Farm pond [印度]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Channabasappa Metri
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
krushi honda (Kannada)
technologies_1474 - 印度
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Benson Roland
Danida KWDP Bijapur
印度
SLM专业人员:
Mujibur Rahman Syed
Danida KWDP Bijapur
印度
SLM专业人员:
Thippeswamaiah
KWDP Daida Bijapur
印度
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Danida assisted Karnataka Watershed Development Project, Bijapur (Danida assisted Karnataka Watershed Development Project, Bijapur) - 印度1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
Stakeholders participation in the project activities [印度]
SWC approach is a participatory methodology to empower the community to plan, implement, monitor, evaluate and manage the SWC technology to bring about sustainability
- 编制者: Pranesh Jahagirdar
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
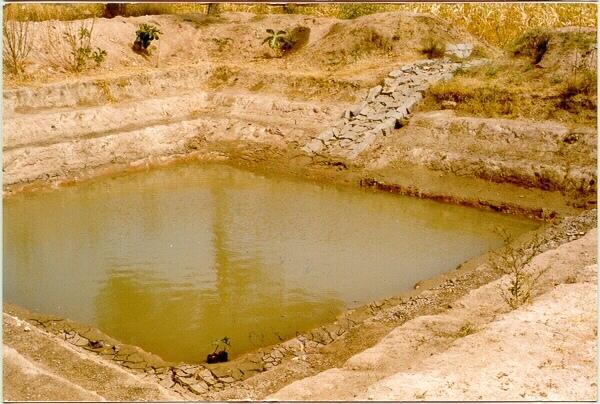
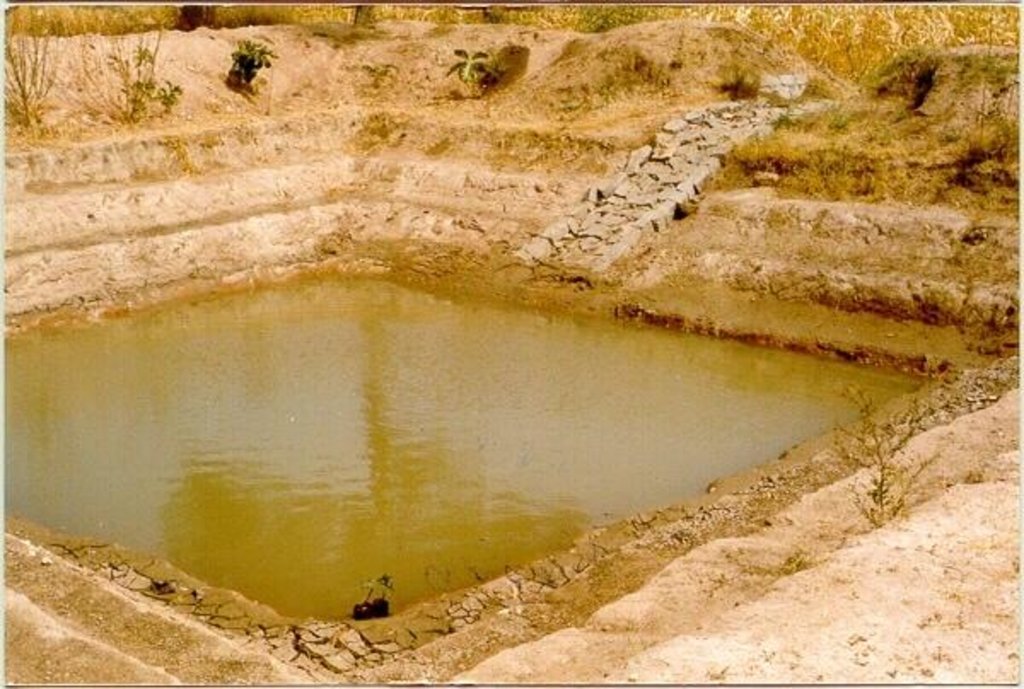
A sunken structure (12 x 12 x 3 m, more suiable), constructed by escavation in arable land with a view of temporary runoff storage tapped for protective irrigation, and to increase percolation for recharge of ground water (to convert surface to subsurface flow)
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
A farm pond comprises of excavated portions of 12 x 12 x 3 m with the steps at 0.6m depth each. The excavated earth is deposited all around the structure as a bund, with a burm space of 1m. An inlet cum outlet provided in the course of flow of rain water to collect and dispose the excess runoff.
Purpose of the Technology: (1). For storage of exess runoff. (2) to increase percolation for ground water recharge, (3). To use for protective irrigation during dry period, (4). To stop further deepening of watercourse in arable lands
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Selection of beneficiary is by the community and site selection, Design/ layout and excavation by the project staff with participation of the beneficiary. Desilting of the structure is by the beneficiary
Natural / human environment: surrounding lands are more slopy and with exposed rocks, most of the surrounding area is left for grazing
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度
区域/州/省:
Karnataka
有关地点的进一步说明:
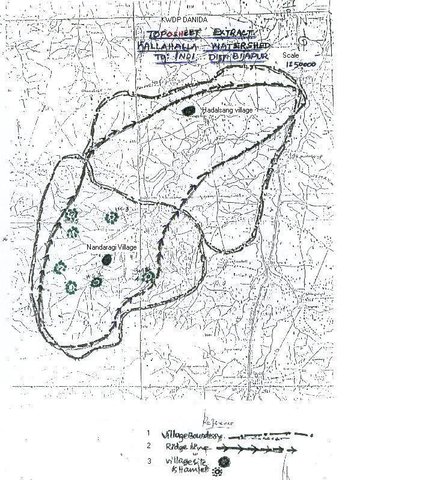
Bijapur district, Hadalsang village
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
0.028
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.028 km2.
The technology area comprising of 2.8 ha within the overall watershed area of 2458 ha. The technology is useful in harvesting the excess rainwater in the arable land and re-use the for protective irigation after the rainy period.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Department of Agriculture, Govet. Of Karnataka
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 保护生态系统
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 高粱
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 其他
- 油料作物 - 蓖麻
- Chili, brinjal (eggplants), lady's finger (okra, kind of peas)
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Dec Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Sep
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The lands are very undulating (Class-V as per the Land Capability Classification), with very shallow soils, feasible for only one rainfed crops.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Poor yields due to shallow soils that too only one crop in one season, undulating lands leading to more runoff.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: minor pulses - cereals (green gram-jowar)
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: Highly eroded, unsuitable for any production purposes.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated (ranked 2)
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (other (migration)), labour availability (lack of labour, cost of labour), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
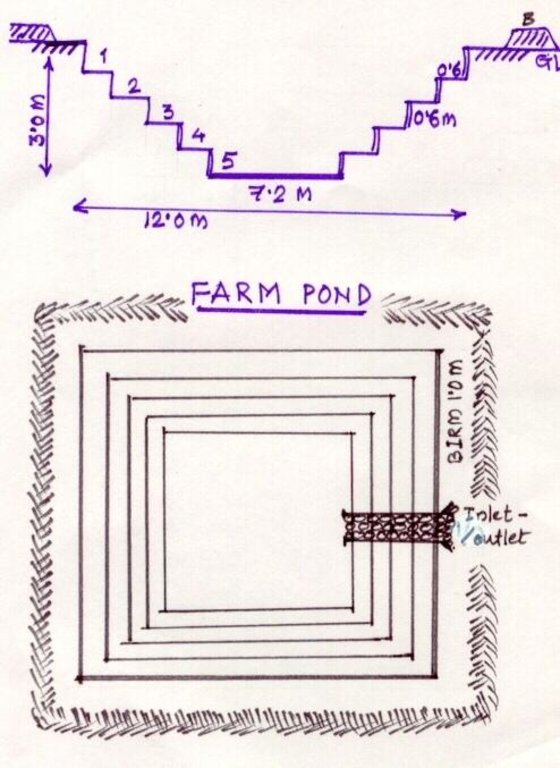
The drawing showing the details of the farm pond. 12 x 12 x 3 m dimension. Five steps cutting on each side with 1:1 side slope. 1m birm (space) between the earthen bund. 1m wide spilway inlet cum outlet at suitable place of the site.
Location: Kallahalla nala watershed, Indi Taluk. Bijapur district of Karnataka state
Date: 20.4.2004
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Structural measure: sediment sand / trap
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 15
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 15
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 15
Construction material (earth): soil excavated from the pond is used to for bunds all around the structure with 1 m birm space.
Construction material (stone): The spillway Inlet cum Outlet is constructed using stones
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:7
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
作者:
C.G Metri, JPO, KWDP Danida Bi
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Ruppes
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
46.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.73
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | selection of site and survey, preparation of estimates | summer |
| 2. | submission for sanction of approval | summer |
| 3. | Excavation of the farmpond | summer |
| 4. | construction of inlet/ outlet | before monsoon starts |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 360.0 | 360.0 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 109.43 | 109.43 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 469.43 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 10.21 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Meeting with the farmer | monsoon/annual |
| 2. | Desilting of farmpond | summer season/once in 2 years |
| 3. | Repair of Inlet/Outlet | summer season/Every year |
| 4. | Trimming of Bund | summer season/Every year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 7.3 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.16 | |||||
注释:
12 m x 12 m x 3 m size with all side slope of 1:1 (five steps of 0.6 m deep), Inlet cum outlet spilway constructed with stones. This indicates only the actual cost of construction. (excavation / earth wotk and stone work for inlet/outlet)
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
If the implementation site is having the hard strata, then the cost will be more.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
550.00
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Located on the latitude 16-49'N and longitude 75-43'E .Characterised by hot dry summer (42 °C) and cold dry winters monsoon (July-September) is characterised by high intensity showers followed by pro
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 501-1000 m a.s.l. (594 m a.s.l.)
Slopes on average: Gentle (ridge and valley portion)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Shallow (30 cm)
Soil texture: Medium (medium in valley portion)
Soil fertility: Low (along the slope of the ridge, ranked 1) and medium (valley portion, ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (in valley portion)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (hill portion, ranked 1) and medium (valley portion, ranked 2)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
15% of the land users are very rich and own 5% of the land.
25% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Through sheep and goat rearing
Level of mechanization: Animal traction, (ranked 1, for ploughing, seed sowing harrowing), manual work (ranked 2, clod crushing, harvesting, threashing) and mechanised (ranked 3, Deep ploughing, levelling)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
1-2 ha (ranked 1, marginal farmers [since the land holding decreases because of the fractionation the production and productivity also reduces])
2-5 ha (ranked 2, small farmers)
5-15 ha (ranked 3, big famers)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Second crop also taken
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
From trees
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
From trees
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
Difference in the crop like on bunds and in the patches of crops.
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
15m x 15m land loss average land holding is very less, thus small & marginal farmers face reduction in the production area with this SWC
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
After implementing SWC less area is left for very small and marginal land holding.
水资源可用性和质量
家畜用水的可用性
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Subsistance agriculture
其它社会经济效应
Input constraints
注释/具体说明:
To bring new area into cultivation
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Water storage in farm pond
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The community is motivated with the benefits from this SWC structure. Some of them have already deepened the farmponds to increase its storage capacity.However, since most of the farmers are having very small land holdings and there was continous dry season from last three years, even if the farmers are motivated and aware of the technology of farmpond, they could not take up on their own (without financial assistance from the project.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increased storage of water How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting by the farmer |
| Reduce gully formation |
|
Bring more area under irrigation How can they be sustained / enhanced? By giving life saving irrigation |
|
Economic benefits How can they be sustained / enhanced? By yields (monocropping to multiple cropping) --> more income |
|
Recycle the silt is beneficial How can they be sustained / enhanced? Other the silt would been lost every year and it is good to retain the soil fertility. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Storage of water How can they be sustained / enhanced? By deepening |
|
Reduced runoff velocity How can they be sustained / enhanced? By mentainance |
|
Breaching of bunds down stream How can they be sustained / enhanced? By reducing the run-off |
|
Replicability How can they be sustained / enhanced? if a famer has his own labour/ man power then he can go for its construction. |
|
Water harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? recycle for protective irrigation during peak season. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Inability to contribute 100% towards cost of construction. | By giving schemes / financial assistance |
| Loosing of portion of cultivable land | By utilizing bunds, change in cropping system/ cropping pattern etc. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Difficult to excavate in hard strata | can be done in shallow soils |
| Silt accumulation, if upper catchment is not treated | Treatment of upper catchment |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Department Guidelines,Project Implementation plan, UAS Dharwad
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
In the office, personal contact
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
PIP
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
in the office
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
University of Agril. Sciences Dharwad
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
personal contact
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Stakeholders participation in the project activities [印度]
SWC approach is a participatory methodology to empower the community to plan, implement, monitor, evaluate and manage the SWC technology to bring about sustainability
- 编制者: Pranesh Jahagirdar
模块
无模块