Gully healing using trash lines [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Patrick Gervas Mbanguka Lameck
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Kingamaji la nyasi
technologies_1393 - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Inades Formation Tanzania (Inades Formation Tanzania)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Gully healing using trash lines reinforced by pegs
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
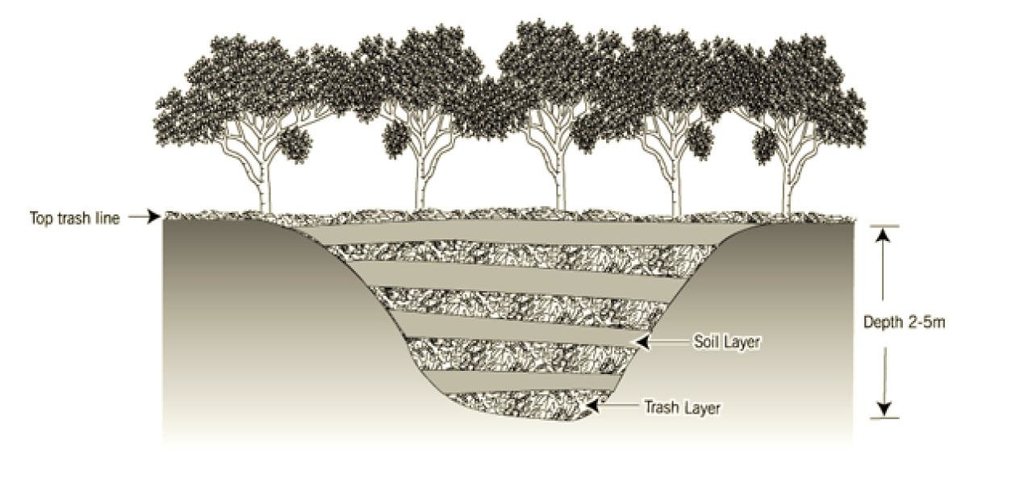
The starting point is to form a layer of trash and soil across the bed of the gully (a typical gully here is 3-10 m wide, and 2 m or more deep), reinforced with
pegs, and to build this up gradually in layers as sediment is captured behind it. On top of the barrier a dense line of mikayeba (tree cassava: Manihot glaziovii) is planted. Trash continues to be added to the nowliving barrier until the gully is fully silted up. The barrier, 1 – 2 metres wide, then appears as a contour line
across her land, and continues to function against erosion. Mikayeba is not just a living structural support: its leaves are also a source of fresh vegetables. Where the gullies are more severe, she is testing cuttings of Commiphora africana.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is reclamation of land from gullies for plant production. Impact is achieved through impeding concentrated runoff and capturing sediment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The treatment does not end with sedimentation of the gully bed. The land is left fallow for one to two seasons. Then, late in the first or second season, the farmer digs in the young volunteer vegetation as a green manure, and plants a ‘catch crop’ of maize. If it produces cobs, well and good. If not, she feeds the
plants to her stall-fed cows. The main maintenance aspect is the continuous addition of soil/trash layer upon previous layers, and tending the living barrier to maintain its density. Maintenance, as well as original establishment, requires
only common farm/household tools including hoes, spades, sacks and pangas.
Natural / human environment: Grace is in her early 50s, and though her farm of 3 hectares is not larger than normal, her homestead buildings indicate that she is rather above average in terms of wealth. This is something she has achieved through her own efforts. Grace has become the main farmer in the family. Her husband is a retired
teacher and professes no interest in developing the land further. In 1982 Grace acquired, and decided to reclaim, some badly gullied land.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
有关地点的进一步说明:
Dodoma/Dodoma rural
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
farmer innovation
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小米
- 谷类 - 高粱
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豌豆
- 油料作物 - 花生
- pigeon peas
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
- Manihot glaziovii
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Dec - Apr
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): formation of new gullies and expansion of the existing ones
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): same as above
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施

结构措施

管理措施
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, management measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Cross-section through a healed gully
Tanzania
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, increase in organic matter
Structural measure: other
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 20
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Construction material (earth): layer of earth line 0.3m thick
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2.00%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2.50%
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.90
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | putting atrash line on the gully bed | establishment |
| 2. | establishment | establishment |
| 3. | putting layers of soil | establishment |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Establishment | persons/day/ha | 821.0 | 1.9 | 1559.9 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 10.6 | 10.6 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1579.5 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1579.5 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | replace the decomposed trash | before rains/each cropping season |
| 2. | incorporate the trash | before rains/each cropping season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Replace and incorporate trash | persons/day/ha | 51.5 | 1.9 | 97.85 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 10.6 | 10.6 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 117.45 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 117.45 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: hoes, spade, matchet and sack
labour hired
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
gully depth and slope
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
- 干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Also rolling and hilly
Landforms: Also mountain and footslopes and valley floors
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Also moderately deep
Soil fertility is low, medium and very low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low - medium
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: local brewing making, charcoal burning, beekeeping and ornament making
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
木材生产
生产区域
收入和成本
农业收入
其它社会经济效应
area of gullies
社会文化影响
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
85
SLM之后的数量:
40
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
其它生态影响
soil fertility
biodiversity
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
4 households covering 10 percent of stated area (1 percent of all households)
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
4 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: production of good crops by the gully attract other people
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| same as above |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
suited to local conditions How can they be sustained / enhanced? select more durable materials. |
|
improves soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? grow vertiver grass in the upper sections |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| takes too long before the returns | grow crops as live barriers |
| tough job | make use of improve tools |
| conflict with livestock keepers | make use of local administration to arbitrate |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
1st farmers innovation workshop report
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
INADES tanzania
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Kithinji M., Critchley W. 2001. Farmers' initiatives in land husbandry: Promising technologies for the drier areas of East Africa. RELMA Technical Report series no. 27
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块