Combined cut-and-carry and fruit-production system with terraces [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Christian Wirz
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Зина бох (tajik for terrace garden)
technologies_1406 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - 吉尔吉斯斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

State-controlled research territory for orcharding [塔吉克斯坦]
Cultivation of an orchard with research activities and research staff with food for work.
- 编制者: Christian Wirz
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
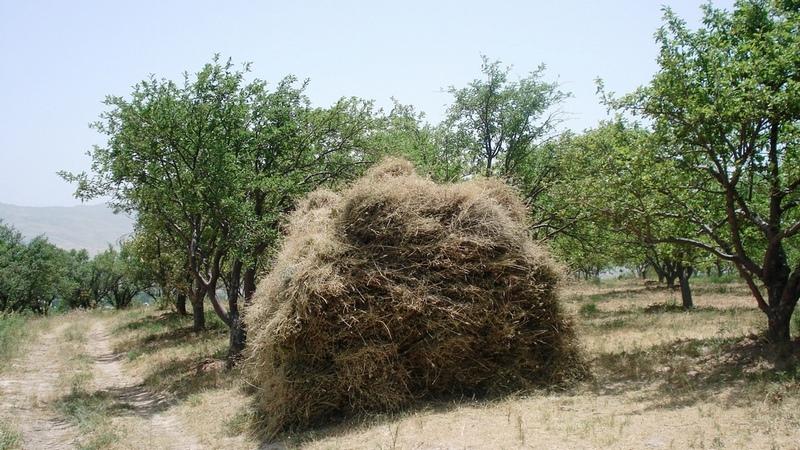
A combination of fruit- and nut-trees together with seminatural trees and shrubs on one side with grass-communities on the other side provide for a diversified production system.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Fruit- and nut-trees give the production system the characteristics of an orchard, whereas sour cherry trees rather provide for a jungle atmosphere. They spread very quickly once they are planted. Hayproduction substitutes other uses of the lowest vegetation layer, since grazing is forbidden. The whole territory is concipied as a research station.
Purpose of the Technology: In general trees act against erosion: By their stabilising function they prevent soil from being washed out. Especially nut-trees with their 20 to 25 m long roots preserve soil moisture and by that consolidate soil structure. Terraces contribute to this moisture-preserving and production-enhancing function. They are very important in order to make rather steep land exploitable by reducing slope. Haymaking does not damage soils, but is only allowed after the end of June so that grasses can reproduce before.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Both the establishment of terraces and the planting of trees on such a big surface are costly in terms of labour and money. Maintenance means taking care of trees, taking measures against diseases and conserving soil fertility. Fertilisers are very costly and therefore dung has been substituting them in the last years.
Natural / human environment: From the two research stations of the orchard institute - one in the upper hill-zone and one close to the village Karsang - only the second one is assessed. This area is surrounded by two rivers in the West and in the East, with its main exposition to the South. It is in direct competition for irrigation water, especially needed for the trees, with the village. The orchard is situated on a ridge that is in the haymaking area, but is accessible for animals from the village.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Region of Republican Subordination
有关地点的进一步说明:
Faizabad
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 km2.
Of the 70 hectares nearly half of the surface can be considered as unproductive with protective functions against erosion (many sour cherry trees planted).
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
1961 the national orchard institute began with developing a research area in Karsang, which should be further enlarged from 1975 onward.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 水果、其他
- 核果(桃、杏、樱桃、李子等)
- 树坚果(巴西坚果、开心果、核桃、杏仁等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 270 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jul

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
- Access for livestock forbidden.
注释:
Livestock density (if relevant):
< 1 LU/km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main problems are arid conditions and the loss of fertility, mainly by processes of water erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gully erosion by water and wind erosion together with droughts are the main problems. Gullly erosion may also be caused by
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Access for livestock forbidden.
Grazingland comments: People have goats, sheep and cows and 1-2 donkeys, if they can afford.
Type of grazing system comments: People have goats, sheep and cows and 1-2 donkeys, if they can afford.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: post-flooding
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S1:阶地

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pi:覆土

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (According to agronomist and elderly persons steady decrease of rainfall Causing aridification..), droughts (No considerable precipitation for one and a half years. Causing compaction, crusting and aridification.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (The lack of fertilisers and other inputs is a consequence of the breakdown of URSS.)
Secondary causes of degradation: floods (Causing gully erosion and loss of topsoil by water.), war and conflicts (Many trees were chopped illegally during war to have energy (charcoal mines were occupied by armed men)), Unsuitable soils especially in the upper part (loe (Causing compaction, crusting and loss of topsoil by wind.), Steep topography with high sun inclination angle (Causing compaction.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
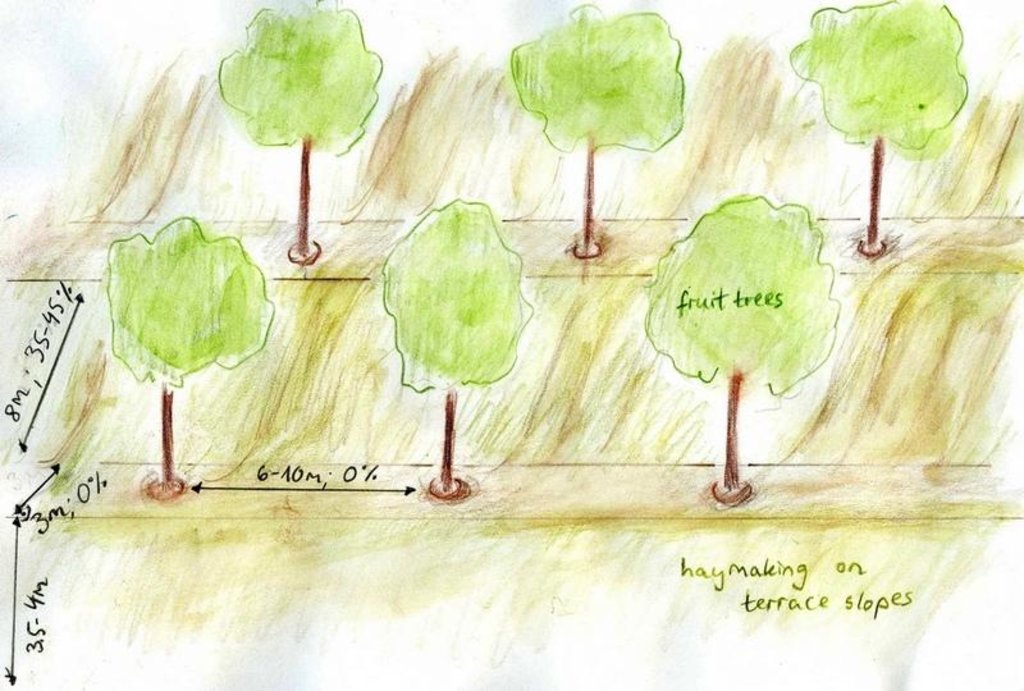
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Terraces with fruit trees.
Location: Karsang. Faizabad / Tajikistan
Date: 25.08.09
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Cutting trees and maintaining tree nurseries)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Fieldwork such as haymaking)
Technical knowledge required for Research coordinator: high (Carrying out of workshops)
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), control of fires, trees protect from snow
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 120
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 9
Trees/ shrubs species: Apple, apricot, almond, walnut, quince, pear, peach trees
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Sour cherries, mostly through vegetative growth
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 45.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Terrace: bench level (earth)
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2.5
Spacing between structures (m): 11
Construction material (earth): endogenous material used
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 33-45%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Strictly regulated haymaking, only after the end of June.
作者:
Christian Wirz, Switzerland
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.70
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of trees with provenance from Russia and Ukraine | Tree plants |
| 2. | Tree-planting, grafting, giving dung | 20 persons for 3 years |
| 3. | Terrace establishment | 2 tractor drivers for 1 year |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Tree planting | ha | 1.0 | 714.0 | 714.0 | |
| 植物材料 | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| 其它 | Terrace establishment | ha | 1.0 | 614.0 | 614.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1428.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1428.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
research stations of the orchard institute
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Yearly replacement of fruit-trees (10-15% per year) | 10 persons plus brigadier, always employed |
| 2. | Aerating soils around trees, each spring | 10 workers, fix employment |
| 3. | Applying animal dung and / or fertilisers | 10 workers, fix employment |
| 4. | Seasonal workers for harvesting | 10 workers, additionally |
| 5. | Planning of activities | 1 director |
| 6. | Haymaking | 1 month |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Maintenance | ha | 1.0 | 93.0 | 93.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 28.0 | 28.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 121.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 121.0 | |||||
注释:
The data on the establishment of the orchard are an estimation of the director. The recurrent costs are based on the director's and other person's declarations and are rather a rough estimation than a precise list of the costs.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The costs today are strongly determinated by labour input, whereas during establishment and till the end of USSR costs for pesticides, fertilisers, new trees and equipment were very high.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
In the long-term average, 600-650 l, but in the years 2007 / 2008 only 200 l, since no rains in autumn.
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zonation: The orchard is located between 1300-1500 m.
Landforms ridges: A part of the area surrounds a ridge
Landforms hill slopes: Generally slopes are of moderate steepness.
Slopes on average gentle: The terraces themselves are quite flat.
Slopes on average hilly: A great share of the area are slopes, either natural ones or from terraces.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average shallow: In the higher part stony soils prevail.
Soil fertility low: When gypsum and loess soils.
Soil fertility medium: In the lower part soils with little humus.
Soil drainage / infiltration good: 3-4 m infiltration capacity.
Soil water storage capacity medium: Thanks to trees not low.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: Insufficient: only permitting to irrigate 5 ha of totally 30 ha classified as "irrigated cropland"
Water quality (untreated): According to expert, water contains iodine, but is otherwise "light" and clean, without calcium carbonate
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Typical plants of the foothills can be found in the area.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land (all smallholders owning additional income by the work for the institute).
Off-farm income specification: Nearly all people have family members (mostly sons) in Russia, who send remittances.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
The employees produce hay on maximally 7 ha.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
Whereas land use rights are restricted to those employed by the research institute, water use is negotiated between the research institute and the village authorities.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
The reason is the decision not to plant wheat anymore, partly because of droughts and partly because of the trees having reached a critical height (shadow).
饲料生产
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Animals eating this fodder give more milk.
木材生产
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
On the neighbour-ridge no irrigation water.
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
Trees require more water than simple pastures, especially in the establishment period.
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Especially fruit production is important, to make jams, dried fruits etc. for winter.
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
The milk is of better quality and leads to less sicknesses
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
The institue is in conflict with the village for irrigation water.
Open-access pasture-area
注释/具体说明:
No strong effect, because it is a research territory.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Is especially a function of cover and infiltration capacity
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Plants are greener and less dusty thanks to moisture
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Plants are taller, wider and denser.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Thanks to strongly reduced erosion, organic matter is conserved
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
Less crusting than without technology, but more than without droughts.
盐度
注释/具体说明:
Due to lacking drainage system
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
More nutrients given, for example by the trees' leaves.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
More than 50 pasture species
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
Forest administration considers the proportion of trees to be one of the decisive factors of fire-risk.
风速
注释/具体说明:
High proportion of trees leads to longer snow cover and thus soil protection in spring
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
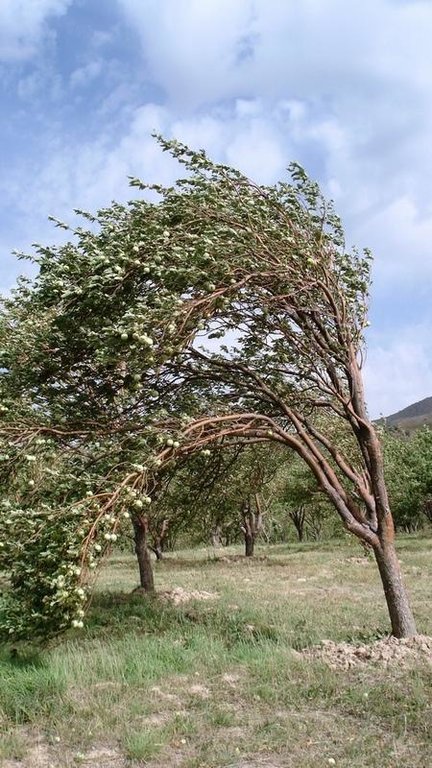
| 局地风暴 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
注释:
No damages by heavy rainfall in the orchard, whereas next to it there is damage. Especially winds cause damages by covering vegetation with dust and impeding them from making fotothynthesis. Plants can die therefore.
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The government wants more people to adopt the technology and their has effectively been an increase of such initiatives over the last years.
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

State-controlled research territory for orcharding [塔吉克斯坦]
Cultivation of an orchard with research activities and research staff with food for work.
- 编制者: Christian Wirz
模块
无模块