Variable rate biosolids management [意大利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Nicola Dal Ferro
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Valentin Zuercher, Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Applicazione dose-variabile di ammendanti organici
technologies_1663 - 意大利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
University of Padova (UNIPD) - 意大利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
Carbon farming [意大利]
Managing land, water, plants and animals to meet the landscape restoration, climate change and food security.
- 编制者: Nicola Dal Ferro
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Application of precision farming and variable rate application technology for spatial optimization of organic amendments use
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Generally, precision farming aims to increase the efficiency of cropping systems by understanding and dealing with the natural variability of the field. Here, the application of precision farming and variable rate technology approach has been proposed as a mean to optimize organic amendment inputs in croplands. Automatic application of organic inputs can be a viable way to increase farm efficiency, productivity and finally profitability.
Purpose of the Technology: Following the natural heterogeneity of the field, precision farming and variable rate technology are here applied as a SLM practice to increase the soil organic carbon (SOC), reduce losses of diffuse polllutants while increasing yield production.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Precision farming is already a feasible and useful technology in terms of automation, data process and management. In this context, site-specific application of mineral nitrogen is one of the most promising techniques to reduce the environmental impacts of nitrogen pollution. In the same way, variable-rate input of organic amendments (manure, slurry, compost etc.) can be useful for increasing the soil fertility. Spatial information of field characteristics can be overlapped with on-the-go sensors information in the field in order to provide the right dose of biosolid input.
Natural / human environment: High efficient organic application systems will provide both environmental and agronomical benefits. Nutrient management will be optimized and the loss in the groundwater will be reduced. Moreover the soil fertility will be improved by the site-specific application of organic matter, providing the best comnbination between organic inputs, nutrient requirements and reduction of nutrient losses.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
意大利
区域/州/省:
Veneto region
注释:
This is only a potential technology that could be applied in the field. At the moment it is not applied in Veneto region.
Map
×2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 210, Longest growing period from month to month: March to October, Second longest growing period in days: 180
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soils in the low Venetian plain of the Veneto region generally suffer from a loss of soil organic matter (SOM) that is strongly affected by their natural texture and climatic conditions. Moreover, in the last 50 years intensive tillage practices contributed to a further SOM decrease, estimated at 0.02-0.58 t/ha/y of carbon. Finally, high intensive agriculture practices increased nonpoint source pollution and in turn caused a decline of surface and groundwater quality.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): To date, few farmers have adopted voluntarily the continuous soil cover to reduce a decline of soil fertility and water quality, symptom of poor perception of the problem. Adoption of SLT by farmers was sustained only by means of regional subsidies.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- precision farming and variable rate application technology
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Specification of other management measures: Manure application management
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, population pressure
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
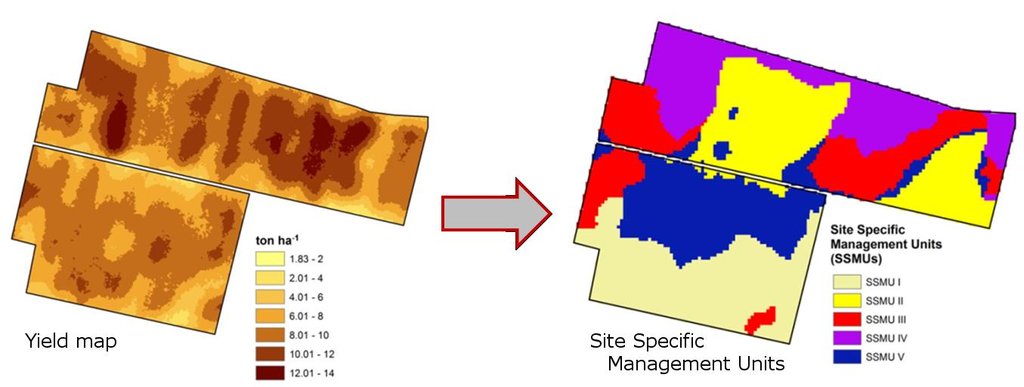
Application of manure is based on site-specific management units as defined by previously field variability.
Location: Veneto region. Italy
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Organic amendments are distributed in variable rate following the spatial and temporal variability and requirements of the field
作者:
Francesco Morari, DAFNAE - University of Padova
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
€
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.8
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
21.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of equipment for technology application (GPS, sensors etc.) | Once |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Purchase of equipment for technology application (GPS, sensors etc.) | |||||
| 设备 | GPS, sensors etc. | 1.0 | 10000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 | |
| 其它 | Training costs | |||||
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 10000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 12500.0 | |||||
注释:
Training for farmres is a cost that should be considered at the initial stage.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Machinery and technological devices
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity:Medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Although water salinity is not spread throughout the Veneto region, some agricultuiral aras along the coasts show problems of salt intrusion that may compromise irrigation.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: Land users that could apply such technology need substantial investments. As a result, only people with high farm income likely adopt such technology.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 租赁
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
水资源可用性和质量
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
社会文化影响
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
土壤
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
注释:
The technology is not yet applied, but only proposed because it is still in research/experimental phase. However stakeholders showed interest in the technology for a future adoption of the technology.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Soil spatial variability is taken into account |
| Reduces diffuse water pollution |
| Optimizes soil organic matter needs |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High intial costs | training |
| High expertise for technology use |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
23/04/2015
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Moshia et al., 2015. Precision Manure Management on Site-specific Management Zones: Nitrogen Mineralization. Journal of Plant Nutrition 39 (1).
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2015.1009547
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Carbon farming [意大利]
Managing land, water, plants and animals to meet the landscape restoration, climate change and food security.
- 编制者: Nicola Dal Ferro
模块
无模块