Soil productivity improvement and BXW control in epidemically affected banana zone [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: ALLAN BUBELWA
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Ursula Gaemperli, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1204 - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Pesha
Kyerwa District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kyerwa District Council - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Restoring banana production through temporal crop substitution and the use of SLM and recommended husbandry practices in controlling the deadly BXW disease.
2.2 技术的详细说明
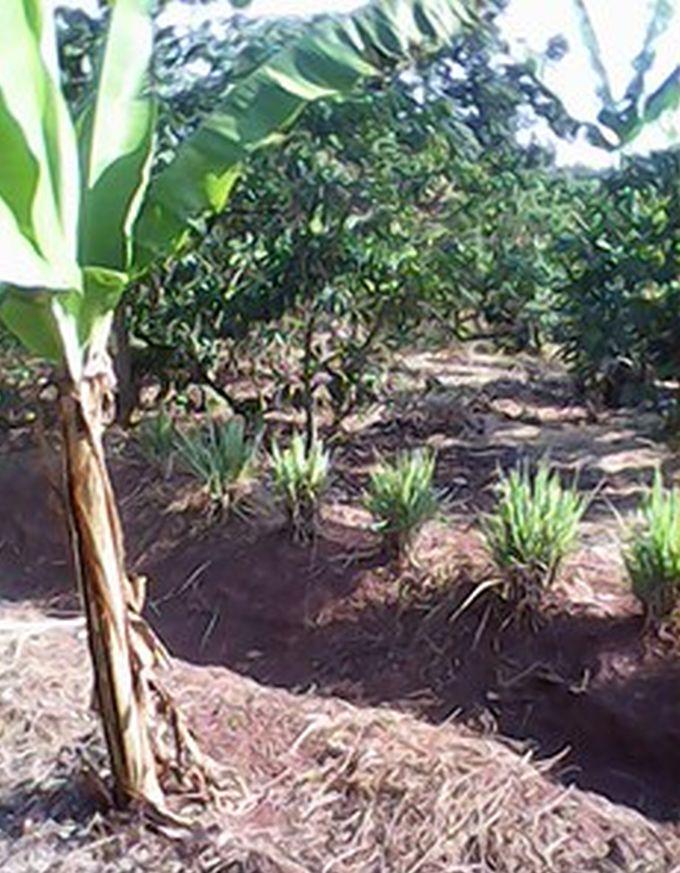
说明:
This conservation measure is used in BXW epidemically affected areas. Land users in affected areas are trained on the principle behind the diseases and means and ways to overcome it. Banana plants in seriously affected farms are uprooted and destroyed and non disease host crops usually maize and common beans are grown for starvation and destruction of BXW pathogen. The land is not used for banana production for a period of 6 months and instead substitute crops ensures food and income security to land users. Leguminous cover crops (beans) and crop residual management skills applied on the farm revitalize the soil health in terms of biomass, moisture and nutrient recycling. After 6 months, banana production is resumed where production is based on recommended husbandry practices combined with SLM conservation measures. The use of certified banana cultivars, optimal plant geometry and disease control cultural practices are some of the basic recommendation. Certified banana cultivars are planted at a space of 3m x 3m. The size of a hole used to plant banana is 0.9x0.9 m wide and 0.6 deep. During digging top soil is separated from subsoil. 2 -3 tins of manure are mixed with the top soil and the mixture is put in the bottom of the hole. The holes are left for microbial decay to take place and banana planting is done after 1 or 2 months. The tied Fanya chini water retention ditches are water harvesting and conserving structures constructed by digging trenches along the contour where dug soil is thrown to the lower side to form an embankment that prevents soil from falling back in. A-FRAME method is used to mark a contour line and on the other hand ARM OUTSTRETCHED LEVEL method determines how far apart the Fanya chini retention ditch should be. Unlike other retention ditches, the dug ditches are not continuous but instead are tied at regular interval with small cross–ties of 0.4-0.6m length. Ties intercept the ditch at right angle to form a series of narrow rectangular segments of infiltration ditches each of 5 meters long, 0.6m wide and 0.6m deep arranged in series within a contour line. Ties helps to prevent irregular flow of runoff and to ensure an evenly distribution of captured water. Fanya chini embankments are stabilized by planting crops on them the common crops are pigeon pea (space used between plant is stand is 1m x 1m), lemon grass (30cm x 30cm) or pineapples (60cm x 60cm). Mulching is done using grasses. The dominant grass species used is Hyperrenia rufa where a mulching depth of 15 cm is used.
Purpose of the Technology: PURPOSE: Improved food and fodder productivity, soil moisture and water holding capacity, nutrient recycling, and organic matter content, biomass cycle, crop tolerance to drought, income and food security, poverty reduction and health. Prevent unproductive evaporation of green water, combating soil erosion by water runoff and biological degradation due the deadly BXW disease.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: ESTABLISHMENT: procurement and mobilization of working tools, uprooting and destruction of infected plants in affected fields, land tilling and harrowing, planting of alternative crops or creation of a productive disease free buffer zone, temporal harvesting of maize and beans, land preparation/ demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting, digging holes, manure application before planting, banana planting, demarcation of contour line for construction of Fanyachini contours with ties, digging and construction of Fanya chini contours with ties, vegetative stabilization of Fanya chini bunds (using lemon grass, pineapples or pigeon pea), random planting of castor oil plants for future anchoring support of plants with heavy bunches and mulching application. MAINTENANCE: hand weeding to control noxious weeds combined with other pest and disease control (control of nematodes and weevils), de-suckering to leave the mother plant and two baby plants, de-trashing or trimming of unproductive leaves, regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence (male bud) using a forked wooden pole once the bunch is completed to prevent BXW transition through insect vector , recurrent manure application, removal of sediments and maintenance of Fanyachini bunds, harvest of bananas, maize, pineapples and pigeon pea. INPUTS USED: largely includes labour (strenuously varying from light, medium and heavy), tools (hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade, mattock and A-frame), seedlings; improved or certified banana varieties, pineapples suckers, lemon grass and castor oil, seeds (beans, maize and pigeon pea), farm yard manure and mulching materials (preferably Hyperennial spps).
Natural / human environment: NATURAL ENV: The land use type is cropland with annual, perennial and some fruit tree crops. The technology involves a combination of agronomic, vegetative, structural and management conservation measures. Management measure involves all activities related to temporal shift to alternative crops for making the farm disease hot free and for staving and destroying the disease pathogen. Climatic zone is sub-humid with an average of 210 days of growing period (LGP). Average slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. A soil texture class is sandy loam with medium depth categories. HUMAN ENV: the level of mechanization is hand tools. Production system is mixed (both subsistence and market or commercial oriented). The average costs of inputs required is 3015.68 USD. Land ownership is largely individual not titled and partly communal.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
区域/州/省:
Kagera Region Tanzania
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kyerwa District Council
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
The area includes the totality of all farms of FFS members who applied the technology after being trained.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
This is one of the technologies tested and demonstrated under the support of the Trans Boundary Agro Ecosystem Management Project. Analysis and documentation of this technology is based on perspectives and experiences of field SLM specialist and FFS group members.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- root crops, pigeon pea, lemon grass
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
- 菠萝
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 咖啡,露天种植
- 咖啡,采树荫栽培
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: September to December; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Major land problems without land conservation are BXW disease, poor soil fertility, and moisture stress and soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): BXW disease.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Banana is the major food crop but in the recent years the crop was substituted by maize and beans due the out break of BXW.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
- crop substitution
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A7:其它

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
- V5:其它

结构措施
- S11:其它

管理措施
- M7:其它
注释:
Specification of other vegetative measures: Use of leguminous plants
Specification of other structural measures: Water retension ditches with fanya chini bunds and ties.
Specification of other management measures: Temporal substitution of a dominant crop by non disease host crops for pathogen distruction
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Flat cultivation on slopy land and nutrient mining without replenishment), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Poor practices that encourage spread of BXW.), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (No use of cross slope barriers.), change in temperature (Unproductive loos of green water due direct hit of of the soil by sunshine), change of seasonal rainfall (Due to climatic change and variability), poverty / wealth (Incapacity to invest in capital heavy conservation measures), labour availability (Rural to Urban migration of the enegetic youths), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (High input expenses.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Ignorance of SLM and shortage of field extension workers.), governance / institutional (Low capacity of rural based environmental/land committees)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Due unpredictable climatic change and variability), population pressure (Continuous land fragmentation)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Most of the concepts and principles were taught to field/agricultural advisers at the college.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (New innovations and change of mind set is crucial e.g. the use of A-frame, the principle behind BXW and cultural methods of controlling the disease.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Mulching
Material/ species: Hyperania grass
Quantity/ density: 15 m3 /ha
Remarks: Across the slope
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farm Yard Manure
Quantity/ density: 40ton/ha
Remarks: 3 tin applied to each banana plant.
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Trees/ shrubs species: pegion peas
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Pineapples
Grass species: lemmon grass
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 12
Spacing between structures (m): 12
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 70
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 70
Construction material (earth): Soil
Other type of management: Temporal substitution of the a diseased plant with other non-host plants for staving and complete wipe out of the disease causing pathogen. (BXW affected bananas substituted with maize and beans)
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.353
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Procurement and mobilization of working tools | |
| 2. | Initial manure application (before banana planting) | |
| 3. | Initial banana seedlings (certified varieties) | |
| 4. | Initial mulching application | |
| 5. | Uprooting and destruction of infected banana plants in affected fields. | Before onstart of rain |
| 6. | Land tilling and harrowing. | Before onstart of rain |
| 7. | Planting of alternative crops (maize and beans) for starving and killing the pathogen. | After the first rains (usually September) |
| 8. | Demarcation of contour line using A-frame for construction of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | December |
| 9. | Digging and construction of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | December |
| 10. | Planting of lemon grass , pineapples and pigeon peas on bunds. | After constrution of fanya chini retension ditches with ties |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Planting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 5.0 | 2.353 | 11.77 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Demarcation of contour line | persons/day | 7.0 | 2.26857 | 15.88 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Digging and construction of Fanya | persons/day | 10.0 | 2.353 | 23.53 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Uprooting and destruction of infected banana plants | persons/day | 11.0 | 2.353 | 25.88 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Procurement and mobilization of working tools | ha | 1.0 | 76.47 | 76.47 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Lemon grass and pidgeon seeds | kgs | 5.0 | 2.94 | 14.7 | |
| 植物材料 | Pineapple seedlings | pieces | 513.0 | 0.0588304 | 30.18 | |
| 植物材料 | Initial banana seedlings | pieces | 660.0 | 0.441181818 | 291.18 | |
| 植物材料 | Maize and bean seeds | kgs | 81.0 | 0.947654 | 76.76 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Initial mulching application | bundles | 900.0 | 0.1764666 | 158.82 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Initial manure application | tons | 28.0 | 10.084 | 282.35 | |
| 其它 | Labour: Land tilling and harrowing | persons/day | 11.0 | 2.353 | 25.88 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Planting of alternative crops | persons/day | 9.0 | 2.353 | 21.18 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1054.58 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1054.58 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 9 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation, demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting and hole digging for planting bananas | Before onstart of rain |
| 2. | Manure application before planting Banana | Before onstart of rain |
| 3. | Banana planting | one to two months after manure application |
| 4. | Recurrent mulching application | once per season |
| 5. | Hand weeding to control noxious weeds, De-suckering, De-trashing and trimming | April and December |
| 6. | Regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence (male bud) using a forked wooden pole once the bunch is completed to prevent BXW transition through insect vector | Routinely as need be |
| 7. | Recurrent manure application | September/October |
| 8. | Banana harvesting | Routinely after mature |
| 9. | Weeding and gap filling of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas. | April |
| 10. | harvesting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | |
| 11. | Removal of sediments and reshaping/maintenance of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | May |
| 12. | Weeding and thinning | (twice) first and second |
| 13. | Harvesting of maize and beans. | January/February |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Land preparation, demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting | persons/day | 35.0 | 2.353 | 82.36 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Manure application before planting Banana | persons/day | 33.0 | 2.353 | 77.65 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Banana planting | persons/day | 13.0 | 2.353 | 30.59 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Recurrent mulching applicatio | persons/day | 6.0 | 2.205 | 13.23 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Mulching material | bundles | 900.0 | 0.176464 | 158.82 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost/manure | tons | 16.0 | 13.235 | 211.76 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Labour: Maintenance of Fanya chini | persons/day | 3.0 | 2.353 | 7.06 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Labour: Weeding an thinning | persons/day | 12.0 | 2.05916 | 24.71 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Labour: Harvesting of maize and beans | persons/day | 12.0 | 2.05915 | 24.71 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Labour: Hand weeding to control noxious weeds | persons/day | 15.0 | 2.353 | 35.3 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Labour: Regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence | persons/day | 15.0 | 2.353 | 35.3 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Labour: Recurrent manure application | persons/day | 22.0 | 2.353 | 51.77 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Labour: Banana harvesting | persons/day | 16.5 | 2.353 | 38.82 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Labour: Weeding and gap filling of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 7.0 | 2.353 | 16.47 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Labour: Harvesting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 7.0 | 2.353 | 16.47 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 825.02 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 825.02 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade and mattocks and forked wooden poles., Hand hoe, forked hole and machetes, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, spade, mattock and A-frame, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade and mattock.
The above cost were calculated per unit of one land user's land (1.5 acres) where the technology was applied and estimate also done per hectare.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Manure is the most determinant factor
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics. average temperature is 21°C
Average length of growing period is 210 days.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil texture (topsoil): The average soil texture is sandy loam
Topsoil organic matter: Low use and application of mulching and cover crops
Soil fertility is low due to continue washout of the soil surface with rainfall runoff
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium because slope effect minimize the time required for water to infiltrate into the soil.
Soil water storage capacity is low because of low amount of humus and underused of mulching
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Only a few perennials and annual crops and minimal fauna diversity due to the washout of organic matter by rainfall runoff
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
15% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
15% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some of the land users who are using the technology are running petty business and groceries (selling local brew).
Level of mechanization: Dominated by the use of small tools/implements.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
5 fingers
SLM之后的数量:
12 fingers
注释/具体说明:
Increased banana yield due to use of SLM and good husbandry practices
生产故障风险
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Risk due to low moisture
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Caused by the use of mulching and manure
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Income accrued from increased production and diversification to pineapples and lemon grass
工作量
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Attributable to added tasks from use of SLM
社会文化影响
健康状况
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Improved nutrition from e.g. introduction of pineapples
社区机构
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Use of FFS have induced togetherness and group working spirit
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
SLM knowledge and skills gained through FFS trainings
社会经济弱势群体的情况
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Indiscriminate participation of all genders, age and ethnicity
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Initially the technology has resulted to increased production, diversification to production of other income generating crops and dietary enrichment crops. The overall result is farmers capacity to meet education and health expenses
attraction to theiving
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Good looking banana bunches attract thieving
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Use of mulching and water retension ditches
土壤
土壤水分
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Following use of mulching and manure
土壤覆盖层
SLM之前的数量:
40%
SLM之后的数量:
90%
注释/具体说明:
Improved soil coved caused by the use of grass mulching
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Controll of soil erosion attributable to use of mulching and construction of water retension ditches.
养分循环/补给
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Use of luguminous plants, application of manure and mulching
土壤有机物/地下C
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Use of manure
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
SLM之前的数量:
40%
SLM之后的数量:
90%
注释/具体说明:
Biomass result from use of mulching and improved managment of crop residuals
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Increased richness of soil fauna caused by the use of manure
害虫/疾病控制
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
95%
注释/具体说明:
Control of BXW
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Increased tolerance to drought and BXW infestation
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Managment of crop residues and manure
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Of the neighbouring Kashasha wetland
对邻近农田的破坏
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Attributable to use of closs slope barriers
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Attributable to use of closs slope barriers
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
注释:
Retention ditches supported with ties to prevent flow of water and to encourage evenly distribution of water. The fanya chini bunds are stabilized by planting vegetation on them (pineapples, pigeon peas and lemon grass).
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The high investment costs cause slight realization of rewards but in the long run very positive benefits are realized by land users.
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
42 households covering 77 percent of the stated area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
42 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Supplied with banana suckers, farm yard manure and grass mulch.
42 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: land users who received suckers from neighbors but procured grass mulch and manure.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: most of the land users are impressed with the results attributable to the technology in terms of control of BXW, increased banana production, control of soil erosion and promising increase in income.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology useful to the community and is easy to learn. |
| Encouraging results in terms of improved productivity and general performance of banana and other crops like coffee within the technology area attributable to use of technology. |
| The technology has made significant achievement in terms of decrease of BXW infestation. |
| Soil health has improved as the result of use of mulching materials, manure, leguminous plants and application water harvesting cross slope barriers. |
| There is positive change of mind set towards the use of SLM |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Good and attractive crops that consumers are willing to purchase at a high price have resulted to emergence of thieving. | Spread the technology and supply improved banana suckers to other farmers so that more farmers are engaged in banana production. Strengthen community police. |
| The technology initially is labour and capital intensive | Encourage group working spirit. |
| Unplanned Changes of service providers which may fall in the hands of untrustworthy service providers. | Pluralism in service delivery should be planned with doubly consciousness to take care of untrustworthy service providers. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
25/07/2014
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块