Soil-protective minimal technology of the tillage and sowing [哈萨克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Ervin Gossen
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Soil-protective system of agriculture
technologies_1092 - 哈萨克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Budnikova Taisia
National Ecological Society
哈萨克斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Kaskarbaev Jaksenbay Aitanovich
SPC for Crain Husbandry
哈萨克斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ministry of Agriculture of Kazakhstan - 哈萨克斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

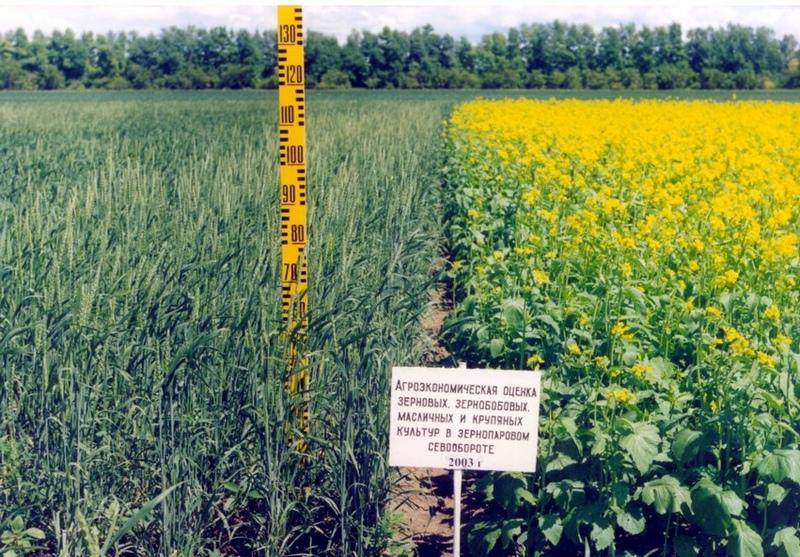
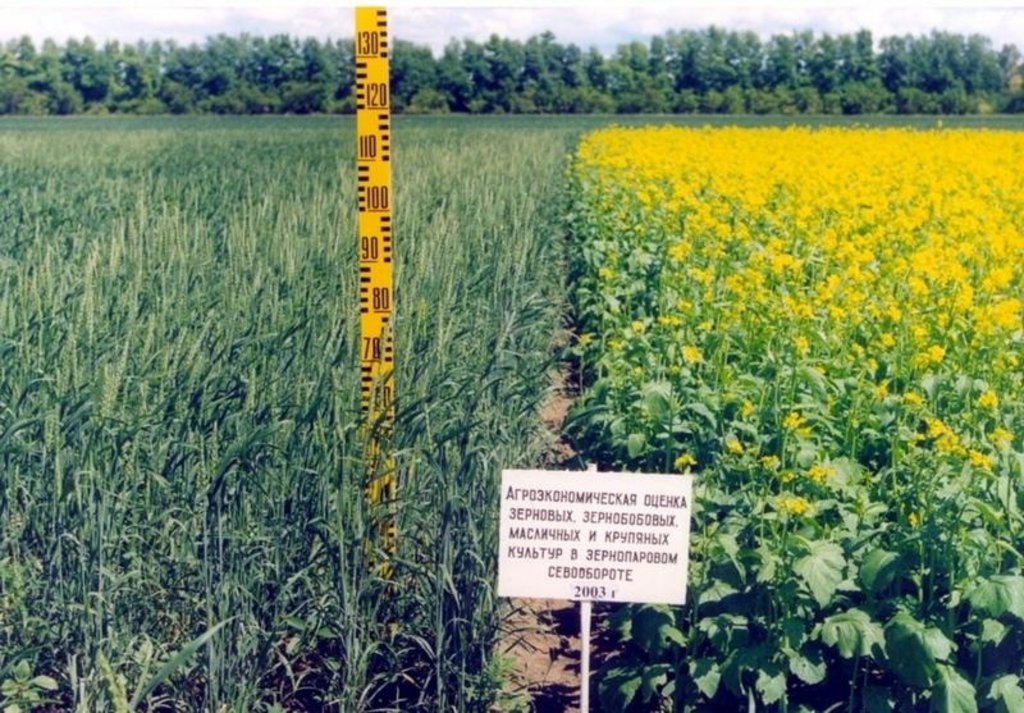
Crop on the stubble background [哈萨克斯坦]
Stubble crop for cultivation of grain crops (spring wheat).
- 编制者: Ervin Gossen
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The minimal tillage for cultivation of grain crops (the second and third culture after fallow).
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The technology is directed on struggle against wind and water erosion.
After harvesting of grain crops on a field it is left stubble background which carries out some functions:
1)Accumulation of moisture.
2)Prevention of water and wind erosion
3)Accumulation of organic in humus layer.
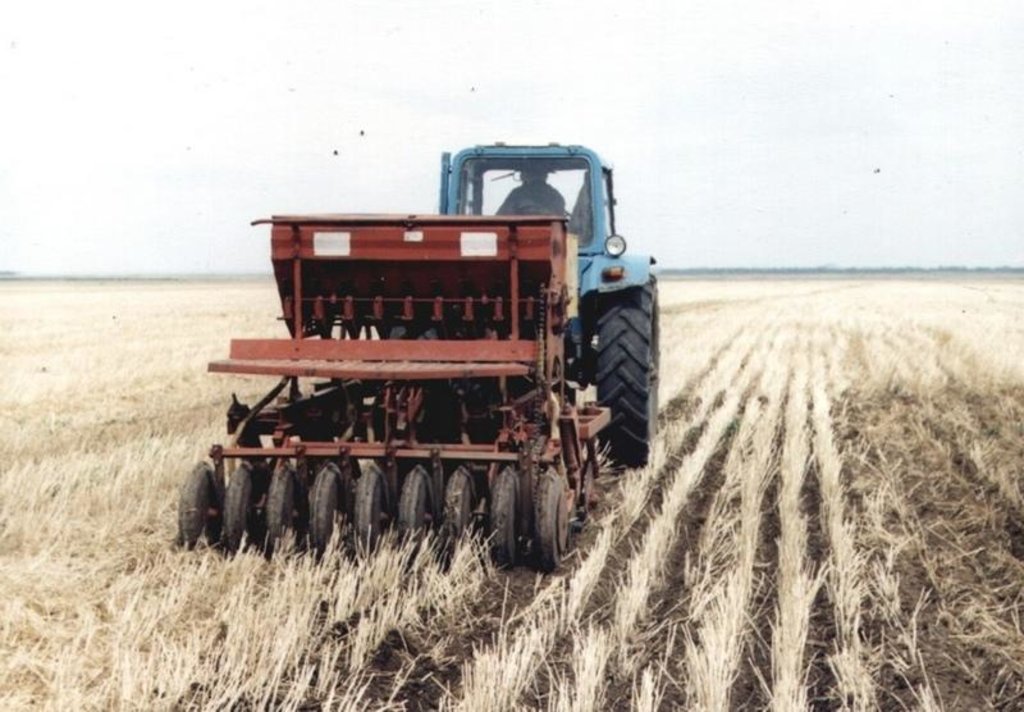
During the spring period on the stubble background there is a sowing of grain crops by the direct or combined seeder there (cultivation, sowing, application of fertilizers, compacting) with covering of seeds on depth of 3,8 centimeters.
After shoots at presence of weeds it is carried out a local tilling of the littered sites of a field.
In the autumn harvesting of the grain is carried out with crushing of strow and formation of the stubble layer.
Productivity of the grain makes 8,6-12,5 c/ha depending on humidity of year.
-fertilized fallow with minimum and chemical tillage;
-sowing of spring rapes on the fallow by seeding-machine “Flexy-Coil” +sowing of winter rye to spring rapes stubble in the second summer half – “direct sowing”
-winter rye of early ripening sorts (August)+ semifallow soil tillage+ fertilizers under sowing of steadfast spring wheat;
-steadfast spring wheat;
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
哈萨克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Northern Kazakhstan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kustanay, Northern Kazakhstan, Akmola
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
28.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 28 km2.
Before disintegration of the USSR the tillage and sowing on the stubble background in 1990 has made the area in 61,4 mill.ha on a steppe droughty zone (chernozem and dark chestnut zone of the USSR).
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
from Canada
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 黑麦
- 谷类 - 小麦(春季)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 166; Longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil-fertility is reduced on 10-25% (humus loss for 50 years).
Deterioration of technique Fertilizers are not brought in full.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Dissociation of farms with the average size of an arable land – 60 ha.
Struggle against wind and water erosion is directed on increase of soil fertility and receptions of steady cultures at full protection.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 轮作制度(轮作、休耕、轮垦)
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, mulching, temporary trashlines, legume inter-planting, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, rotations / fallows, zero tillage / no-till, minimum tillage
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cp:土壤污染
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wm: mass movements / landslides, Cp: soil pollution
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Development vergin and lay lands.)
Secondary causes of degradation: land tenure (land subdivision), poverty / wealth (lack of capital)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Also rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase in soil fertility
Mulching
Material/ species: straw 100%
Temporary trashlines
Material/ species: stubble 100%
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: herbicides
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: fallows-rape-wheat 100% 2,5 mln seeds for hectar
Zero tillage / no-till
Material/ species: Sowing on a stubble
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: on depth of 3,8 centm
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
10.00
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | persons/day/ha | 5.0 | 10.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 90.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 90.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fallows creating | autumn / in 3 years |
| 2. | Rape sowing + winter rye | early spring, august / in 3 years |
| 3. | Winter rye + semi-fallow + fertilizing | early spring, august / in 3 years |
| 4. | Wheat sowing | early spring / in 3 years |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | persons/day/ha | 5.0 | 10.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 90.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 90.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: SZS-2,1, K-700, Kamaz-with tractor carriages PTS-9,3 PTS-12, combine Enisey
Calculation of expenses is made on 1 ha an arable land.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Rent of the mechanized means for creation the fallow crop and harvesting of cultures of a crop rotation make the most part of article of expenses on SWS technologies (tractor K-700, combine “Enisey”, automobile – Kamaz seeders – 2,1 carriages to tractors PTC-9,3 PTC-12).
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Steppe
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Wavy plain
Altitudinal zone: 150-340 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Humus horizon up to 80 cm
Soil texture (topsoil): Heavy and average
Soil fertility is medium with a humus content of 4-5%
Topsoil organic matter: 1-5%
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium at bottom part of the slopes and otherwise low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
6% of the land users are very rich and own 3% of the land (5).
5% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land (3).
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land (2).
4% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land (1).
4% of the land users are poor and own 2% of the land (4).
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
By means of struggle against erosion and deflation
其它社会经济效应
input contstraints
注释/具体说明:
High cost
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Promotes stubble creation
土壤流失
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
注释/具体说明:
Promotes stubble creation
其它生态影响
soil fertility
注释/具体说明:
Due to introduction of fertilizers reduces erosion
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
Reduces adjournment of melkozem
erosion processes
注释/具体说明:
Reduces intensity of erosive processes
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
100 households covering 40 percent of stated area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
100 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: At low cost of petroleum products fertilizers small and average farm with pleasure apply SWC technology . Cost of petroleum products and fertilizers sharply changes from year to year
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It is accessible in application How can they be sustained / enhanced? Constantly |
|
Improves agromeliorative conditions How can they be sustained / enhanced? Constantly |
|
Allows to receive guaranteed profit How can they be sustained / enhanced? At presence of means for SWC introduction |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It is traditional for region How can they be sustained / enhanced? Constantly |
|
It is effective as a measure of struggle against wind erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? At threat of processes of wind erosion |
|
It is effective at struggle against water erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? At threat of processes of water erosion |
|
Promotes accumulation of a moisture in ground How can they be sustained / enhanced? Constantly |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Opportunity of application SWC to the limited circles of farmers. | Additional grants investments are necessary for small farms or the sponsor’s help. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Soil protective agriculture Baraev A.I., Moscow, "Floc". Without rotation of the Almaty layer , 2000y, Gossen E.F.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SPC for Crain Husbandry Shartandy city
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Crop on the stubble background [哈萨克斯坦]
Stubble crop for cultivation of grain crops (spring wheat).
- 编制者: Ervin Gossen
模块
无模块