Plastic film technology [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Shreedip Sigdel
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Plastic proyog gari kheti garne prabidhi (Main Contributor: Samden Sherpa, ICIMOD)
technologies_1687 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Sherpa Samden Lama
ICIMOD
尼泊尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
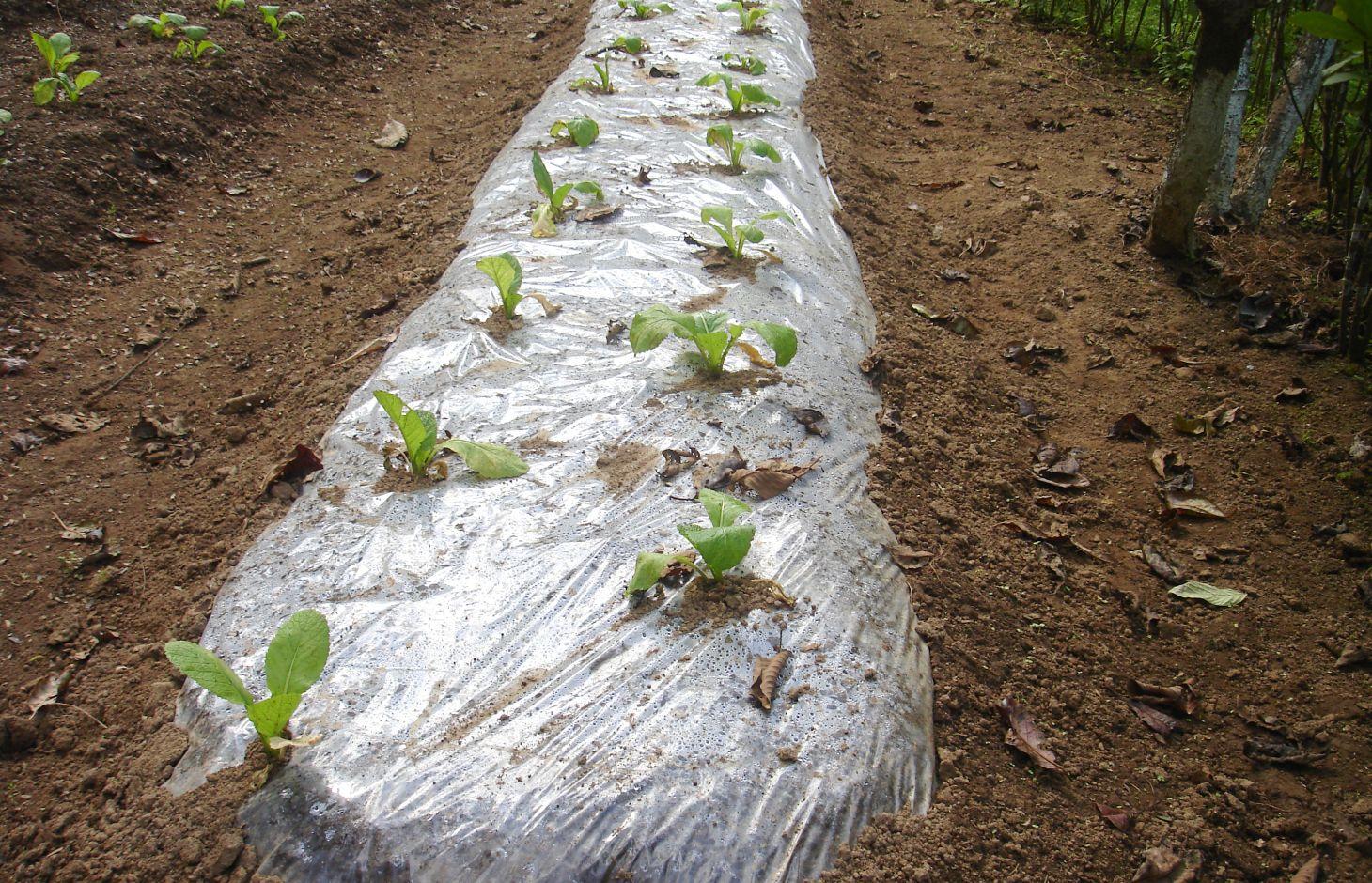
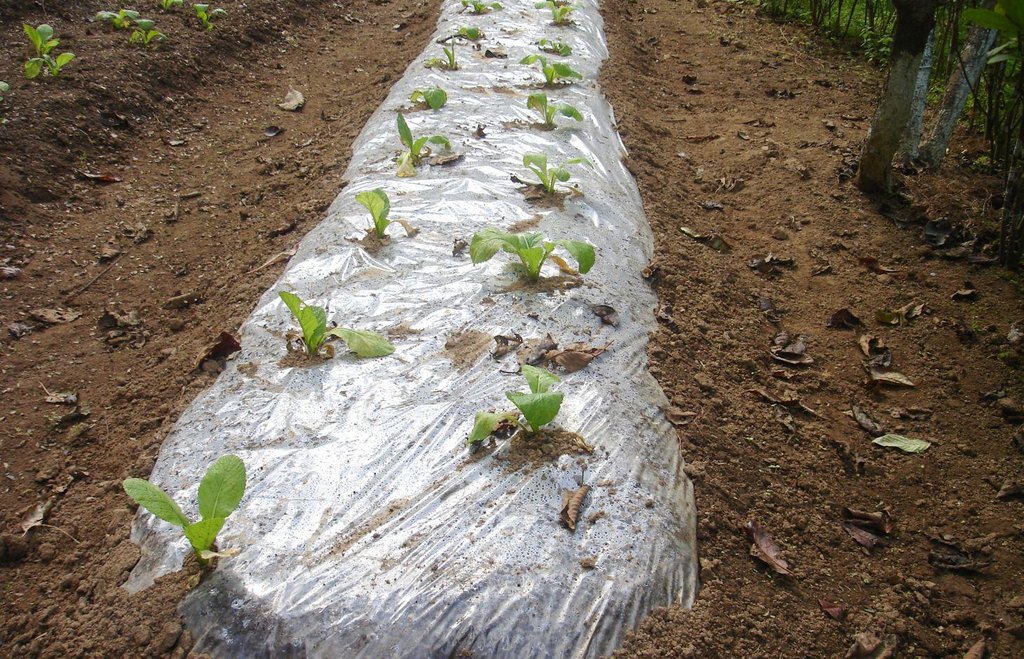
Plastic film technology, sometimes called plastic mulching, is an important breakthrough that can transform traditional agriculture into modern agriculture by helping to circumvent many of the limitations of temperature and moisture. Plastic film is used to cover the surface of the soil in order to increase the temperature, to retain moisture, and to promote the germination of seeds.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Agricultural production by traditional methods is constrained by extremes in temperature and by extremes in the availability of water; freezing temperatures as well as droughts and waterlogging have long daunted farmers. When plastic film is used on the soil, the solar energy absorbed by the soil during the day is retained at night since the plastic film prevents water from evaporating. Higher night time temperatures and higher levels of moisture in the ground promote active micro-organisms, which diminish the need for fertilizer and improve the physical properties of the soil.
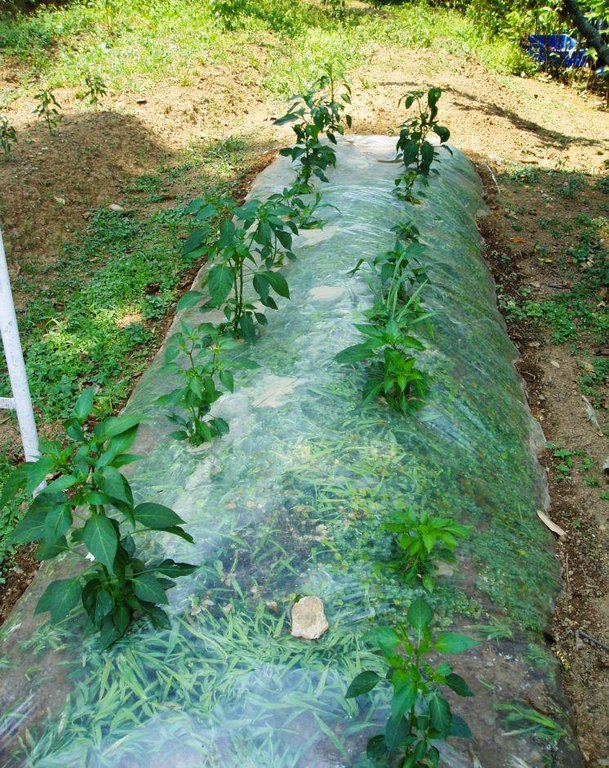
Purpose of the Technology: Plastic film can be used in one of two ways. In the first method, the plastic film is spread on ridges of soil, the plastic is perforated at regular intervals, and the seedlings are planted through these openings. In the other method, seeds are planted on the ridges as in the traditional method, and when the seedlings have grown to a reasonable size, the ridge is covered by a plastic film and holes are cut at the position of the seedlings to allow them to pass through the film. Depending on the condition of the film after the crops are harvested, the covered ridges can be used to grow another crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Experiments at ICIMOD show that the use of plastic film can, on average, double the crop yield as compared to traditional methods. Previous studies by Lu Rongsen (1994) showed that the plastic film method can increase chilli production by 74%, tomato production by 52%, and the production of garden peas by 31%.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
有关地点的进一步说明:
Lalitpur District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
注释:
It was done in demonstration plote
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
每年的生长季节数:
- 2

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 薪材
- 其它森林产品
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Farmers have traditionally used mulching to retain moisture in the soil and to help plants withstand ground frost. Mulching is useful but has many limitations. Recently, plastic film technology has been successfully introduced to help retain moisture in the soil and to promote seed germination. Since moisture is retained, the temperature of the soil does not drop as low as it would otherwise; this accelerates the growth and the development of both the roots and the whole plant, resulting in good crops and high yields.
Forest products and services: fuelwood
Other forest products and services: Fodder
Constraints of Scrubland
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M7:其它
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
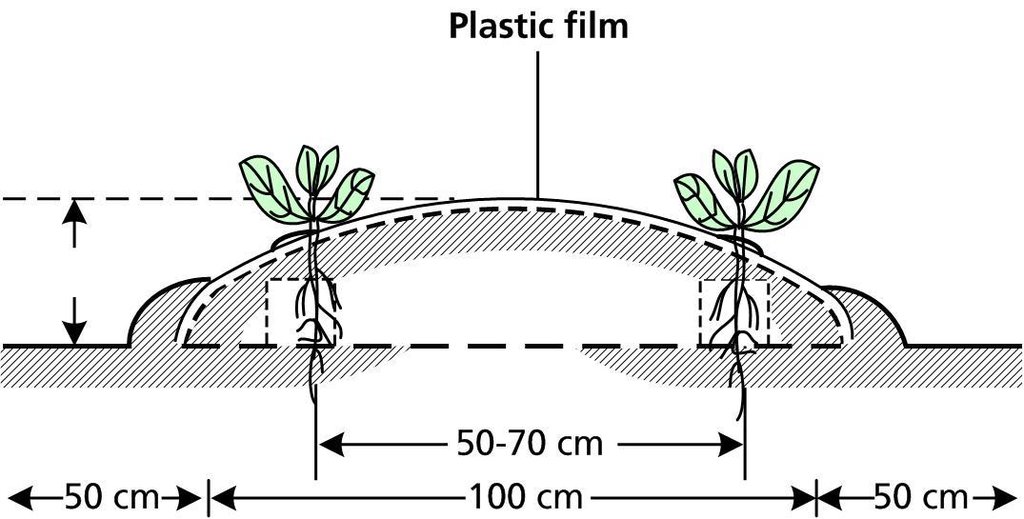
The diagram shows a cross-section of a ridge planted using plastic film technology. The plants grow through holes punched in the plastic. The plastic helps to retain moisture in the soil and, in so doing, also helps to increase the soil temperature. Weeds trapped below the plastic are inhibited from interfering with the crop.
The ridges (or beds) are typically 20 m long, 1 m wide and spaced 1 m apart (for access); they are usually 10–20 cm high. The distances shown in the diagram are averages for crops such as chillies where the row-to-row distance is 50–70 cm and the plant-to plant distance is 40–50 cm. These distances vary according to the crop.
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: Increase the temperature of the soil and promote seed germination and emergence, Retain soil moisture and reduce soil erosion
Secondary technical functions: Accelerates the growth and development of roots and plants in areas where the temperature is low dur, Hastens maturation of crops and increase yield and promote good quality crop
Change of land use practices / intensity level
作者:
AK Thaku
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
ha
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | The plot of land to be planted is prepared by first fertilizing it with a mixture of soil, compost, and/or farmyard manure. The soil is gathered into parallel ridges, typically 20 m long, 1 m wide, and 10–20 cm high; the distance between two ridges is usually 40–50 cm. For many crops the seedlings are spaced 50–70 cm apart. | |
| 2. | Method #1 Plastic film (approx. thickness 0.014–0.003 mm) is used to cover the ridges and anchored into the ground. Round holes are punched in the film at regular intervals. Some soil is excavated through the holes and the seedlings are planted through the holes and thoroughly watered. The holes in the plastic are sealed using soil. | |
| 3. | Method#2 Seeds are sown on the ridges and seedlings are allowed to develop. The ridge is covered in plastic film and the film is anchored. Holes are punched into the plastic at the position of the seedlings so that they pass through. | |
| 4. | For either method, when the crops are harvested all residue should be removed. Depending on local conditions and on whether the plastic film is still viable, the plastic covered ridges can be reused to grow another crop without replacing the film. |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Preparing land plot | persons/day/ha | 80.0 | 3.875 | 310.0 | |
| 设备 | Spade, secateurs | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| 设备 | Plastic film | kg/ha | 48.0 | 1.0 | 48.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 618.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 618.0 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Provide crop support such as staking and removal of excess leaves as required |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Support the crops | persons/day/ha | 30.0 | 3.6668 | 110.0 | |
| 设备 | Bamboo poles | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 130.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 130.0 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
This was a demonstration project conducted by ICIMOD.
All costs and amounts are rough estimates by the technicians and authors.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water quality (untreated): Also for agricultural use (irrigation)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
Labour:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
in areas with a long winter season
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
less time is spent weeding
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
improved crops and higher yields benefit the entire community because more food is available and the harvest brings in cash income.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
其它生态影响
soil erosion and nutrient loss
soil temperature
weeds are controlled
discarded plastic
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Downstream farmers benefit because soil is conserved and runoff is reduced
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| long spell of low temperature, frost and snowfall | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Acceptance/adoption:
This demonstration of plastic film technology was used mainly to show that it is viable both in the mid-hills and at higher elevations where temperatures can be very low during the winter season. Plastic film technology can be used to cultivate high-value horticultural crops such as vegetables, strawberries, and melons. In China, it has been successfully used to cultivate more than 80 species (Lu Rongsen 1994).
Driver for adoption:
Improved income for farmers and less time is spent weeding. Greater awareness among farmers is being spread through participatory research and development in rural areas.
Constraints
Plastic film is not always available in rural areas
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Plastic film technology can increase the yield of some crops by as much as 100% as compared to conventional farming. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Since this technology is still relatively new, it will be necessary to continue sharing experiences and to promote awareness. |
|
Plastic film technology can be used to grow crops in hilly areas where the long winter season is usually too cold to support crops. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Need to create greater awareness of the benefits of using plastic film technology in mountain areas |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| As farmers begin to use plastic film technology more plastic is being discarded in rural areas. | Plastic film needs to be retrieved and recycled. In China it has been shown that this is possible. |
| Discarded plastic film can pollute agricultural lands | Farmers need to be made aware of hazards and encouraged to form networks for collection and recycling the used plastic. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
The application of plastic film technology in China: Plastic film technology data collected and analyzed in ICIMOD D&T Centre, Godavari. Kathmandu, Nepal: ICIMOD, Rongsen, L (1994)
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块