Minimum tillage in UK arable cropping systems: Tivington [英国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Ceris A. Jones
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
non-inversion tillage (eng); conservation tillage (eng)
technologies_984 - 英国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Oborn Jo
jeoborn@somerset.gov.uk
Farming wildlife advisory group
E,T&E Dept., County Hall, Taunton TA1 4DY, UK
英国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Farmin & wildlife advisory group (FWAG) - 英国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
21/02/2005
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷
Individual experimental farmer: Tivington [英国]
Individual farmer experimenting with machinery to maintain economic viability and reduce time spent on land preparation.
- 编制者: Ceris A. Jones
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Non-inversion tillage to create a seedbed
2.2 技术的详细说明
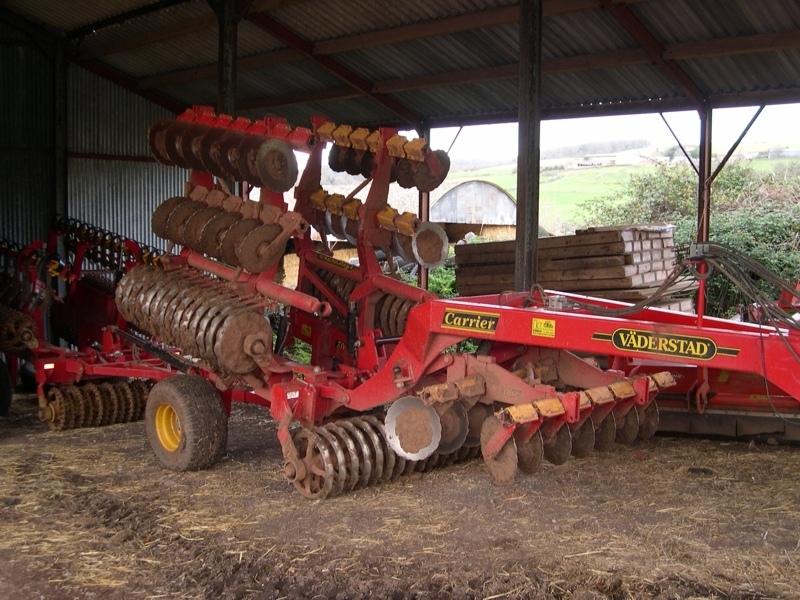
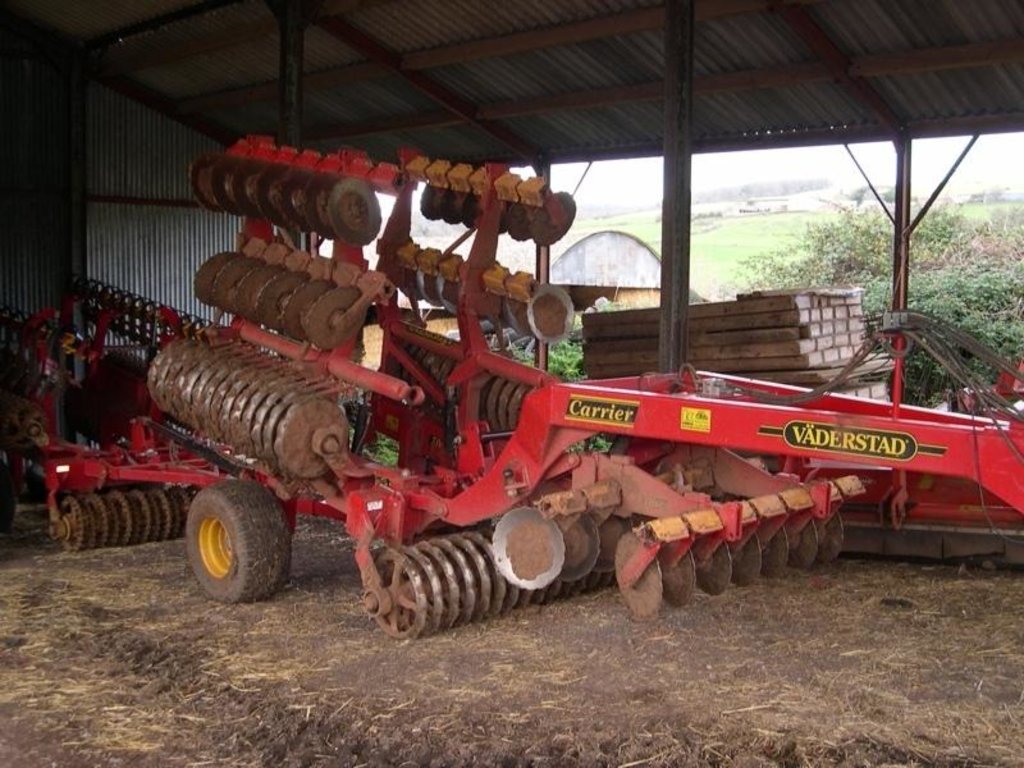
说明:
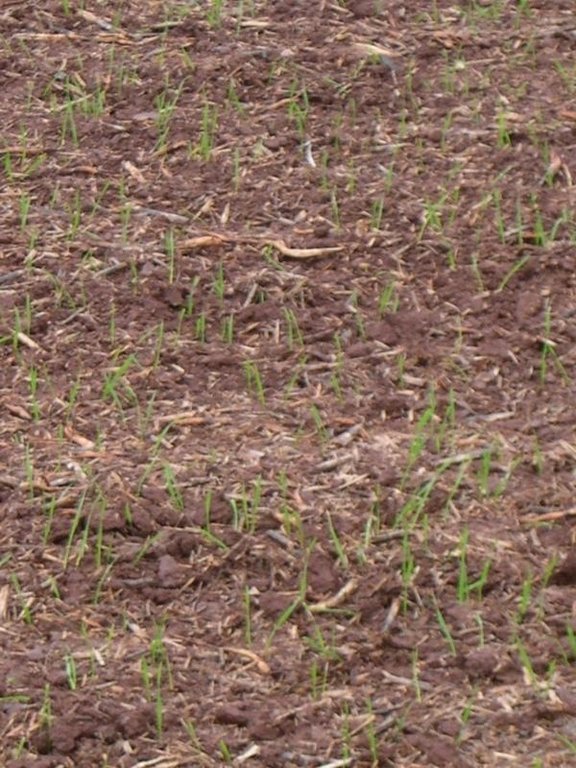
Non-inversion tillage to provide suitable seedbed for following crop.
Purpose of the Technology: Even and cost-effective crop establishment, saving time and benefiting the environment. Maintenance: annually, per crop,
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: innovative farmer reducing impacts of farming on the environemnt, expanding his businesss and saving time
2.3 技术照片
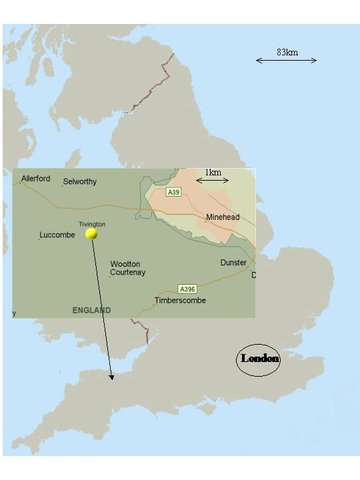
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
英国
区域/州/省:
Somerset
有关地点的进一步说明:
Minehead
Map
×3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crops: Wheat, oilseed rape
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion and compaction caused by inappropriate land use and intensive grazing respectively
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion and capping of the soil
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: winter wheat - winter oilseed rape - winter wheat - beans - winter wheat
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 300 Longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Jul
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.78 m2.
Farm is a total of 126ha of which 28ha are grazed, 9ha are under environmental stewardship and 7ha are set aside
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (economic viability), poverty / wealth (lack of captial), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in soil fertility
Early planting
Material/ species: crop
Quantity/ density: depends on
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: crop residue
Quantity/ density: 2-5 t/ha
Remarks: residue chopped + spread over width of combine
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Remarks: broadcast
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: biosolids (from Aug05)
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: when required
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
£
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
0.56
4.4 技术建立活动
注释:
Additional info: - Year2: surface cultivation: mid September / per crop - Year2: drill: mid September / per crop - Year2: roll: mid September / per crop - Year3: shallow sub-soil: November / per crop - Year3: drill: November / per crop
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Year1: shallow sub-soil | 农业学的 | 3rd-4th week in August / annual |
| 2. | Year1: spray with non-selective herbicide (glyphosate) | 农业学的 | late August/ early September / annual |
| 3. | Year1: drill | 农业学的 | late August/ early September, 3-4 days after spraying / annual |
| 4. | Year1: roll (optional) | 农业学的 | after drilling / annual |
| 5. | Year2: surface cultivation (more in Annex 3) | 农业学的 | mid August / per crop |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Equipment (year1)-machine hour | |||||
| 设备 | Equipment (year2)-machine hour | |||||
| 设备 | Equipment (year3)-machine hour |
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Vaderstad Carrier, Vaderstad drill and roller
Only crop establishment costs are included as all other costs - seed, fertilisers, pesticides - are equivalent with those for conventionally mouldboard ploughing. The costs highlghted include labour. Equivalent crop establishment costs by ploughing are 225 (year1), 231 (year2), 190 (year3)
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
slope (steeper slopes require more horsepower), state of the soil, climate, crop
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
800.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 20% of the land.
10% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
85% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Contracting work forms greater part of income
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
126 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
- Other
土地使用权:
- 租赁
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
In early years
其它社会经济效应
Timeliness of operations
注释/具体说明:
Operation twice as quick as ploughing
Economic viability
Input constraints
注释/具体说明:
Possible increasing herbicide costs
Hindered farm opperations
注释/具体说明:
timing of operations critical
High machinery costs
注释/具体说明:
High capital investment but low running costs
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
Preparation for new legislation
注释/具体说明:
CAP reform, Soil Action Plan for England, EU Water Framework directive
Acceptance by society
注释/具体说明:
Age difference: Technology tends to be taken up by younger farmers
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
0.01
SLM之后的数量:
1
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
Possibility
土壤压实
生物多样性:植被、动物
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
More earthworms compared to land that has been ploughed
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Driven by economics
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increased work rate making operations quicker |
| Better trafficability |
| Less at risk of weather |
| Earlier drilling. It is a systems approach - minimum tillage combined with early drilling and low seed rates |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increased work rate How can they be sustained / enhanced? Better planning |
| Improved soil organic matter |
| (Possible) soil structure improvements |
| Improved soil ecology and other wildlife benefits |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Dependent on dry weather | Co-operation with other farmers or larger acreage |
| Machinery more complex and expensive | A combination of crop rotation, pesticides and stale seedbeds |
| Increasing grass weed populations | Does not necessarily mean spending money eg utilising old equipment on farm like subsoilers. However, need the right attitude |
| Need to be experimental | Accept advice for varying sources, talk to different people |
| Advice can be fragmented/ confusing |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Technological knowledge of farmer | Training and education, dissemination |
| Initial high capital investment | Extended finance |
| Possible increasing weed populations | More diverse management options - cultural and chemical |
| Need to expand acreage to cover capital costs | More diverse crop rotation but perhaps this is insufficient to retain economic viability |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
SOWAP project
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
www.sowap.org
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
L and D farming
URL:
www.landdfarming.co.uk
标题/说明:
Vaderstad machinery
URL:
www.vaderstad.com
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Individual experimental farmer: Tivington [英国]
Individual farmer experimenting with machinery to maintain economic viability and reduce time spent on land preparation.
- 编制者: Ceris A. Jones
模块
无模块