Straw mulching to improve soil quality [西班牙]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Artemi Cerda
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Efecto de la cubierta de paja en la calidad del suelo (spanish)
technologies_1255 - 西班牙
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Universidad de Valencia (Universidad de Valencia) - 西班牙1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
28/05/2015
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
It is a good way to restore land
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
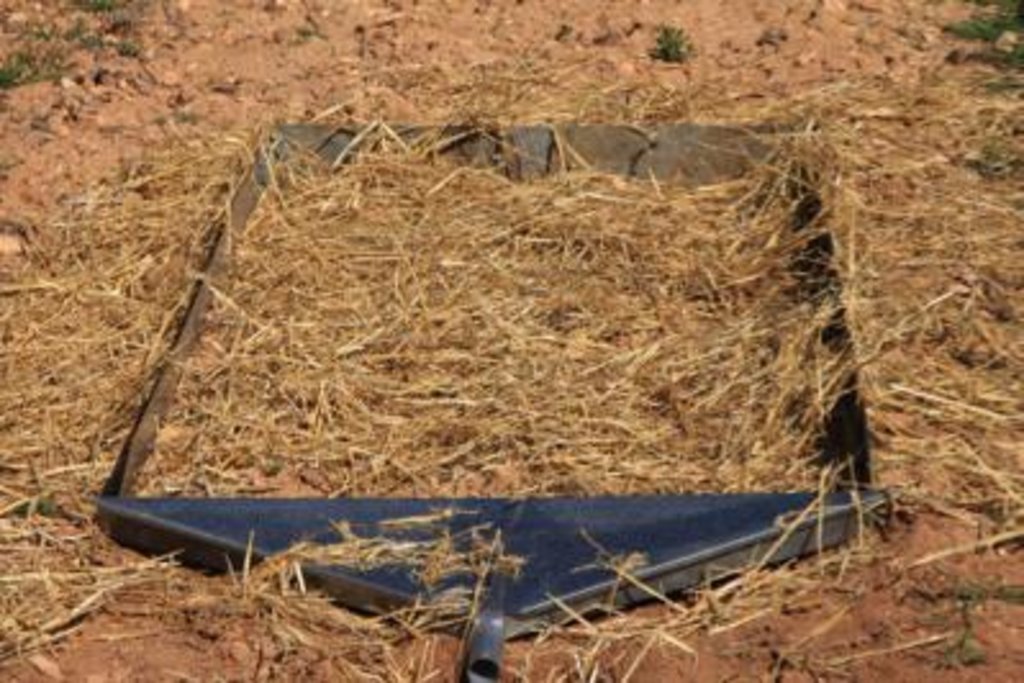
Straw mulch application on bare soil in order to prevent soil erosion, reduce overland flow, and increase soil organic matter.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
In a persimmon crop area near Valencia (South-East Spain), the research team of the University of Valencia has set up an experiment in 2015 to test the effect of the straw mulch technique in order to avoid water erosion and improve soil properties. Straw mulch was applied at a rate of 75 g per m2 and spread over 40 erosion plots (20 treated/20 non-treated). Afterwards, rainfall simulations at 78 mm h-1 of I30 mimic a high-magnitude storm.
The straw provides an initial cover of 60%, and was found to reduce runoff from 60% (in non-treated plots) to 29% (in treated plots), and erosion from 5.1 Mg ha-1 to 0.2 Mg ha-1.
Purpose of the Technology: The increase in ground cover will decrease soil erosion by reducing raindrop impact over the bare soil. Runoff also decreases by increasing water surface storage, decrease of runoff velocity, and increase infiltration.
Its application must to be done before high-storm events in the Mediterranean; namely end of summer to early autumn, in order to protect raindrop impact and avoid detachment of bare soil.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The straw mulch was delivered from a nearby farm in straw bales and was manually applied to the research plots.
Natural / human environment: The wine production in the area was implemented by old civilizations. Nowadays, vineyards production is spread over the entire study area, together with new plantations of persimmon, apricots, olives and oranges. The landscape reflects the long history of management where several constructions related with wine production depicted its importance on this region. Since the late 1960s, conventional agriculture with fertilizers and herbicides has led to a seasonally bare soil surface, triggering huge erosion rates.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
西班牙
区域/州/省:
Spain
有关地点的进一步说明:
Valencia district
注释:
Specify the spread of the Technology:
evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
< 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 水果和坚果
- 其它森林产品
- grapes, persimmon, apricots, olives and oranges

不毛之地
具体说明:
shrub vegetation: quercus ilex, quercus coccifera, pistacia lentiscus, rosmarinus officinalis; Grass species: brachypodium retusum
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Increased runoff and soil erosion, resulting in a decrease of on-site fertility, water reservoir, and weakness of hydrological soil properties.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of water-soil resources and productivity.
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
The landscape reflects the long history of management where several constructions related with wine production depicted its importance on this region. Since the late 1960s, conventional agriculture with fertilizers and herbicides has led to a seasonally bare soil surface, triggering huge erosion rates.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: yes, change due to diminish herbicides application, and minimize bare soil exposition.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180, Longest growing period from month to month: February to July
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
注释:
Causes of degradation: soil management, crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
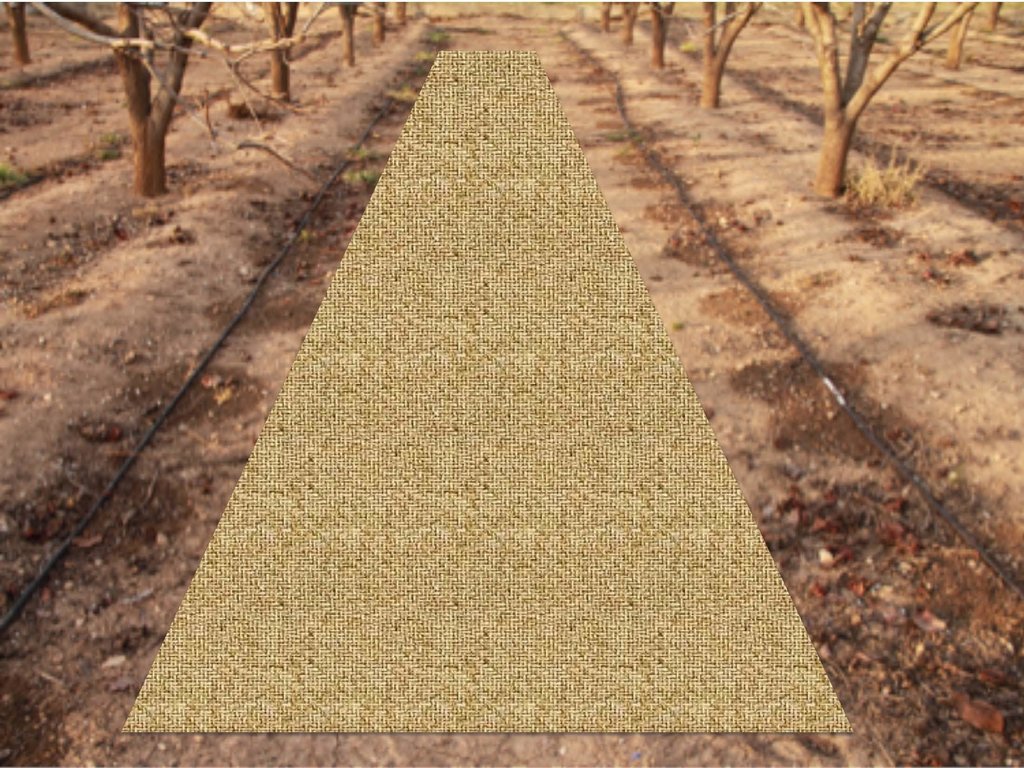
Straw mulch must be spread homogeneously in bare soil areas between trees lines in order to keep as much as possible the soil covered.
Location: Canals. Valencia, Spain
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (It is easy to implement)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Mulching
Material/ species: SPRING BARLEY
Quantity/ density: 75g/m2
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2%
Change of land use practices / intensity level: yes, change due to diminish herbicides application, and minimize bare soil exposition.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
ha
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
800.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
80
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Apply straw mulch (75g/m) | 农业学的 | summer |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Straw | Kg | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The price of straw varies, depending on the quality. Transport and application will increase the cost.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Dry spells of 3 months (june, august, september)
Other rainfall annual averages are 250-500mm (ranked 2) or >250mm or 750-1000 mm (both ranked 3)
农业气候带
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: excess, poor/ none (surface water is only available when rains. Heavy rains produce overland flow)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Only trees on cultivations and anual herbs and grasses.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
木材生产
生产故障风险
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
经济差异
工作量
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
注释:
Mulch is seen as an expensive treatment without any advantage.
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
Comments on adoption trend: The owners are not aware because of the costs, but they will change if the government start funding it.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It will prevent soil losses and promotes soil organic matter incorporation. High levels of soil moisture will prevent for drought periods. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It is a technology very easy to apply, with low failure possibilities and a strong soil erosion control and local soil properties improvement. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The costs are not very high, but enough to discourage the landowners to cover the expenses. | Look for Government funding. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| When applying high-density mulches the application labours will be higher. High decomposition rate. | Distribute the mulch in strips, and try to reduce the application rate. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块