Diversion Weir [印度]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Niranjan Sahu
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Cement muda
technologies_1481 - 印度
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Mohanty Rajib Kumar
印度
SLM专业人员:
Khatua Santosh
印度
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Common Interest Group Approach in Watershed Development [印度]
Group is formed based on a common interest such as irrigation to their fileds from the diversion weir.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
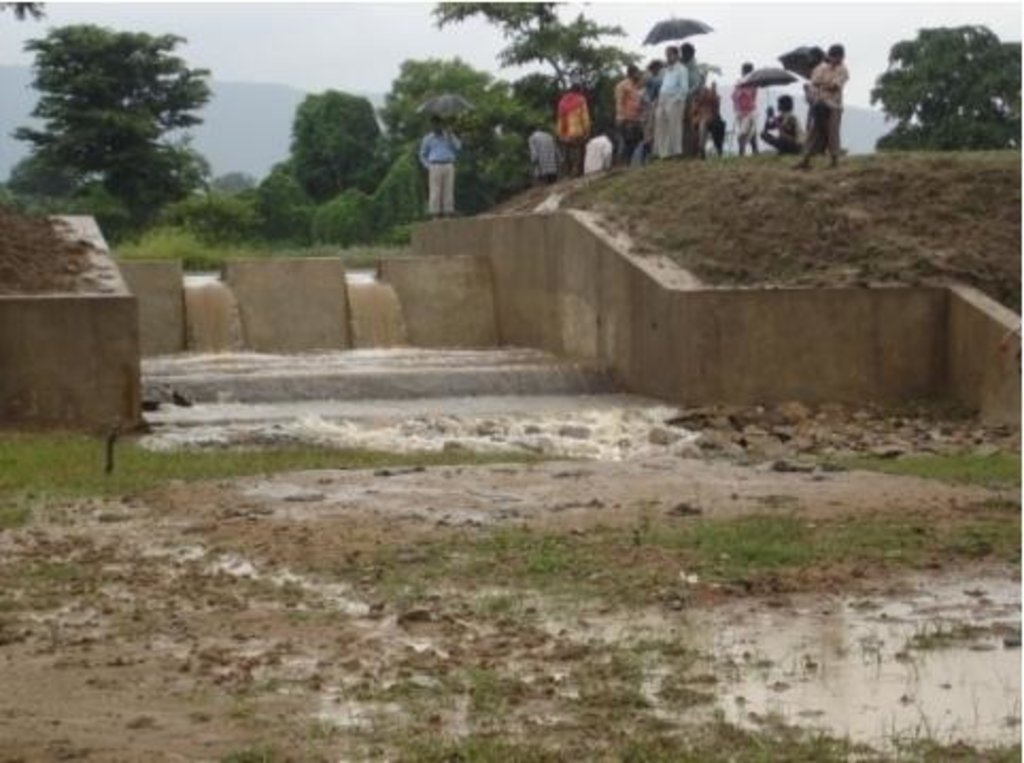
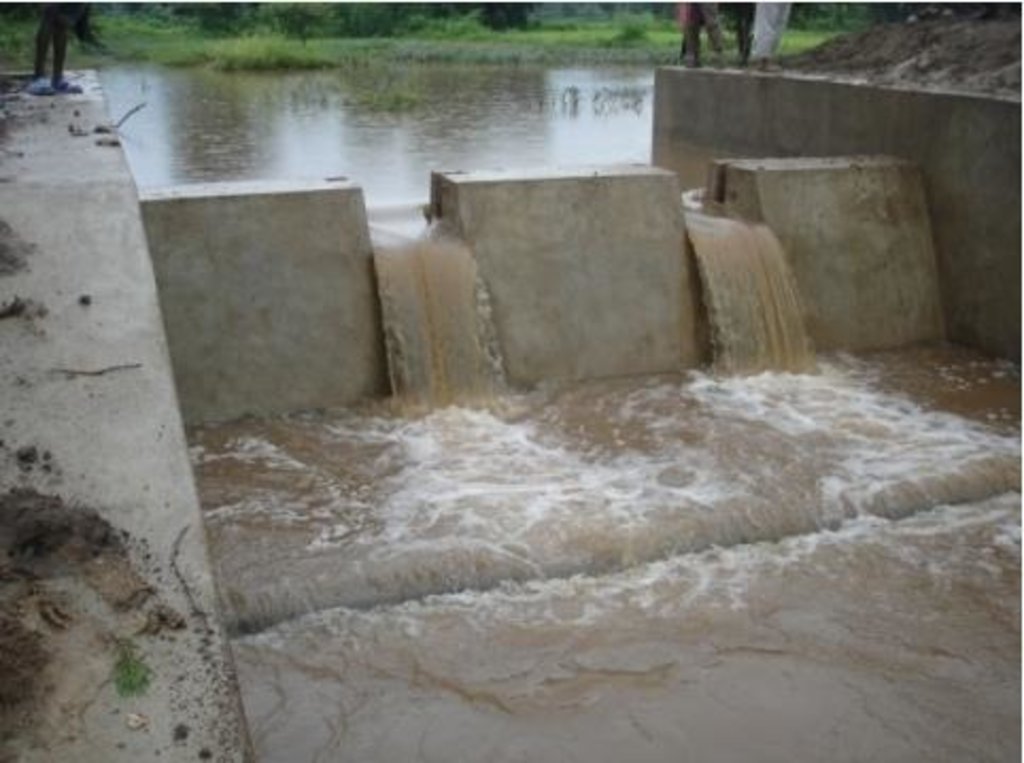
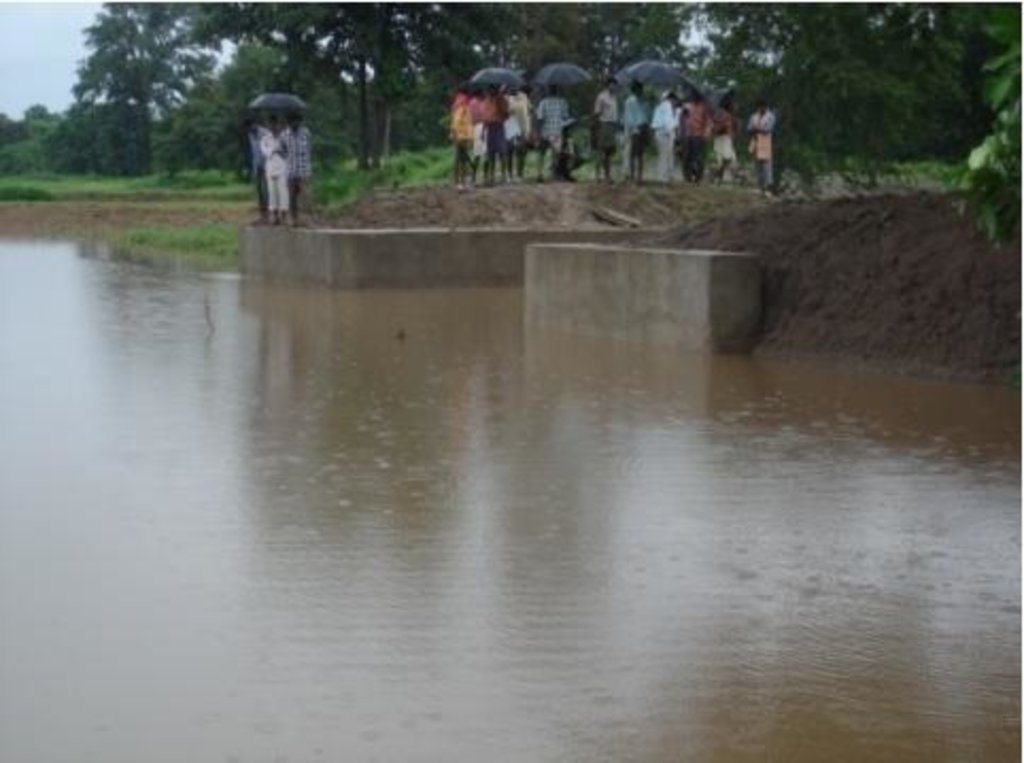
Diversion weir is a masonary check dam constructed across a perinnial or semi perinnial stream to divert the runoff water into land users field for irrigation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Reduce the velocity and volume of runoff in the down stream. Use the runoff water for irrigation purpose. Sand casting and flash flood is reduced. More land is brought under cultivation due to increased water availability.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度
区域/州/省:
Orissa
有关地点的进一步说明:
Koksara, Kalahandi
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 50 km2.
Diversion weir is a masonary check dam constructed across a nala/drainage line which is perenneial or semiperenneial. After a temporary storage in the upstream, water is diverted to land user filed as irrigation water.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Soil Conservation Department
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 水稻(湿地)
- 油料作物 - 花生
- 蔬菜 - 其他
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 140Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - SepSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Feb
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Small land holding, Volme and duration of availability of water. Sand casting, Flash flooding, wash out of field bunds.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Sand casting and flash flood destroy our crops frequently when the rainfall is high where as crop loss and drought occur due to low rainfall.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Paddy-Onion; Paddy-vegetables
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 引水和排水
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wr: riverbank erosion, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), land tenure (land subdivision), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
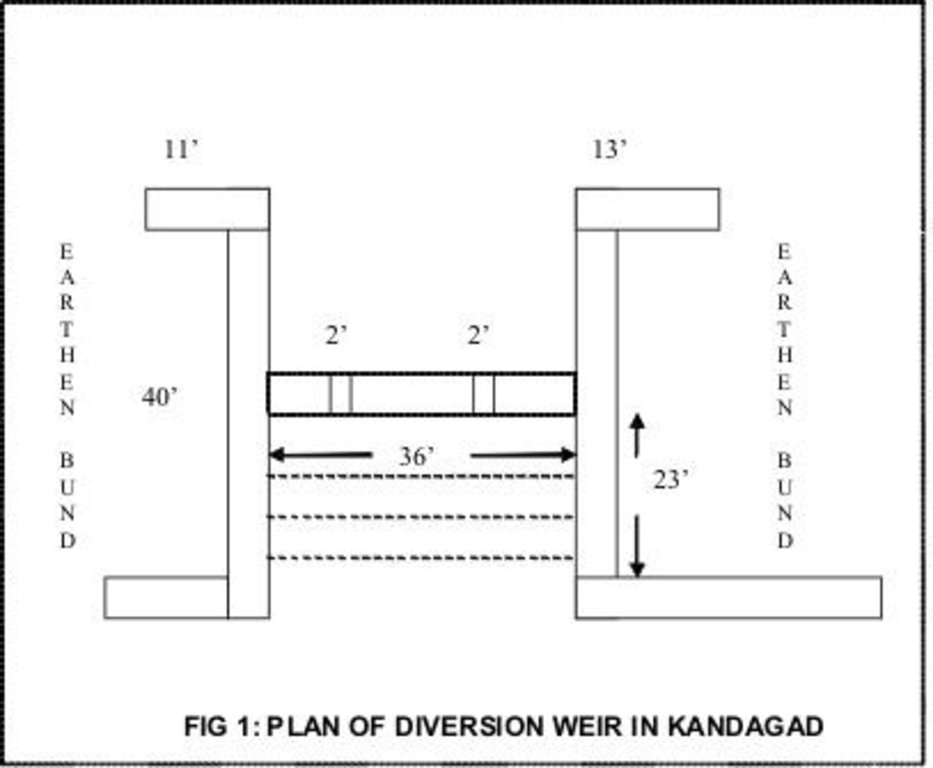
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Plan of diversion weir in Kandagad
Location: Kandagad. Orissa
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 15 feet
Spacing between structures (m): 1500 feet
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10 feet
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 35
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 45
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 12
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 40
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 1%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Crop plan as per water availability
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
INR
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
40.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Layout of the structure | May |
| 2. | Digging of foundation | May |
| 3. | Construction of foundation and superstructure | June |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 2700.0 | 2700.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 900.0 | 900.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 3600.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 90.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 24060 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Operation of the scoure sluice | rainy season/ |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Length of the structure
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Cost of cement, stone and transportation
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Also Hill slopes and valley floors (both ranked 2)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility : Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Low (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
23% of the land users are average wealthy.
47% of the land users are poor.
18% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Off farm employment opportunities are created due to better cropping system and production
Level of mechanization: Manual work (ranked 1, bullock drawn implements) and mechanised (ranked 2, tractor for ploughing the field and transportation)
Market orientation: Mixed (Paddy as staple food and onion as a commercial crop)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 2-5 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,有命名
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产区域
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤流失
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
Sand casting
Flash floods
Washout of bunds
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游淤积
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
45 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Due to heavy initial investments
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Earlier the runoff was passing through a single nala, now the irrigation channels have been opened at three points which are commanding more are |
| Sand casting is stopped now |
| water table in the wells have increased |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Crop loss is minimised due to long dry spell How can they be sustained / enhanced? The command area needs to be developed with surplus and field channels |
| Productivity of the land has increased |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| A corpus needs to be developed for future maintenance of the structure |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Common Interest Group Approach in Watershed Development [印度]
Group is formed based on a common interest such as irrigation to their fileds from the diversion weir.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
模块
无模块