No-till [波兰]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Magdalena Frac
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
No-till
technologies_2851 - 波兰
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
Lipiec Jerzy
Institute of Agrophysics, Polish Academy of Sciences
波兰
Usowicz Boguslaw
Institute of Agrophysics, Polish Academy of Sciences
波兰
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Institute of Agrophysics, Polish Academy of Sciences (IA PAS) - 波兰1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
No-till is a system where crops are planted into the soil without primary tillage.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
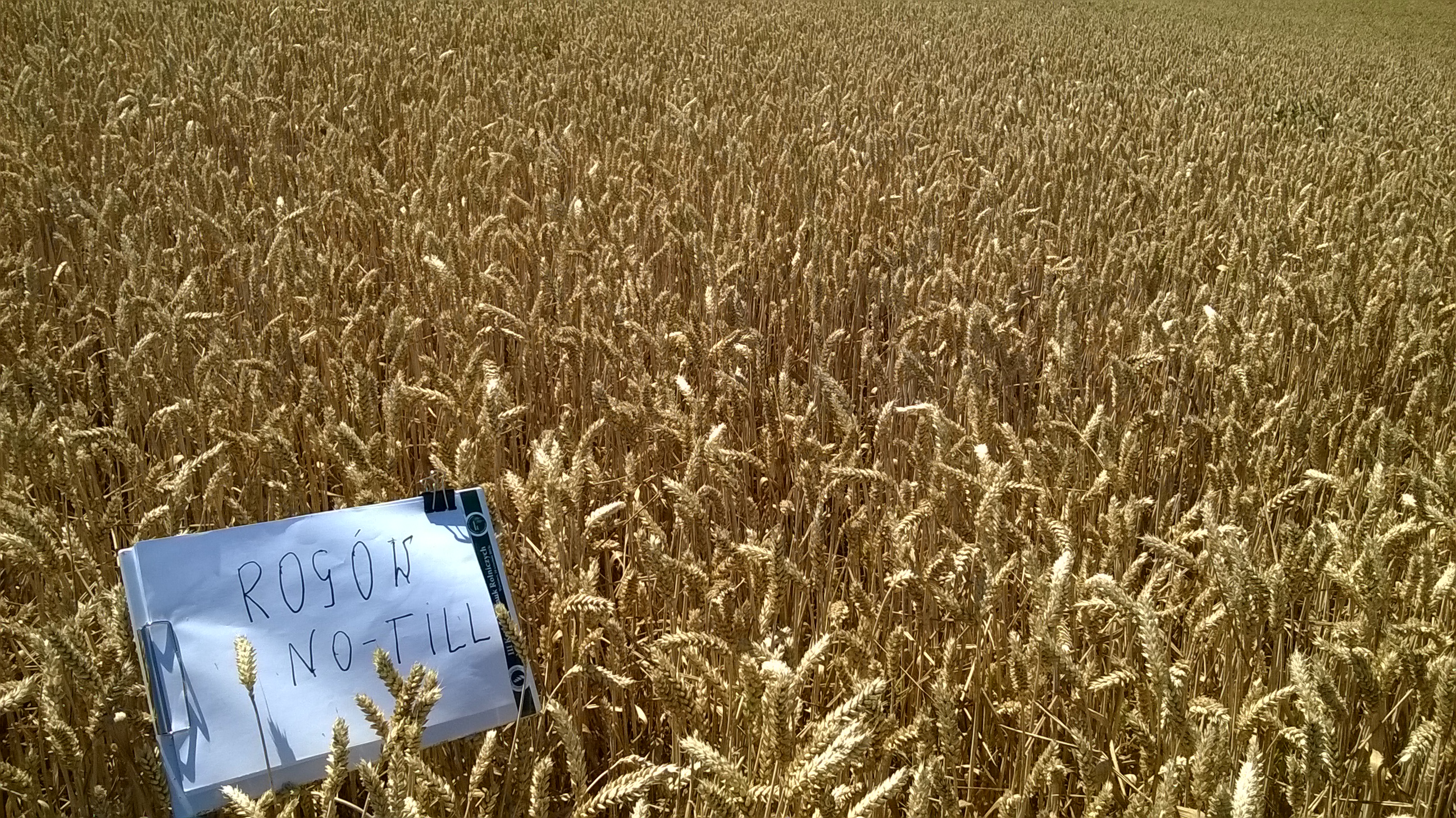
The technology is used in Rogów (N 50.80018 E 23.44883), in Zamosc Region in Poland under cereals or oil crops. The technology is used on about 700 ha area. The case study is embedded in a typical agricultural region on rather fertile soils formed from loess. The altitude at the study site is 238 m.a.s.l., average temperature 17.6°C and precipitation 563 mm. The farmer uses direct sowing technique and the following machines: stubble cultivator, seed drill with disc coulters and combine harvesters. The crop rotation includes the following crops: wheat/maize/wheat/rape. No-till, as well as minimum and reduced tillage, provides the opportunity to reduce energy requirements, increase soil organic matter content and protects the soil against erosion, runoff and compaction. No-till may often increase crop yields. The costs reduction for fuel making this technology more attractive commercially. No-till reduces CO2 emission from fuel during machinery usage. The presence of crop residues on the surface of soil layer can cause plant diseases. It is necessary to use some low amount of herbicides and fungicides in no-till.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
波兰
有关地点的进一步说明:
Rogów
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Rogów, Poland, no-till, Coordinates: N 50.79988, E 23.4884
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
The farmer visited farms in the USA where the no-till technology is widely used. Then, he introduced the technology on his own farm in collaboration with local agricultural research units, including Institute of Soil Science and Plant Cultivation in Pulawy and Life Sciences University in Lublin.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 降低灾害风险
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- wheat
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A3:土壤表面处理
A3:区分耕作制度:
A 3.1:免耕
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Fig. 1. Crop residues on no-till field under rape
Fig. 2. Seed drill with disc coulters (seeds are introduced into the soil pneumatically)
作者:
Magdalena Frąc
日期:
21/07/2016
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 ha
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
PLN
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.28
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
50-100 PLN
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Rill opening of soil | Spring or autumn depending on the crop type |
| 2. | Direct sowing and fertilizing applied at once through direct sowing machine | Spring or autumn depending on the crop type |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
360.0
注释:
The costs refer to 1 hectare managed and include fertilizers, equipment and labour.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Cost of machinery appropriate to no-till and costs to meet bill of machinery contractor
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
- family
土地使用权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
The farmer observed increase of crop productivity in Mg per ha for the following plants: wheat, rape and maize. Grain yield of wheat under no-till vary from 8.8 to 11 t/ha. The yields are greater than those from average yield under conventional plough system.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology increases crop quality by improving soil water retention.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology decreases the risk of production failure due to greater yield stability.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology simplified land management by less intense machinery traffic on the field.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
The expenses on agricultural inputs in no-till technology are reduced due to lower fuel costs.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
The workload in no-till technology decreases by lower number of agricultural practices.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology improves the food security by increased yield stability.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Land degradation knowledge is improved by the promotion of the no-till technology.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
The water quantity increases in no-till technology due to less evaporation caused by crop residues on the surface of the soil.
水质
注释/具体说明:
The water quality increases in no-till technology due to protection of soil against erosion and runoff.
水的回收/收集
注释/具体说明:
The water collection in no-till technology is improved due to better infiltration of rainfall water through earthworms macropores open at the soil surface.
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
The surface runoff in no-till technology decreased due to presence of crop residues on the field surface and open earthworms macropores increasing infiltration of rainfall water.
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology decreases evaporation due to crop residues on the soil surface.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology increases soil moisture by reduced evaporation due to crop residues on the soil surface and increasing soil organic matter content.
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology increases soil cover due to crop residues on the soil surface.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology decreases soil loss due to reduced soil erosion and runoff.
土壤堆积
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology increases soil accumulation due to increase of soil organic matter content.
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology reduces soil crusting and sealing by the presence of crop residuses and greater soil aggregates stability.
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology reduces soil compaction due to greater bearing capacity of soil and due to less traffic on the soil.
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology increases nutrient cycling / recharge due to reduced surface runoff and associated nutrient losses and greated biodiversity.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology increases soil soil organic matter content due to crop residues on the soil and less mineralization of organic matter.
酸度
SLM之前的数量:
5.8
SLM之后的数量:
6.9
注释/具体说明:
We observed increase of pH value (6.9) in no-till coil compared to conventionally tilled soil (5.8) that can be related with greater soil organic matter content in no-till soil.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
The farmer observed increase of crop productivity.
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
We observed greater quantity of earthworms under no-till compared to the conventional tilled soil.
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Pest/disease control increased in no-till technology due to proper application of pesticides.
减少气候和灾害风险
滑坡/泥石流
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology decreases landslides/ debris flows by protection of soil against erosion and greater water storage. However, no landslides were not observed in the area.
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
The no-till technology desreases emission of carbon and greenhouse gases due to reduction of CO2 and other greenhouse gases realising by mechanical soil loosening.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
The farmer covered about 700 ha by no-till technology.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
The farmer saw this technology in the USA and wanted to try it in Poland.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The increase of crop yield and production. |
| Prevention and reduction of erosion is widely observed under no-till. |
| Soil organic matter content increase is observed. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Soil structure improvement. |
| Decrease of environmental damage associated with soil inversion by ploughing. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Weed expansion | Herbicides application |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Plant diseases | Fungicides application |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
4
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
6
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
21/07/2016
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块