Planted Vegetative Strips (PVS) [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1105 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Crisologo Victor
Cagayan Valley Integrated Agricultural Resources Research Center (CVIARRC)
菲律宾
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
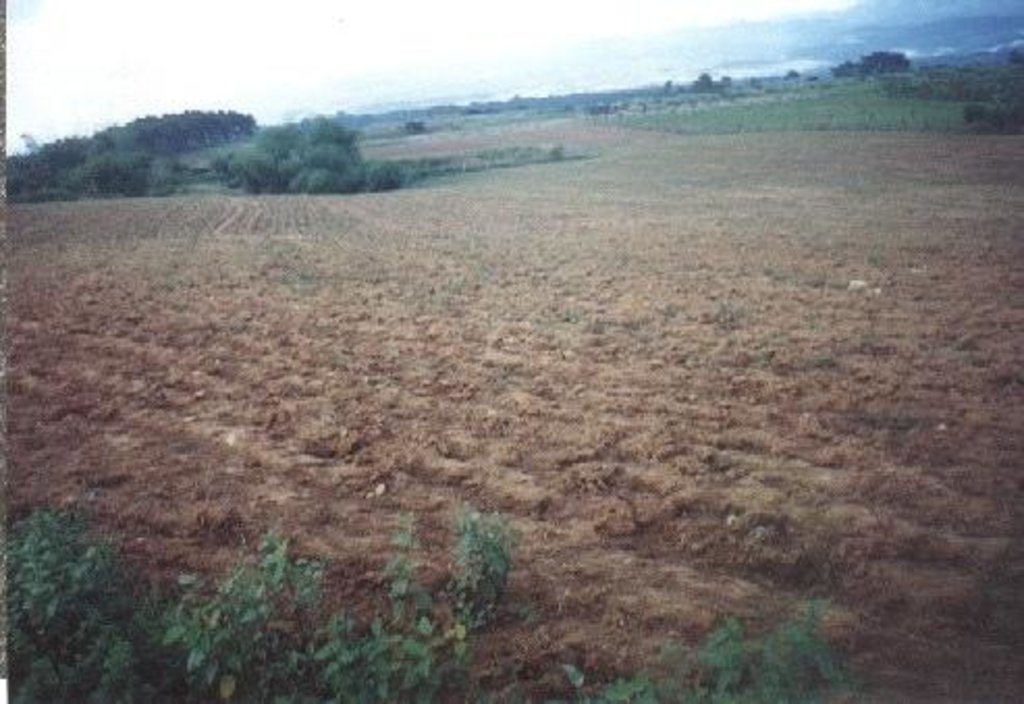
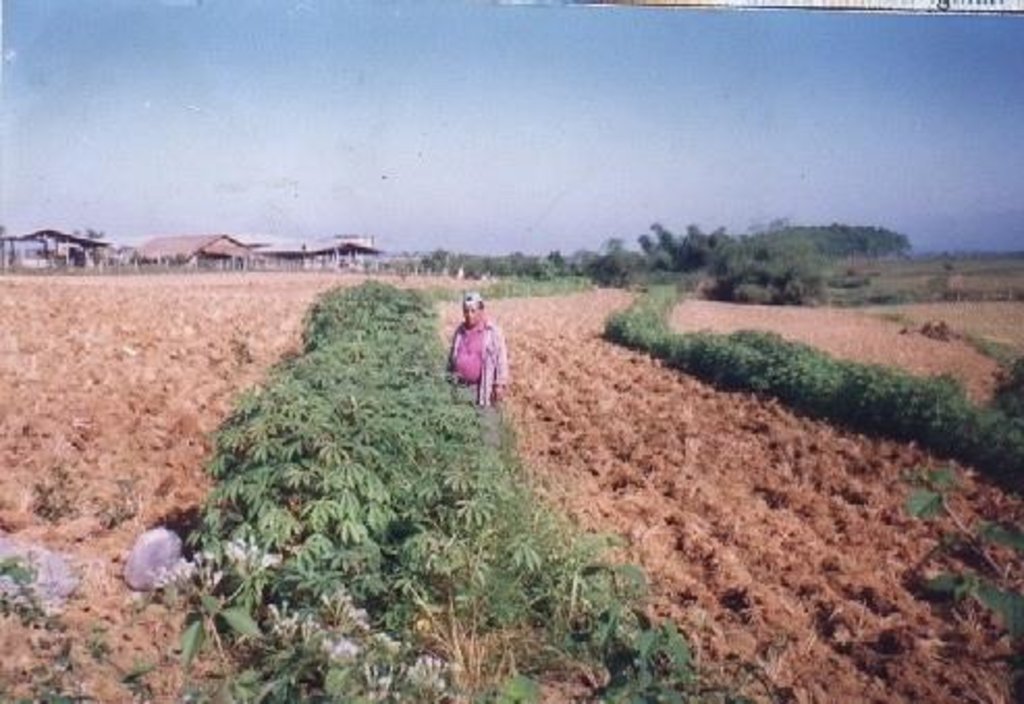
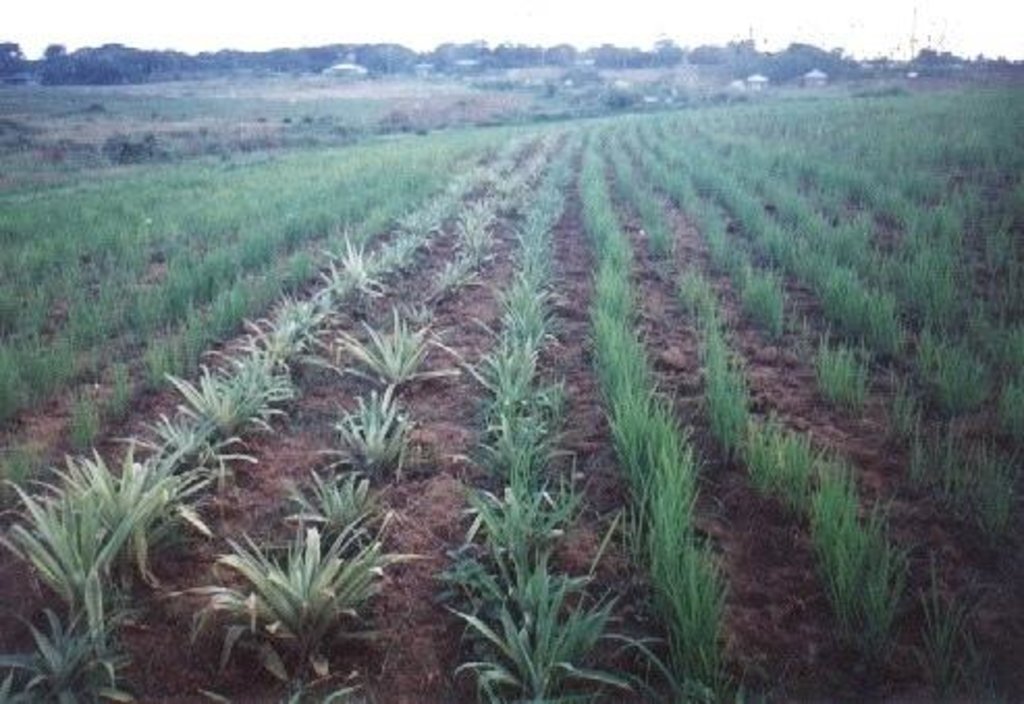
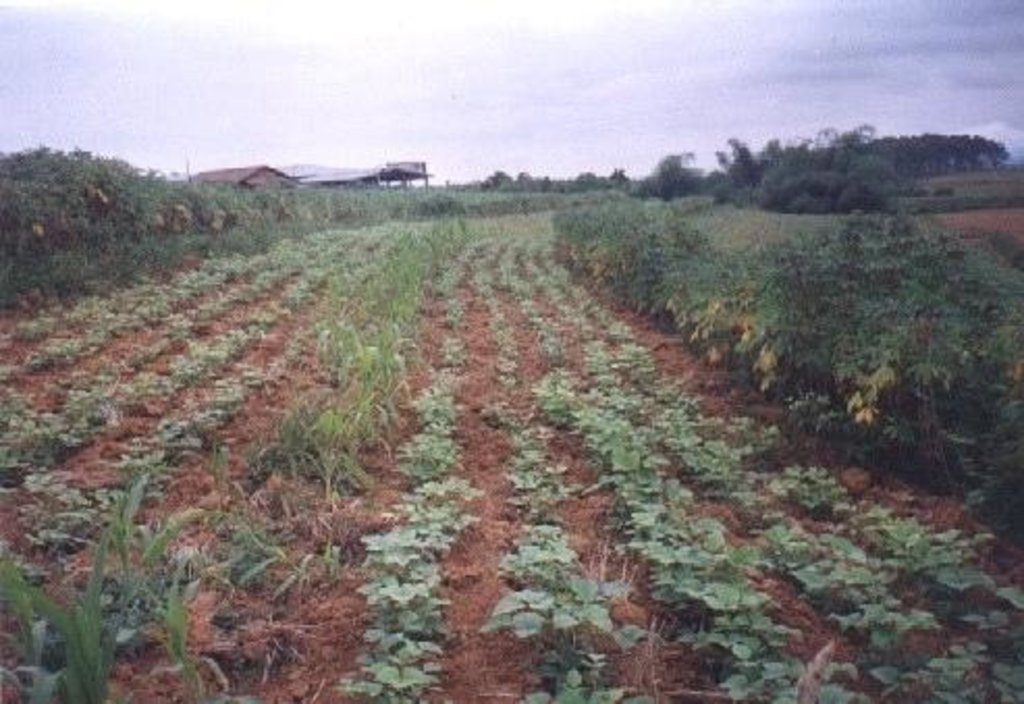
Planting of economic crops/forages in strips along the contour to control soil loss through erosion.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
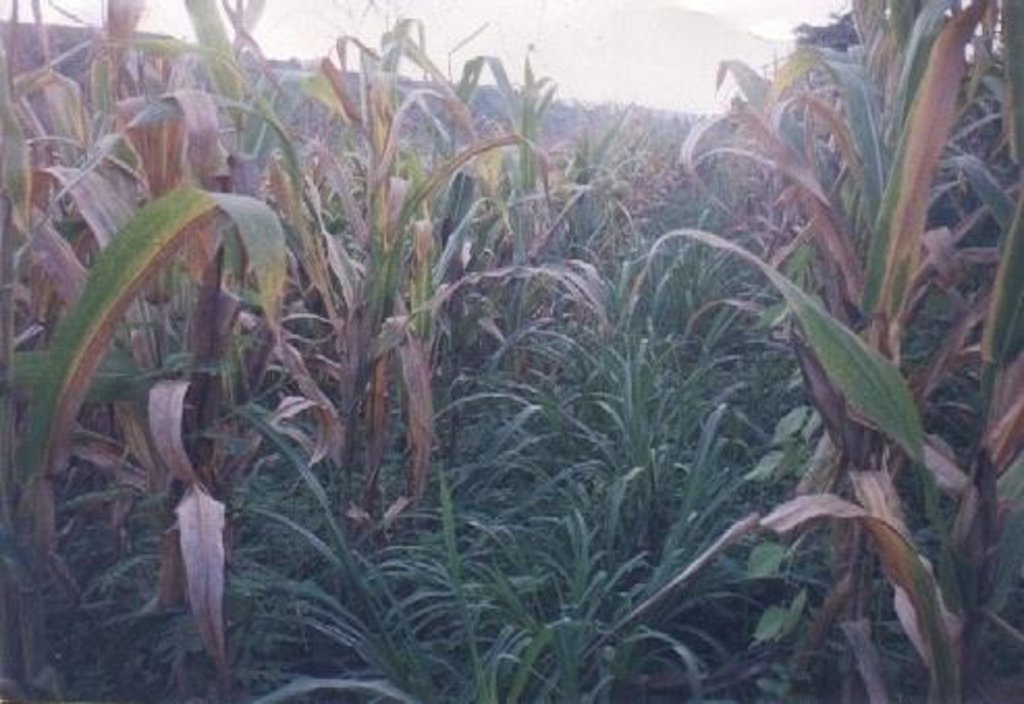
The technology was introduced in the upland corn growing areas in Isabela province. The province is one of the main corn growing areas in the Philippines. As a means of minimizing/controlling soil erosion, economic crops like cassava and pineapple and forage grasses are planted in strips along the contour. Cassava and pineapple strips are established together with forage grass. When the cassava and pineapple is harvested, the forage will continue to provide protection against soil erosion. Planting of cassava is done yearly, while the replanting cycle for pineapple is 2 to 3 years. In some cases, forage grass is grown alone. It is more or less permanent and it is trimmed regularly. Overtime, natural terraces are formed and soil erosion is minimized. The system is advatageous in the economic benefit can be gained from both the alley crops is there on the contour strips.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Isabela
有关地点的进一步说明:
Isabela
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
2.5
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2.5 km2.
The technology was introduced in the upland corn growing area of Isabela. It was project-initiated
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Introduced by extension staff
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 240, Longest growing period from month to month: May - Dec; Second longest growing period in days: 180,Second longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Nov
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Severe soil erosion and fertility decline caused by intensive cropping (soil mining)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Productivity decline - increased application of fertilizers to obtain the same yield level.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A3:土壤表面处理

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: contour planting / strip cropping, contour tillage
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
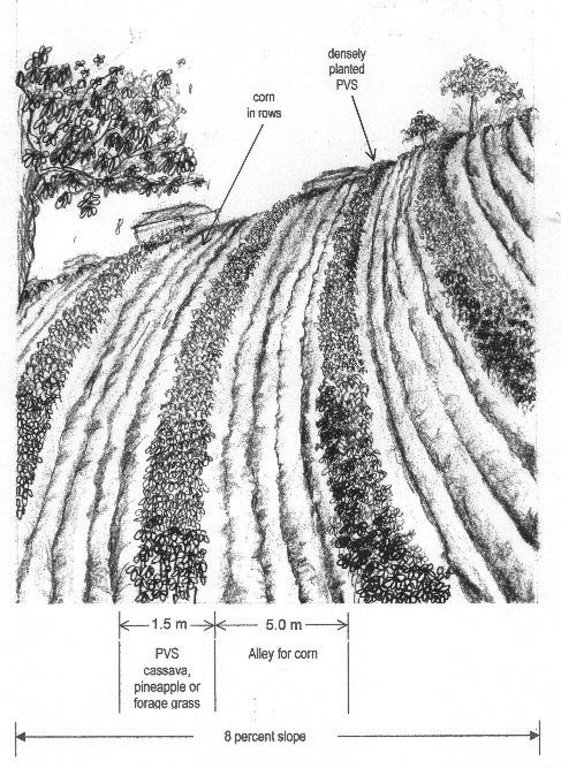
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Artist impression about planted vegetative strips (PVS) technology
Location: Isabela
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: seeds/seedlings
Quantity/ density: 4000
Remarks: in strips along the contour
Contour tillage
Remarks: strip cropping
Vegetative measure: contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 4000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.2
Vegetative measure: in rows
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 4000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.2
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Perennial crops species: pineapple
Grass species: napier
Other species: cassava
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 3.00%
作者:
Boyet Yambot-BSWM
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Philippine Peso
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
50.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | contouring | dry season |
| 2. | planting of vegetative strips (PVS) | onset of wet season |
| 3. | planting of alley crops | June/October |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 144.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 2.88 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of vegetative strips (PVS) | onset of rainy season / once |
| 2. | Planting of alley crops | June/October / twice a year |
| 3. | Contouring | dry season / once |
| 4. | pruning/trimming (grass) | regular /every 2 weeks |
| 5. | fertilization (pineapple) | onset of rainy season /once a year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 40.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.8 | |||||
注释:
The total area to be used for PVS which is approximately 2000 square meters.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labor and inputs costs are the main factors involved.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
60% of the land users are very rich and own 60% of the land.
4% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
1% of the land users are average wealthy and own 10% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Trading, working in other farms, carpentry or a family member working abroad
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Land subdivision due to inheritance
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Napier grass for work animals
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Napier grass for work animals
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
from the PVS
收入和成本
经济差异
工作量
注释/具体说明:
PVS serves as barrier for field operation
社会文化影响
国家机构
注释/具体说明:
created awareness
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
70
SLM之后的数量:
40
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
50
SLM之后的数量:
10
生物多样性:植被、动物
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
PVS can harbor pests
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
Production of extra food crops
注释/具体说明:
from the PVS
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. They can clearly see the benefit of adapting SWC practices in terms of added benefits (additional products, ecological)
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Training and provision of planting materials/inputs |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Easy to establish and not capital intensive |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| PVS can harbor pests (e.g. rats) | Proper maintenance/cleanliness |
| Interfere with cultivation | Align PVS in a straight manner if the contour allows |
| Need additional capital | Provisions of incentives (e.g. subsidized inputs) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Low effectivity of some PVS species/materials | Supplementary control measures (mulching, temporary barriers) |
| Yearly establishment (e.g. cassava) | Consider perennial species as PVS (e.g. forage grass) |
| Competition for nutrient and water | Application of fertilizer and use of water harvesting techniques. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
24/08/2001
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块