Permanent grass cover in vineyards [匈牙利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Brigitta Szabó
- 编辑者: Piroska Kassai, Zoltan Toth
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Sorközök füvesítése szőlőben
technologies_6194 - 匈牙利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
匈牙利
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Institute for Soil Sciences, Centre for Agricultural Research (ATK TAKI) - 匈牙利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Integrated Pasture Management Planning in Mountainous Regions [乔治亚]
The unsustainable use of pastures and forest areas has led to soil erosion, degradation, desertification and loss of biodiversity in the high mountain areas of the South Caucasus. The development of pasture passports is part of a broader approach to a strategic pasture management plan for Tusheti. This showcase includes …
- 编制者: Hanns Kirchmeir
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
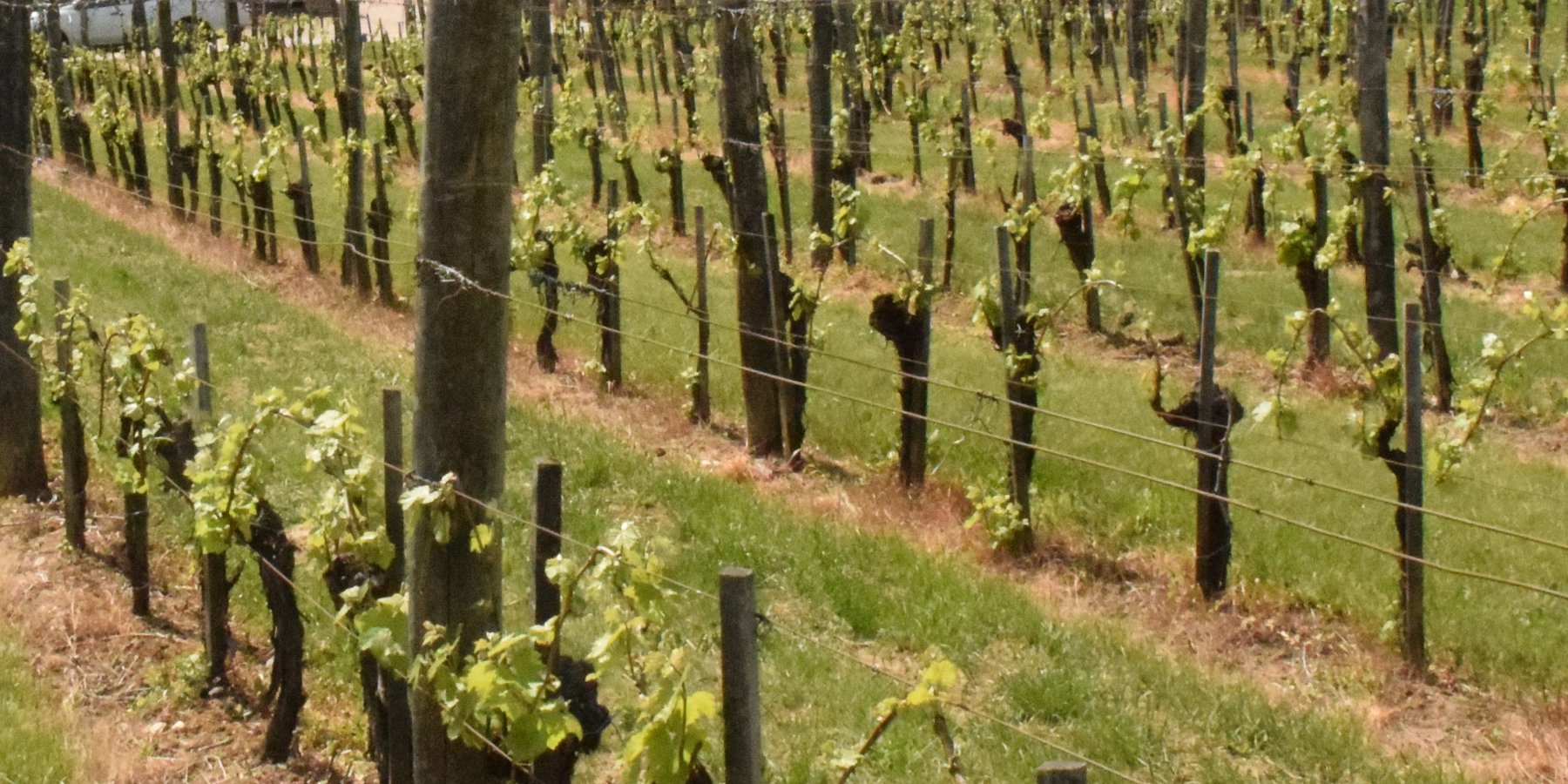
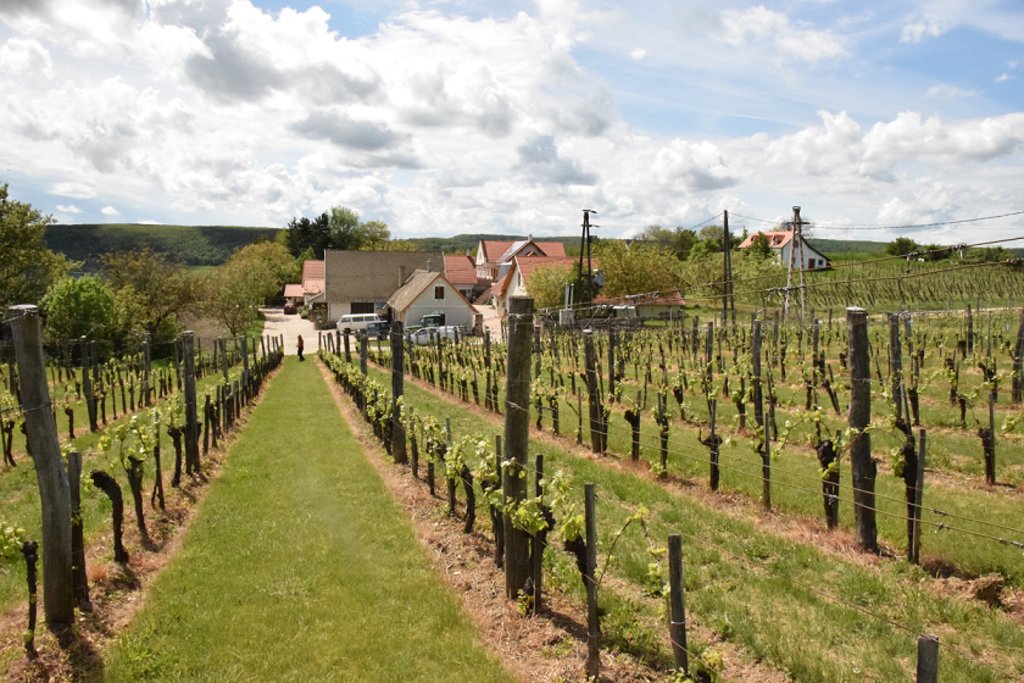
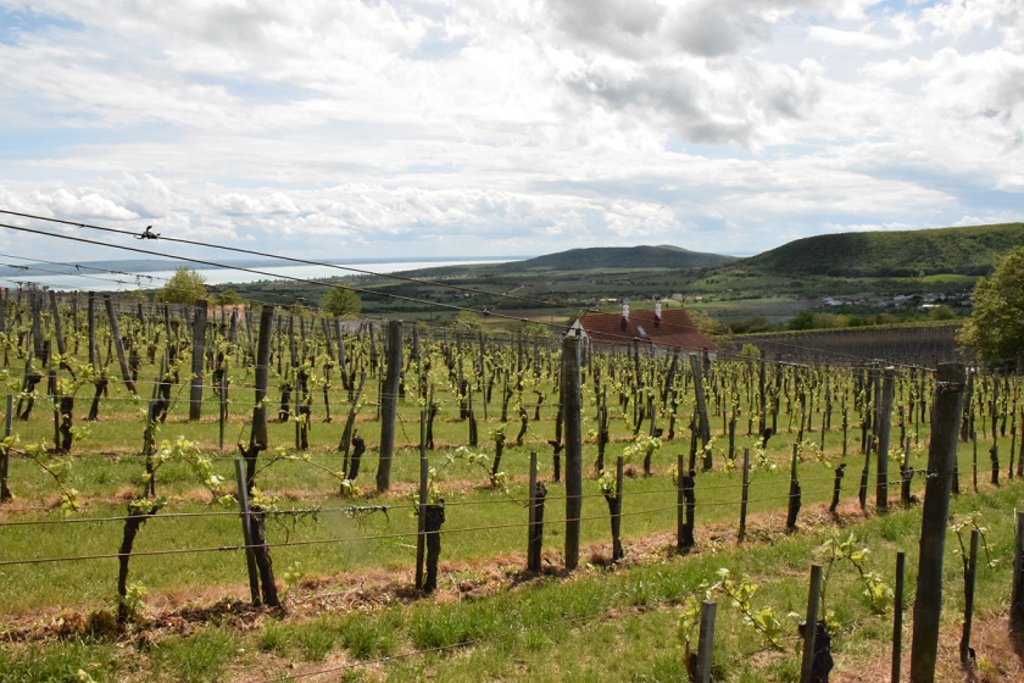
Permanent grass cover under grape vines protects the soil surface against erosion and compaction - and provides better conditions for traffic within the rows during mechanised field operations
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Permanent grass cover under grape vines protects the soil surface against erosion and compaction - and provides better conditions for traffic within the rows during mechanised field operations. Grass can be sown using a mixture of grass and legume species - white clover, red clover, tall fescue are the most widely used - or it can be allowed to germinate naturally after stopping regular tillage applications. For the maintenance of grass cover and to avoid the disadvantages of tall grass it must be regularly cut. The height of the grass is most important directly below the grape rows. Grass clippings are a great source of nitrogen and break down quickly, so it can be used as mulch. But winegrowers/farmers who deal with animal husbandry too, prefer to use grass clippings as fodder. Herbicides are often used to control the grass in narrow strips underneath the grape rows.
One benefit of the grass cover is the good soil protection on slopes - where vineyards are often established due to better exposure to the sun. In addition, it gives better traction for machines, especially on steep gradients: this is appreciated by land users. Permanent grass cover makes for a cooler and more humid microclimate in the vineyard, but this means a greater risk of fungal diseases and loss of moisture due to the transpiration demand of the grass.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
video is not available
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
匈牙利
区域/州/省:
Veszprém County
有关地点的进一步说明:
Szentantalfa
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 葡萄
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 适应土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
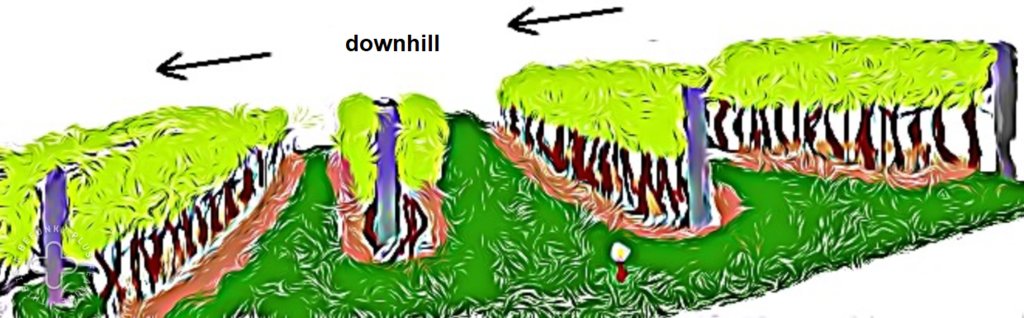
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The interrow space between grape lines are covered by permanent grass. Interrow space is 2-3 m.
作者:
Piroska Kassai
日期:
31/10/2022
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
ha
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
50
4.3 技术建立活动
注释:
Regular soil tillage is finished between the interrow space of vineyard. As a consequence permanent green cover will be developed. Grass cover will be dominant within a year.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Permanent grass cover develops after the regular soil tillage is finished without any investment
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | cutting grass | 4-5 times a year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 其它 | 1st cutting grass is carried out by a contractor | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | 2nd cutting grass is carried out by a contractor | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | 3rd cutting grass is carried out by a contractor | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | 4th cutting grass is carried out by a contractor | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | 5th cutting grass is carried out by a contractor | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 175.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 175.0 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
fuel prices
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
600.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Surface runoff decreases because infiltration improves significantly in vineyards with grass cover crops
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Grass cover crops in vineyards can reduce soil erosion rates by four- to six-times compared to tillage.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
植物多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
微气候
注释/具体说明:
Humidity of microclimate is increased, resulting in higher risk of diseases
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 夏季 | 减少 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 热浪 | 适度 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 非常不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 气候变化/极端气候
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Using drought-tolerant grass species
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| good soil conservation - increases soil organic carbon and improves aggregate stability |
| reduces soil loss |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Less nutrient load through erosion (off-site effect) |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| cutting grass is regulary needed |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| vineyard microclimate is more humid, resulting in higher risk of diseases |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
5
- 与土地使用者的访谈
5
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
14/06/2022
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Cover cropping in vineyards - A grower's handbook, Published by Agriculture & Natural Resources 2002-01-01, 2002, ISBN 10: 187990635X / ISBN 13: 9781879906358
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
From LowKeyBooks (Sumas, WA, U.S.A.)
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Overview of Vineyard Floor Management
URL:
https://grapes.extension.org/overview-of-vineyard-floor-management/
7.4 一般注释
filling out the questionnaire is time consuming
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Integrated Pasture Management Planning in Mountainous Regions [乔治亚]
The unsustainable use of pastures and forest areas has led to soil erosion, degradation, desertification and loss of biodiversity in the high mountain areas of the South Caucasus. The development of pasture passports is part of a broader approach to a strategic pasture management plan for Tusheti. This showcase includes …
- 编制者: Hanns Kirchmeir
模块
无模块