Drainage of coastal areas in north- western Germany [德国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Martin Maier
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Tiefliegenden Küstenlandschaften mit künstlicher Entwässerung in Nordwestdeutschland
technologies_1714 - 德国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Kleyer Michael
University of Oldenburg
德国
SLM专业人员:
Karrasch Leena
University of Oldenburg
德国
SLM专业人员:
Mayer Martin
University of Oldenburg
德国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Sustainable Coastal Land Management (COMTESS / GLUES)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
University of Oldenburg (University of Oldenburg) - 德国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Land reclaimed from the sea – ‘the coastal region in north-western Germany needs to be artificially drained, and this will be an increasing challenge with climate change.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
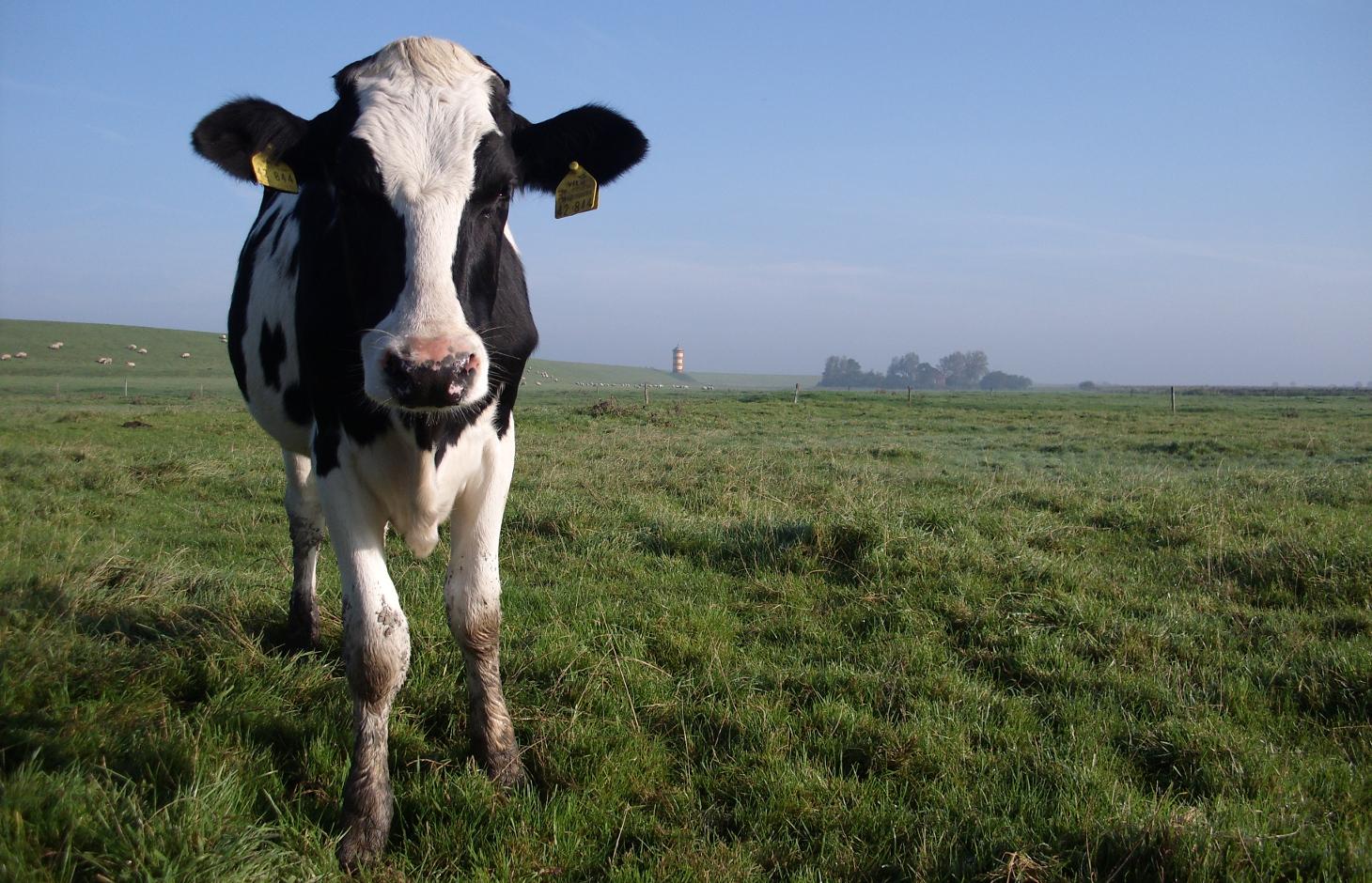
In some coastal locations of north-western Germany, during the 19th and 20th century, land was reclaimed from the sea: at present, the land lies below sea level. It is protected from the sea by a wall called ‘dyke’. The reason for reclamation by drainage and walls was to make use of the fertile soil for intensive cropland or pastures. In the Landkreis Aurich region, agriculture is the most important form of land use: it is the main source of income, supplemented by tourism.
Purpose of the Technology: However, in anticipation of the expected increase in winter precipitation due to climate change, extra freshwater discharge will need to be dealt with. Furthermore, the periods when natural discharge of freshwater into the sea can occur is likely to become shorter, due to the sea level rising – again as a result of climate change. Consequently, in autumn and winter, more freshwater will have to be pumped into the sea rather than being discharged naturally during low tides.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A dense drainage network enables intensive agriculture on the landward side of the primary sea wall. In total, one third of the Krummhörn community’s land is used for crops and one third as pasture. Drainage water from land which lies below sea level is pumped into the main drainage channels - which are at higher elevations and discharge naturally into the sea during low tides.
Natural / human environment: During storm tides when the sea level is high, large amounts of excess drainage water need to be pumped into the sea instead of naturally discharging. However, with climate change the present drainage network will no longer be capable of discharging all of the excess freshwater as a result of increased precipitation and sea level rise. This will require considerable investments in higher pumping capacities and an adapted drainage system with increased dimensions of ditches, as well as additional ditches in areas with a high flooding risk.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
德国
区域/州/省:
Germany, Lower Saxony
有关地点的进一步说明:
Landkreis Aurich
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 33.7 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
Traditional land use with dense drainage network to enable intensive agricultural land use in low elevated coastal landscapes.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- wheat
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 240 Longest growing period from month to month: March to October

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- 牛 - 奶制品
- 牛 - 非奶牛牛肉
产品和服务:
- 肉类
- 奶类
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Flood events and droughts may substantially disrupt the current land use system in the future and lead to higher drainage costs and higher economic risks for agricultural production. This will reduce the ecological and economic viability of the current intensive and highly productive land use under a changing climate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There is no awareness of risks due to climate change.
Livestock density: > 100 LU /km2
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
注释:
Mixed: Mp: Agro-pastoralism
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 引水和排水
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Climate change, higher rainfall in winter, lower in summer), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy rainfall in winter due to climate change expected), floods (Flooding due to heavy rainfall in winter)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Droughts due to less rainfall in summer (climate change))
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
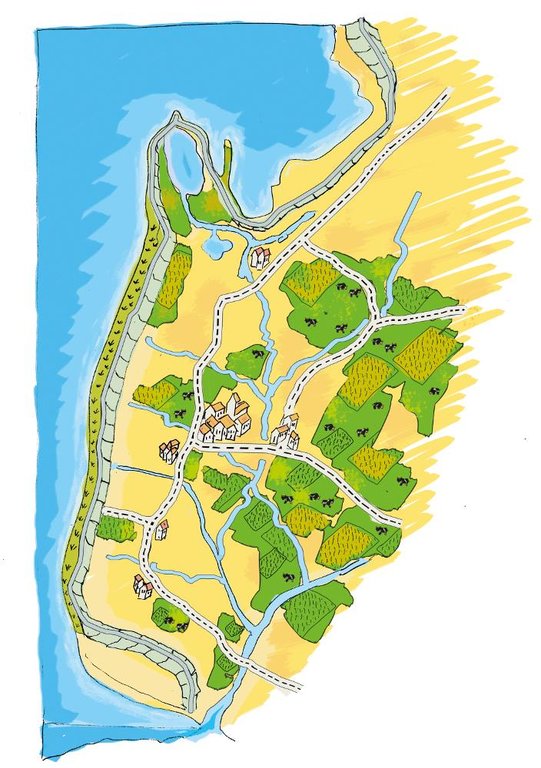
The figure shows the study region, located on the North Sea coast. The whole area is protected by a sea wall (grey). Crop fields (yellow), grasslands (green) and the drainage system (light blue) characterize the region. The traditional dense drainage network sometimes lacks the capacity to drain the lower land. This leads to flooding and limits agricultural productivity. It is expected that this flooding will increase with climate change. Agricultural production is faced with increased risks of crop failure in the future, unless the drainage system is strengthened.
Location: Krummhörn. County of Aurich, Lower Saxony
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: decrease groundwater level by artificial drainage
Construction material (earth): digged in soil, no specific material needed
作者:
Udo Schotten
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
EURO
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.94
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
100.00
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of drainage system (ditches) | once per year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 其它 | Maintenance cost pre km ditch | km ditch | 2270.7 |
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Cost are affected by soil types and cost of labour. The calculation is based on the mean costs over many years. This gives a mean annual cost of Euro 2,270 per km ditch per year. With 1,145 km of ditches this totals Euro 2,600,000 per year for the whole area (approx. 49,000 ha).
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 1% of the land.
49% of the land users are rich and own 24% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Many farmers do additional work in companies
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha, 100-500 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
生产故障风险
生产区域
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
灌溉用水的可用性
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
娱乐机会
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
土壤
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Reduced crop diversity
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
Increased habitat fragmentation
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
Excess water
Hazard towards adverse events
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
| climate change | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Development of dense drainage network is very cost intensive but last for very long time. Maintainance cost are quite low compared to the benefits of intensive land use.
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Well established technology in the whole region.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Optimal for agricultural production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Invest in infrastructure to maintain the system |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
High agricultural production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Strengthen the drainage system to adapt to climate change |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High drainage costs | Development of water retention areas ( see A_GER001_en, A_GER002_en and A_GER003_en) |
| Landscape vulnerable to climate change | Development of water retention areas (see A_GER001_en, A_GER002_en and A_GER003_en) |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
http://www.comtess.uni-oldenburg.de/
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
http://www.comtess.uni-oldenburg.de/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块