Restoration of degraded rangeland [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Klaus Kellner
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Rehabilitation/restoration of an area, after control of alien invasive species.
technologies_1416 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Van Rensburg Leon
南非
SLM专业人员:
Fulls Erich
南非
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Sustainable Land Management Practices of South Africa (SLM South Africa)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
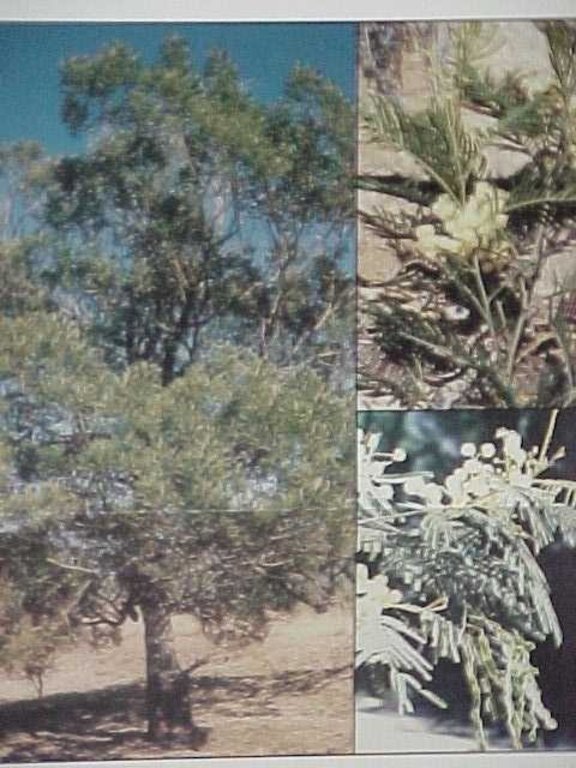
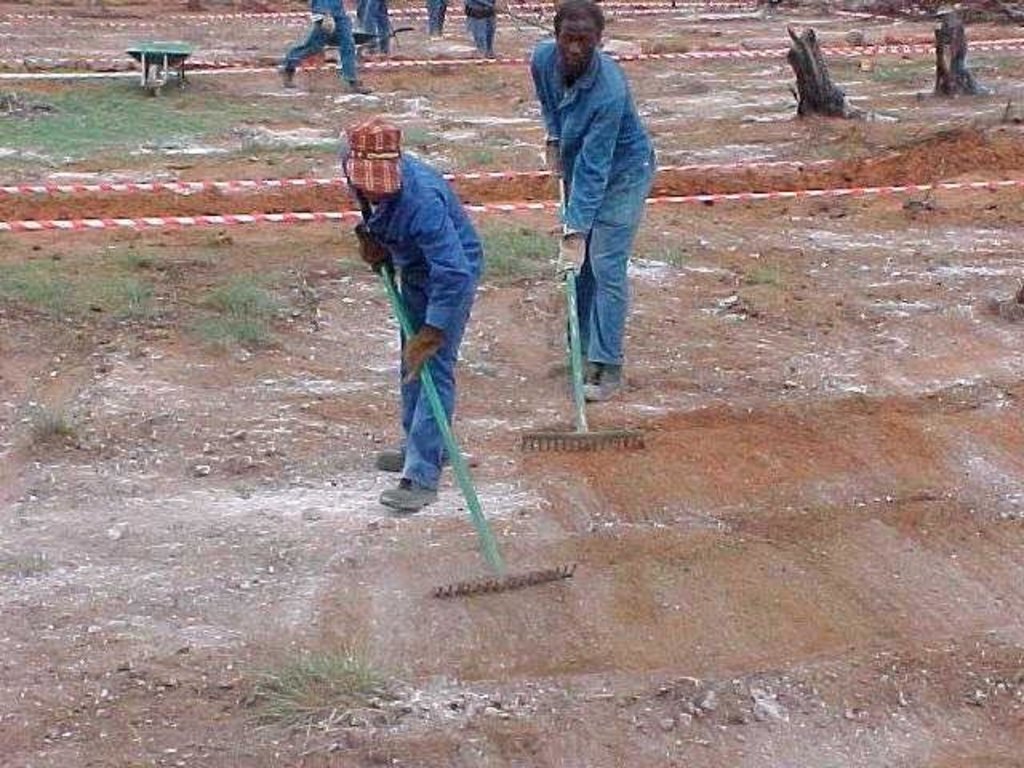
Eradication of invasive species and revegetation of degraded rangelands by different treatments, including oversowing with grass seed mixture, supplementing with lime, cattle dung, and "brush packing" (laid out branches).
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
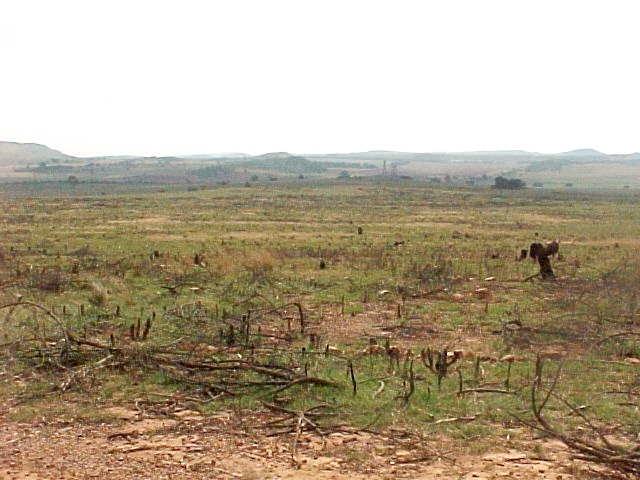
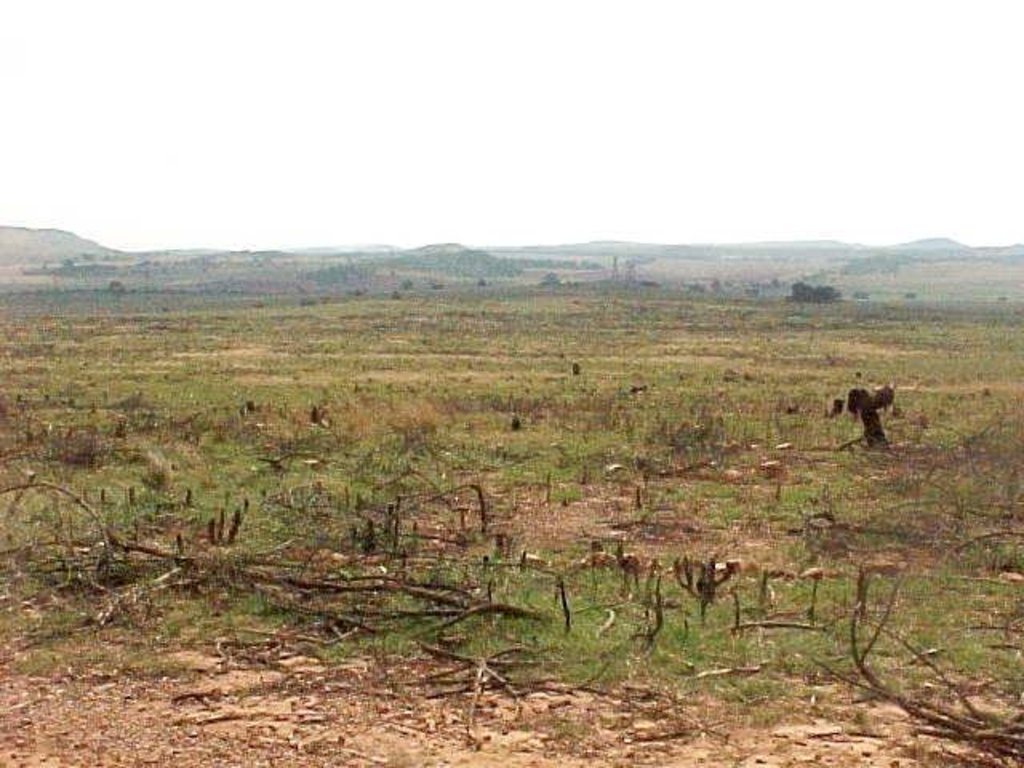
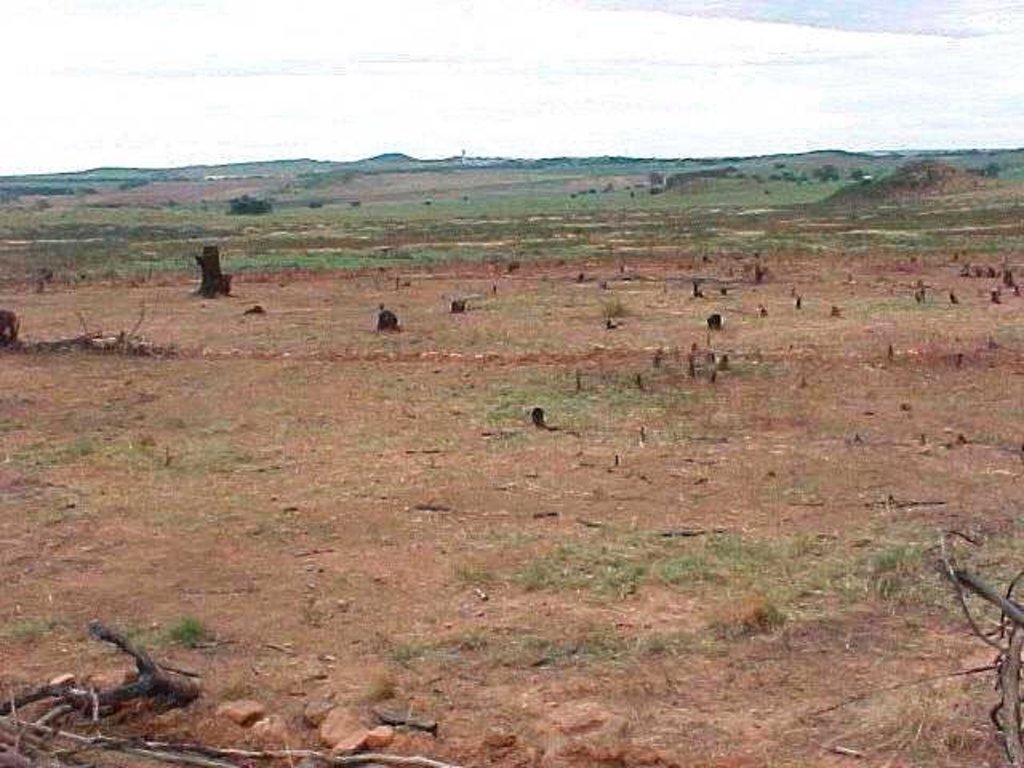
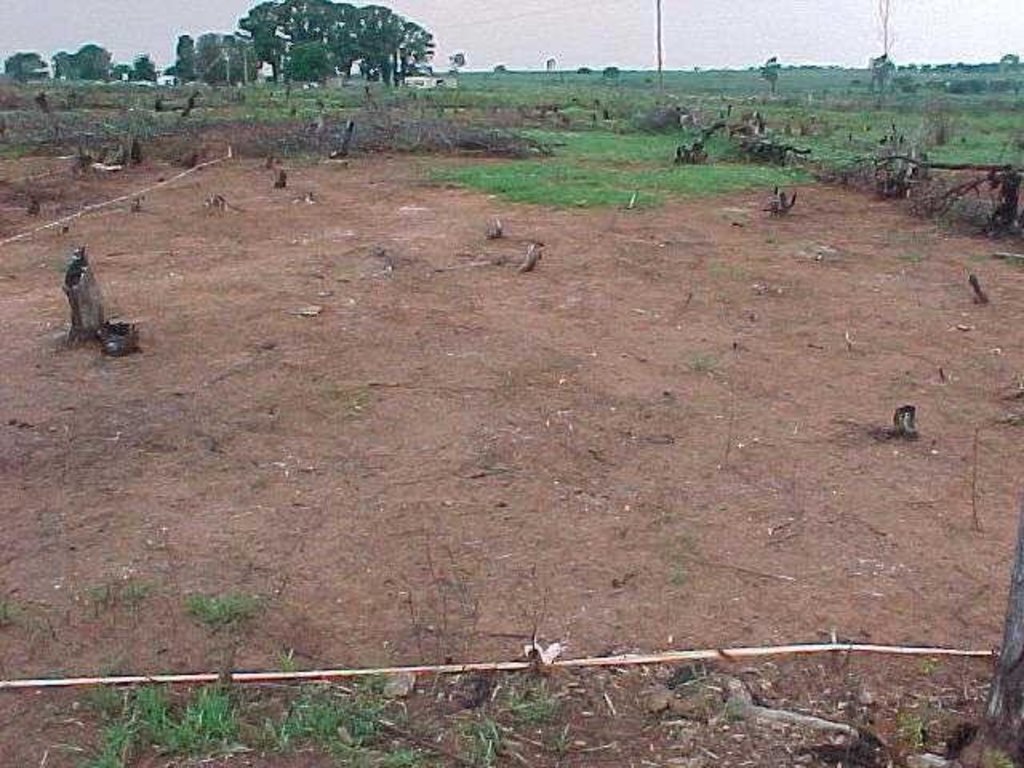
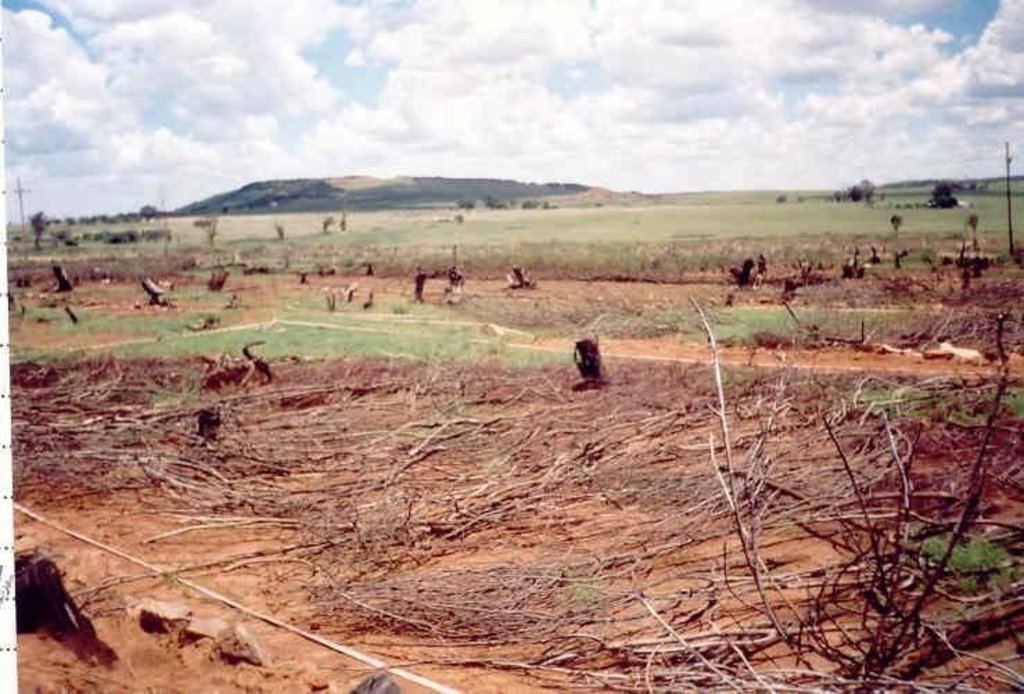
A research investigation was undertaken in an area of degraded communal rangeland, which had been invaded by an alien tree species (Acacia mearnsii – black wattle). Competition from the water-demanding A. mearnsii, combined with overgrazing, had resulted in an almost total absence of palatable grasses. All that was left were a few patches of star grass (or ‘bermuda grass’: Cynodon dactylon). Prior to the research, discussions were held between personnel of the ‘Working for Water’ programme of the South African government and community members.
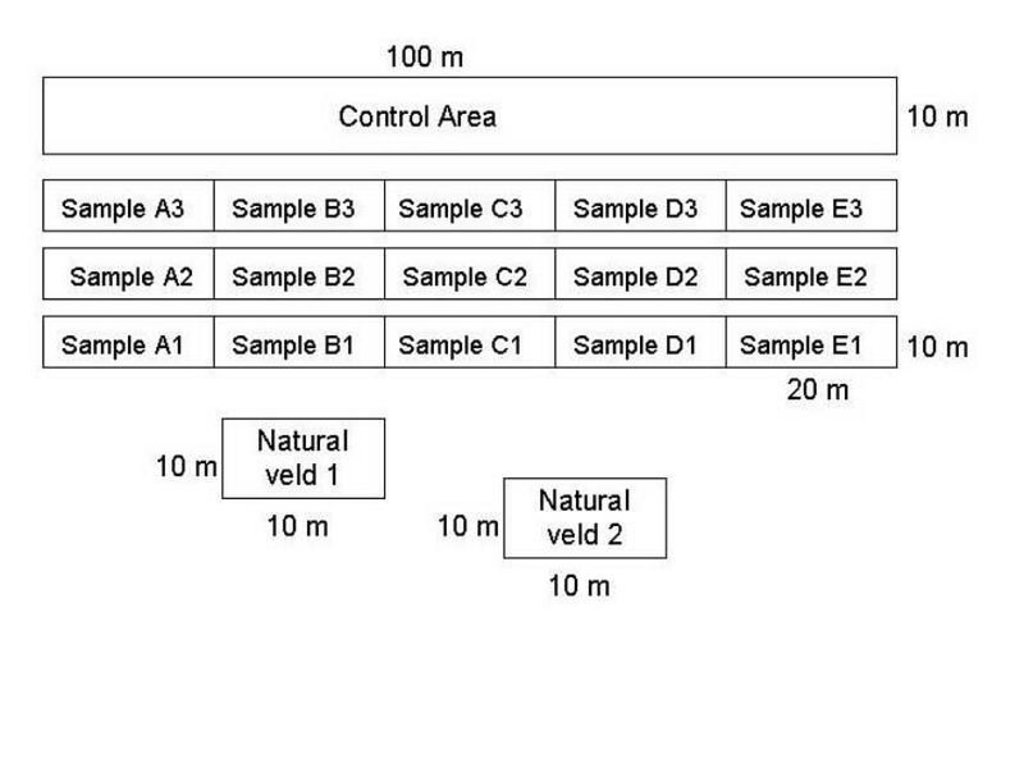
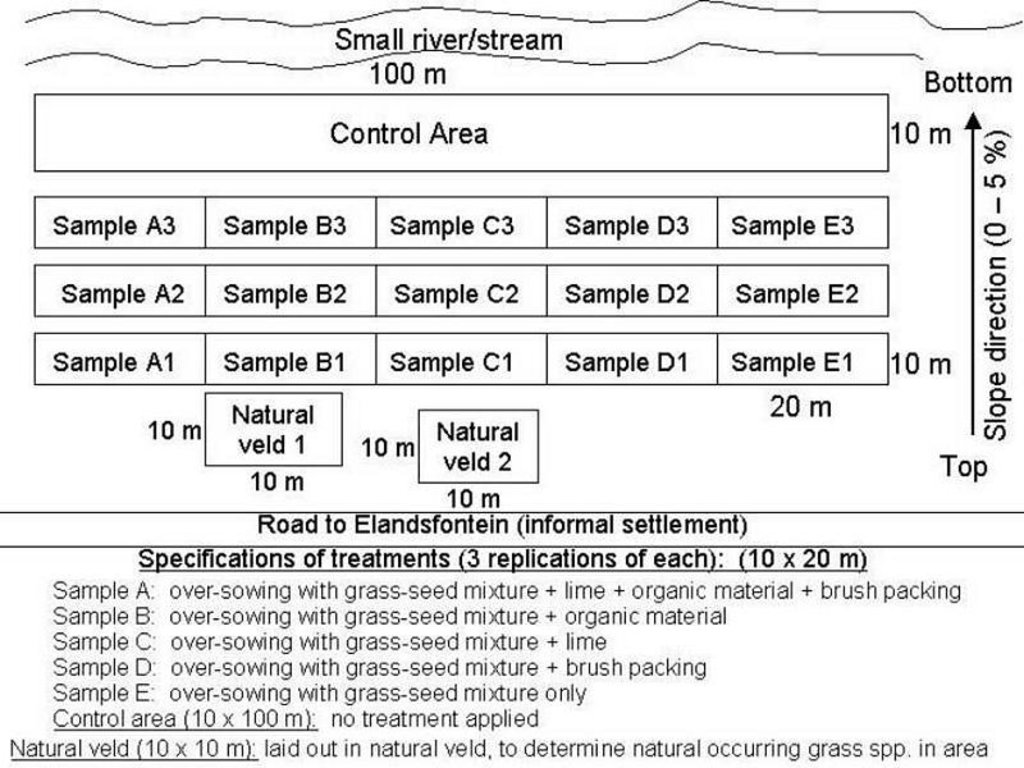
The purpose of the trials was to determine how best to eradicate the invasive trees and revegetate the rangeland. The restoration area was not fenced off and was thus open to grazing. The trials comprised five treatments, with three replicates each, on plots of 10 m by 20 m. In all treatments the A. mearnsii was eradicated manually, and chemical biocide applied to the stumps to prevent regrowth. Lime and grass seed (of palatable species) were applied to the loosened surface and covered with soil. The five treatments were:
(A) oversowing with grass seed mixture, supplementing of dolomitic lime, cattle dung, and ‘brush packing’ (see below for explanation of term);
(B) oversowing with grass seed mixture and supplementing with cattle dung;
(C) oversowing with grass seed mixture and supplementing with dolomitic lime;
(D) oversowing with grass seed mixture and brush packing;
(E) oversowing with grass seed mixture only.
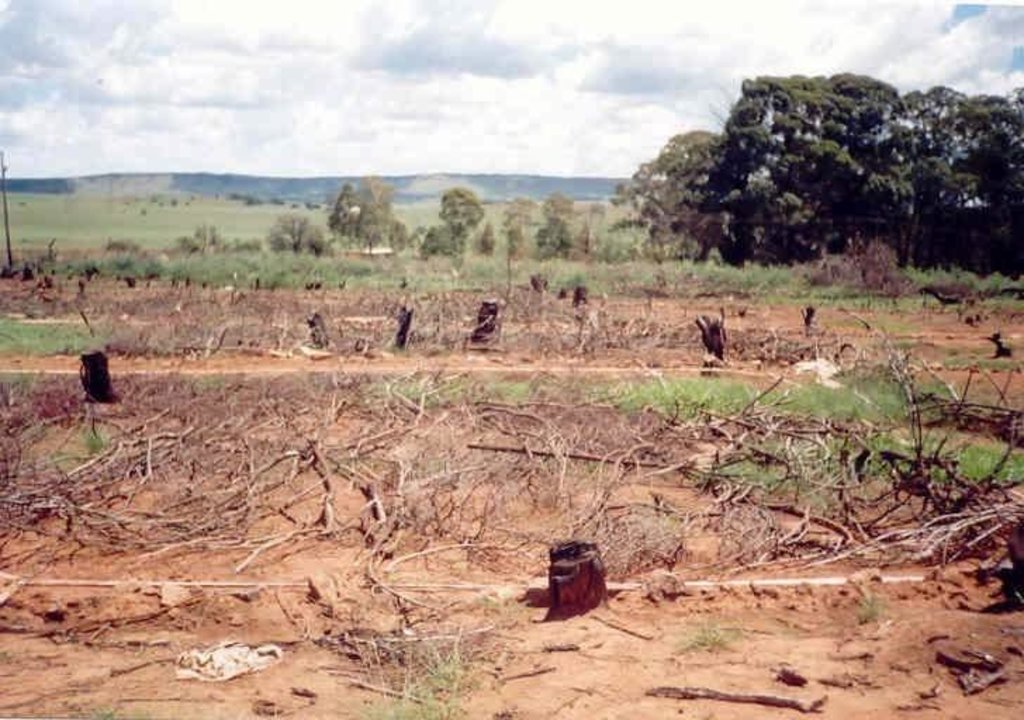
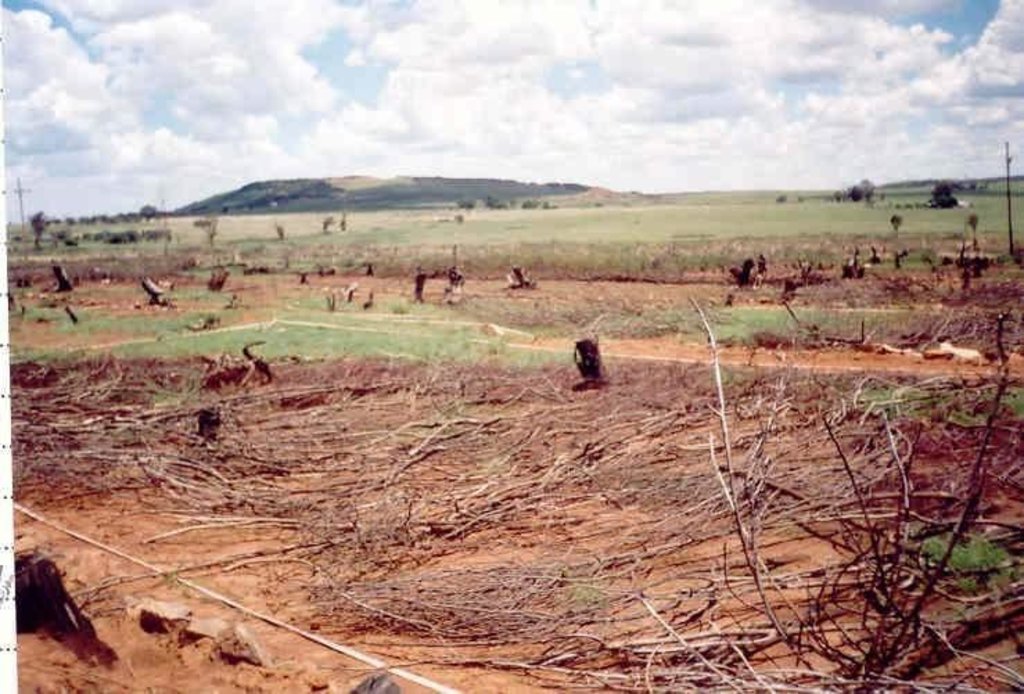
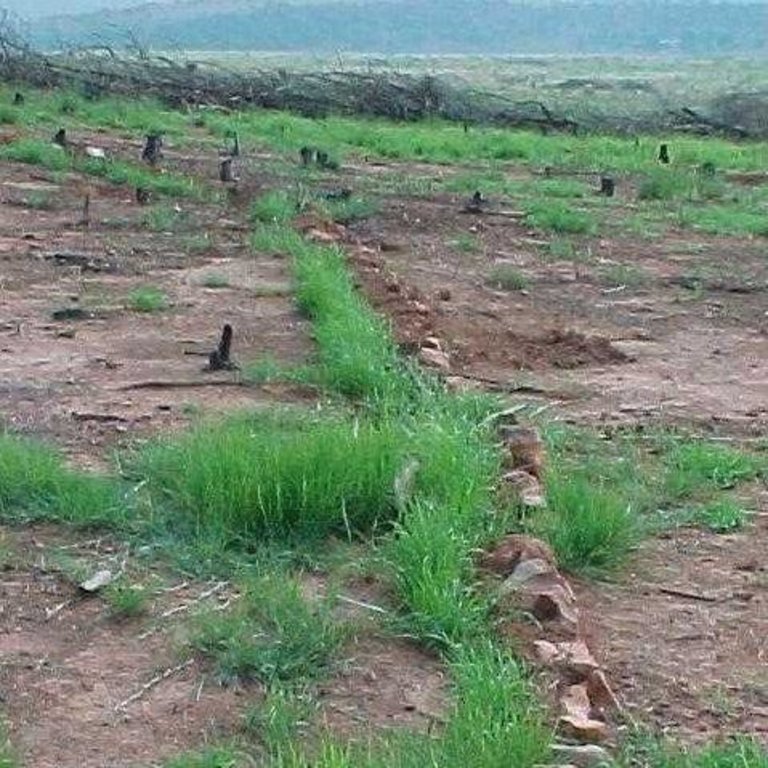
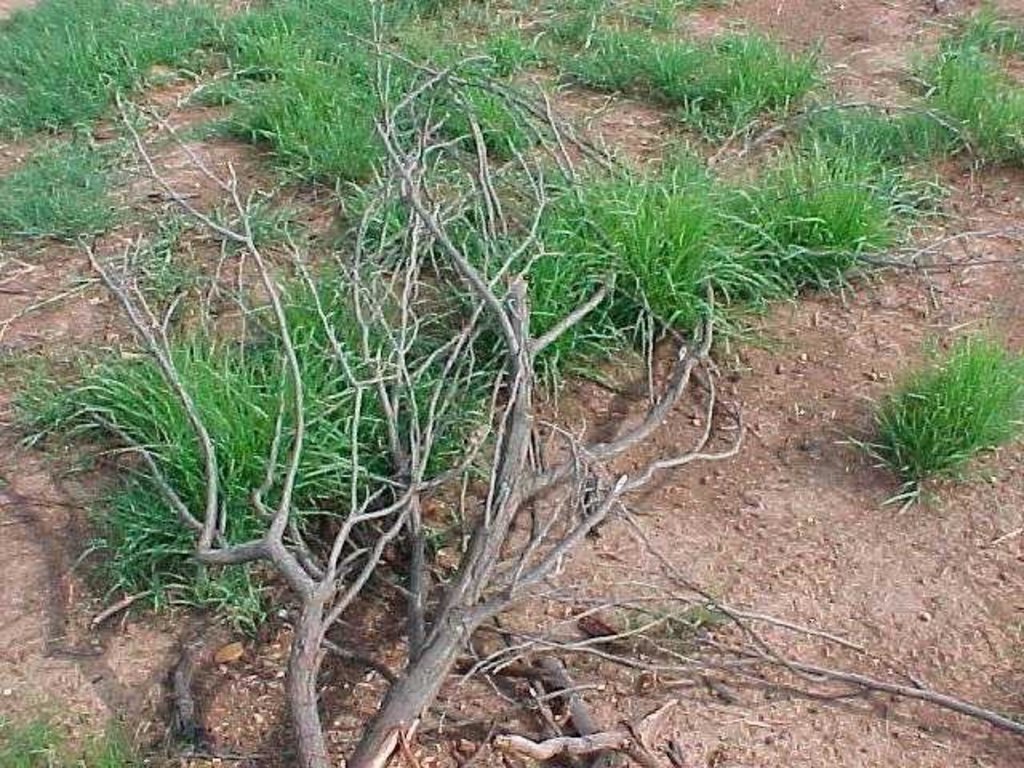
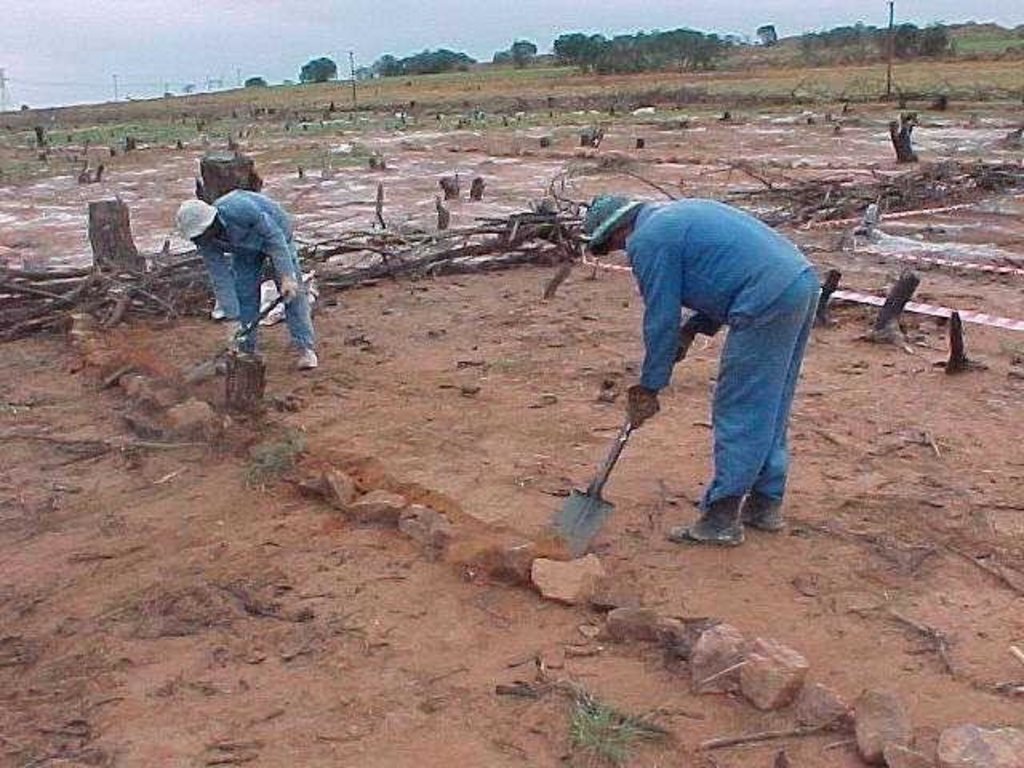
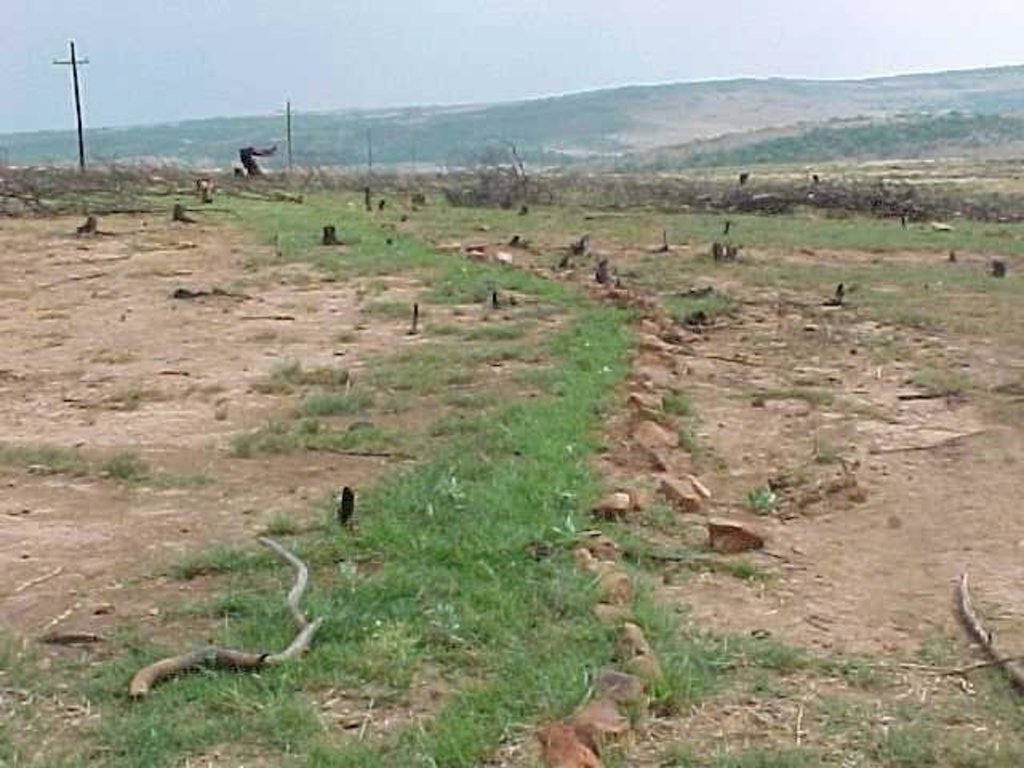
In addition stone lines were laid out along the contour, between plots. The ‘brush packing’, referred to in treatments A and D comprised branches laid out in strips across the slope to retard runoff, trap soil, improve the micro-climate for establishing grass seedlings and protect the young plants from browsing by animals. The results showed treatment A to be the most effective in restoring the productive and protective function of the rangeland. From the trials, the estimated costs of applying the best technology would be US$ 230 per hectare. The key constraints for successful adoption however are not just technical, but include: (1) the need to protect the area from grazing and trampling by animals during the establishment period; (2) stopping removal of brushwood for firewood; and (3) the need for community agreement on initial protection and subsequent sustainable utilisation of the restored range.
Establishment activities:
1.Manual eradication of trees with chain saw and axe
2.Application of chemical biocide to the stumps to prevent any regrowth
3.Ripping of soil surface to a depth of 5 cm using a three tined hand implement
4.Application of dolomitic lime and raking it into soil after ripping of the soil
5.Application of organic material (cattle dung) after ripping and lime application
6.Oversowing with grass seed mixture after ripping of the soil and application of lime and organic material
7.Brush packing against contour and packing of rock contours against the slope All the branches and stones were collected from the restoration area. Rock contours were packed against (perpendicular) to the slope in the study area at varying intervals (approximately 10-15 m apart) in order to retard runoff water, trap soil, and improve conditions for seed germination (see inserted drawing below and attachment). Branches were packed (brush packing) along the slope in certain treatments within the study site in order to trap soil, retard runoff water en serve as a micro-climate for germinating and establishing grass seedlings
Total duration of restoration took 3 years, from removal of trees till revegetation trials were laid out and technology was established.
Maintenance / recurrent activities per year:
Following initial establishment maintenance was limited to 2 follow up applications of herbicide (after 3 and 5 months). Maintenance of contours was not done after restoration.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
Gauteng
有关地点的进一步说明:
Johannesburg
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
9.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 9 km2.
Big area near settlement, was previously invaded by alien invasive species (such as A. mearnsii). Aim was to eradicate this species by using chemical/manual methods and to revegetate area with grass species occurring naturally.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
It originated from the overall need to restore degraded rangelands.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
- cattle
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Occurrence of bare areas after control of alien invasive.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Minimal grazing for cattle, due to the occurrence of bare areas.
Grazingland comments: No area closure, thus livestock graze freely on statelands and thus causes overgrazing over a large area.
This is a constraint to management in grazing lands. No rotational grazing. No area closure, thus livestock graze freely on statelands and thus causes overgrazing over a large area.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 210, Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - April
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A7:其它

植物措施
- V5:其它

结构措施
- S11:其它
注释:
Specification of other agronomic measures: manuring, lime, 'brush packing' (trash lines)
Specification of other vegetative measures: oversowing grass seed mixture
Specification of other structural measures: stone lines
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Alien invasives.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Trampling.), overgrazing (Cattle and goat.)
Secondary causes of degradation: poverty / wealth (Lack of captial - To pay labours to apply technologies.), labour availability (Lack of labour - To remove alien species.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Specifications
Location: Elandsfontein. Gauteng
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase in organic matter, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase in soil fertility, improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, increase of surface roughness, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, reduction in wind speed, improvement of soil structure
Vegetative measure: contour
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 0
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Grass species: Mixture of perennial and annual grasses
Other species: rocks
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5.00%
作者:
Anuschka Barac
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rand
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
8.2
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.30
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Eradication of trees, Follow-up with herbicide | beginning of project |
| 2. | Loosening of soil, Lime application | 6 months |
| 3. | Application of organic material | 6 months |
| 4. | Oversowing with grass seed mixture | 6 months |
| 5. | Brush packing | 6 months |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | |
| 设备 | machine use | ha | 1.0 | 65.0 | 65.0 | |
| 设备 | tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| 植物材料 | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 70.0 | 70.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | biocides | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 230.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 28.05 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 35 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 2 Follow-ups with herbicide | after 3 & 5 months after application of technology /twice (at 3 and 5 months ) |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | |
| 设备 | tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | biocides | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 32.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 3.9 | |||||
注释:
Eradication, seed purchasing, materials.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Biocides, fertilisers (lime), seeds and labour have a great effect on costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
600 - 800 mm/annum
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 非常丰富
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
80% of the land users are very rich (informal settlers and own 60% of the land (government).
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land (farmers).
Off-farm income specification: Informal settlers work in the city/mine, also mostly live of old age pension funds. Farmers (low percentage) have an income on-farm by means of selling cattle, crops and dairy products.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- provincial government
- provincial government
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Brush packing was removed by community members for firewood.
收入和成本
农业收入
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Not all labourers could be employed, more would have like to have the job (money).
社会文化影响
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Capacity building awareness
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
Farmers not positive about SWC project and effect.
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
2
SLM之后的数量:
1
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
轻度消极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
10 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Gazing improvement. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improvement of grazing resources. |
| Improved soil moisture availability by removing an alien species with a high water demand. |
| Reduced erosion by controlling runoff. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The question of controlling ‘open access’ grazing by the community is the key to long-term success of rehabilitation | It is incumbent on the local municipal council to negotiate with communities regarding grazing control and community-based natural resource management more generally. |
| Removal of brushwood for firewood by community members and other aspects of long-term maintenance | See above: perhaps also seeking funds to pay labourers and buy biocides |
| Too many cattle and goats. | Reduce numbers to match grazing resources available |
| Insufficient aftercare. | Secure additional funds to pay labourers and buy biocides. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
28/09/2001
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Soil classification: A taxonomic system for South Africa.. 1991.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ARC -Institute for Soil, Climate and Water, Pretoria. 012 - 3102500.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Harris J.A., Birch P., Palmer J.P. Land restoration and reclamation.. 1996.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Kent M, Coker P. Vegetation description and analysis.. 1997.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Tainton N. Veld management in South Africa.. 1999.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Acocks. Veld types of South Africa.. 1988.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
HARRIS, J. A., BIRCH, P. AND PALMER, J. P. Land restoration and reclamation – Principles and Practices. Addison Wesley Longman, England. 230 p.. 1996.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块