Hararghie Soil Bund [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Daga Biyye (Oromigna)
technologies_1045 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Nigusie Tshome
Natural Resources Development and Environmental Protection Authority
埃塞俄比亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Natural Resources Development (MNRD) - 埃塞俄比亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
an embankment of soil constructed along the contour to reduce runoff and maintain soil moisture.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Soil bund is an earth embankment constructed along the contour inorder to avoid runoff down slope and shorten the slope length. Ditch/basin is dig at the upper side of the bund.
Purpose of the Technology: To obtain the maximum sustainable level of production from a given area of land by reducing soil loss below a thrushold level and maintaining soil moisture.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: During establishment and maintenance the materials needed are graduated poles, pegs, plastic string and water level and other materials related to the work.
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
West Hareghe/Oromia
有关地点的进一步说明:
Habro
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1.68 km2.
the SWC technology area is defined by sub-watershed. It is implemented by programmee
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
through the extension programme
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 高粱
- haricot bean, teff, chickpea
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 咖啡,露天种植
- Catha edulis
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Jul
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
maize and haricot beans

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
- free grazing, stall feeding
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): low productivity, gully formation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): erosion, low soil fertility, high runoff, low production
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: in the case of intercropping maize is sown in rows and between the rows harcot bean is sown
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, poverty / wealth (lack of captial), land subdivision
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
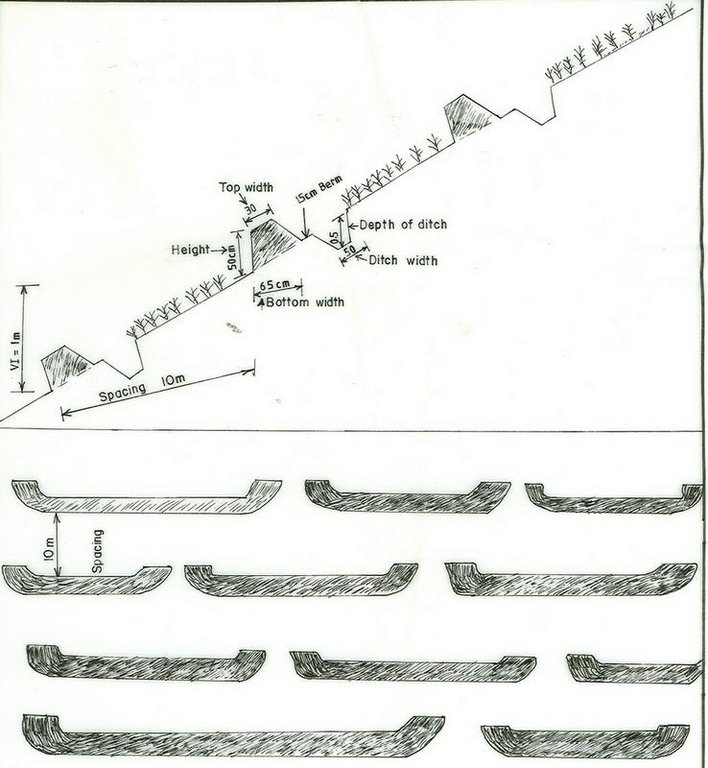
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Oromia
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Relay cropping
Material/ species: maize, teff and chick pea
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: haricot bean and maize
Bund/ bank: level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1m
Spacing between structures (m): 10m
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5m
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5m
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5m
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Birr
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
8.5
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.94
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | surveying and layout | dry season |
| 2. | excavation work | onset of rain |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 89.0 | 89.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 67.0 | 67.0 | |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 23.5 | 23.5 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 18.8 | 18.8 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | Ha | 1.0 | 35.3 | 35.3 | |
| 其它 | cultivation cost | ha | 1.0 | 36.5 | 36.5 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 270.1 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 31.78 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ploughing along the contour | dry season / 4 times |
| 2. | Sowing | onset of rain / each cropping season |
| 3. | Digging the ditch/basin | dry season/two times |
| 4. | maintain the height of the bund | dry season/two times |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 11.75 | 11.75 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 56.0 | 56.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | cultivation cost | ha | 1.0 | 109.4 | 109.4 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 179.45 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 21.11 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: 5 shovel, 5 hoe
the cost is culculated based on the spesification of structures (length, width and height), tools required. For the cost given above we assumed 1 km of soil bund per hectar of cultivated land
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
excavation work requires more labour and it affects the cost of construction and maintenance
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium-low
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low-medium
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 5% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
9% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: no other forms of income generating means
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产区域
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
工作量
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
20
SLM之后的数量:
10
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
42
SLM之后的数量:
20
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
Waterlogging
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
625 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: the majority of the farming communities are poor and they are not able to pay for SWC activities and incentive is required in some cases
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
reduce soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? frequent maintenance of the structure |
|
maintain soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? upgrading of ditches and embankment |
|
increase production How can they be sustained / enhanced? increasing the productivity of land per unit area |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? frequent maintenance of the structure |
|
moisture maintenance How can they be sustained / enhanced? frequent maintenance of the ditches |
| reduction of slope length |
| increasing of infltration rate |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块