Water and soil conservation by using rock fragments [希腊]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Costas Kosmas
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
Προστασια νερού και εδάφους με την χρήση λίθων και χαλικιών
technologies_2911 - 希腊
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Kounalaki Aikaterine
希腊
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Agricultural University of Athens (AUAb) - 希腊1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The described SLM technology is conserving soil water and soil from erosion
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The presented technology of leaving rock fragments in/on the soil in order to reduce soil evaporation and erosion in sloping areas greatly contributes to soil and water conservation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
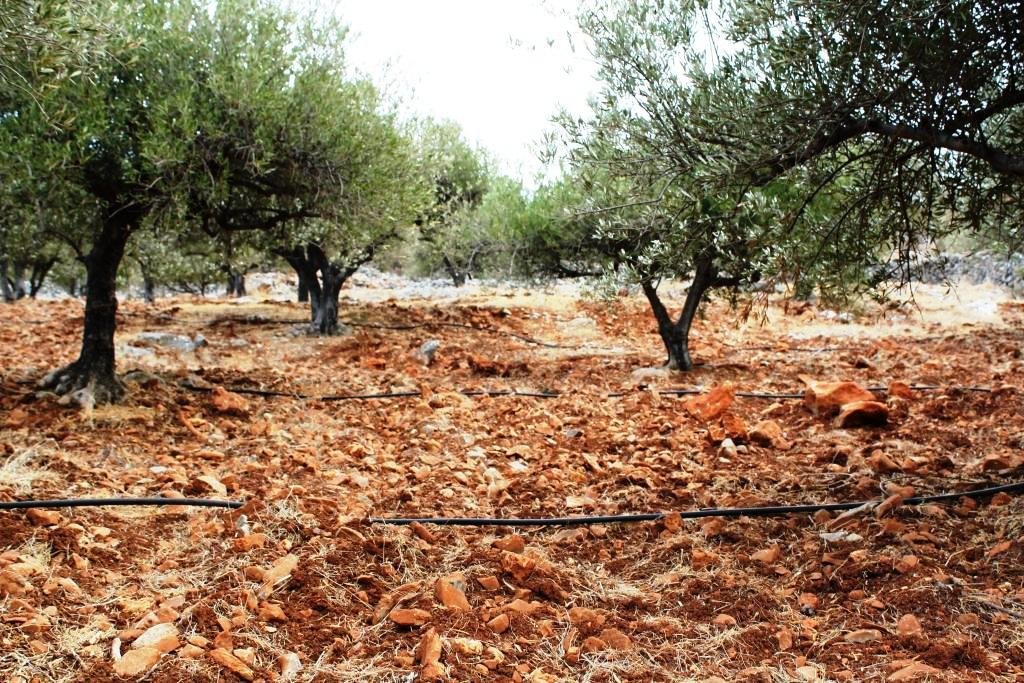
The described technology is applied in semi-arid or dry sub-humid environments with an annual rainfall between 250-500 mm. This technology was mainly found in environments of the before mentioned climatic conditions on hilly areas (slope: 11-30%) and in shallow (depth: 21-50 cm) or moderately deep soils (depth: 51-80 cm) cultivated with perennial crops. These soils present moderate concentrations of soil organic matter (1-3%) and do not face any flood or salinity problems. The socioeconomic environment of these areas is characterized by middle-aged or elderly producers who mainly cultivate leased medium-sized fields with mechanical equipment. The orientation of the market is mixed (subsistence/commercial) and the off farm income of producers is greater than 50% of their total income.
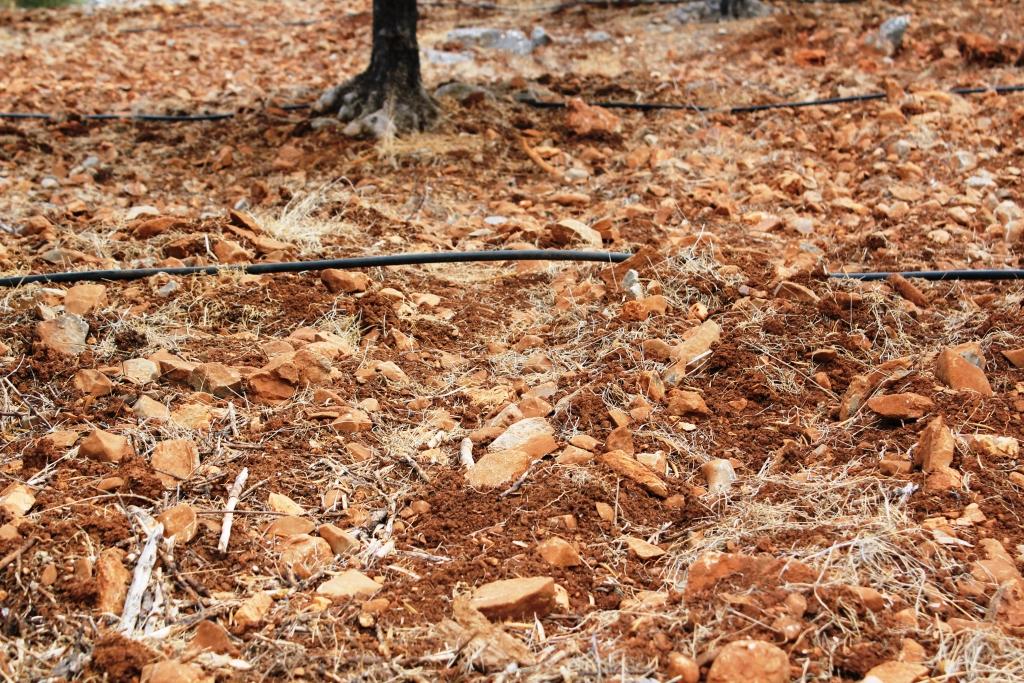
The main characteristics of the technology is the presence of an adequate amount of rock fragments especially on the soil surface. Rock fragments are found, in many cases, in the soil. Farmers used to remove them for clearing the soil but in case that the area is located in semi-arid or dry sub-humid climatic conditions, then the leaving of rock fragments in the field is of high importance for soil and water conservation. An amount of more than 20 percent of rock fragments on the soil surface is highly efficient in protecting soil and water.
The purpose of the technology is to conserve soil water from evaporation and to reduce soil loss under heavy rainfalls. The technology can be established in areas with soils formed on consolidated parent materials such as limestone, shale, conglomerates, etc. The benefit of the technology is the conservation of soil and water but the negative impact is the decrease of the effective soil depth which can be used by the growing plants. Land users usually do not like rock fragments in the field since they create problems during land cultivation activities. The technology is applied mainly in olive groves.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
希腊
区域/州/省:
Crete
有关地点的进一步说明:
Area cultivated mainly with olive groves in Crete (Municipal District of Shinias, Municipality of Arkalohori) with soils formed on limestone, shale, and conglomerates parent materials.
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
The application of technology depends on the presence in the soil of rock fragments
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
The above-mentioned experimental research has been carried out during the execution of the EU research project MEDALUS
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 橄榄树
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 集水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A3:土壤表面处理

管理措施
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The proposed technology is related to the management of soils containing high amounts of rock fragments especially on the soil surface. Unattached pieces of rocks of 2 mm diameter or larger that are strongly cemented or more resistant to rupture are called rock fragments. They are present on the soil surface or distributed in various quantities into the soil body. Rock fragments are classified according to their diameter to the following categories: pebbles (diameter 2-75 mm), cobbles (diameter 75-250 mm), stones (diameter 250-600 mm), and boulders (diameter >600 mm). Based on the existing research, rock fragments in the soil surface are defined according to the percentage cover in three classes: >40%, 15-40%, and <15%. As the percentage increase, the effectiveness on soil water conservation increases and the rate of soil erosion decreases. Pebbles and cobbles are more effective on soil water conservation, while stones are more effective on soil erosion reduction.
作者:
Costas Kosmas
日期:
13/09/2016
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 hectare
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
40
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing only large stones (rocks) | any time |
注释:
The proposed technology does not require any cost. The idea is to keep rock fragments in the soil and not removing them which will cost some money
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Clearing rocks | hours | 12.0 | 7.0 | 84.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Bulldozer | machine hours | 1.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 204.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 204.0 | |||||
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
-8.0
4.5 维护/经常性活动
注释:
No maintenance
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Rainfall is falling mainly from Octomber to May.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Sitia
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Hilly areas of various topography configuration.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water is transported from mountainous areas
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
用水权:
- 租赁
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Increase crop production
收入和成本
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Reduces labour and workload
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
-1
SLM之后的数量:
1
蒸发
SLM之前的数量:
-2
SLM之后的数量:
1
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Reduces soil water evaporation therefore increase water availability to the growing plants
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Decreases run-off and soil erosion and therefore increase plant productivity. But the negative impact is the decrease of the effective soil depth which can be used by the growing plant.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
SLM之前的数量:
-1
SLM之后的数量:
2
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The advantages of the technology is to support the opportunity which nature offer in conserving soil water and reducing soil erosion by the presence of rock fragments in hilly areas under semiarid or dry climatic conditions |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reducing labour, increasing production and protecting soil and water resources |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The presence of rock fragments create problems in cultivating the land. Technology works only for rather undemanding woody plants like olive trees. | use the appopriate cultivation machineries |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Rock fragments affects negatively the quality of product of plant such as potatoes, onion, etc |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
soils have been mapped in which rock fragments have been measured
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
09/09/2015
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Danalatos, N.G., C.S. Kosmas, N.C. Moustakas and N. Yassoglou, 1995. Rock fragments II: Their impact on soil physical properties and biomass production under Mediterranean conditions. Soil Use and Management, 11:121-126
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
The MEDALUS projects
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Kosmas, C.S., Moustakas, N., Danalatos, N.G., and Yassoglou, N. 1993. The effect of rock fragments on wheat biomass production under highly variable moisture conditions in Mediterranean environments. Catena 23:191-198.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
The MEDALUS projects
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Evaporation from cultivated soils containing rock fragments
URL:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0022169495029311
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块