Vegetative riparian buffers [匈牙利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Brigitta Szabó
- 编辑者: Piroska Kassai, Zoltan Toth
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Vízparti erdős puffersáv
technologies_6204 - 匈牙利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Institute for Soil Sciences, Centre for Agricultural Research (ATK TAKI) - 匈牙利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
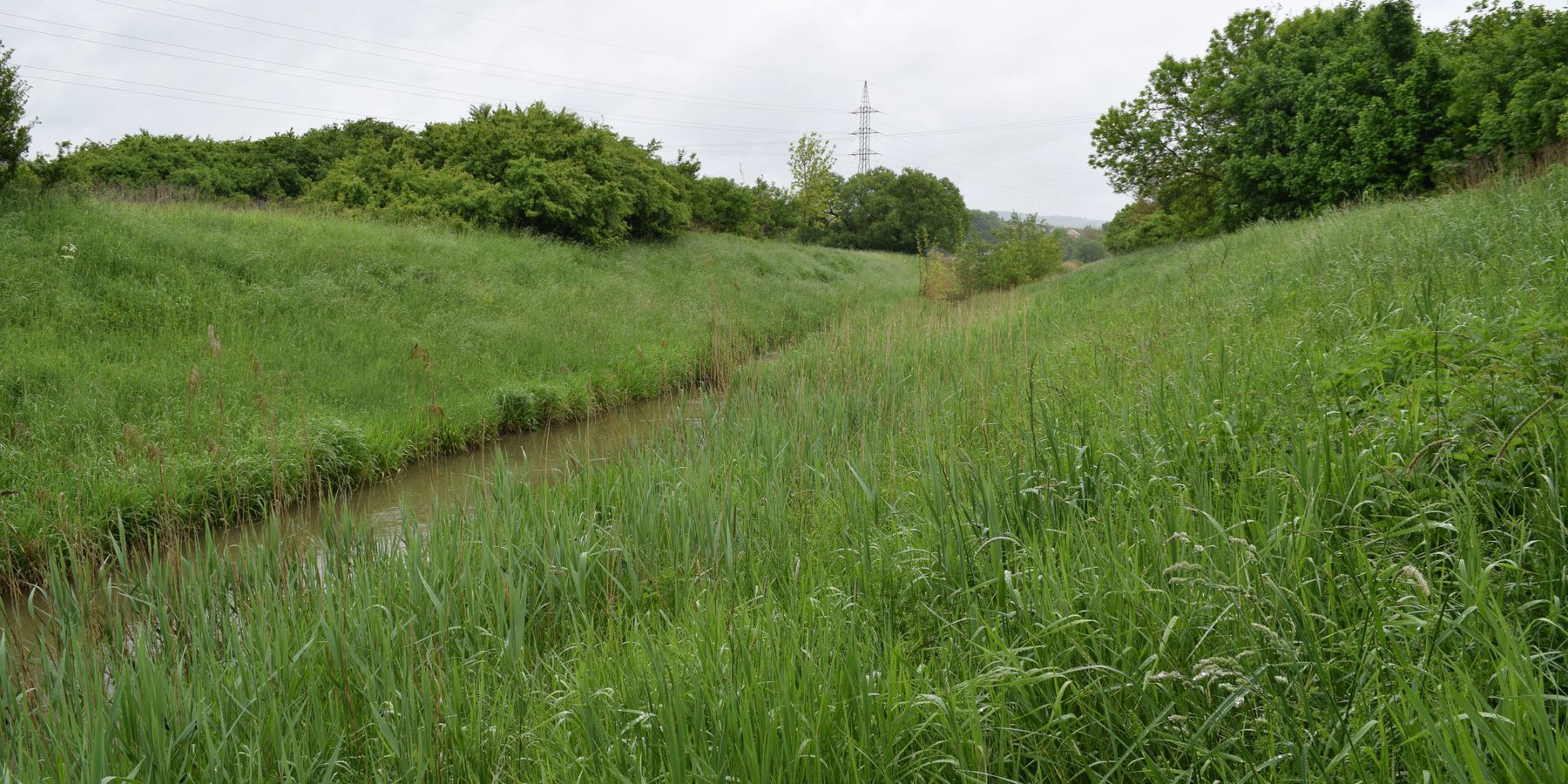
Vegetative riparian buffers are strips of trees, bushes and grass alongside surface water bodies such as streams or ponds. Their main function is to provide a natural buffer strip to filter out nutrient and sediment transported from agricultural fields and prevent it reaching the water bodies - as well as maintaining undisturbed green corridors.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Vegetative riparian buffers are strips of trees and other vegetation alongside surface water bodies such as streams or ponds. They are used in natural environments, as well as in urban, agricultural and wetland areas. Their main function is to provide a natural buffer to increase infiltration, and to filter out nutrients and sediment transported from agricultural fields – thus preventing it reaching (and polluting) water bodies. Riparian buffers also help moderate flow. Creating such green corridors alongside waterlines is advantageous ecologically as well. However, land users usually prefer cultivating the largest possible area of land, so they dislike leaving significant areas abandoned to nature. Another complaint is that riparian buffers provide habitats for wildlife, often resulting in damage to cropland.
Where a natural buffer does not exist - mostly in the neighbourhood of agricultural fields - it can be created by planting trees and bushes alongside the water body. Variable buffer width design with an average width of 15 m (max. 20 m) is recommended.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
no videos available
位置:
-
摄影师的名字:
-
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
匈牙利
区域/州/省:
Somogy
有关地点的进一步说明:
The site where the technology is applied is situated within the catchment of Tetves stream, which belongs to the Balaton Catchment Area in the western Hungary. The climate is moderately warm, moderately humid, mean annual temperature is about 10 ˚C. The average amount of rainfall is between 600 and 700 mm / year.
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
- 油料作物 - 向日葵、菜籽、其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
winter wheat-maize-sunflower-barley

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
动物类型:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)

水道、水体、湿地
- 排水管道、水道
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
- 植树造林
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 清除枯木/剪枝
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 混交品种
植树造林类型:
- 温带大陆林人工林
树木类型:
- Salix species
- Alnus glutionosa
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 落叶植物
产品和服务:
- 自然保持/保护
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 天然和半天然森林管理
- 森林种植管理
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
- Hq:地下水水质下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
A variable buffer width design with a basic width of 15 m (max 20 m) is recommended.
作者:
Piroska Kassai
日期:
15/03/2023
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
hectare (20X500 m)
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
50
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil preparation | any season |
| 2. | Planting | autumn |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Soil preparation | person-day | 2.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Planting (4000 seedlings on 1 hectare) | person-day | 3.0 | 50.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Soil preparation | hiring cost/day | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Planting | hiring cost/day | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | piece | 4000.0 | 0.1 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1150.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1150.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
-
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | No maintenance required |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | No maintenance required |
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
-
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
-
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
653.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
the distribution of the precipitation is uneven
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Keszthely meteorological station
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Crop production will decrease slightly because the cultivated area will be less, but it is not significant from an economic point of view.
生产区域
社会文化影响
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
It creates shade and a pleasant space for recreation.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
注释/具体说明:
Both on-site and off-site positive effect can be observed because the inflow waters (e.g Tetves) quality can help to protect Lake Balaton from eutrophication.
土壤
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Riparian buffers are permanent vegetation covers.
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
It provides a wildlife habitat and corridors for terrestrial organisms
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
It can filter nutrients, pesticides, and animal waste from agricultural land runoff
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 夏季 | 减少 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 滑坡 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Soil erosion/sediment control |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Trees in riparian areas can efficiently take up excess nutrients |
| It can decrease sediment inputs to surface waters |
| It can create riparian habitat |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| cutting grass is regulary needed | |
| Wild animals living there can cause damages on croplands | |
| Can cause the spread of weeds on the neighboring parcels |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Conflicts can occur between the water managment authority and farmers regarding the border of the cultivated area |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
2
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
11/05/2021
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Jiang et al. 2020: Riparian buffer effectiveness as a function of buffer design and input loads
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://acsess.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jeq2.20149
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
EUROPEAN NWRM PLATFORM
URL:
http://nwrm.eu/
7.4 一般注释
no comments
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块