Technology of fastening Aral sea's drained bottom' s soil [哈萨克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Vladimir Kaverin
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
no
technologies_1089 - 哈萨克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Salimov Abdul
RGP, SPC of forest facility
哈萨克斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
SPC of Forest Facility (SPC of Forest Facility) - 哈萨克斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

The approach of groove fastening sandy loam and … [哈萨克斯坦]
The approach of groove fastening sandy-loam and sandy soils of the Aral sea's drained bottom
- 编制者: Vladimir Kaverin
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Technology of fastening Aral Sea's drained bottom's soil
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
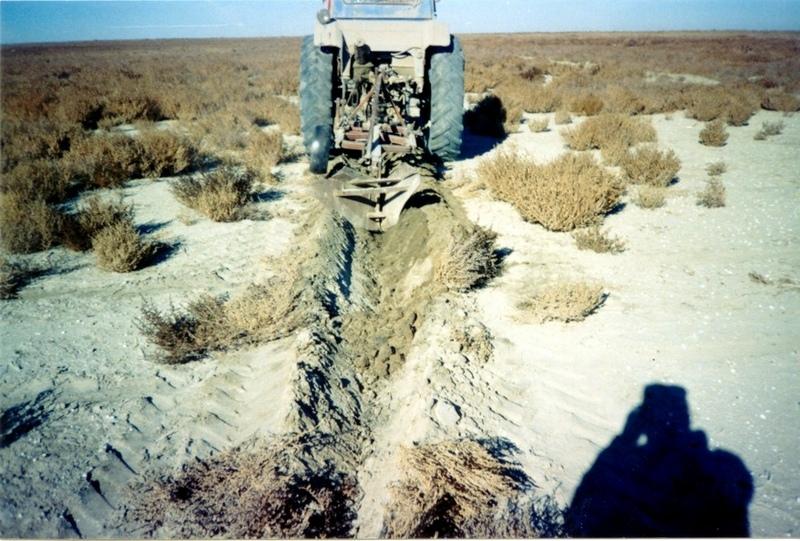
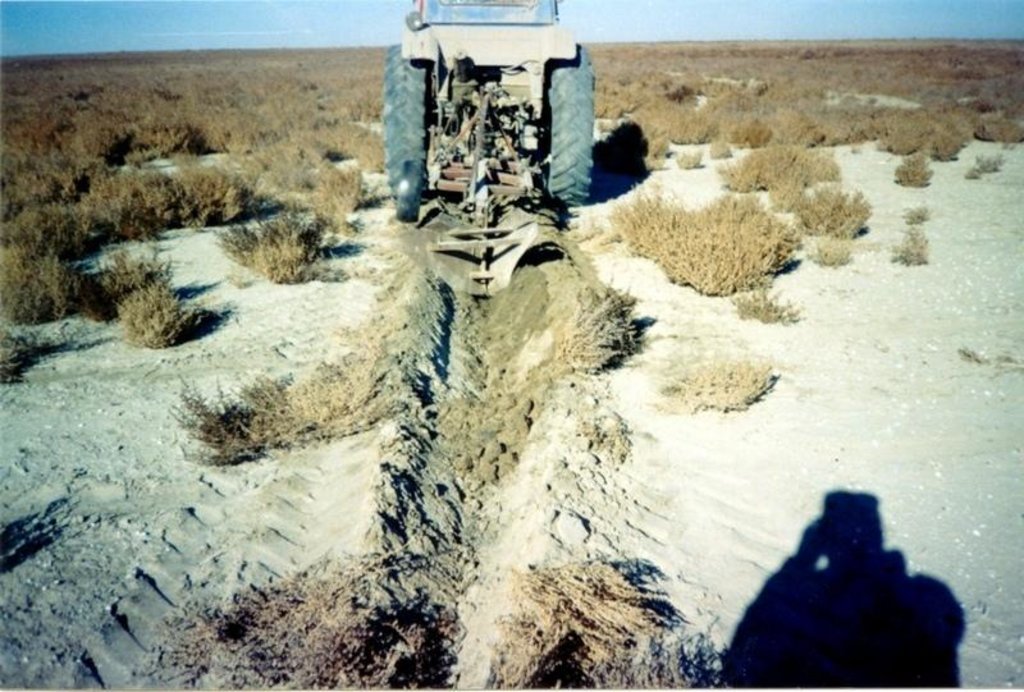
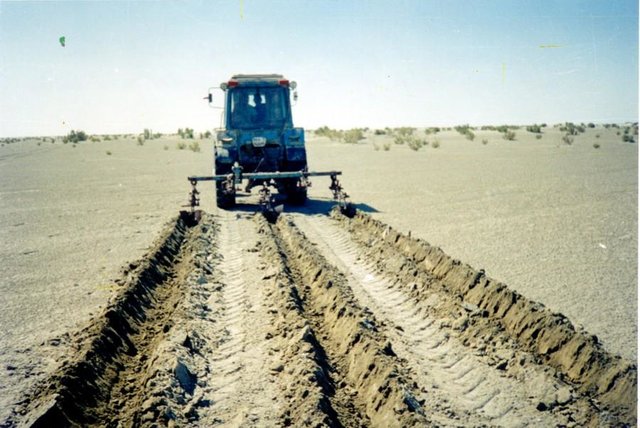
Planting of the saplings on the lots of the dried seabed of the Aral Sea was done in holes and uninterrupted furrows, which were formed by hands or cultivated KON – 2.8 PM . Depth of holes and furrows is 20-25 cm. Distance between holes was 1.5-2 m. Furrows were perpendicular to the prevailing winds (west-east) and placing mould in several options: 1 – moulds on both sides; 2 – the same from the southern side of a furrow; 3 – the same from the northern side. Furrows alternated with holes rows. Length of rows variants in repetition was 100 m. Saplings were filled up by hands or in rows in 1-2 meters, distance between rows was 2-2.5 meters. For the last 30 years Aral Sea level is falling and in 2001 it fell by 20 meters. More over 35 thousands sq. km of sea bottom came to the surface. Pace of falling during the last ten years is 0.9-0.8 meters per year according to the instrumental observations, that’s why area of dry land increases by 3-4 thousand sq. km annually.
Formation of moving sand dunes with the height of 2-5 meters, which move at the speed 20-30 meters per year in the southern and south-eastern direction, occurs on the area of more over 10 thousand sq. km. Width of dune ridges and ranges achieves 10-15 km and length up to 40-60 km. Ecosystems of brackish waste grounds lacking flora, difficult to traverse and dangerous were formed non the area 20 thousand sq. km of the former sea bottom. They are the source of dust-salt material to the major oasis agriculture in the delta of Syrdaria River.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
哈萨克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Kyzylorda
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kazalinsk state
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
4.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 4 km2.
only 2% from 35000 sq.km of Aral sea's drained bottom
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
Was developed by kazakh - investigation institute of forest facility (1996-2001)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 林牧业

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 208; Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 游牧

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 皆伐
- tugay forests and combseller
- Saxaul (cf. Haloxylon ammodendron)
产品和服务:
- 薪材
- 放牧/啃牧
- 自然保持/保护
注释:
Trees/ shrubs species: saxsaul, combseller
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): exudative salinization, forming of the salty ring on the surface, lov percent of natural overgroving.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): rarely distribution of the bush-trees and presence of bared heathlands, which makes territory useful for land-use.
Grazingland comments: private sector of peasanting and farming predominate
Clear felling of (semi-)natural forests: stocking up for fuel, every year
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Degradation of saxaul and tugay forests in result of desertification processes: subsoil waters level reduction, deflation, poverty of population. Constant reorganization of forest facilities.
Forest products and services: fuelwood, grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection
Type of grazing system comments: private sector of peasanting and farming predominate
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 减少基于生态系统的灾害风险
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A4:地表下处理

结构措施
注释:
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, breaking compacted topsoil
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Excessive water-fence on an irrigation from the rivers Syrdarya and Amurdarya.)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (High wind activity in region (prevalence of winds with a speed up to 5 min/sec).)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
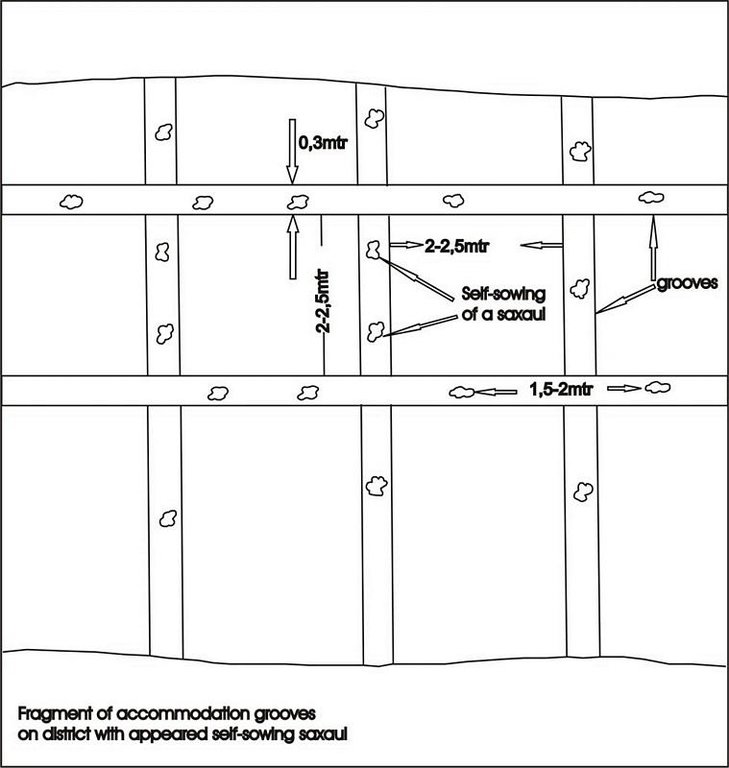
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
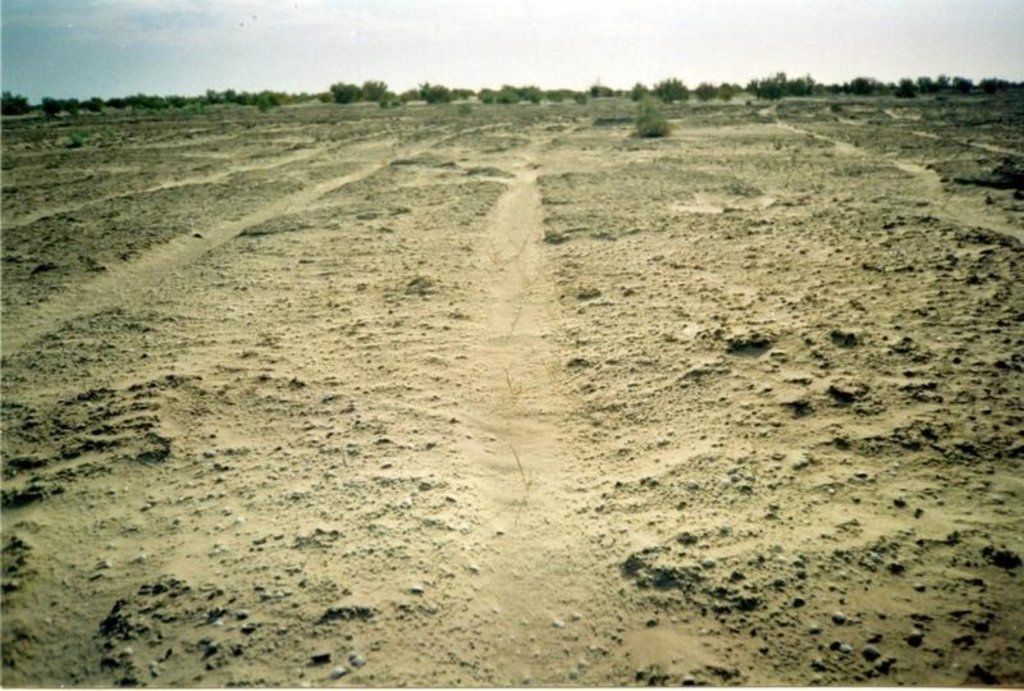
Fragment of accommodation grooves on district with appeared self-sowing saxaul
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, improvement of soil structure
Cover cropping
Material/ species: saxsaul
Quantity/ density: 150
Remarks: protective planting
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: breaking salturing up before planting by layout
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 150
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1,5-2,0
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 30-35
Trees/ shrubs species: saxsaul, combseller
Structural measure: sediment sand / trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3
Spacing between structures (m): 2
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,7
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,7
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0,5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0,7
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Construction material (earth): fine-grained sand
Construction material (wood): saxsaul
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
15.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | groove cutting | summer |
| 2. | slips planting | spring, autumn |
| 3. | groove cutting | summer |
| 4. | creating traps for sand | after planting |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Traps for sand, cutting and planting | persons/day | 3.0 | 15.0 | 45.0 | 66.0 |
| 设备 | Others | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 29.0 |
| 植物材料 | Others | ha | 1.0 | 125.0 | 125.0 | 83.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 190.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 190.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | groove cutting | spring, autumn / every year |
| 2. | slips planting | spring, autumn / every year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
saxsaul planting in the 100m * 100m. Sized beared heathlands due to enclosed SWC circuit
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
transportation of technique to the work place and gooves cutting
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Average long-termed rainfall quantity makes 124 mm per year
农业气候带
- 干旱
Arid deserted
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Weak inclined primary -sea plain
Landforms: It is complicated with accumulative forms of colian relief
Altitudinal zone: 36 - 51 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Soils were not formed yet, horizons are absent
Topsoil organic matter: 0,19%-0,24%
Soil fertility is low with 0,24% of humus
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor in suclay, medium for clay and good loam-sandy and sandy soils
Soil water storage capacity is low - very low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: catche fish grow vegetable - melon cultures and realizate them
Market orientation of production system: Firewood stocking and raise of forage capasity.
Level of mechanization: Using shovel for manual labour and tractor MTZ-30 for mechanised labour.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Also 2-5 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
In adverse years
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
In adverse years
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Exspenses for fuel decrease
其它社会经济效应
employment at farm
注释/具体说明:
Production increase
groove cuting tools
注释/具体说明:
High rent payment for technique
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Population's employment
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Ecological education
educational and cultural level of former members
注释/具体说明:
Native population's not understanding benefits of using SWC
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
Humus accumulation
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Salt removal of top horizons
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
30
SLM之后的数量:
10
注释/具体说明:
Increase of kinds structure
其它生态影响
biodiversity
注释/具体说明:
Activity of wind stream decrease
soil fertility
注释/具体说明:
Avoidance of blowing
fuel supply
注释/具体说明:
4-5 hectare per year
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
Soil surface's erosion stop's
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
13 households covering 1 percent of stated area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
10 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
3 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: small farmer's economical vell-being improves
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
forest territory are restoring How can they be sustained / enhanced? during saxaul communities life |
|
soil deflation's speed and temps decrease How can they be sustained / enhanced? during saxaul communities life |
|
microclimate conditions increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? during saxaul communities life |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
forests area and output of fuel increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? during saxauls plantings life (40-50) years |
|
field-dust carrying out is prevented How can they be sustained / enhanced? during communities vitual activity |
|
environmental and sanitary-epidemiological contitions improves How can they be sustained / enhanced? during technology SWC existence |
|
Additional work places are created How can they be sustained / enhanced? in period technology SWC application |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| absence of enough qvantity of enough quantity of technique | by means of cooperative association of facilities |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| high rent payment for technique | additional purchase of the mechanised means |
| Low interest of local social institutions | to pay big attention for ecological education |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
"to study process of overgroving and to develop offers on assistance to natural reneval of saxaul black on the grounds of Aral Sea's naked bottom"
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
RGP,SPC of forest facility. Kirov str.,58 city Schuchinsk, Akmola region
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

The approach of groove fastening sandy loam and … [哈萨克斯坦]
The approach of groove fastening sandy-loam and sandy soils of the Aral sea's drained bottom
- 编制者: Vladimir Kaverin
模块
无模块