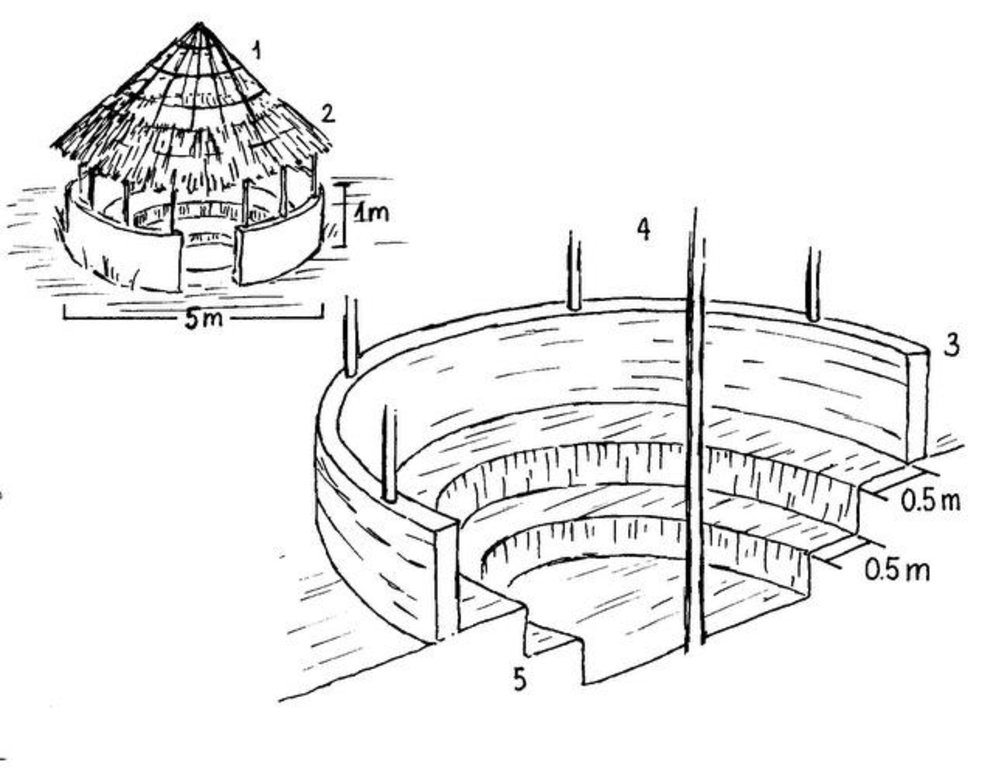
The main item within this practice is the so-called fosse fumière - a 1-2 m deep and 3-4 m diameter circular pit, enclosed by a stone wall. The pit has a double function: it is the place where manure is produced and it serves as shed for small ruminants (goats, sheep), particularly to avoid uncontrolled grazing /browsing during the cropping season (from April until November). Animals are fed in the fosse, and they drop their faeces, which together with chopped organic material accruing from the kitchen and field activities, piles up in the pit for decomposition. The fosse is partly roofed to provide optimal micro-climatic conditions: partial shading, partial exposure to sunlight and appropriate moistening through rainfall. Inside the pit, one or more circular terraces (0.5 m high, 0.5 m wide) serve as resting area for the animals. The terrace riser need to be plastered or reinforced with stones, particularly in case of loose soil, to avoid damage caused by animal trampling. After decomposition the manure is removed from the pit and distributed on the fields beginning of each cropping season (March). Then straw bedding is renewed and the process starts from scratch. During the dry season from December to March smallstock is left to graze freely on the fields and pastures.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
多哥
区域/州/省:
Kara
有关地点的进一步说明:
Lassa
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was early traditional and passed from father to son. It was improved in 1987.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil fertility decline
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180
Longest growing period from month to month: May-October
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.15 m2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Dimensions and main components of a manure production pit: (1) open part of the roof; (2) covered part of the roof; (3) stone wall; (4) poles (holding the roof); (5) terraces (where animals can rest)
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: compost (mixture of animal faeces and vegetative scraps
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Continuous depositing and piling up of vegetative material (dung, kitchen waste, crop residues) | 农业学的 | |
| 2. | Let decompose the organic material inside the pit. Twice a year (between April and November) the material is actively mixed for aeration | 农业学的 | Twice a year (between April and November |
| 3. | Distribute the manure on the fields (during rainy season) | 农业学的 | during rainy season |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Machinery/ tools: shovel, cutlass, rope, mattock,
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Main cost-relevant factor is labour. Material such as stones and straw are available on the farm (no monetary costs)
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
- 生计(自给)
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产区域
收入和成本
农业收入
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
注释:
Technology not much affected by climatic extremes or changes.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
60 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: depending mainly on the availability of livestock
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Production of green manure How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance of the pit |
|
Increase of crop yield through fertilization How can they be sustained / enhanced? renewal of litter |
| Rehabilitation of degraded soils |
|
Limited animal roaming and destroying of crops How can they be sustained / enhanced? corrall livestock in the pit |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Manual construction is very labour-intensive | mechanized excavation |
| Air pollution through smelly animal dung | add products which attenuate the smell; establish the manure pit outside the residential area |
| Accident risk for children | establish the manure pit outside the residential area |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块