Hedgerows as shelter belts along agricultural fields [法国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Alan Radbourne
- 编辑者: David Robinson, David Norris, Sabine Reinsch
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
gestion des haies
technologies_5644 - 法国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Pivain Yann
Chambre d’agriculture de Normandie
法国
土地使用者:
Odienne Eric
EARL Bril Odienne
法国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
European Interreg project FABulous Farmers有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (CEH) - 英国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Association des Chambres d’agriculture de l’Arc Atlantique (AC3A) - 法国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Hedgerows are important to shelter the functional biodiversity necessary for natural regulation of crop pests. The extent of this effect depends on hedgerow management at farm level.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
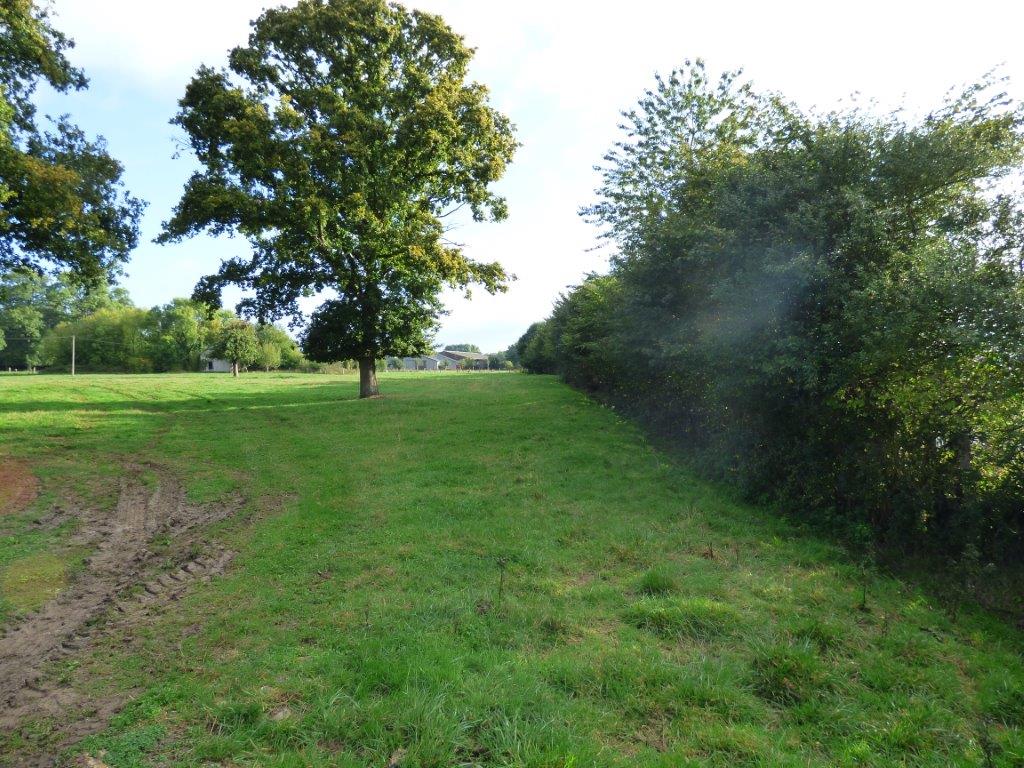
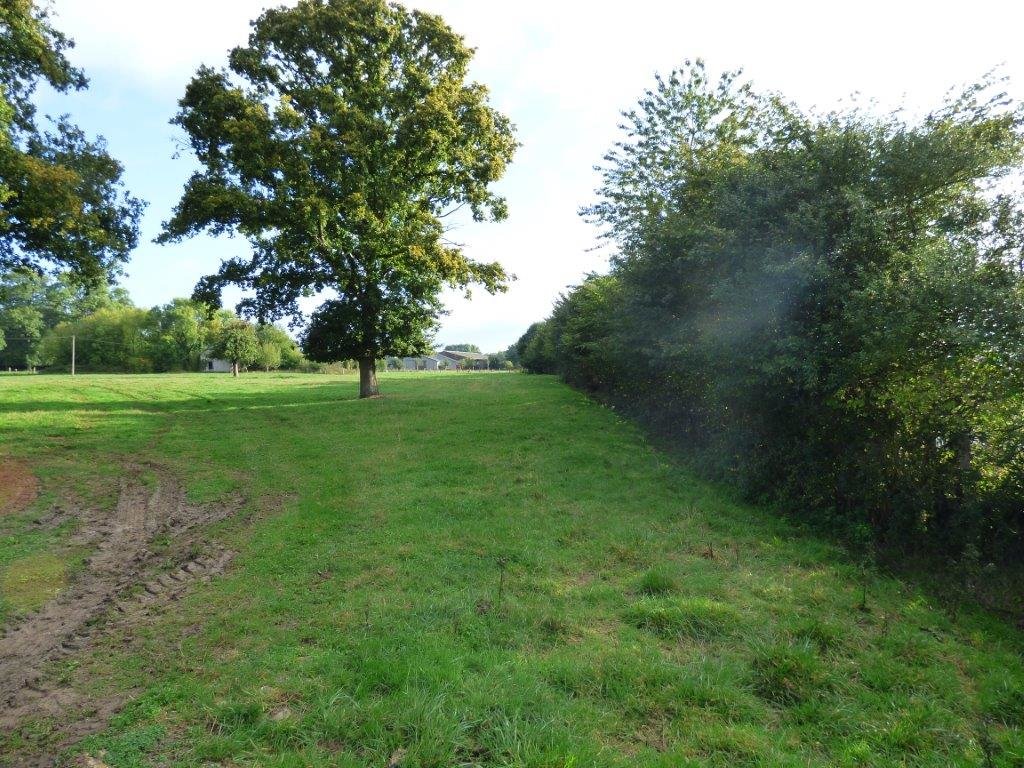
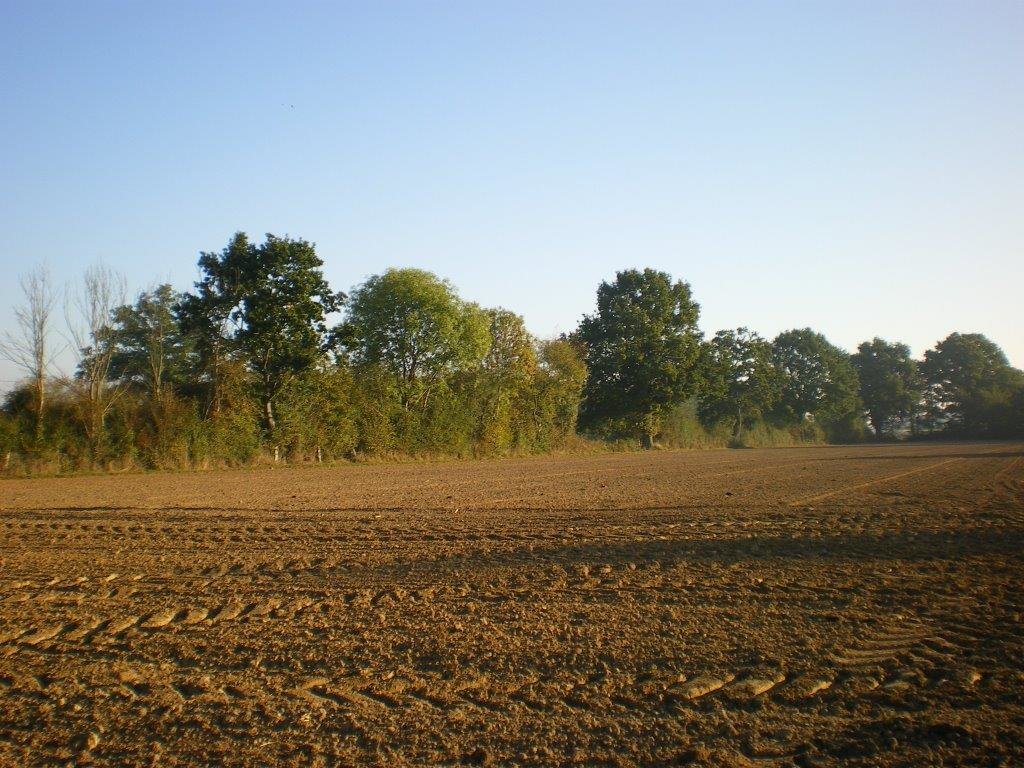
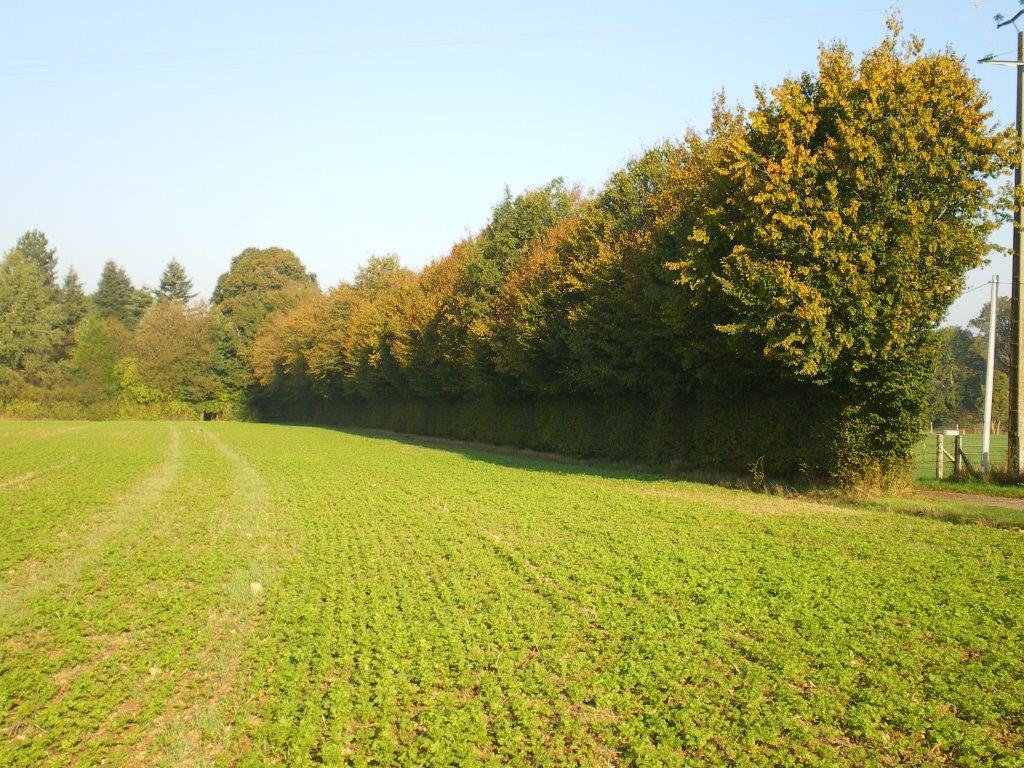
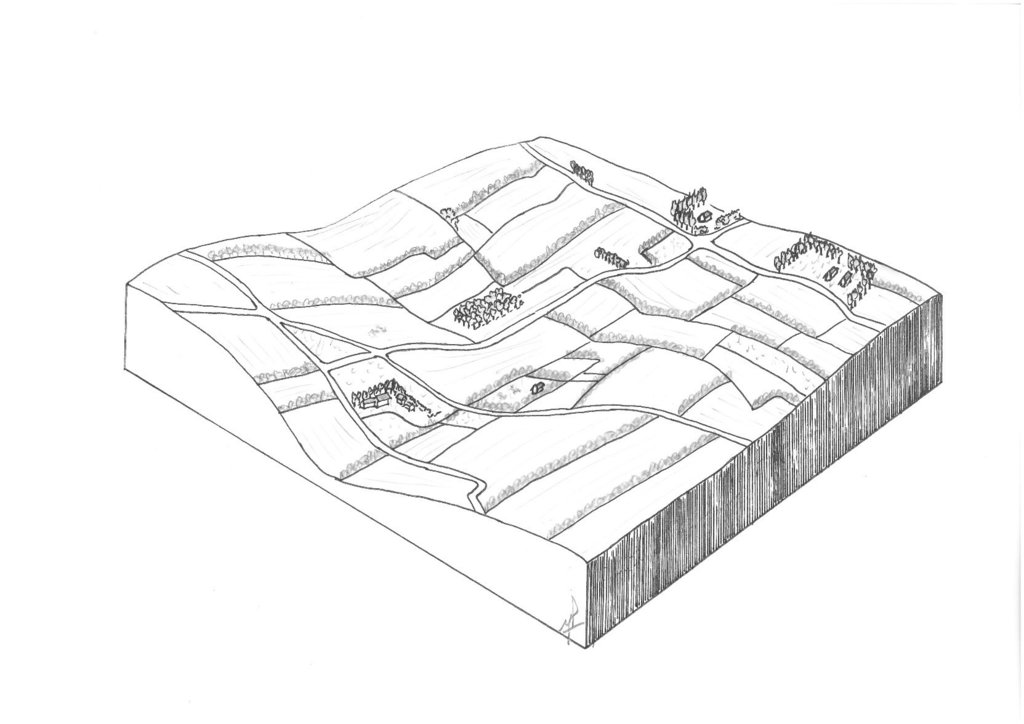
Hedgerows are typical landscape features of rural Normandy. They surround agricultural fields, whether cultivated or under grassland. Hedges were already prominent in Normandy during the 19th century, and they reached a peak between the first and second world wars. However, since the 1960s, the restructuring of agricultural land and technical and technological developments in agriculture have led to the disappearance of hedgerows. The challenge since the beginning of the 21st century has been to maintain the existing hedgerows and to establish others. This is important in the light of today’s agri-environmental and climate issues.
The technology of replacing, restoring or planting new hedgerows has been applied in an area of mixed farming for the benefit of crop and animal protection, watercourse and soil erosion buffering and protection, and landscape and habitat connectivity improvements. The technology has been applied in a locality by a small number of farmers over a number of recent years.
Hedgerows are planted on the periphery of the fields with species spaced at 0.5 to 1 m apart. There are between 1 and 3, sometimes even 4 different vegetative types used in establishing the hedgerows - herbaceous, bushy, and shrubby plants and trees. The current average length is 36 metres of hedge per hectare. The position of ancient hedgerows in the landscape is the result of the history of parcels of land. In contrast, over the last ten years, agri-environmental criteria have been taken into account in selecting planting sites. The main local species used for new hedges are: Fraxinus, Quercus, Tilia, Carpinus, Acer campestre, Crataegus, Corylus and Ilex. Each hedge is considered to have an influence ranging from 50 to 200 m away from it in terms of windspeed, runoff, and biodiversity.
Hedgerows play a very important role in preventing:
- Biological degradation through maintaining and increasing wildlife biodiversity and stimulating biological regulation of crop pests
- Climate-induced impacts both at the local level (decrease of wind speeds, decrease of evapotranspiration, shade for animals) and at global level (carbon storage, substitution of fossil energies by renewable energy)
- Water degradation through maintaining and improving qualitative and quantitative regulation of water at the watershed scale
- Soil erosion by water and chemical deterioration through the conservation of soils
- Soil erosion by wind
Despite these benefits, this SLM technology has not yet been taken up widely. It is more than necessary to restart hedgerow management with Normandy farmers, especially as the use of external inputs (e.g. fertilizers and pesticides) is increasingly expensive for both farmers and society.
The compilation of this SLM is a part of the European Interreg project FABulous Farmers which aims to reduce the reliance on external inputs by encouraging the use of methods and interventions that increase the farm’s Functional AgroBiodiversity (FAB). Visit www.fabulousfarmers.eu and www.nweurope.eu/Fabulous-Farmers for more information.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
法国
区域/州/省:
Normandy
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
- various root and cereal crops over time
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
A variety of crops are grown in rotation, usually cereal or root crops dependent upon market demand - this technology is less dependent on the crop grown but the benefits of a hedgerow planted at the edges reduce the cropping area into smaller parcels.

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- 牛 - 非奶牛牛肉
是否实行作物与牲畜的综合管理?:
否
品种:
牛 - 非奶牛牛肉
计数:
20

森林/林地
- 植树造林
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 混交品种
植树造林类型:
- 温带大陆林人工林
- Main local species Fraxinus, Quercus, Tilia, Carpinus, Acer campestre, Crataegus, Corylus, Ilex
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 混合落叶或常绿
产品和服务:
- 薪材
- 自然保持/保护
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 防风林/防护林带
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S11:其它

管理措施
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
- M5:物种组成的控制/变化
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Hedgerows are planted on the periphery of the plots. The trees are spaced 0.5 to 1 m apart. The height varies from 1.5 m to more than 20 m. There are between 1 and 3, even 4 different vegetative strata (herbaceous, bushy, shrubby, tree). The local average length is 36 m of hedge per hectare (the departmental average is 19 m / ha). The position of old hedges is more the result of the history of parcels (properties) than linked to agri-environmental criteria. Over the last ten years, agri-environmental criteria have been taken into account in choosing planting sites. The main local species: Fraxinus, Quercus, Tilia, Carpinus, Acer campestre, Crataegus, Corylus and Ilex.
Each hedge is considered to have an influence ranging from 50 to 200 m away from it (in terms of wind, runoff, biodiversity).
作者:
Yann Pivain
日期:
01/11/2019
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
per 1 km of new / replanted hedgerow
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
€
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.9
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
120
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Decide on planting site, the design/layout of the hedge and the species | Spring |
| 2. | Soil preparation through clearing of land and harrowing | After harvest of crops |
| 3. | Application of mulch to planting strip | After harvest of crops |
| 4. | Planting of trees & protections (e.g. deer guards) | November to January |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Design and planning | person-days | 0.3 | 120.0 | 36.0 | 50.0 |
| 劳动力 | Surface preparation for planting | person-days | 0.1 | 120.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Application of mulch | person-days | 0.3 | 120.0 | 36.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Planting trees | person-days | 11.0 | 120.0 | 1320.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tractor with harrow | machine-days | 0.1 | 50.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Trees | Piece | 1000.0 | 2.0 | 2000.0 | 50.0 |
| 植物材料 | Tree protection (i.e. wild animal guards) | Piece | 1000.0 | 0.5 | 500.0 | 80.0 |
| 植物材料 | Mulching | Piece | 1000.0 | 1.3 | 1300.0 | 80.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 5209.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 5787.78 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
local community / subsidy
注释:
Costs do not include training of farmers.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hedgerow maintenance (cutting/pruning) | From June to December every 3rd year |
| 2. | Wood harvest (20 years after planting) | December to March |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Hedgerow maintenance (cutting/pruning) | day | 0.2 | 120.0 | 24.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Maintenance cutter | day | 0.2 | 50.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 34.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 37.78 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Time necessary for maintenance,
Good training to do quality work
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
850.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
No dry season or marked rainy season. The rains fall fairly regularly
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Evreux (27000)
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Possible loss of some cropland replaced with hedgerows, although most hedging in this instance was reinstating old field boundaries - i.e. where historic boundary lines existed but were removed for machenery or to enlarge field size.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Greater crop protection and more beneficial species improve crop quality
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Shelter belts improve animal welfare leading to better weight gain.
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
Hedgerows can be coppiced for wood crop.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Shelter belt reduces risk of crop failure from weather extremes (i.e. wind)
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
Wood crop added to diversity of products
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Although loss of crop land, this is replaced with wood crop diversity
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Smaller parcels of land make land management more restrictive for large machinery.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Balance of increased time and management of a diversity of crops, yet less crop management with improved pest control and phyicsl stress reduction from more shelter.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
No change in balance of less crop production but addition of woody crop.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Diversity added with option of woody crop
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Smaller field parcels make crop management harder having to use smaller machinery and there is an addition of hedgerow maintenence workload.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
注释/具体说明:
Hedgerows act as buffer strips capturing wash off from fields before it reaches the water course
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Hedgerows act as buffer strips capturing wash from fields
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
Improved soil infiltration in hedgerows helps drain excess water
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Improved soil infiltration in hedgerows helps maintain soil moisture capacity
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Hedgerows act as buffer strips capturing soil wash from fields
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
Reduced machinery size (in places) reduces compaction, plus less soil compaction by hedgerows.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Increased organic matter in hedgerows
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
More year round cover
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Increased wih hedgerows
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
More diverse species with planting for hedgerows
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Increased habitat diversity and area for more animal presence and diversity
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
Encouragement of beneficial species with habitat creation in hedgerows that can aid natural pest and disease control through the presence of predator species that control pest species.
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
Within hedgerow habitat addition
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Encouragement of beneficial species with habitat creation in hedgerows that can aid natural pest and disease control through the presence of predator species that control pest species.
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
Improved soil infiltration reduces flooding risk
风速
注释/具体说明:
Shelter belts reduce wind velocity over crops
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
Hedgerows act as buffer strips capturing wash off from fields before it reaches the water course
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
Hedgerows act as buffer strips capturing wash off from fields before it reaches the water course
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
Shelter belts reduce wind velocity over crops and bare soil for less erosion & transportation
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Shelter belts reduce wind velocity over crops and bare soil for less erosion & transportation
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
Increased tree cover supports a reduction in GHG
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 适度 |
| 局地风暴 | 适度 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
| 森林火灾 | 不好 |
| 陆地火灾 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 适度 |
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 适度 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 延长生长期 | 不好 |
| 缩短生长期 | 非常不好 |
| 海平面上升 | 非常不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
其它(具体说明):
Over the last ten years, agri-environmental criteria have been taken into account in choosing planting sites
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reduced winds and wind erosion |
| Creation of spaces for wildlife leading to increased biodiversity |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Creation of climate zone "temperate" favourable to crops and / or animals |
| More space for biodiversity and habitat, particularly those that provide a beneficial return for agricultural production |
| Diversification to add woody crops |
| Connected landscape and habitats through hedgerow linkages to each other and woodlands. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Cost and maintenance time | Use harvested wood/material to cover increased costs for farmer to maintain hedgerows |
| Competition between cropping areas for natural resources | Increase the technical understanding of tree management / crop fringes |
| Unclear EU financial support for hedge management (instability of the common agricultural policy) | Unknown / public or private payment for ecosystem services and goods |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Unclear EU financial support for hedge management (instability of the common agricultural policy) | Unknown / public or private payment for ecosystem services and goods |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1 field visit
- 与土地使用者的访谈
2 land users who have implemented hedgerow planting
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1 SLM expert consulted as information compiled
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Les haies Rurales : rôles, création, entretien
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
08/10/2019
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Les haies Rurales : rôles, création, entretien / Fabien LIAGRE / 2006 / ISBN 2-85557-137-5
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Edition France Agricole / 40 €
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块