Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Christian Rumbaur
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
膜下滴灌 (Chinese)
technologies_1305 - 中国
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: March 9, 2017 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: March 9, 2017 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: April 4, 2018 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: March 13, 2019 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Müller Joachim
University of Hohenheim
德国
SLM专业人员:
Zia-Kahn Shamaila
University of Hohenheim
德国
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Sustainable Management of River Oases along the Tarim River, China (SuMaRiO / GLUES)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Universität Hohenheim - 德国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Drip irrigation under plastic mulch, associated with drainage, to reduce water demand and improve cotton yields in Xinjiang Province, China.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
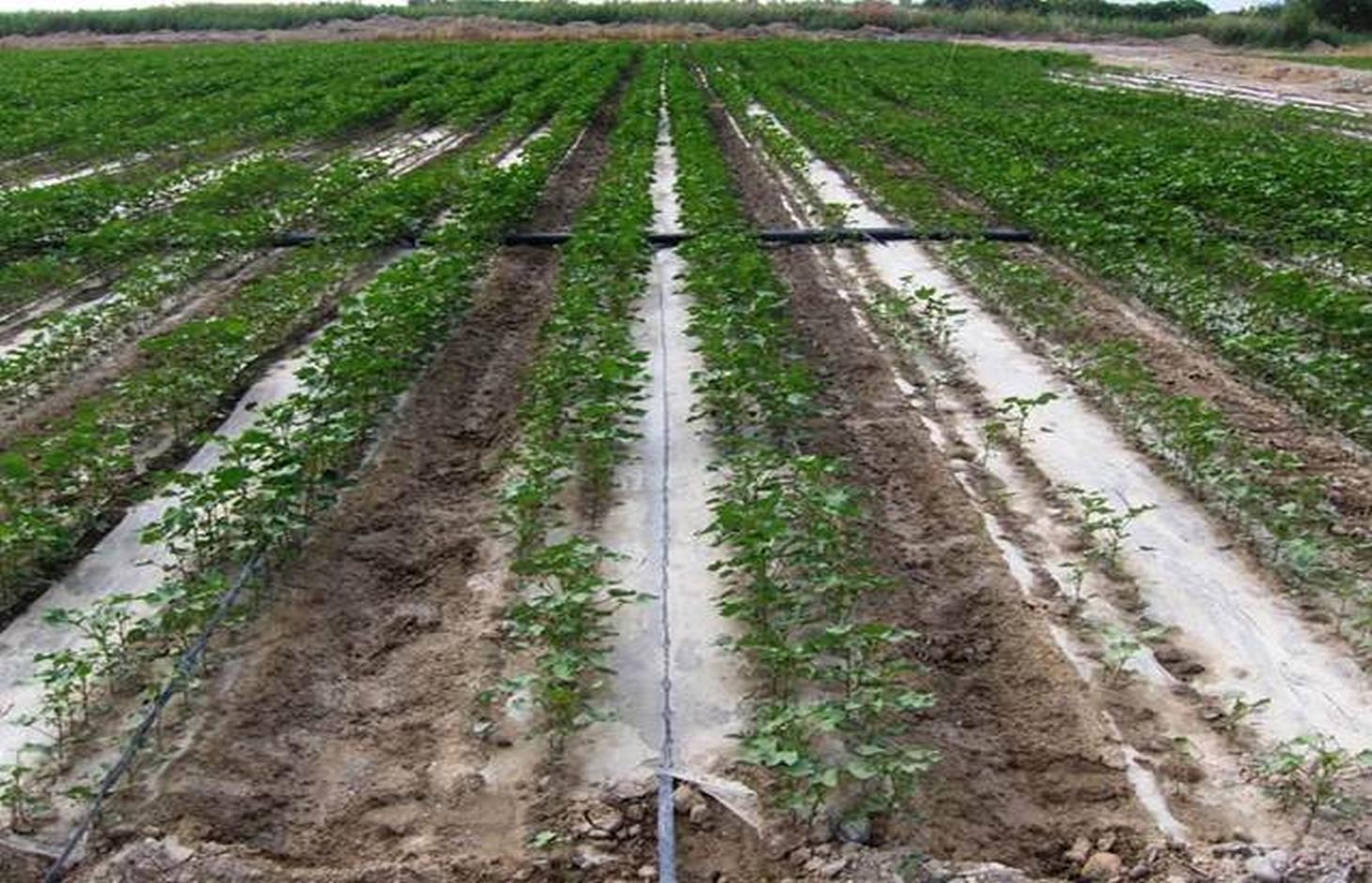
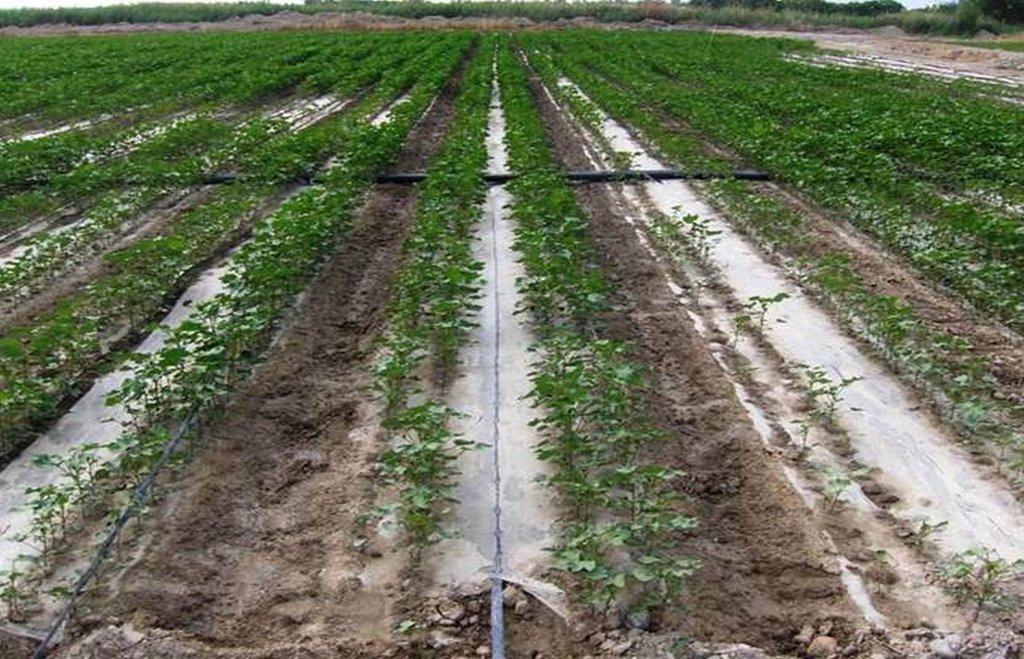
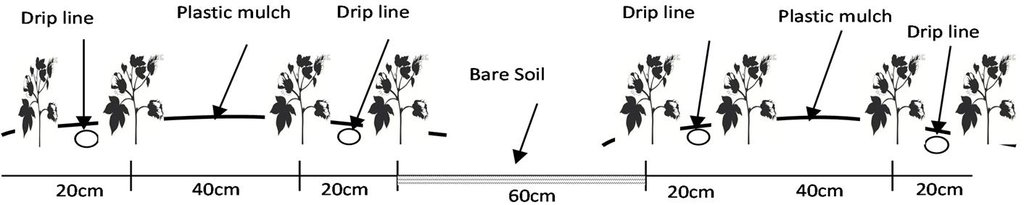
The dry climate and the long hours of sunshine make Xinjiang especially suitable for production of high quality cotton, and as a result some 40% of China’s cotton is grown here. But there are two main problems: shortage of water and salinization of the soil. Farmers who use the traditional flood irrigation method, and don’t have a drainage system, tend to abandon their fields when they become too saline - and then they look for new land to cultivate. A combination of mulching and drip irrigation can be very effective but still needs careful management. Drip irrigation helps to save water for farmers - and for the environment. But it is still very important to install a drainage system to dispose of surplus water in order to reduce the risk of salinization of the soils. Every four cotton rows are covered with transparent polyethylene film and as a result approximately 80% of the ground surface is covered by the plastic mulch. Plastic mulch and drip lines are placed with a specially equipped tractor.
Purpose of the Technology: Low temperatures and dry soil at sowing, in combination with soil salinity, hinder early plant growth. Plastic mulching increases soil temperature, reduces the need for irrigation, and also helps control salinity in the root zone and suppresses weeds, thereby increasing yields by 10–30% (and improving quality also) (Wang, R. et al., 2011). In the first stages after sowing the climate is particularly cold. With plastic mulching the cotton plants can be sown earlier, because the soil will not cool down during the night as much as without plastic mulch.
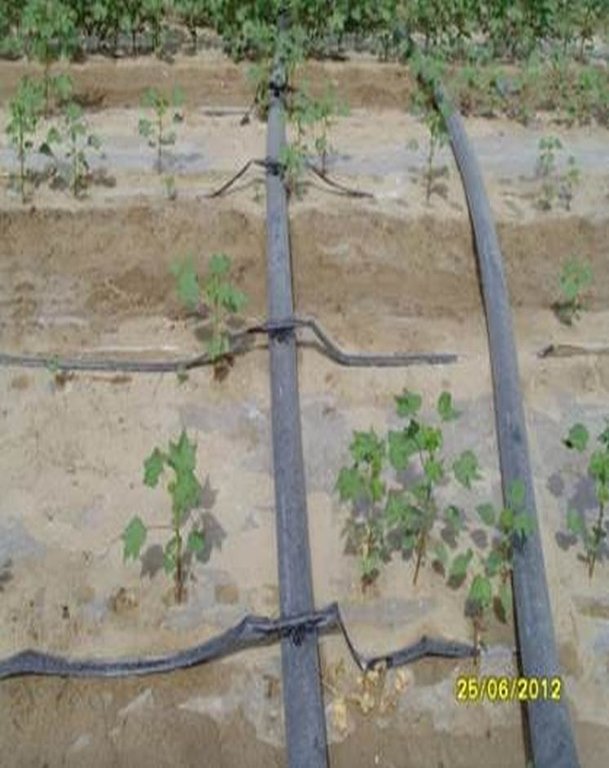
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of the new technology of drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is simultaneously essential to install a drainage system to avoid raising the groundwater level and causing salinity. For the installation of the drip lines, the transparent plastic film and the seeding, a tractor and a special tool for the installationis needed: one acre can be installed in a day. After the emerging of the cotton plants, holes must be cut in the plastic film so that the cotton plants can emerge. After harvesting, the drip lines and the plastic film must be collected and recycled. If the plastic is left behind it will pollute the soils and injure livestock if they eat it. Furthermore plastic residues in the soil can reduce subsequent yields, as roots are physically inhibited. After the collection of the plastic residues, if there is no adequate drainage system, the field needs to be flooded to flush the salt layer, which has accumulated below the root zone, deeper into the soil. If the field is not flooded the salt will negatively affect the next years’ cotton plantation.
Natural / human environment: Southern Xinjiang is an arid region with 50 to 90 mm per year. Most precipitation occurs between June and August. It is classified as a temperate cold desert climate. For drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is principally surface water that is used, which is delivered to the field via channels from reservoirs to the fields. The reservoirs are filled in summer with the floods along the Tarim River. The untreated surface water is of poor quality - for agricultural use only. For drip irrigation, the water needs to be treated to avoid blocking the drip outlets. The overall technology is expensive, and only land user groups and communities can afford the machines and the materials.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
China / Xinjiang Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Tarim River Basin
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- > 10,000 平方千米
注释:
It might be used also in other provinces. But this not known to the author.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
注释(项目类型等):
It is not clear how the technology was invented.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 纤维作物 - 棉花
- wheat
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 水果、其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: March to October with irrigation
注释:
major cash crop: cotton
major food crop: wheat
other: fruit trees
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water use conflicts between agriculture and natural vegetation, soil salinization, desertification.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil salinization and water shortage.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: water availability, evaporation
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 引水和排水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M4:活动时间安排的重大变化
- M6:废物管理(回收、再利用或减少)
注释:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化

物理性土壤退化
- Pw:水浸

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pw: waterlogging
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Most fields have no drainage - Increase of groundwater - salinization of soils), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (cotton monoculture), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation to gain new arable land), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), wind storms / dust storms (Dust storms, blow out of top soil), droughts (It is an arid climate), population pressure (Doubling of population during the last thirty years.), land tenure (Land belongs to the state), poverty / wealth (Family farmers are poorer than city dwellers), education, access to knowledge and support services (Poorer farmers have less access to extension services.)
Secondary causes of degradation: industrial activities and mining (There is oil production in the region, but it was not studied), discharges (point contamination of water) (Non-point source pollution and drainage water discharge from the fields.), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (use of surface and ground water for large scale irrigation), floods (Floods are necessary for the region (riparian forests))
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
There are double rows of cotton 20 cm apart, with a drip line between. 40 cm then separates each double row. Two double rows are covered by one length of plastic mulch. There is a small strip of bare soil between each length of plastic mulch. Mulch covers around 80% of the soil surface.
Location: Korla City. Xinjiang Province / China
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (For the easy and fast installation a tractor is needed)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of biomass (quantity), increase of water use efficiency
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Mulching
Material/ species: transparent plastic (Polyethylene), thickness: 0.08 mm
Quantity/ density: 7100 m/ha
Remarks: 1.4 m width in lines with spacing of 20 cm between lines
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Change from flood irrigation to drip irrigation
Major change in timing of activities: Plastic mulch enables early sowing of cotton
作者:
Shamaila Zia-Khan
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tractor | |
| 2. | Drip line installation, plastic mulch and seeding tool | At sowing |
| 3. | Making holes for the (cotton) plants in the plastic mulch.Maintaining hoses | After emerging |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Drip line installation | ha | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tractor | Piece | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | seeds | kg | 30.0 | 3.0 | 90.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Plastic mulch | 1.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 50.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Black dripe lines | Set | 1.0 | 380.0 | 380.0 | 50.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 5510.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 5510.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.33 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing and leveling of field. | Before sowing |
| 2. | Irrigation | |
| 3. | Removal of the drip lines and the plastic mulch |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Collecting mulch | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 98.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Irrigation and flooding water | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 13.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 13.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: tractor with installation tool for the drip irrigation under plastic mulch, other tools: hoe
The costs for the machine, the plastic hoses and the plastic mulch are calculated above are for 1 ha and were calculated on the basis of 2013 (subsequently costs have risen). Water price: 0.019 CNY/m3. Farmers need 3000 m3 per ha.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
90 mm per year. Jan, Feb, Apr and May: 3 mm; Mar, Sept: 5 mm; Jun: 33 mm; Jul: 18 mm; Oct: 0 mm; Dec: 8 mm
农业气候带
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate. cold desert climate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: altitudes of 800 to 1300 meters
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: medium high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: also < 5 m and the installation of drip irrigation under plastic mulch should be installed with a drainage system. If the groundwater table is too high salinisation of the soil will be the result
Availability of surface water: For the drip irrigation under plastic mulch mostly surface water is used. It is diverted by channels to the agricultural fields. There must be a good water availability at the fields.
Water quality (untreated): For the drip irrigation under plastic mulch the water quality must be quite high, otherwise the small holes of the drip lines will be blocked soon.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
- 非常丰富
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Man are doing the earth works in the fields, women do more the harvesting
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 7%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land (income from large fields of cash crops).
20% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land (income from cash crops (fruits, cotton)).
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (income from cash crops (fruits, cotton)).
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers who have not implemented the drip irrigation under plastic mulch also generate off-farm income.
Manual labour: harvesting
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
5-15 ha: state farms
< 0.5 ha: family farmers
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 租赁
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 租赁
注释:
All the land belongs to the state. Farmers have the right to use the land for 70 years.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
15% of more cotton yield
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
社会文化影响
社会经济弱势群体的情况
Livelihoods and human well-being
生态影响
水循环/径流
蒸发
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
盐度
其它生态影响
salinization below root zone
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
No number on households
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The government gives subsidies to the farmers who are installing the drip irrigation under plastic mulch.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The government want to spread the technology in the whole region by giving subsidies to the farmers.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
helps to save water thus saves costs. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It is subsidies by the government. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It helps to save water during the vegetation period and thus helps to reduce the conflicts between the upstream and downstream farmers. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology (drip + mulch) needs to be supplemented by installing a drainage system in the fields otherwise there will be a build-up of salinity and farmers will abandon land and move on. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Salinization of the soils is increasing The consequence is that the fields are flooded after harvest in November/December to leach out the salt. The water used for drip irrigation plus the water to flush the salts to lower soil layers add up to almost the same amount as if farmers were using the original flood irrigation technology. | drainage system in the fields required. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Zia-Khan,S., Spreer, W., et al. Effect of dust deposition on stomatal conductance and leaf temperature of cotton in Northwest China.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Water 2015, 7, 116-131; doi: 10.3390/w7010116. www.mdpi.com/journal/water open access.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块