Small retention ponds in the forest [挪威]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Dominika Krzeminska
- 编辑者: Jannes Stolte
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
“Mindre” fordrøyningsdammer
technologies_6156 - 挪威
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Norwegian Institute of Bioeconomy Research (NIBIO) - 挪威1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Regional Environmental program [挪威]
Regulations and financial grants for reduction of pollution and promotion of the cultural landscape.
- 编制者: Kamilla Skaalsveen
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
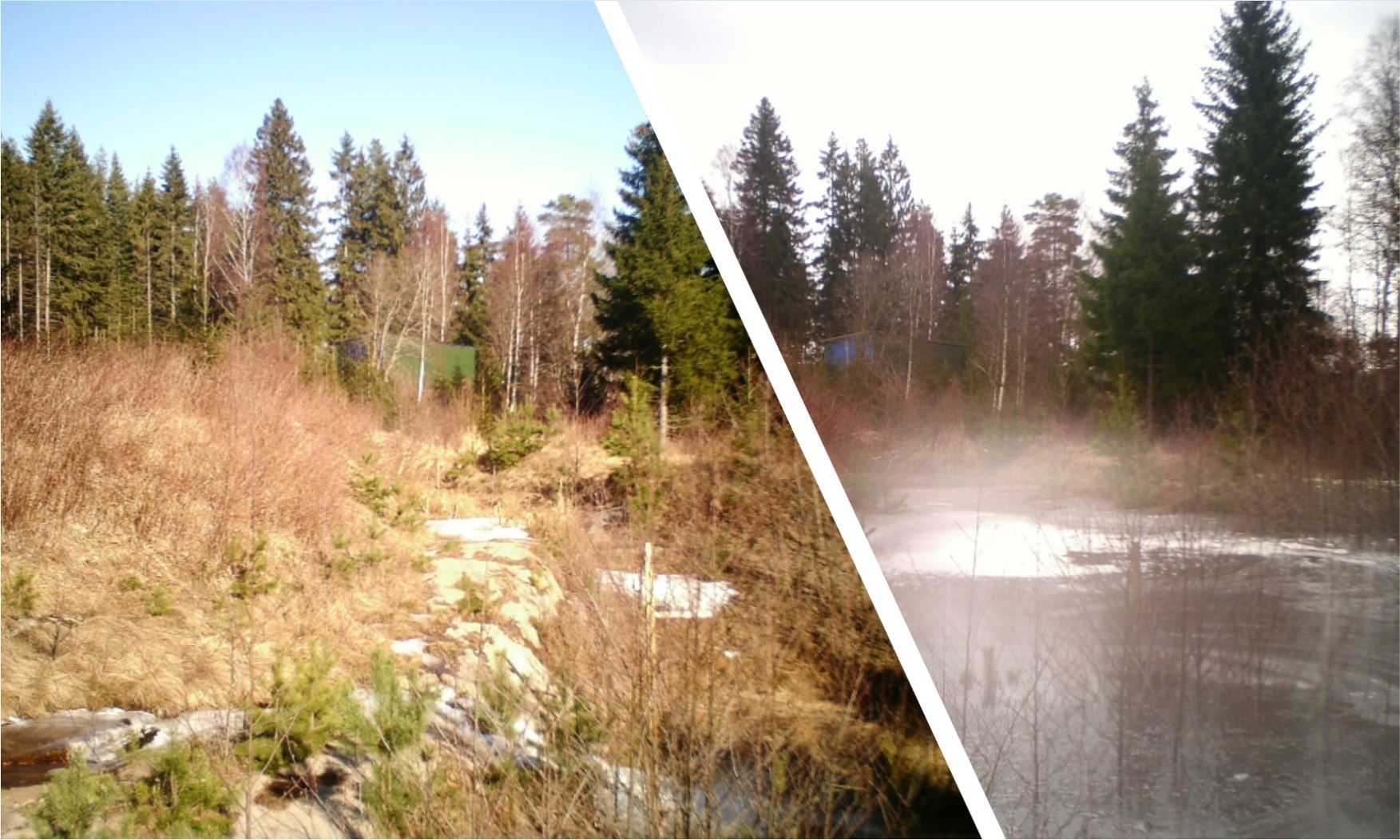
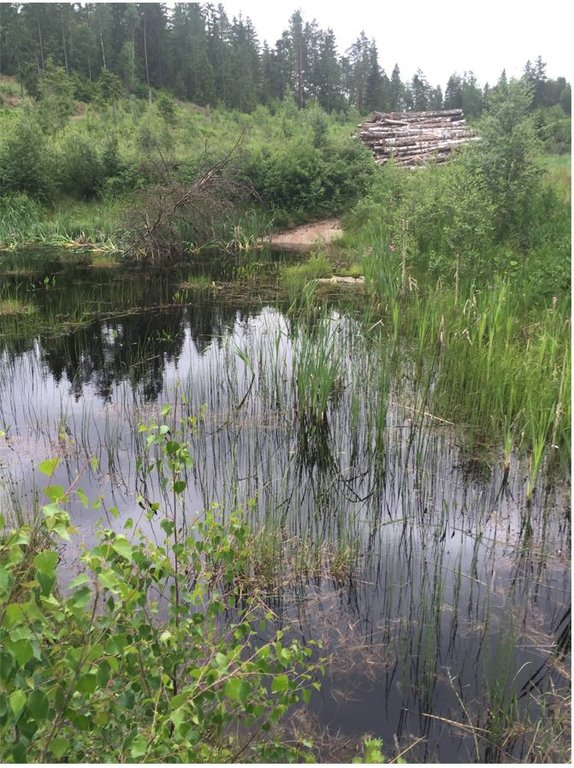
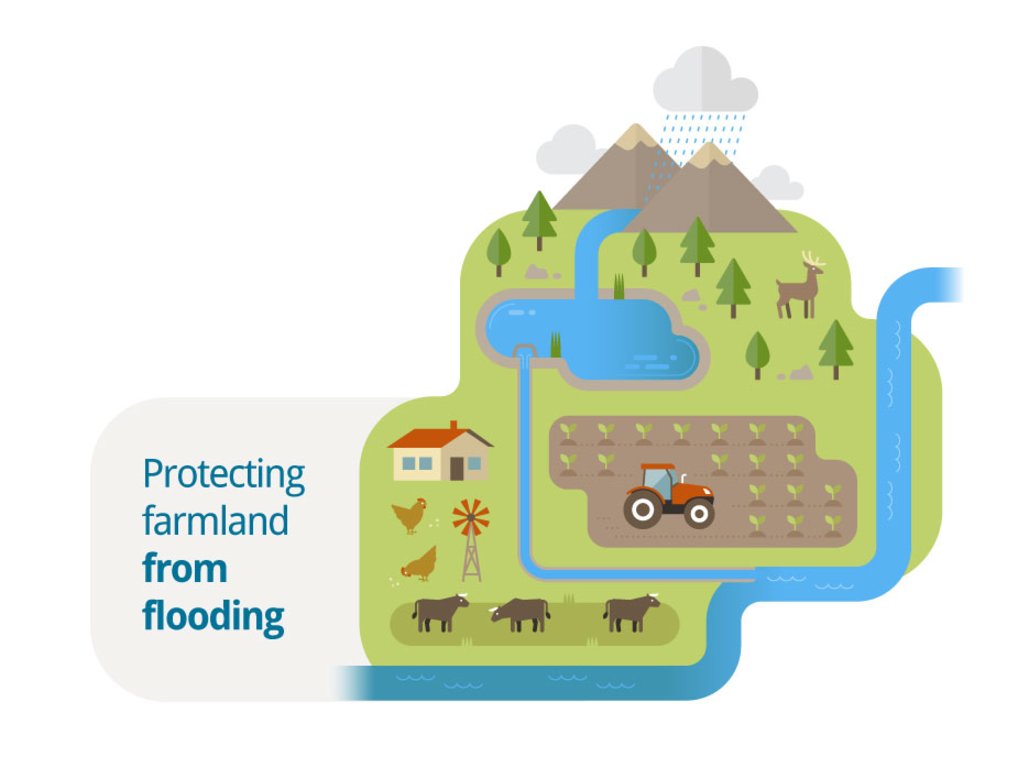
Small retention ponds, located in the forest, are ponds or pools with sufficient storage capacity to store the surface runoff to prevent flooding during heavy rainfall events. Ponds contain limited or no water during dry weather, but are designed to retain water during rain events.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The aim of the small retention ponds is to provide additional storage capacity to hold runoff to attenuate surface runoff - and thus reduce its impact on flooding - during rainfall events. The measure will primarily be useful in connection with short-term extreme episodes and have less effect during prolonged rain – this is because once the dam is filled up it no longer has a flood-reducing effect.
Small retention ponds located in forest areas are artificial dams (up to 2m height, for security reasons) made of soil, stone and/or gabions, with additional storage capacity to attenuate surface runoff during rainfall events. The ponds use local topography to provide space to store discharge peaks. The size of the ponds vary greatly between c. 50-150 m3. The dams can either be established in waterways, or next to the stream so that water is diverted during a flood event. Continuous water flow through the dam is ensured by a spillway located at the bottom of the dam. In this way, the dam can temporarily store water during rainfall episodes and thus decrease the flood peak downstream. The pond must be designed correctly, and calculations of cost-benefit should be carried out before implementation.
As for now, the implementation of small retention ponds in the forests are initiated by landowners. The ponds are getting more and more interest from the local communities however, they are not yet commonly implemented.
In general, there is agreement between experts (researchers) and other stakeholders about the benefits of the implementation of small retention ponds in the forest. However, it is not always the case that such retention ponds decrease floods - as the level of influence depends on the scale and the number of ponds within the catchment. When it comes to drawbacks, stakeholders were particularly worried about the cost of building and maintaining the retention ponds as well as the security of the construction. They placed less emphasis on possible decreases in forest production, which was one of the disadvantages identified by researchers.
Information about the technology is based on investigations and/or reports from different catchments in Norway. For the purpose of the OPTAIN project, the technology is further presented in the natural and human environment context of the Kråkstad River catchment - a Norwegian Case Study catchment within the OPTAIN project.
The Kråkstad River is mainly situated in Ski municipality in South-Eastern parts of Norway. The river catchment is a western tributary of the Vansjø-Hobøl watercourse, also known as the Morsa watercourse. The Kråkstad River catchment area is about 51 km², 43% of which is agricultural land, where cereals are produced on heavy clay soils. The main environmental challenge in the area is water quality (incl. high phosphorus pollution) and soil erosion (incl. riverbank erosion and quick-clay landslides).The Morsa watercourse is a drinking water resource and there are specific environmental regulations for land management followed by subsidies through the Regional Environmental Programme (RMP).
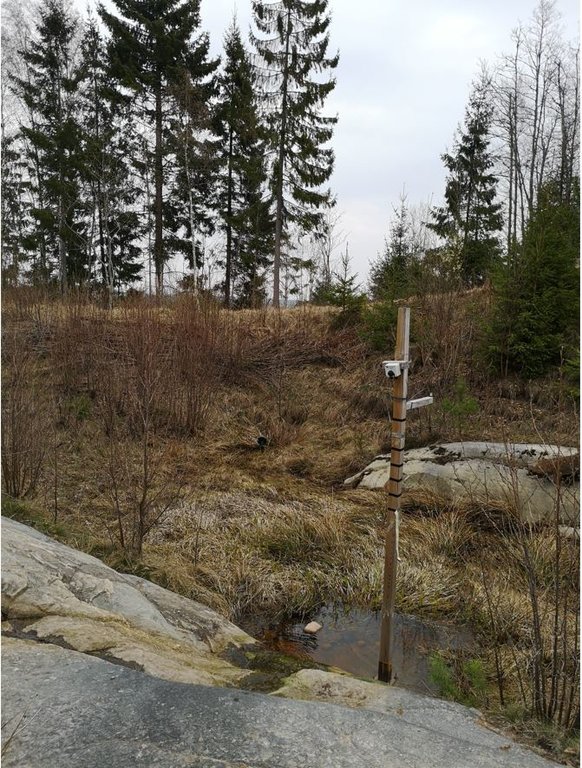
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
挪威
区域/州/省:
Viken county
有关地点的进一步说明:
The Vansjø - Hobøl catchment
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 在实验/研究期间
- SMIL
注释(项目类型等):
Establishment of the retention ponds presented in this documentation was initiated by landowners. Monitoring of their effectiveness was part of the research project (RECARE: https://www.recare-hub.eu/).
Retention ponds are part of SMIL subside system (Special Environmental measures in Agriculture)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

森林/林地
- natural forest
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 引水和排水
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
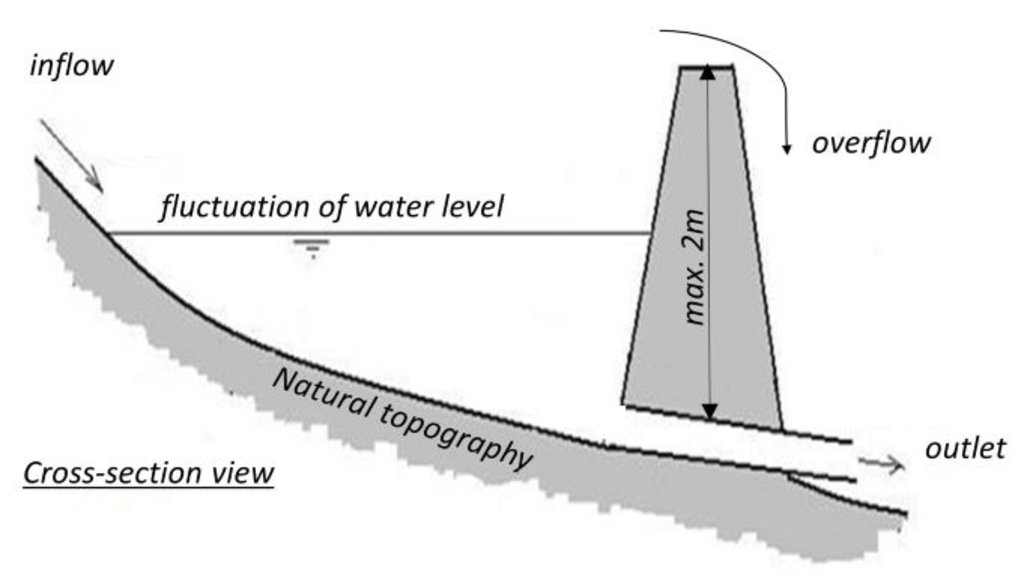
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Cross-section view on the small retention pond
作者:
Dominika Krzeminska
日期:
26/01/2022
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Pond
指定单位面积(如相关):
c. 50-150 m3
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
NOK
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
8.89
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
c.a. 3000 NOK (it is only the cost of the time assuming 8h work per day, 320-500 NOK/hour; person; machinery, equipment, materials not included)
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construct the dam | dry period of the year |
注释:
We are talking here about “small” dams, up to 2 m (restrictions due to safety regulations). The dams can be built with the use of typical machinery available at the farms: digger, tractor etc. or with help of company.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
35000.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The landowners can apply for subsidies to establish and maintenance sedimentation pond, within SMIL system (Special Environmental measures in Agriculture). Local county authorities are responsible for the administration of these schemes.
注释:
Approximately NOK 35,000 has been used to establish the retention pond (monitoried withn RECARE project). It is mostly to rent the equipment and buy the material (soil). The work was done made by the landowner.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of the dam | on demand |
| 2. | Maintenance of the pond area | on demand |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
10000.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The landowners can apply for subsidies to establish and maintenance sedimentation pond, within SMIL system (Special Environmental measures in Agriculture). Local county authorities are responsible for the administration of these schemes.
注释:
An estimate for maintenance costs is set at NOK 10,000 annually, most of it is for clearing the area.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
- The terrain setup,
- Type of material used to construct the dam and its durability (establishment and maintenance costs).
- Need for maintenance
The landowners can apply for subsidies to establish and maintenance sedimentation pond, within SMIL system (Special Environmental measures in Agriculture). Local county authorities are responsible for the administration of these schemes.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
频繁
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产故障风险
生产区域
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Less flooding events--> crop grown
生态影响
土壤
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Less flooding events--> lower soil erosion
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
栖息地多样性
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Depending on the scale and number of retention pond in the catchment, it may affect the discharge behavior of the river system (less peak flows).
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 适度 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improvement of the water conditions down-slope: reduce amount of overland flow and lower erosion rate in the agriculture land located below the pond. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Depending on the scale and number of retention pond in the catchment, it may affect the discharge behaviour of the river system (lower peak flows) |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Security of the construction | |
| Costs of maintenance |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Decreases in forest prodcution |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Several field visits during the course of RECARE project (2014-2018).
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Stakeholders workshops carried out within RECARE project.
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
NIBIO, and its SLM specialists, has been conducting several national projects related to planning and monitoring the efficiency of small retention ponds within agricultural catchments.
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
See the references
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
26/01/2022
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Fact Sheets: Case study experiments preventing flooding through small retention ponds. Krzeminska D.; Bøe F.; Stolte J. (2018)
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
RECARE project website https://www.recare-hub.eu
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Assessing Impacts of Soil Management Measures on Ecosystem Services. Schwilch G. et al. (2018)
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Mdpi Sustainability
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Helping stakeholders select and apply appraisal tools to mitigate soil threats: Researchers’ experiences from across Europe. Okpara et al (2020)
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Journal of Environmental Management
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Fordrøyningsdammer i tilknytning til jordbruksarealer. Stolte J and Barneveld R. (2019)
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NIBIO raport
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Fact Sheets: Case study experiments preventing flooding through small retention ponds
URL:
https://www.recare-hub.eu/images/articles/Case_Studies/Fact_Sheets/RECARE_Experiment_Fact_Sheet_NorwayPondsFinal.pdf
标题/说明:
Assessing Impacts of Soil Management Measures on Ecosystem Services
URL:
https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/10/12/4416
标题/说明:
Helping stakeholders select and apply appraisal tools to mitigate soil threats: Researchers’ experiences from across Europe
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301479719317232?via%253Dihub
标题/说明:
Fordrøyningsdammer i tilknytning til jordbruksarealer.
URL:
https://nibio.brage.unit.no/nibio-xmlui/bitstream/handle/11250/2606099/NIBIO_RAPPORT_2019_5_65.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
7.4 一般注释
no remarks
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Regional Environmental program [挪威]
Regulations and financial grants for reduction of pollution and promotion of the cultural landscape.
- 编制者: Kamilla Skaalsveen
模块
无模块