Vegetable Terracing [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1289 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Agriculture-Region VIII (DA-8) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Benguet State University (Benguet State University) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
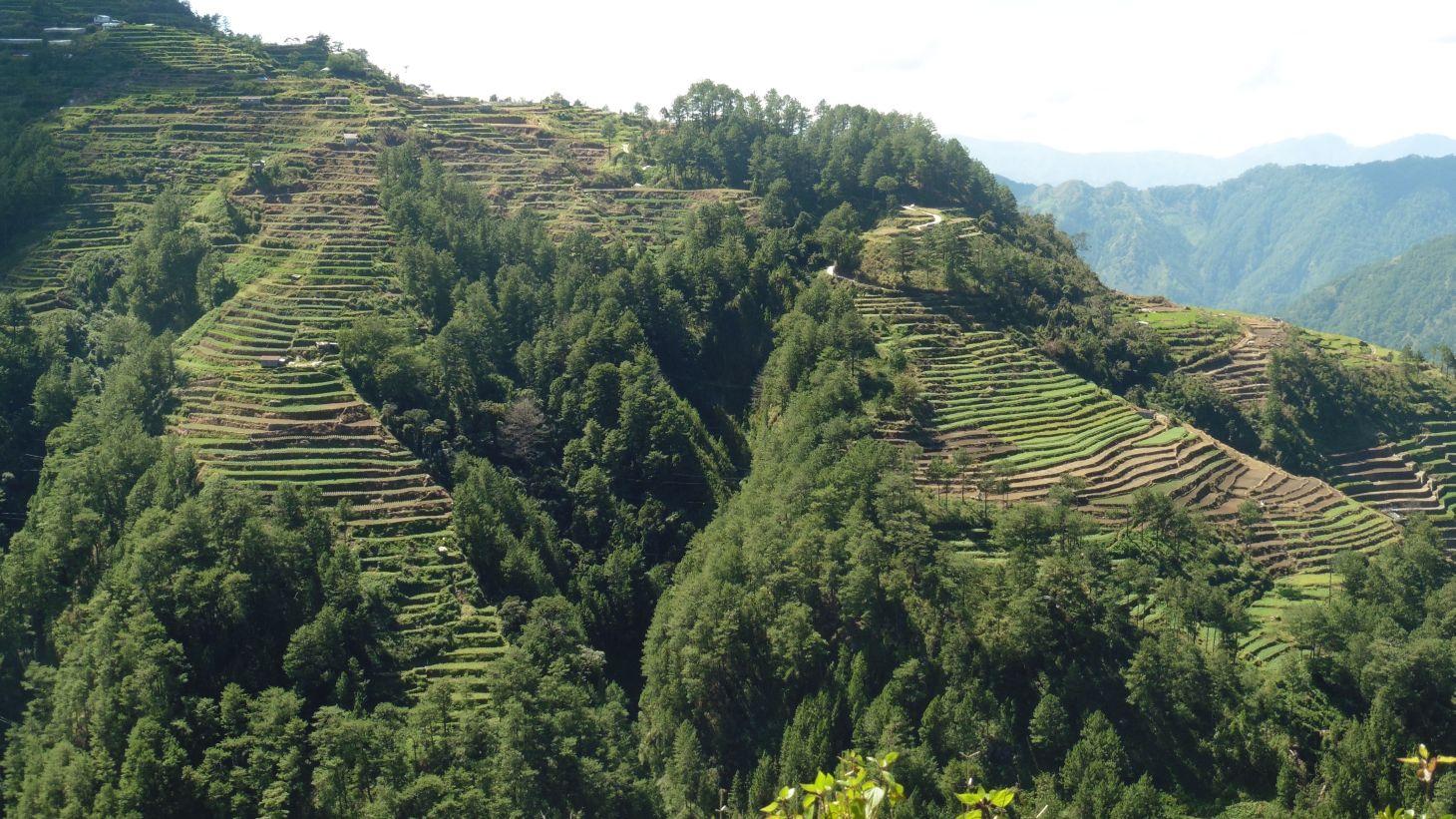
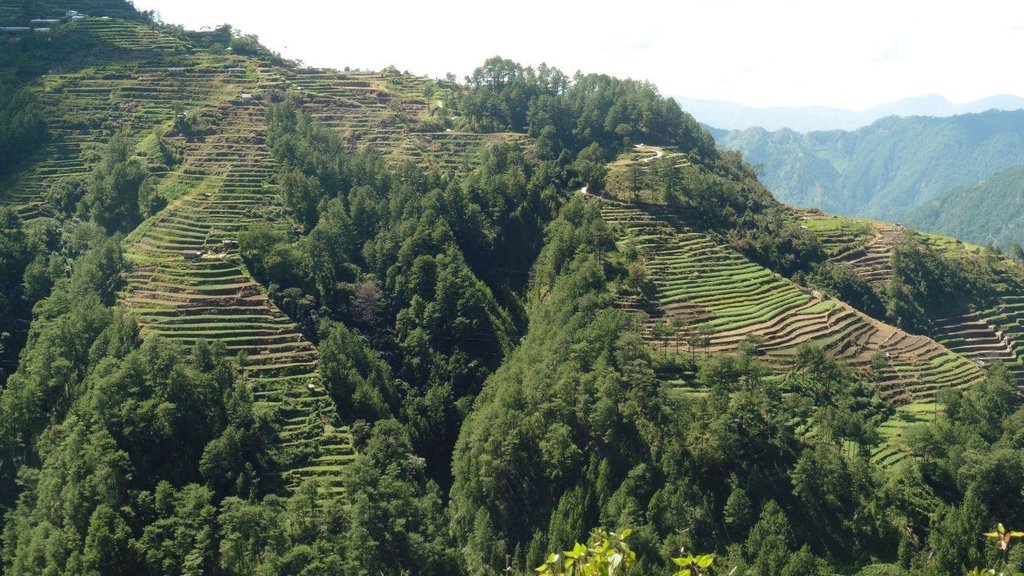
Vegetable terracing is a technology practiced at which point terraces are established from the contours along mountain slope for crop production.
2.2 技术的详细说明
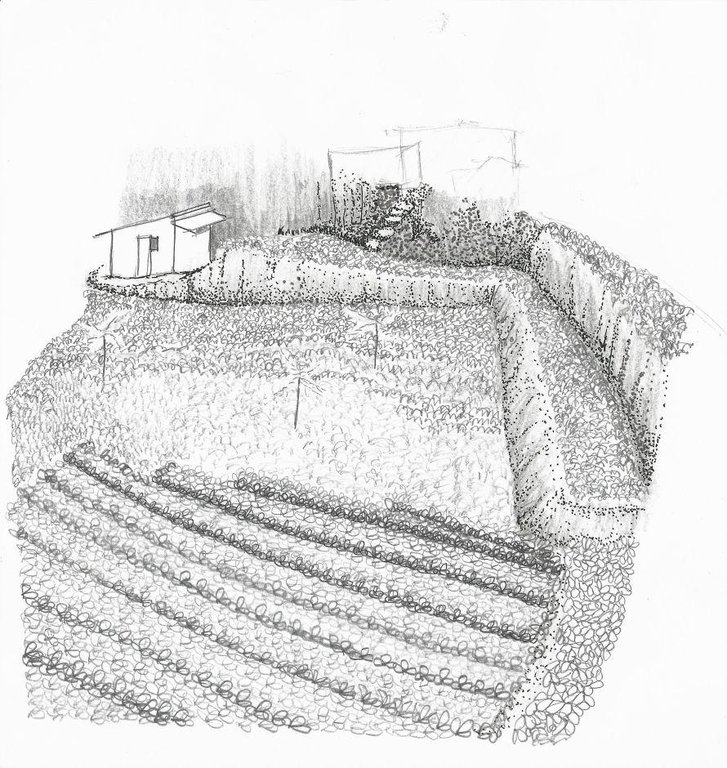
说明:
Vegetables are mostly produced in the mountains of the Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR). It is extensively practiced in the Municipalities of Atok, Buguias, Mankayan, Kibungan, Bakun, Kabayan in Benguet; Bauko in Mountain Province and Tinoc in Ifugao. Benguet is known as the "Salad Bowl of the Philippines" and major producer of temperate vegetables. This is mainly due to the climatic condition of the province which is suitable for vegetable production.Vegetable industry in Benguet is very vital in the country since it supplies 60-70% of the total sub-tropical vegetables in the Philippines. Major vegetable crops grown are potato, cabbage, chinese cabbage, carrots, chayote, beans, lettuce and broccoli. These are sold to traders, consolidators, wholesalers who transport the produce at the La Trinidad Vegetable Trading Post or other local markets in the region.
Purpose of the Technology: Available arable lands are not expanding but the population is increasing. This situation contributes to the conversion of sloping areas to a suitable land for agricultural production,thus, the technology was developed. This had become an economic practicality to the land user as source of livelihood and income. Vegetable terracing is also a conservation measure to minimize soil degradation by varying the terrace type and plot orientation. Some follow the contour while other plots are parallel to the slopes.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Prior to terrace establishment, vegetation is partly removed. Residues are cleared for the establishment of the contour lines of the area. From the established contour lines, terraces will be graded and leveled depending on the slope of the area. Most of these activities are done manually. After the establishment of the terraces, land preparation is done followed by planting of the vegetables.
Natural / human environment: The area is under humid agro-climate condition with an average annual rainfall of approximately 1000-1500 mm per year. Its elevation ranges from 2000-2500 meter above sea level. Majority of the population is dependent on agricultural activities as their source of income and livelihood. The average farm size of the land users ranges from 0.5 to 1 hectare. Most of these lands are not owned by the farmers but have a tax declaration. These are owned by the government classified as forest reservations or watershed areas.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Atok and Buguias
有关地点的进一步说明:
Benguet
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
This technology is widely practiced in the municipalities of Benguet.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was inherited from ancestors who started it during 1960's.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
注释:
Major cash crop: cabbage, carrot, potato
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): low productivity, intensive land cultivation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion, decreased soil fertility and excessive chemical inputs
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
注释:
Forests / woodlands: Fn: Natural
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

结构措施
- S1:阶地
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: contour planting / strip cropping
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Excessive chemical inputs)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
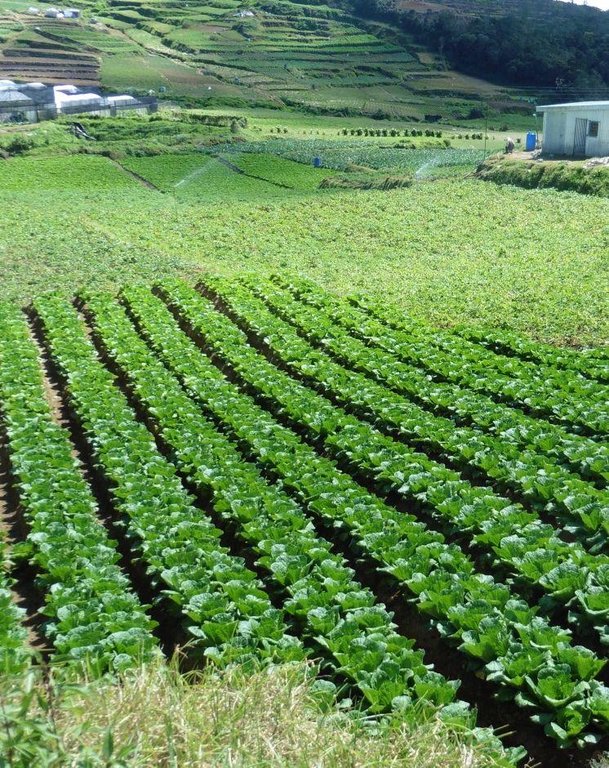
Vegetables planted in raised beds.
Location: Buguias. Benguet
Date: 11-13-15
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Cabbage
Quantity/ density: 40 tons/ha
Agronomic measure: contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Carrots
Quantity/ density: 20 tons/ha
Agronomic measure: contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Potato
Quantity/ density: 20 tons/ha
Structural measure: terrace: forward sloping (earth and stone)
作者:
Mr. Patricio A. Yambot, Bureau of Soils and Water Management
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3.33333
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establishment of terraces |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Building terraces | Persons/day | 120.0 | 4.44166666 | 533.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | tools | pieces | 2.0 | 6.666666 | 13.33 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 546.33 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 546.33 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land Preparation | |
| 2. | Application of chicken manure | |
| 3. | Planting | |
| 4. | Side raising including application of fertilizer | |
| 5. | Weeding | |
| 6. | Spraying of insecticide | |
| 7. | Harvesting |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Land preparation | Persons/day | 30.0 | 3.3333333 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Planting | Persons/day | 15.0 | 3.333333 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Applying Fertilizer and sprying insecticide | Persons/day | 31.0 | 3.333333 | 103.33 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Weeding/Harvesting | Persons/day | 18.0 | 3.333333 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 11.11 | 11.11 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Inseciticides | litres | 2.5 | 13.156 | 32.89 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | bags | 7.0 | 26.66714 | 186.67 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Chicken manure | bags | 15.0 | 5.5553333 | 83.33 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 627.33 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 627.33 | |||||
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 2375 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility low: Needs high fertilizer input
Soil drainage / infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: from river pumped in the farm through gravity
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 2%
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
Market orientation of production system: Products were delivered to the La Trinidad trading post
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 1-2 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
生产故障风险
生产区域
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
娱乐机会
社区机构
Livelihoods and human well-beeing
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
土壤
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Natural vegetation such as forest is partially reduced for vegetable production
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
缓冲/过滤能力
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
NA
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Source of livelihood for the land users in the mountainous area. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It should be balanced by relevant environmental protective measures and alternative farming systems such as agroforestry. |
|
Minimize soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Construction of Small Water Impounding System (SWIS) and proper drainage canal. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Vegetation is partially removed for vegetable production. | Protection of remaining areas through regulations and implementations of related policies. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块