Roof rain water harvesting [阿富汗]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Aqila Haidery
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano
Jam aware ab-e-baran az bam
technologies_1728 - 阿富汗
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
People in Need (PIN) (People in Need (PIN)) - 阿富汗有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Stone masonry reservoir linked with roof rain water through a pipe scheme to provide safe drinking/low cost water supply in the remote areas.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
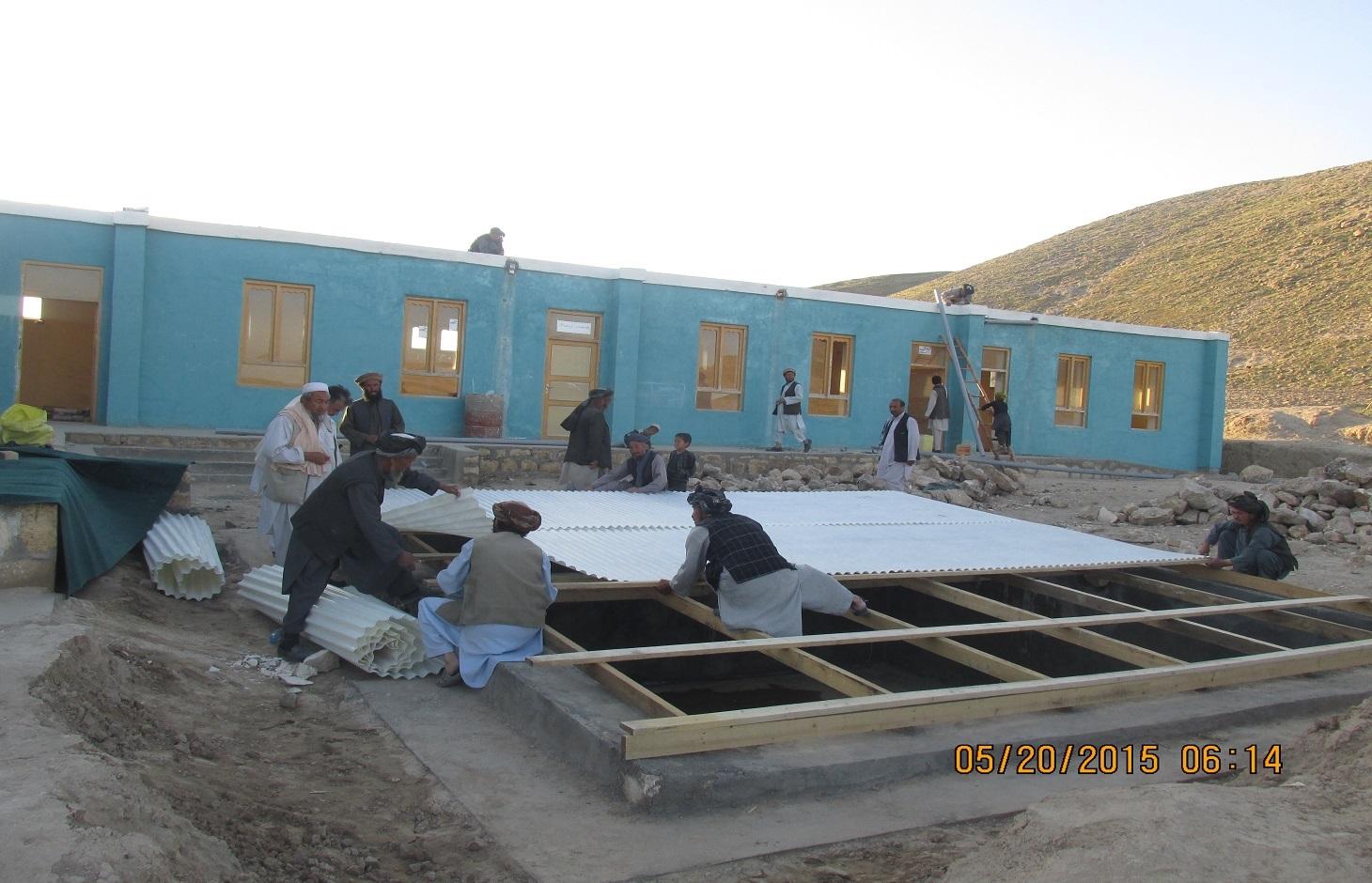
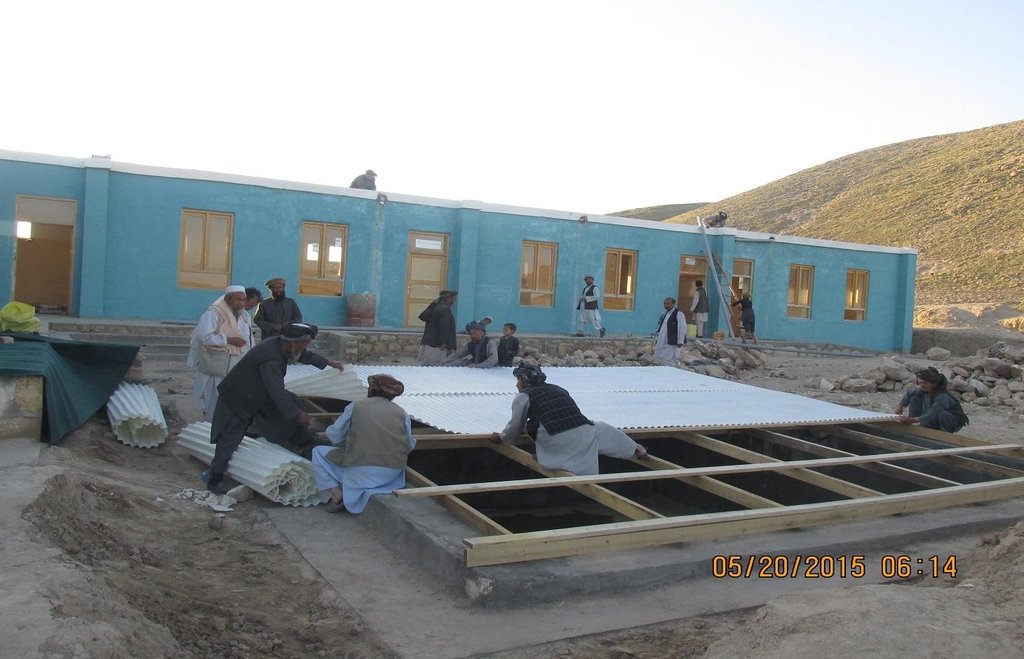
Kishendeh district is extremely mountainous with low precipitation and with a shortage of water storage facilities. Underground reservoirs, called kandas, traditionally serve as water storage, catching rain water over the two/three wet months of the year for use throughout the rest of the year. The kandas tend to run out of water before the next rains come, and tend to be positioned very far away from villages in difficult to reach spots. Alika village, where this technology is implemented, suffers from the scarcity and unavailability of irrigation, livestock and even safe drinking water. Scarcity of water during the summer season makes the lives of the community members more difficult and results in their immigration from the village in the past.
Purpose of the Technology: To ease water shortage in the target community, in addition to the introduction of drought-resistant crops and soil and water conservation techniques, People in Need (PIN) has applied roof rain water harvesting technology in Alika elementary school, Alika village, Chakana cluster. The site where this technology has been applied belongs to the state. The water use right is common and poor families that do not have access to kandas are given priority for using this reservoir. The school and households near the school use this water for drinking and washing.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The project started in October, 2014 and was completed in April, 2015. For the establishment of the roof rain water harvesting technology the following inputs were used:
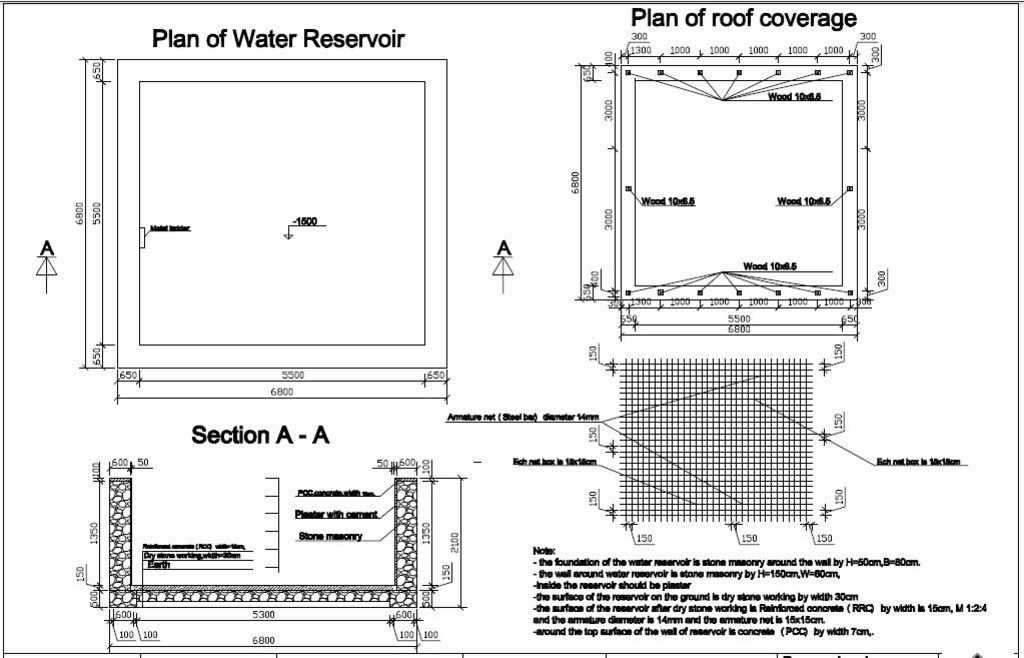
360 square meter tin was used to cover the roof. The pipe system is 45 meters in total. Three inch PVC pipes as well as elbows and T-joints were used. The water reservoir’s dimension of 0.80x0.50 m stone masonry foundation and 0.60x1.50x24.4 m wall; The dry stone masonry is 30cm wide; the surface of the reservoir, reinforced concrete (RCC) is 15cm wide. The reservoir was plastered with water proofing. The roof of the reservoir was constructed using wooden sketch covered with hard plastic material.
141 person/day were required for accomplishing this project. The establishment cost was 5,296$. The total value of community contribution is 7,500 Afghani/145 US$. Excavation by community members of a 50 m3 area is valued at 20,000 Afghani/385 US$. Thus the total community contribution is 10% of the total costs.
The head master of the school assumes the responsibility for maintenance. The reservoir needs to be cleaned five times a year, this is a low cost exercise. In the rainfall season it needs to be done once a month. Cleaning can be done by one person. The estimated cost for the maintenance is 500 Afghani or 10 US$ and is fully contributed by the community members.
Natural / human environment: Balkh province has a semi-arid climate and receives about 280 mm rainfall per year. The main economic activities are agriculture and livestock. The community members of the Kishendeh district have a low access to health services, employment, roads and transport and to drinking water and sanitation. Lack and scarcity of water in this village has caused many internal displacements as well.
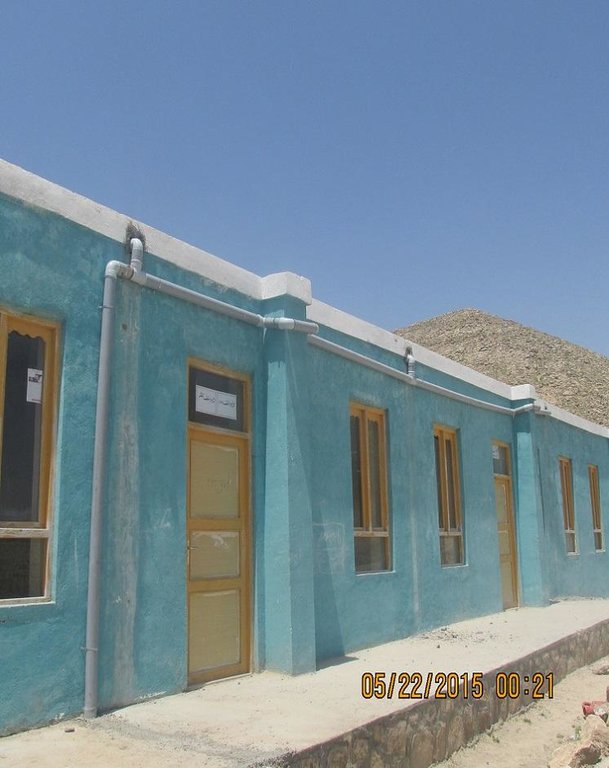
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿富汗
区域/州/省:
Balkh
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kishendeh
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
0.00105
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
The area where the technology is applied is 35*30 m which is equal to 1050m2
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The project started in October, 2014 and was completed in April, 2015.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- access to water
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

定居点、基础设施
- 定居点、建筑物
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Scarcity of drinking water for human and livestock consumption and as well as unavailability of irrigation water for the home gardening. Loss of roof rain water, Soil erosion, Occurrence of flash floods and environmental pollution
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Carrying water from distant places by donkeys is very time consuming and a burden on families.
Constraints of settlement / urban: no constraints
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: February till end of June
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

水质恶化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
Main causes of degradation: disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), population pressure
Secondary causes of degradation: poverty / wealth
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Detailed technical drawing of the water reservoir constructed for roof rain water harvesting in Alika village, Kishendeh district.
Location: Alika village. Kishendeh district, Balkh province
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Structural measure: Water reservoir
作者:
Eng. Saboor Popal, People In Need (PIN)
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation of the foundationConstruction of the reservoirExtending pipes from roof coverage to the reservoir |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Excavation of the foundation Construction of the reservoir | persons/day | 141.0 | 5.0 | 705.0 | 10.0 |
| 设备 | Tools and pipes | ha | 1.0 | 344.0 | 344.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Cement | bags | 1.0 | 376.0 | 376.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Stone | m3 | 159.575 | 24.25818 | 3871.0 | 10.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 5296.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 5296.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 7 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of the reservoir (5 times a year) | 5 times a year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cleaning of the reservoir | persons/day | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 50.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 50.0 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labor, cement and stone are the main factors affecting the total cost. After couple of years as well pipes may require to be changed.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: In Afghanistan the constructional and heavy physical activities which are done outside of the houses are mainly done by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Relative level of wealth: rich, average, poor
5% of the land users are rich.
55% of the land users are average wealthy.
40% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
产品多样性
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
社会经济弱势群体的情况
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
It has provided the access to drinking water for human beings and livestock. As well as it provides irrigation water to kitchen gardens for the HHs who lives near by the Alika Elementary School.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
水的回收/收集
地表径流
蒸发
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Once roof rain water harvesting project is implemented and constructed in a place, It will not need much recurrent costs.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
24 households covering 10 percent of stated area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
24 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The land users has not implemented the technology with the same specifications but has implemented it with using their own available local materials.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Provides low cost safe drinking water to the community members (Alika school and HHs who lives near the reservoir free of charge). Further more it provides irrigation water for the kitchen gardens in some extent. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Safe drinking water can be easily available during the winter season but during the three months of summer the water should be carefully used only for drinking. |
|
Requires minimum maintenance when constructed properly. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Pipe scheme, roof coverage area of the reservoir, should be cleaned, if any leakages occurs in the pipes or reservoir , they should be sealed. |
|
Application of the technology has provided the chance of having leisure time for the families. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Families and community members should use the water effectively. |
|
Roof rain water harvesting technology has supported the community members, economically. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Community members should take active participation in the maintenance of the reservoirs. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| This technology is difficult to be applied without external financial support. | Adoption of local materials should be promoted and as well as reservoirs be properly cleaned after the heavy rainfalls. |
| Technical knowledge is required for the application of this technology. | The technical knowledge should be transferred to the extension workers or local people to provide technical support in the future. |
| During the drought season with no rain fall enough water cannot be harvested inside the reservoir. | Water can be transferred to this reservoir through water tanks from other villages. |
| Social conflicts can occur during the distribution of water. | Meetings and awareness sharing events should be held. Water in keeper can be introduced by CDCs for the distribution of water. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块