Agroforestry homegarden [塞内加尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Julie Zähringer
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1166 - 塞内加尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CSE (CSE) - 塞内加尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
07/08/2009
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
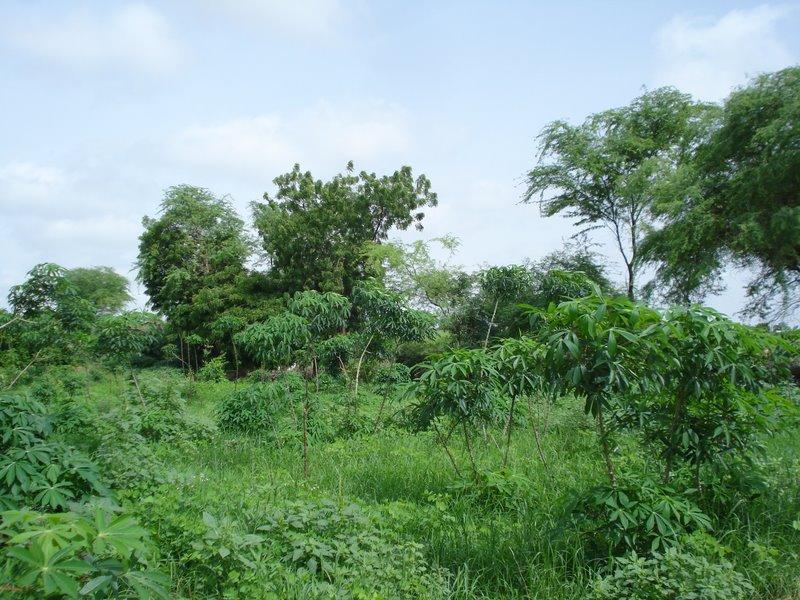
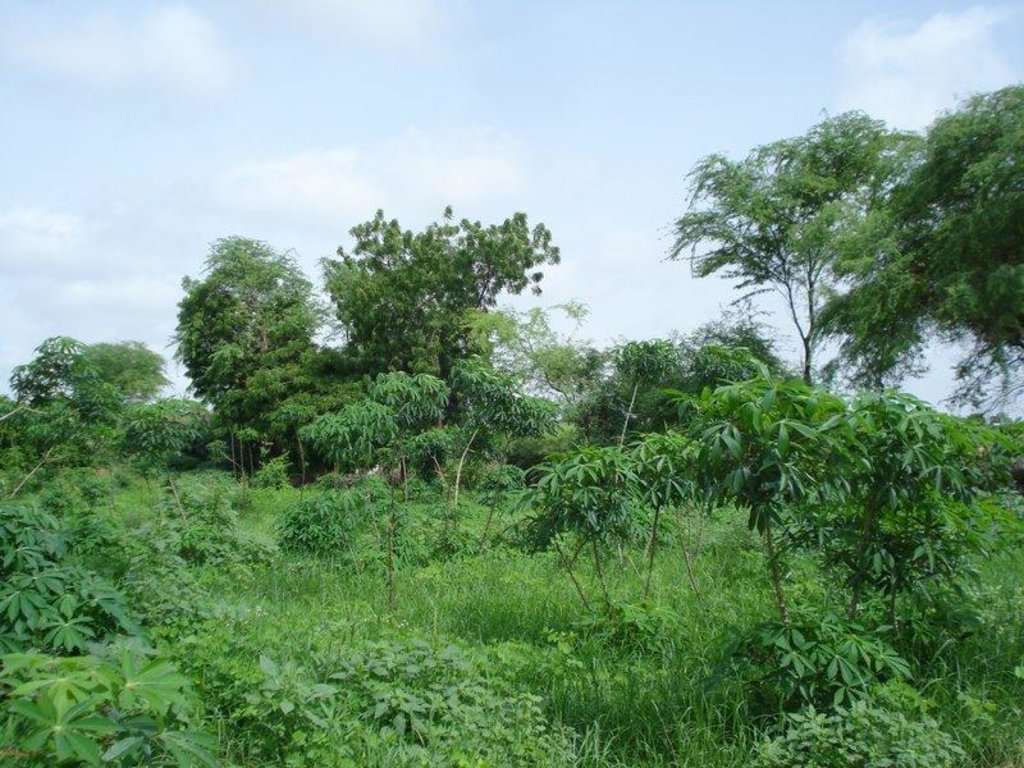
A tropical homegarden of about 0.5 ha with a variety of exotic and indigenous tree species, planted or raised for fruit production, medicinal value and / or other services, intercropped with vegetables in the herbaceous layer.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
During the dry season, tomato, eggplant, chili, beans, cabbage, okra and bissap are cultivated, in the rainy season replaced with maïz. One part of the garden is cultivated with cassava, planted in the rainy season and harvested all year round. Main tree species are Prosopis juliflora, Citrus sp. and Eucalyptus camaldulensis. A hedge of mainly dead wood, alive Euphorbia balsamifera shrubs and few Eucalyptus camaldulensis trees is protecting the homegarden from roaming animals. It has the positive off-site effect of preventing the temporary pond beneath the plot from being filled up with sediments, as a consequence of wind erosion. Organic manure obtained from cattle faeces is used as a natural fertilizer.
Purpose of the Technology: The garden was established and is managed by a single land user and his family. Main objectives are to provide food security for his family, to make a wide range of fruits and vegetables available in a zone far from the next market and to improve income through diversification. As the plot is situated on a slope (7 %) and prone to water erosion during heavy rains, a further objective is to prevent the formation of gullies and ravines through better soil stabilization.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Trees planted in this plot were chosen upon seed or seedling availability in other peoples land as the land user planted whatever he could obtain. He constructed a fence of dead wood with the aim to turn it into a life fence of Eucalyptus camaldulensis trees later. A small retention basin was built to assure the storage of water tapped from the village borehole. However, because of breakdowns of the pump and the generally low outflow of the borehole, lack of water caused high mortality in the tree nursery of Eucalyptus camaldulensis seedlings. The fence therefore remains a mainly dead fence and is very weak in certain places. The main cost of the technology is the access to the borehole which costs the landuser 20'000 CFA (US-Dollar 45) per month. For the purchase of seeds for horticulture about 15'000 CFA (US-Dollar 33.50) are spent per year. The use of organic manure does not involve any costs as cattle is abundant in the area.
Natural / human environment: This SLM technology site is located in the sylvopastoral region of the Ferlo in the north of Sénégal. The agro-climatic zone is classified as semi-arid with mean annual precipitation of 300-400 mm. The main land use type in the area is extensive pastoralism followed by rainfed agriculture. Pastoralism is primarily practiced by transhumant Fula (Peulh) herders and further by Mauritanian Moor herders with herds of dromedaries. Vegetation cover in the area has largely been degraded due to cutting for domestic uses and cattle feeding, bushfires and overgrazing. The soil is exposed to wind erosion which carries away nutrients in the topsoil and therefore declines soil fertility. During intense rains in the rainy season, surface runoff is accelerated and leads to the formation of gullies and ravines.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塞内加尔
区域/州/省:
Louga / Linguère
有关地点的进一步说明:
Barkédji / Diagali
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农林业
主要产品/服务:
Maïz, manioc
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): degradation of vegetation cover, wind erosion, increased surface runoff, formation of gullies and ravines, management of natural water sources (people using temporary ponds for laundry and body hygiene and at the same time as sources of drinking water)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): surface runoff, formation of gullies and ravines, decrease of soil fertility, wind erosion, limited water access, presence of insect pests
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
注释:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: Jul-Oct
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 防风林/防护林带
- 轮作制度(轮作、休耕、轮垦)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
The surface of this homegarden is about 0.5 ha
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: retaining more vegetation cover, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
- Eo:场外劣化效应

生物性退化
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Eo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (for domestic uses), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (by oversized cattle and dromadaires herds), poverty / wealth (poverty), education, access to knowledge and support services
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (absence (or insufficient use) of inorganic and organic fertilizers)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: (the landuser concerned does not have this level of knowledge)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: trees
Quantity/ density: 118 / ha
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: organic manure
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 118
Trees/ shrubs species: Citrus sp. (planted), Eucalyptus camaldulensis (planted), Azadirachta indica (planted), Tamarindus i
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
CFA
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
455.0
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | access to irrigation water for tree nursery | 植物性的 | per month |
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | seeds or seedlings for horticulture | 植物性的 | once a year |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 33.0 | 33.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Irrigation water | ha | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 78.0 | |||||
注释:
Costs indicated apply to an agroforestry plot of 0.5 ha surface. No costs were involved with the initial planting of trees in the plot, as seedlings were either given by the extensive agent for "Water and Forest" or obtained from other landusers. Organic manure can be obtained for free due to the strong presence of cattle in the area. For the construction of the fence, dead wood was collected in the area.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
rainfall regime: water for irrigation needed during dry season
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
300-400 mm during one rainy season / length of dry season: 9 months
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Valley floors (depression)
Slopes on average: Moderate (7%)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Very low
Topsoil organic matter: Low (carbon in the labile fraction: 0.09 g / kg soil)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, ranked 1, groundwater during dry season) and for agricultural use only (irrigation, ranked 2, surface water from temporary ponds during rainy season)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Compared to other regions of the country
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: women can not aquire land to cultivate unless it is attributed to them by their husbands
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
22% of the land users are average wealthy.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Apart from the plot the landuser is cultivating some village fields
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
产品多样性
生产区域
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Increased food security, improved diversification of alimentation
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
蒸发
土壤
土壤覆盖层
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: many inhabitants of this village try to establish similar plots
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| increase of product diversification, availability of vegetables in village |
|
increase of revenues How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase production and fight against soil fertility decline |
| increased food security |
| increased availability of plants used in traditional medicine |
|
mitigation of gully formation How can they be sustained / enhanced? improve strenght of fence |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
increased woody plant diversity and density How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintain trees in plot |
|
the fence reduces siltation of the village's most important temporary pond beneath the plot How can they be sustained / enhanced? improve the fence with live trees |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| outflow of village borehole too weak to maintain irrigation of seedlings in tree nursery and vegetables | better maintenance of borehole |
| high mortality in tree nursery because insufficience of water | improve access to water from borehole |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| use of chemical pesticides against soil insects which are believed to be a cause for decline in soil fertility | research to know more about cause of fertility decline or use of biological pesticides |
| degradation of soil properties because of inappropriate soil management in parts of the plot | training in soil management for landuser |
| removal of herbaceous cover to gain space for cultivation | training |
| no system applied to distribution of trees in the field | apply structural soil conservation measures, such as terraces etc. |
| gully formation because of slope and weak fence threatens future maintenance of plot |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块