Multi-Storey Cropping [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Maramihang Pagtatanim or Planting in Great Numbers
technologies_1103 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Rondal Jose
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Mojica Alejandro
Cavite State University
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Rojales Joseph
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Cavite State University (CvSU) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Farming Systems and Soil Resources Institute, University of the Philippines Los (Farming Systems and Soil Resources Institute, University of the Philippines Los) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Cultivating a mixture of crops with different heights (multi-storey) and growth characteristics which together optimise the use of soil, moisture and space.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
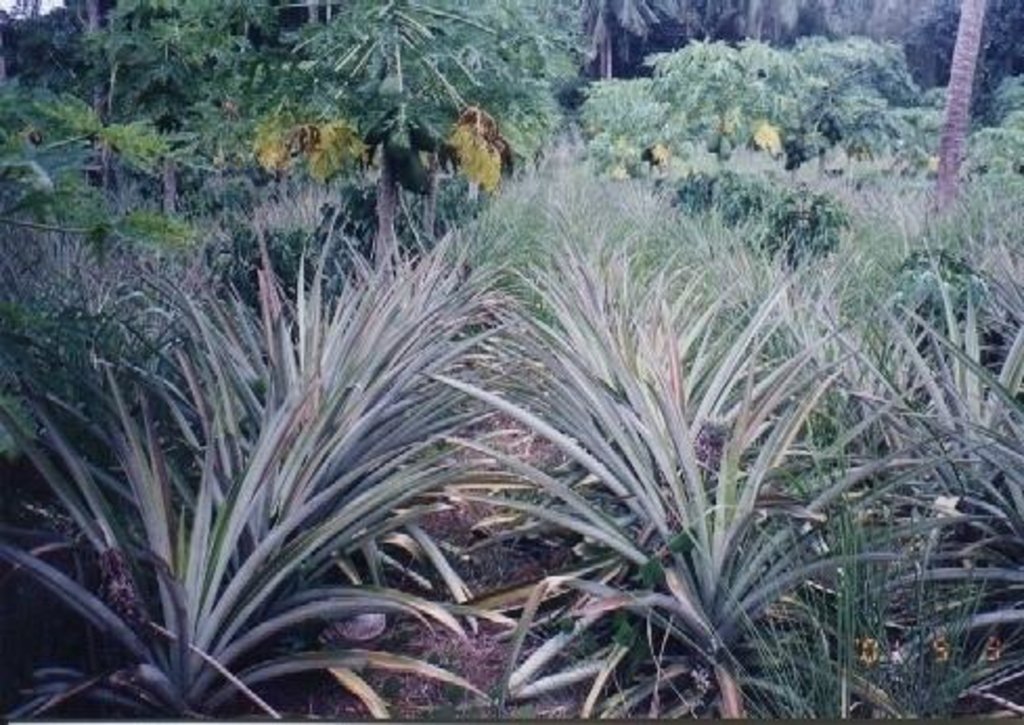
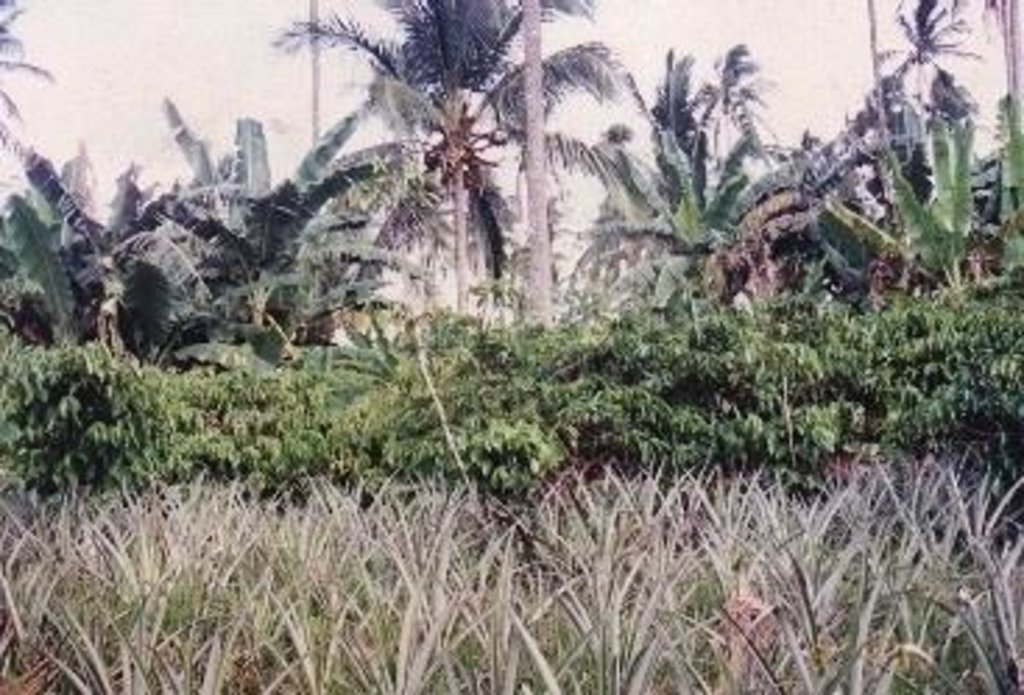
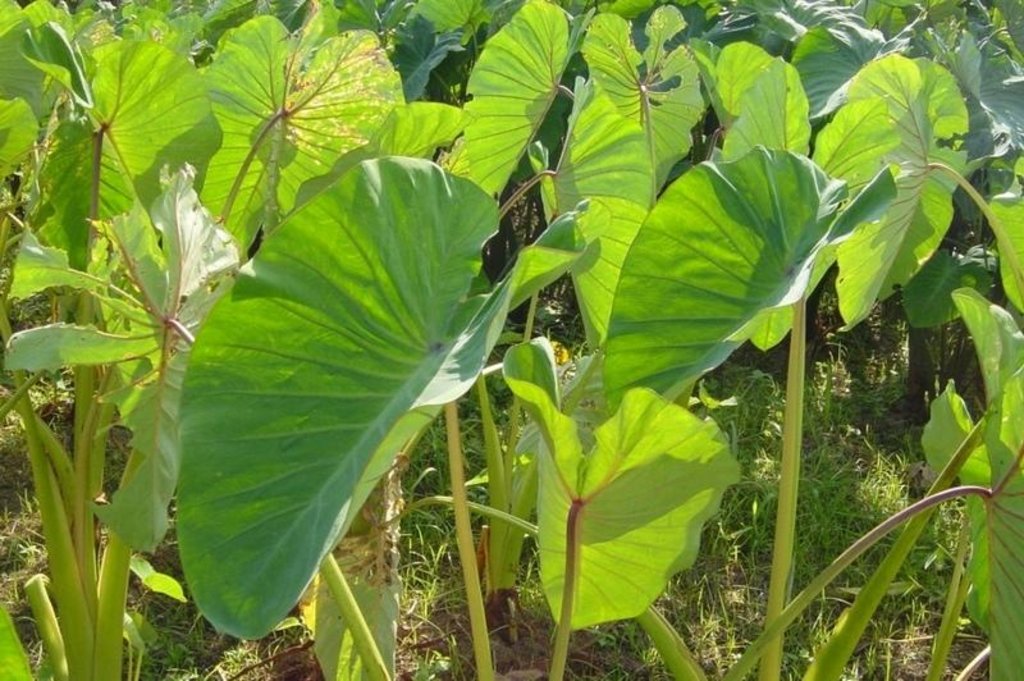
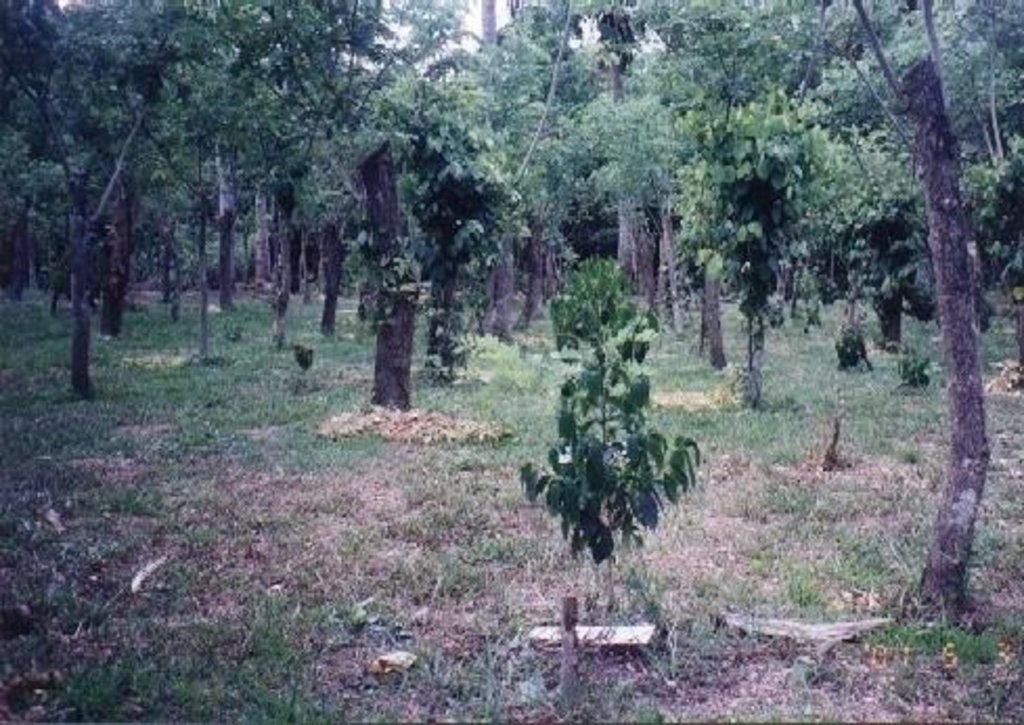
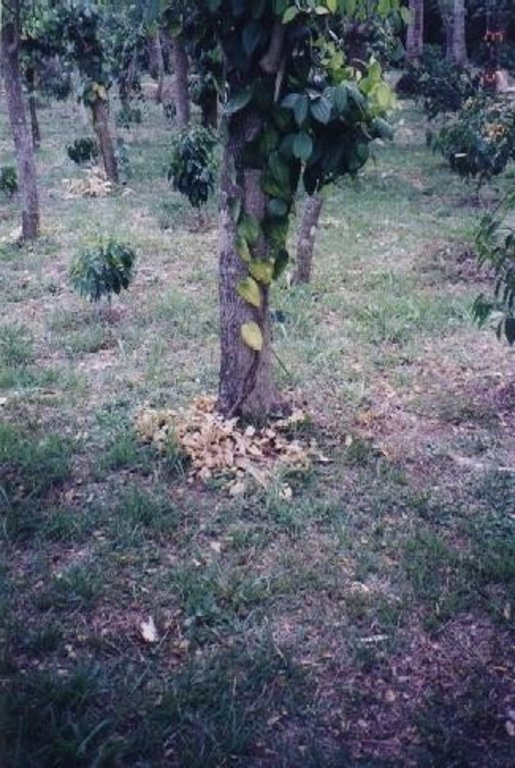
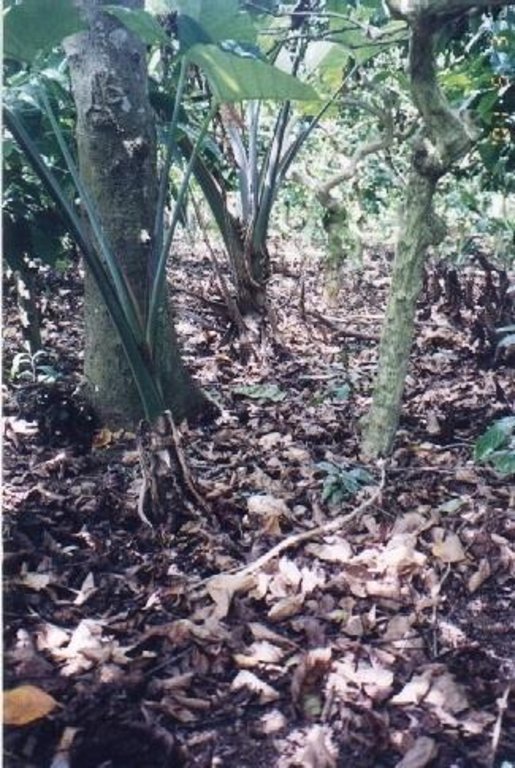
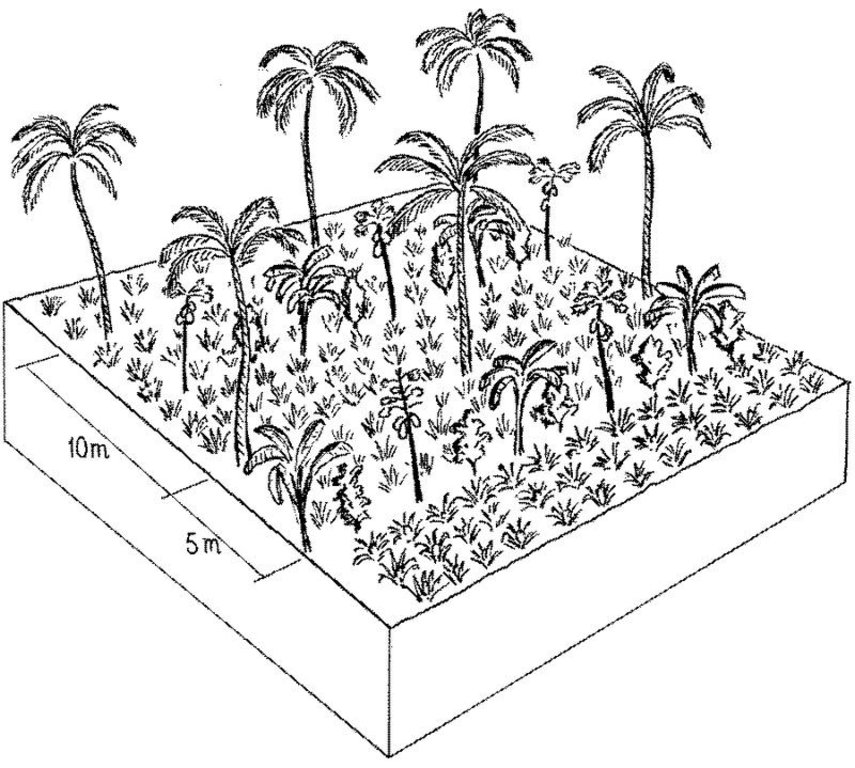
Under the maramihang pagtatanim multi-storey cropping system, perennial crops (coconut, banana, coffee, papaya, pineapple) and annuals/biennials (root crops: taro, yam, sweet potato etc) are interplanted to maximise productivity and income. This is most applicable where farms are small and the system needs to be intensive. In this particular area, Cavite, coconuts are usually planted first. When they reach a height of 4.5 meters (after 3-4 years), bananas, coffee and/or papaya are planted underneath. Black pepper may also be part of the system. After sufficient space has developed at ground level in about three to four years, root crops are planted. At full establishment, the system develops different layers: coconut (tallest) followed by banana, coffee, papaya (middle), root crops and pineapple (lowest). In recent years, because of its relatively low productivity and decreasing price, coconut has tended to be replaced in the system with higher value crops like the fruit tree santol (Sandoricum koetjape), papaya and sometimes black pepper. However most multi-storey farms adhere to no specific planting layout. The multi-storey agroforestry system is intended to make the best use of resources (soil, moisture and space) for increased farm income. It is also very effective against soil erosion. Previously, continuous monocropping of annual crops resulted in erosion and serious soil fertility decline. Even though the land is sloping and rainfall during the monsoon is extremely intensive, multi-storey cropping provides adequate soil cover throughout the year, protecting the land from erosion.
Fertilization, weeding and pruning are necessary elements of maintenance. ‘Natural’ mulching through fallen leaves from leguminous trees helps restore and maintain soil fertility The system is applied in a volcanic-derived soil with distinct wet and dry periods (6 months wet season, 6 months dry season). There is the risk of a destructive typhoon every 10 years. Farm income is relatively high, but labour and input costs are also high - and the technology is mostly used by relatively wealthy landowners. There is strong spontaneous adoption, as maramihang pagtatanim has been proven to be effective and remunerative. This technology has been practiced in Cavite since the 1970s. Implementation is by individual farmers with strong extension support from the Local Government Units (LGUs), NGOs and the Cavite State University.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Philippines, Cavite
有关地点的进一步说明:
Cavite
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
40.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 40 km2.
Six adjacent municipalities are practicing multi-storey cropping as a system. This is meant to increase income particularly for small farmers.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
It evolved in the area due to necessity.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 240, Longest growing period from month to month: May - Jan; Second longest growing period in days: 210, Second longest growing period from month to month: May - Dec

森林/林地
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Productivity decline, unstable prices of agricultural products and high costs of inputs are the main land use problems. Inputs also have to be increased to maintain the same yield level in annual cropping systems. There is a severe land use competition: a large proportion of the land is being converted to non-agricultural uses, especially residential and industrial areas because of the proximity to the rapidly expanding capital.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Productivity decline and unfavourable prices of agricultural products. High costs of inputs.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
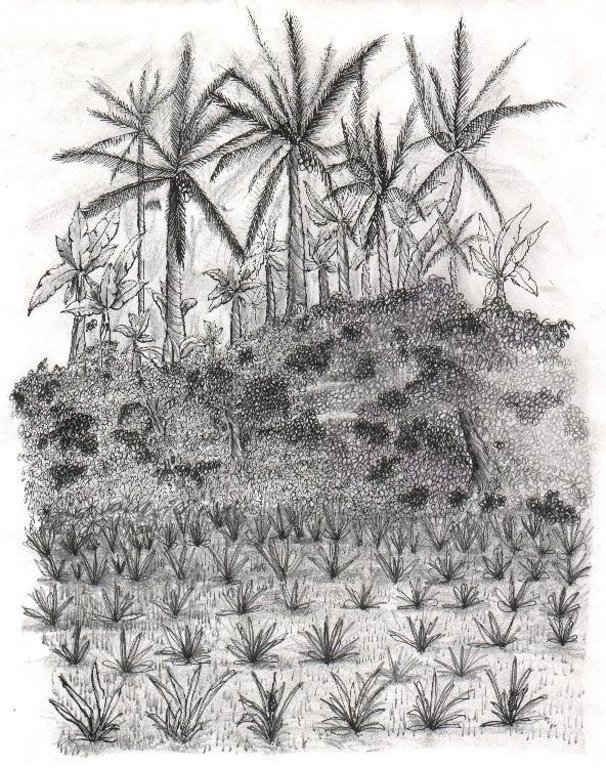
Multi-storey cropping includes various species interplanted systematically to optimise use of resources: pineapple and other
root crops (lowest storey); rows of banana trees, coffee and papaya (middle storey); rows of coconut (highest storey). Note: in practice farmers adjust this layout to meet their needs.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase in organic matter
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: coconut, papaya, coffee, banana, pineapple, black pepper, taro, yam...
Quantity/ density: 2500
Remarks: in rows random
Vegetative measure: tree/shrub cover (multi-storey, aligned)
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Fruit trees / shrubs species: coconut, coffee, banana, pineapple, black pepper
作者:
Mats Gurtner
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Peso
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
50.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1. Planting of tallest storey (coconut). | early rainy season |
| 2. | 2. Planting of middle storey (coffee and banana). | early rainy season |
| 3. | 3. Planting of lowest storey (pineapple). | early rainy season |
| 4. | 4. Planting of lowest storey continued (root crops). | early rainy season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | tools | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 840.0 | 840.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 160.0 | 160.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | biocides | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1390.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 27.8 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1. Pruning. | |
| 2. | 3. Harvesting. | |
| 3. | 2.Weeding | |
| 4. | 4. Spraying. | |
| 5. | 5. Fertilizing. |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 160.0 | 160.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | biocides | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 490.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 9.8 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: animal draft wooden plough, machete, iron bar and spade, machetes, harrows, bolo.
Cost was calculated assuming a per hectare population of 100 coconuts, 400 coffee plants and 3,000 pineapples.
Maintenance activities entail more work than during the establishment phase. Note that the establishment phase usually lasts for 4-5 years, so the labour is spread, unlike during the maintenance phase when all of the components have to be attended to.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labor is the most crucial especially during land preparation and planting, maintenance and harvesting.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
- 中(1-3%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are very rich and own 40% of the land.
60% of the land users are rich and own 40% of the land.
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 15% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: remittances from employment of at least one member of the household. Trading is also important.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Landholding is continuosly being sub-divided due to inheritance
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
due to high plant population (density)
木材生产
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Farmers in the area are coming the richest
工作量
注释/具体说明:
during planting/harvesting
其它社会经济效应
Input constraints
注释/具体说明:
system is capital intensive
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
through the formation of cooperatives or farmers organisation
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
through the involvement of line agencies and strengthening of research component
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
70
SLM之后的数量:
40
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
almost 100 % soil cover
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
10
SLM之后的数量:
0
注释/具体说明:
reduced run-offf
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
注释/具体说明:
organic matter accumulation
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
注释/具体说明:
increase aquifer recharge
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
run-off is reduced
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
100 % protection of surface
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1000 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. The technology has been proven to be very effective
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Generates high farm income |
| Failure of one crop component can be compensated by the other component |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology is flexible. It can be modified to suit market condition. Failure of one crop component can be compensated by other components (improved food security) |
| It maintains soil fertility through the recycling of nutrients |
| It is a very effective way of using and conserving water |
| Strong research and development: because of its importance in the economy, the technology has spawned various research activities |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High investment cost | Government to provide low interest production loans (seeds, fertilizers). |
| Highly fluctuating farm prices | Spread out production schedule. Target off-season harvesting of crop (eg pineapple). |
| Pest and diseases (eg papaya virus, which may have developed because it has been part of the system for a long time) | Intensified research and development. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Prone to typhoon damage | Establishment of windbreaks: Leguminous trees such as Acacias could provide wind protection for lower crops like papaya or coffee. |
| High labour requirement (eg weeding, harvesting).Weeding may be reduced for some components (eg coffee), but pineapple always requires difficult (due to its thorny leaves) and intensive weeding. | (1) Use labour-reducing techniques (eg mulching), (2) spread activities over the growing season. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
15/06/2001
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Field Report: Multi-Storey Cropping System of Silang, Cavite, Philippines
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Bureau of Soils and Water Management, Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
FAO and IIRR. Resource management for upland areas in Southeast Asia. FARM Field Document 2. 1995.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations, Bangkok, Thailand and International Institute of Rural Reconstruction, Silang, Cavite, Philippines.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块