Pressing of Cogon Grass (Imperata cylindrica) [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1729 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Padilla Alberto
Danao Municipality, Local Government Unit
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Dacumos Evangeline
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Espanto Patrick Benson
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Dinamling Djolly Ma
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Castillo Forester Emma
Department of Environment and Natural Resources-Forest Management Bureau
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Danao Municipality - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Forest Management Bureau (Forest Management Bureau) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR) [菲律宾]
A process of rehabilitating degraded forest lands by taking advantage of trees already growing in the area.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
An indigenous technology of enhancing wildling growth by pressing of cogon grass.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
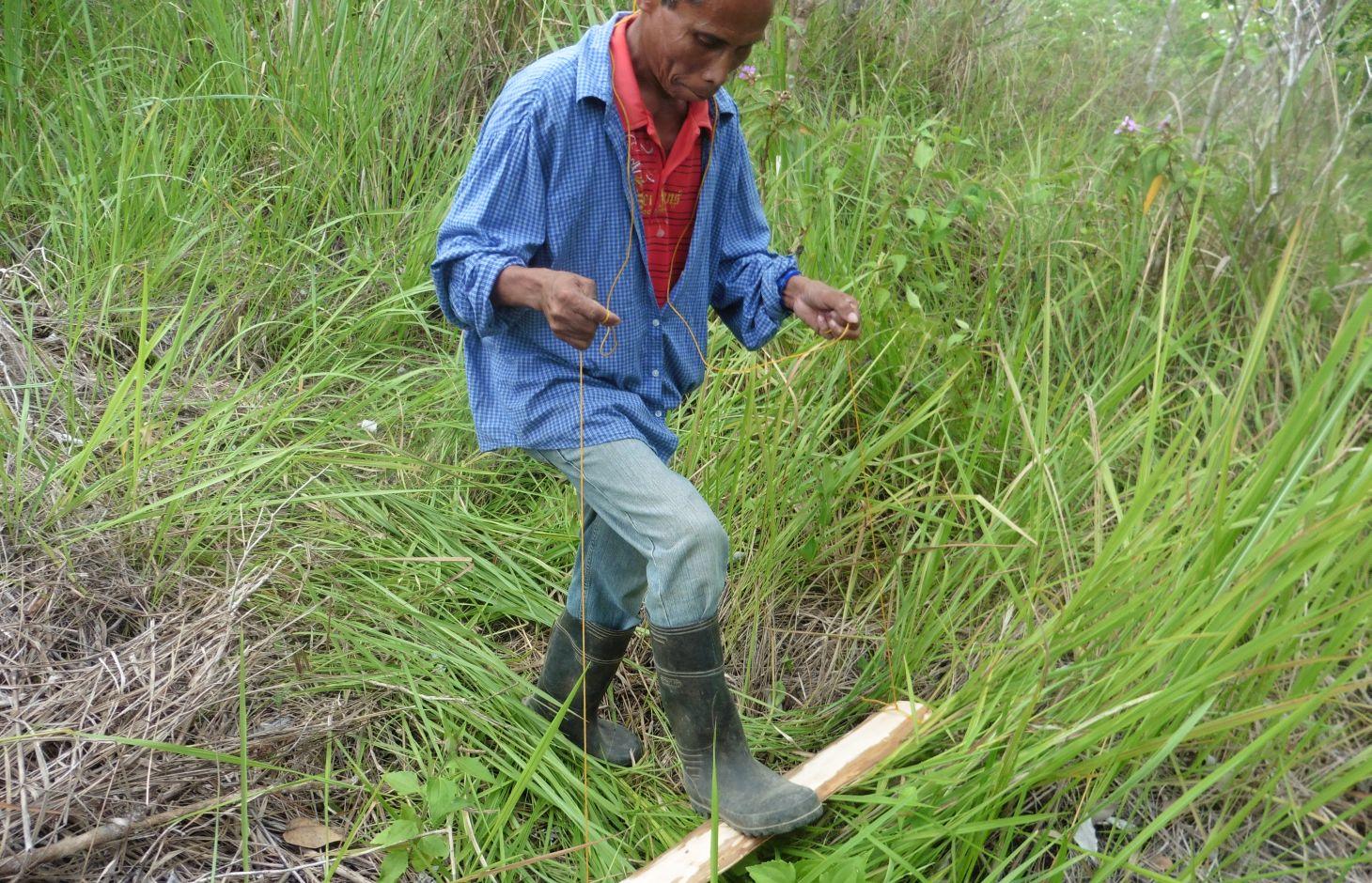
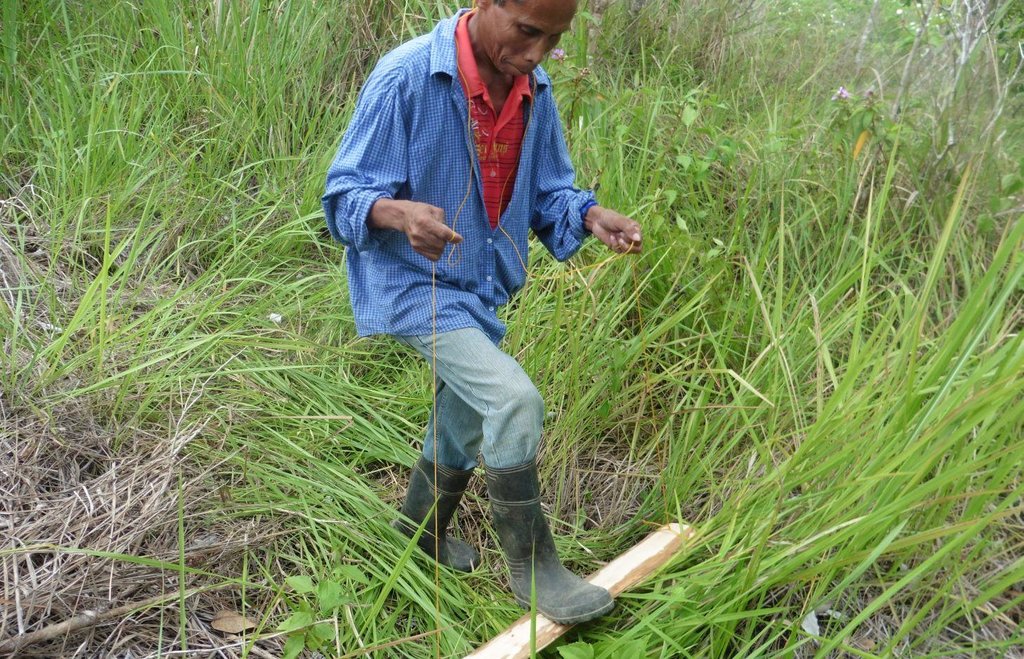
Cogon pressing is a simple low-cost technique of deterring the rapid growth of grasses that serve as competitors of wildlings for nutrient, water and light in the natural forest. The technology is described as the pressing down of cogon grass using a wooden plank tied in a rope, manually-operated by foot of the land user. Instead of cutting or burning the cogon, this technology is being used by the land user it was proven to be more effective in controlling cogon grass to grow fast. Wildlings are seedlings derived from seeds scattered by birds, insects, animals and wind without human intervention. By pressing the cogon, the wildlings can grow faster in the natural forest.
Purpose of the Technology: Cogon grass is a weed which grows quickly. It is difficult to control due to its small seeds carried by wind and rhizomes that are very resilient even to low soil fertility and harsh environment. In regenerating wildlings in the natural forest, these invasive weeds are the main competitor for nutrients water and space. The land user's common practice is to cut or burn the cogon grass in order to plant trees. However, this cannot be done in a natural forest because it destroys the flora and fauna. Thus, the indigenous technology of pressing the cogon grass was adapted to nurture wildlings of indigenous tree species. It allows the wildlings to grow naturally by reducing the competition from weedy species. It also provides an alternative technique of controlling weeds/grasses without burning. Burning grasses release greenhouse gases to the atmosphere.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Prior to the pressing of cogon grass, the selection of wildlings for natural regeneration is done by marking it with a peg. The wildling must be a robust/healthy indigenous tree species. Ring weeding is done at least one half meter radius around the wildling. Then, the surrounding cogon grass are suppressed through a method called “ pressing” or “lodging” using a wooden plank approximately 1” x 6-12” x 3-4’. A rope is knotted on both ends of the plank and looped over the shoulder of the land user for support and ease the pressing operation. The length of the rope is adjusted according to the height of the land user. The land user holds the rope on both side to lift the plank, and then, stepping on it to press the cogon grass repeatedly. The activity is done before and after the onset of rainy season. It is best to practice the technology when the stems of the cogon grass are still soft. The pressed cogon will last up to six months before it will produce new shoot and regenerate again.
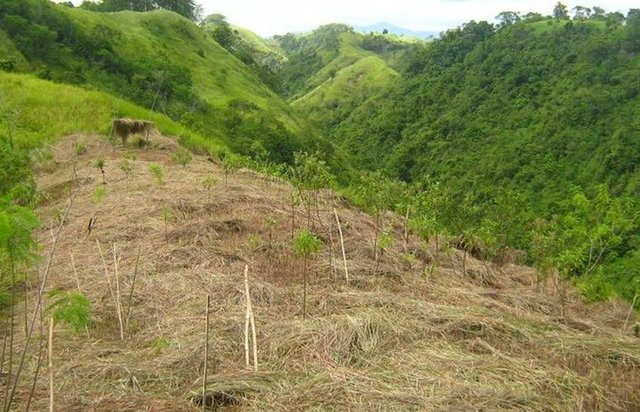
Natural / human environment: The area is part of the forest reserve in Danao, Bohol primarily intended for nature conservation and protection. It is about 100-500 m.a.s.l with moderately rolling to hilly slopes. It is under humid tropics climate with an average annual rainfall of 1500-2000 mm per year. The soil is loam, shallow depth, low fertility, with good drainage and medium water storage capacity. The area has high biodiversity as indicated by the presence of different indigenous trees and plants species, and wild birds. The land users who apply the technology are small holder farmers. They are members of a local cooperative. The population density is about 10-50 persons per sq. km. Since extraction of resources from the forest is prohibited, off-farm income is very important to the land users. Access to basic services and infrastructures are low.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Brgy. San Miguel
有关地点的进一步说明:
Danao, Bohol
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
0.2
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.2 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was introduced through the Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR) Project.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
- Deforested land
产品和服务:
- 自然保持/保护
- 自然灾害防护
- Increase in biodiversity
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Competition with speedy species and recurring disturbances such as fire
Other type of forest: Deforested land
Forest products and services: nature conservation / protection, protection against natural hazards
Other forest products and services: increase biodiversity
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 天然和半天然森林管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V5:其它
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Specification of other vegetative measures: Suppressing of cogon grasses
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

生物性退化
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bf:火灾的有害影响
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bh: loss of habitats
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bf: detrimental effects of fires
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), other human induced causes (specify) (fire)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Pressing grass with the use of wooden board
Location: Brgy. San Miguel. Danao, Bohol
Date: June 10, 2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Hands-on training for land users, they should learn the craft of pressing)
Main technical functions: control of fires
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: dipterocarps and indigenous species, naturally regenarated
作者:
Mr. Patricio A. Yambot, Bureau of Soils and Water Management
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
peso
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
45.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.44
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Identification of wildlings (2 feet high) | |
| 2. | ring weeding | |
| 3. | pressing of cogon away from wildlings | 3 times/year |
| 4. | Application of fertilizer |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 24.44 | 24.44 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Wood | ha | 1.0 | 2.22 | 2.22 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Rope | ha | 1.0 | 1.78 | 1.78 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 28.44 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.63 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pressing of Cogon | every other month |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 26.68 | 26.68 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 26.68 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.59 | |||||
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (220m)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is: Medium
Soil water storage capacity is: Medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
中等
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 1%
Off-farm income specification: Since extraction of resources from the forest is prohibited, off- farm income is very important to the land users.
Market orientation of production system: Forest conservation. Green braks are planted with cash crops as immediate source of food for subistence.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
生产故障风险
收入和成本
工作量
社会文化影响
社区机构
冲突缓解
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
yes little, it generated jobs
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
其它生态影响
Regeneration of indigenous species
Adaption to climate change
Accidents/injuries induced by humans
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 未知 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) provided financial and technical support for the implementation of the technology. The Local Government Unit (LGU) of Bohol provided additional labor force for the maintenance.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Low cost technology How can they be sustained / enhanced? Re-use and proper safe keeping of material. |
|
Limits height of fire How can they be sustained / enhanced? Frequent regular conduct of "pressing" activity |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Labor may cause some injury to workers | Extra care in conducting pressing activity particularly in steep areas |
| Increased dry matter susceptible to forest fire | Maintenance of fire lines |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Labor intensive | Thorough "pressing" of cogon grass to deter growth |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR) [菲律宾]
A process of rehabilitating degraded forest lands by taking advantage of trees already growing in the area.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
模块
无模块