SPRING GROUND WATER RESERVOIR FOR WATER SUPPLY AND FISH PRODUCTION [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: betty adoch
- 编辑者: JOY TUKAHIRWA, Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- 审查者: Udo Höggel
gwoko pii i tengom
technologies_2834 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Okecocon Alex
0712262059 / 0788945199
Goba Farmers group
Amuru district. Palwong Subcounty, Rubangadeg parish, Goba village.
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
26/05/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Spring ground water reservoir to supply water for the fish pond during dry season to be harvested throughout the year.
2.2 技术的详细说明
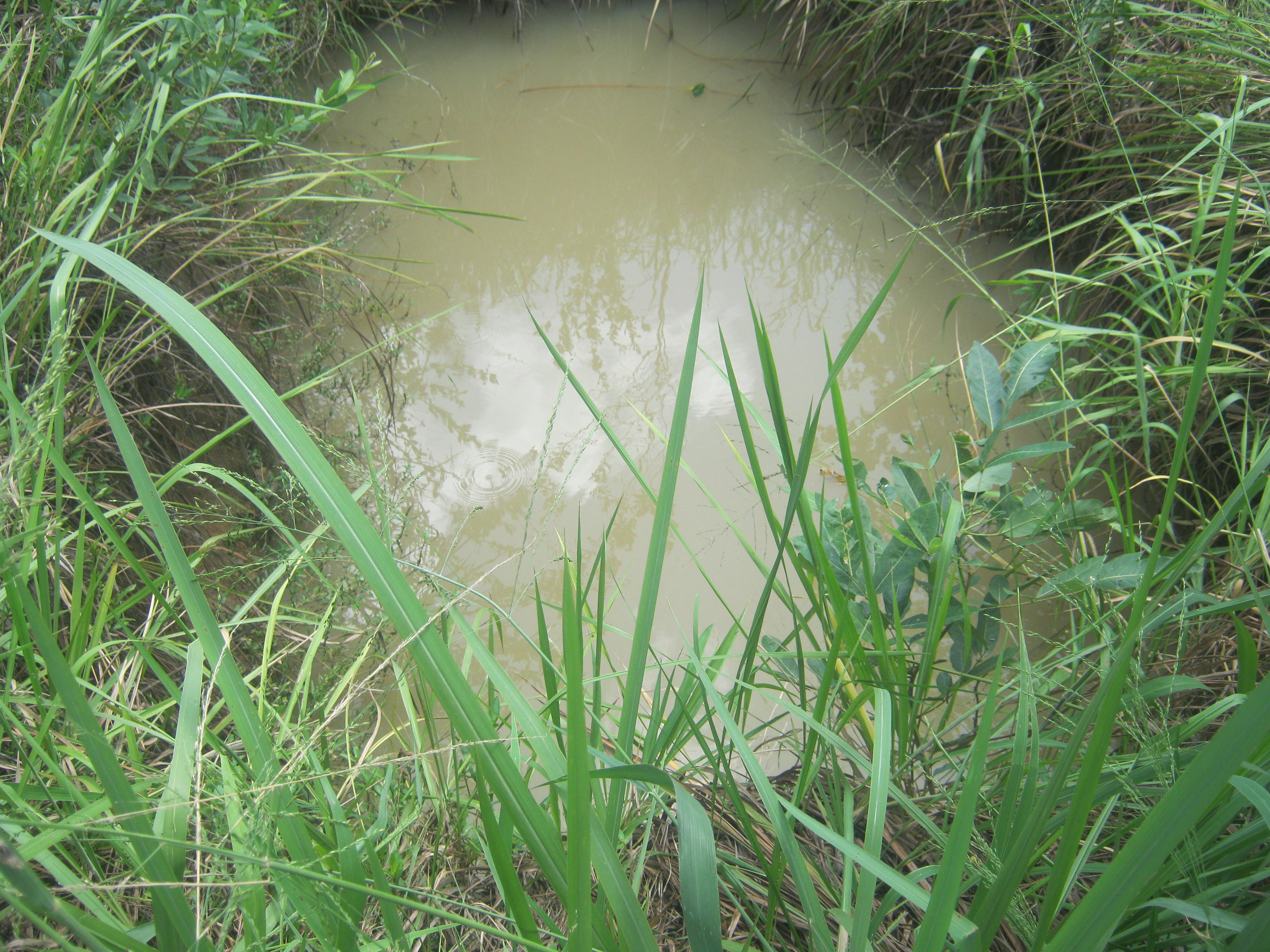
说明:
The spring ground water harvesting technology is one of the practices promoted by farmers in Northern Uganda with the aim of protecting and storing water which is used to refill the fish pond during dry season and also for fish production and household income both in the short, medium and long term.
Using hoes, spades, panga and labour, the water reservoir is dug at a length and width of 5*7 meters and a depth of 29 feet. Water fills the reservoir from ground water minor channels that drains at a specific point. Hence the reservoir fills up relatively fast. The reservoir site is well protected being fenced by barbed wire to avoid accidents from humans and animals who might fall into the reservoir.
Ridges are dug to prevent running external water from entering into the reservoir thus contaminating it. Grass grows around the cliff and around the reservoir to protect and compact the soil and prevent it from collapsing into the water, during dry season, water from reservoir is pumped into the fish pond. The water reservoir keeps water through out the year and fingerlings of 2 types or more of fish species kept in the fish pond. Sunlight can generally penetrate the pond waters to a depth of about 30-80 cm depending on the water level.
The fish species mostly kept include Tilapia, Nile Perch and wild fish. Once the technology is established the spring water reservior system requires only maintenance costs for removing weeds, feeding, restocking and slashing around spring water reservior. What is not liked about this technology is that it relies on a natural spring for its water supply. In case of drought survival of the fish is not guaranteed.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Northern Uganda.
有关地点的进一步说明:
Amuru Town Council
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2012
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The land-user wanted to have a constant supply of water for the fish pond.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

水道、水体、湿地
- 池塘、大坝
注释:
By water-harvesting, water can be stored in the soil.
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
The area was used for crop growing.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
具体说明:
Throughout the year.
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
- 地下水管理
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

其它措施
注释:
The water reservoir store excess water that would, otherwise cause flooding at the valley bottom.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

水质恶化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 不适用
注释:
The technology promotes storing of excess water in water reservoirs. Without this, flooding would occur in times of heavy rains thus creating hazards for life.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
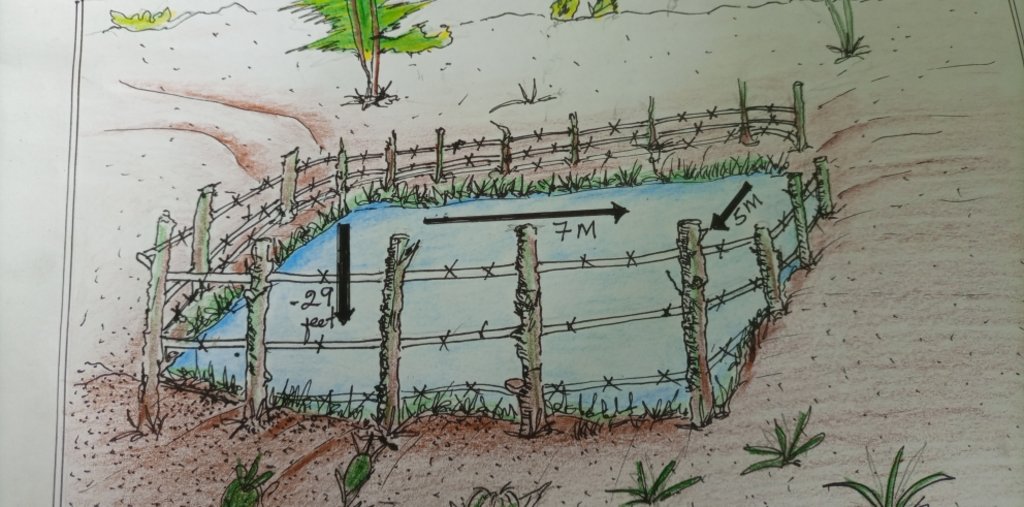
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
The water reservoir is dug at a length and width of 5*7 meters and a depth of 29 feet. The reservoir site is well protected being fenced by barbed wire to avoid accidents for humans and animals who might fall into the pool.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
0.5 acre
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UGX
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3600.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3000shs
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | site clearing | 结构性的 | dry and wet |
| 2. | digging pit | 结构性的 | dry and wet |
注释:
The technology is easy to establish.
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | Manday | 30.0 | 5000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hoes | pieces | 3.0 | 10000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Spades | pieces | 3.0 | 10000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Panga | pieces | 3.0 | 10000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Barbed wire | roll | 1.0 | 100000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Wooden poles | pieces | 10.0 | 5000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Fingerlings | Animals | 50.0 | 1000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 440000.0 | |||||
注释:
Labour, barbed wire and fingerlings take the most costs for this technology.
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fenching to avoid accidents | 管理 | dry and wet |
| 2. | Slashing the area | 管理 | dry and wet |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour for cleaning | Manday | 30.0 | 5000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 150000.0 | |||||
注释:
The cost of maintenance is manageable for the land user.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour costs are the main maintenance costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1000.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Heavy rain is usually received during wet seasons.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Gulu weather station.
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Savanna climate.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
There is a nearby stream that floods the valley bottom periodically thereby lowering the water quality.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Aquatic animals survive in the reservoir.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The land user grows crops such as rice, maize, cassava, cabbages and has home fruit gardens as well as aquaculture.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
The land user needs to aqcuire land title.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Due to the water harvested and stored.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Due to additional water stored.
水资源可用性和质量
家畜用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
For fish production.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Expenses incurred only on the purchase fish feeds and maintenance of the reservoir.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
From the sale of fish.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Only labour for cleaning around the reservoir and purchase of feeds.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Constant water supply in the fish pond to enhance production.
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Water harvesting helps mitigating climate change impacts.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Ground water is harvested.
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Due to the excess water stored.
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Due to a more constant supply of available water.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 季节性温度 | 湿季/雨季 | 增加 | 适度 |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 不好 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 减少 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The maintenance of the technology is very easy.
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
Other farmers are still learning about the technology.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology provides fresh water and high volume to the fish pond. |
| The stored water irrigates gardens of rice, cocoa and cabbage. |
| Storage of water provides water for domestic purposes. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology retains soil moisture. |
| The technology is good at conserving the soil. |
| The technology helps preventing soil degradation by flooding. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Sometimes the cliff tends to collapse into the water which may affect the fish. | Plan to cement the cliff. |
| Easily liked by thieves in need for scraps. Yet, the constant replacement of barbed wires may turn out to be costly. | Plan to buy new wires for fencing. 24 hour security guard. |
| Sometimes periodic flooding may lead to continued lowering of the water quality. | Ridges can be created to control flooding. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The technology relies on a natural spring. In case of drought survival of the fish is not guaranteed. | Harvest rainwater and have alternatives for pumping water to the fishpond during the dry season. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
01
- 与土地使用者的访谈
01
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Water quality of improved water sources and associated factors in Kibuku District, Eastern Uganda Abel Wilson Walekhwa, Moses Ntaro, Peter Kawungezi, Evas Nimusiima, Chiara Achangwa, David Musoke & Edgar Mugema Mulogo, 50 (2022).
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00604-5
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Spring ground water level summary
URL:
https://www.lpsnrd.org/spring-groundwater-levels-summary
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块