Subsoiling [波兰]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Tymoteusz Bolewski
- 编辑者: Marek Giełczewski
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Głęboszowanie
technologies_6250 - 波兰
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
- Tadeusz
Self-employed farmer
波兰
土地使用者:
- Marcin
Self-employed farmer
波兰
土地使用者:
- Jaroslaw
medium scale enterprise
波兰
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Institute of Technology and Life Sciences – National Research Institute, Poland (ITP) - 波兰1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
-
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Subsoiling [中国]
Subsoiling with mulching is one of the conservative tillage using subsoiling plough to loose subsoils with surface soil undisturbed.
- 编制者: Zhanguo Bai
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Subsoiling is defined as tillage below a depth of about 35-40 cm which doesn't invert the soil. It breaks up compacted layers to improve rooting and infiltration. Subsoiling is not needed on light soils, because these are rarely at risk of compaction.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
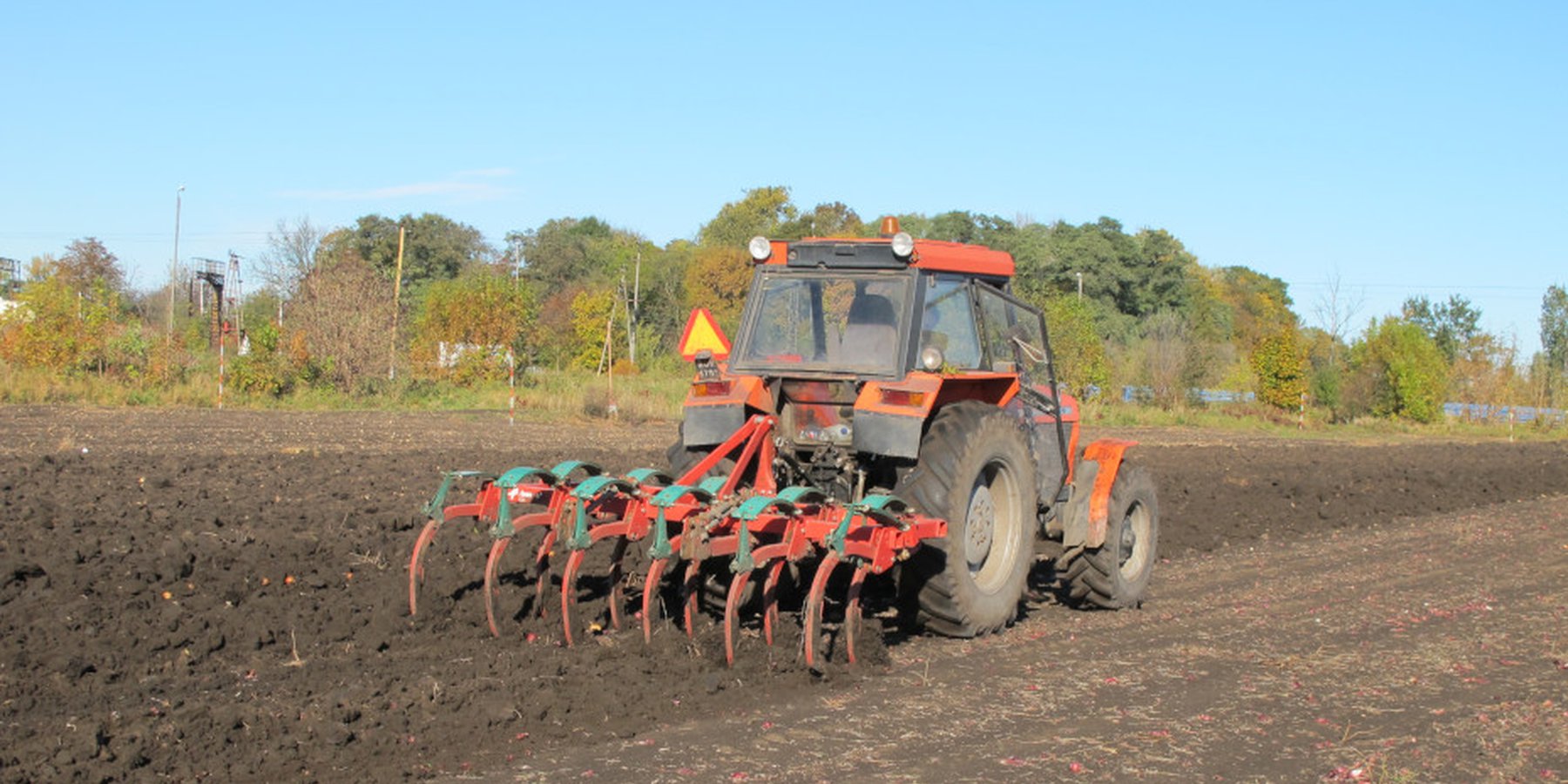
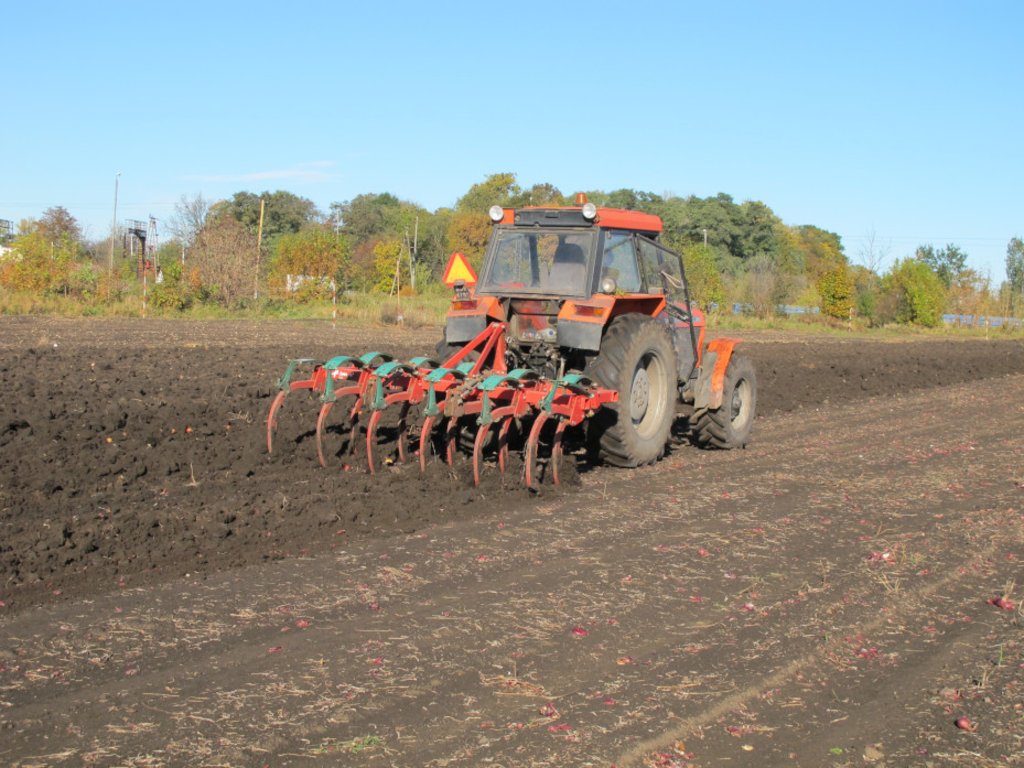
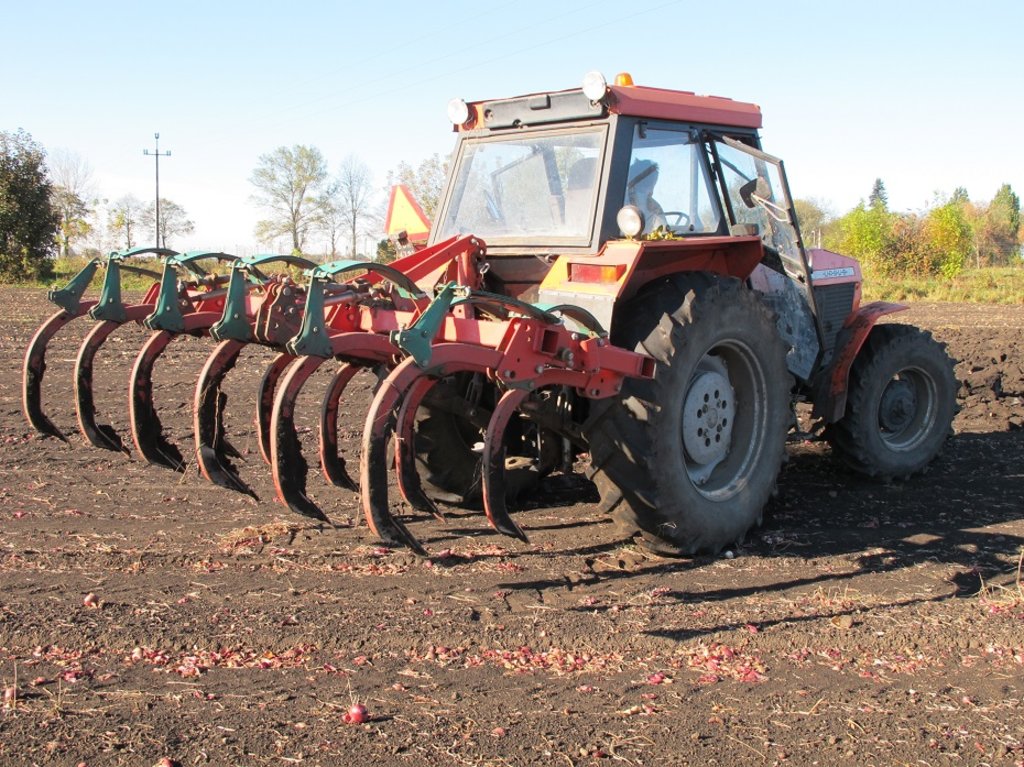
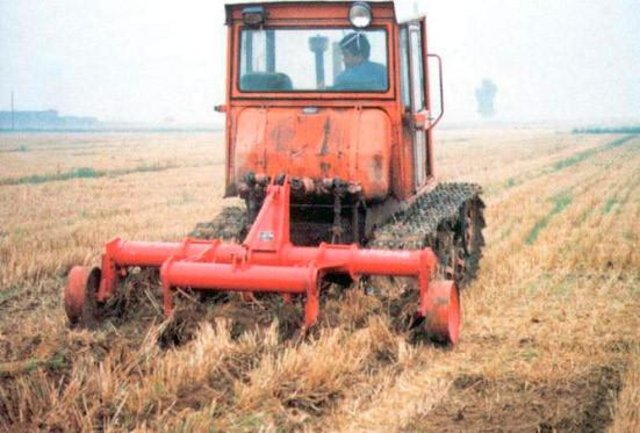
Subsoiling is carried out on arable land. Subsolier is pulled by a tractor and chisels (tines) break up a compacted layer below the surface. Subsoiling disturbs this dense layer and loosens the soil. This treatment improves air-water relations in the soil. The depth of subsoiling can be adjusted. On heavier soils, deeper subsoiling may be necessary. The farmer surveyed (who has a medium sized enterprise of about 400 ha) subsoils at a depth of 40-45 cm. Subsoiling is used especially for root crops such as sugar beet - and for other crops to a lesser extent, depending on the needs and condition of the soil. It is possible to adjust the spacing of the chisels (tines) and the power of the tractor. An average spacing between the chisels is 50 cm. A 200 horsepower tractor is able to pull a five-tine subsoiler. If time permits, the whole field should be subsoiled. Subsoiling takes quite a long time (about 10 ha per day). This technology is required every year when sugar beet is planted. In other fields, only machinery tracks and headlands (where the machine turns) should be subsoiled every year. Subsoiling is often used after harvest and before other field operations such as ploughing etc. On average, due to crop rotation, the whole field is only subsoiled once every four years. Subsoiling is a form of tillage which can be used instead of traditional ploughing to loosen soil without inverting it: thus it can form part of a reduced tillage system.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
-
位置:
-
摄影师的名字:
-
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
波兰
区域/州/省:
Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship
有关地点的进一步说明:
Southern part of the region called Kujawy
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
Most often used as a part of conventional tillage technology, as an additional activity. Subsoiling is performed on about 25% of total farm area.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
-
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 燕麦
- 谷类 - 小麦(春季)
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
- 根/块茎作物 - 甜菜
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A4:地表下处理
A3:区分耕作制度:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
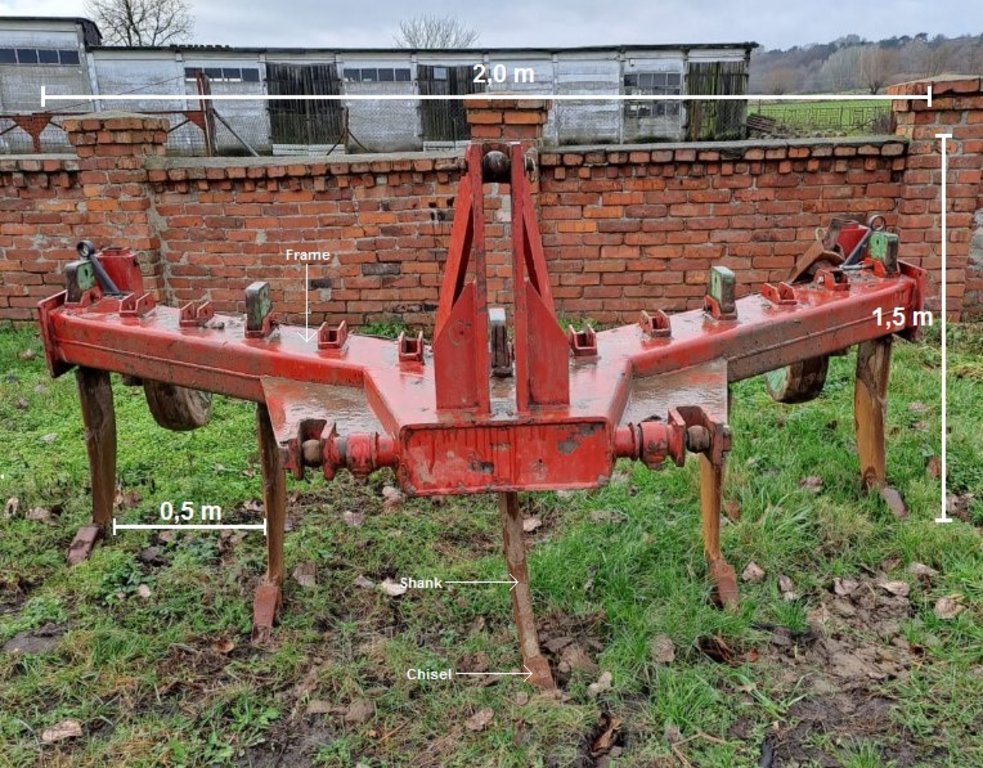
The activity is performed with a subsoiler. This is a cultivation device connected to the tractor. In the case of the subsoiler with five working parts (shanks ended with chisels): (i) width between two chisels is 50 cm and total width is about 2.0-2.5 m, (ii) height is about 1.5 m; (iii) weight about 800 kg.
A tractor with at least 200 horsepower is needed for a subsoiler with 5 chisels.
作者:
Jarosław
日期:
15/11/2022
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
ha
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
-
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
4.45
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
300.00 PLN
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | - | - |
注释:
-
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | - | |||||
| 设备 | - | |||||
| 植物材料 | - | |||||
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | - | |||||
| 施工材料 | - | |||||
| 其它 | - |
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Subsoiling | late summer, early autumn (after harvest of crops) |
注释:
The exact date of performing subsoiling depends on several conditions, for example: (i) soil moisture conditions in the field; (ii) date of harvest crop in the field intended to be subsoil; (iii) subsoiler and tractor availability.
The subsoiler is a simple machine, the frame is durable but the chisels wear out very fast, especially due to dry soil conditions.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | skill labour | person-hour | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | tractor and subsoiler (depreciation) | machine-hour | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | chisels | machine-hour | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | tractor fuel | liter per hour | 20.0 | 7.0 | 140.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 205.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 46.07 | |||||
注释:
It is assumed, that within 1 hour the worker is subsoiling 1 ha in average conditions (field size = 40 ha; subsoiling about 10 ha per day and costings given for 1 hectare)
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
price of fuel, area needed to subsoling, moisture conditions in the fields, granulometric compisition of the soil
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
500.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Summer months (IV-IX) rainfalls are 60% of total amounts in a year; not equal disrtibution in time and place; climatic water balance (precipitation - Penman-Monteith reference evapotranspiration) on average about -190 mm; every year two dry periods of 11–15 days and one period lasting 15–20 days occur on the average, the period lasting more then 20 days occurrs every second year. About 50–60 days with atmospheric drought may be expected every year.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Samszyce and Bydgoszcz
农业气候带
- 半湿润
mean annual temperature: 8,5 deg. C
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
The technology is used on big (> 100 ha) and medium sized farms
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
The yield-forming effect of this treatment is visible throughout the entire crop rotation.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
These notes especially concern sugar beet and root crops.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
-
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Relatively expensive measure.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Guarantee of high and stable crop yield (e.g. sugar beet).
工作量
注释/具体说明:
-
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
-
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Increased rate of infiltration.
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Especially when subsoiling is performed instead of ploughing.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Increased soil water capacity and soil aeration.
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
-
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
The main purpose of the measure is to remove soil excessive compaction.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Subsoiling as a part of reduced tillage technology (as a tillage performed instead traditional ploughing) causes lower rate of organic matter decomposition comparing to the ploughing.
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Subsoilng as a part of reduced tillage technology (as a tillage performed instead traditional ploughing) reduces CO2 emission from soil comparing to traditional ploughing.
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
Changes that can be measured: soil density decrease, soil porosity increase, infiltration rate increase, plant rooting depth increase, stable yield, reduced emission of CO2.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
Using subsoiling instead of conventional ploughing reduces emission of CO2 from soil.
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
Changes that can be measured: decreased CO2 emission.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 季雨量 | 夏季 | 减少 | 适度 |
| 季雨量 | 秋季 | 减少 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 适度 |
注释:
In order to obtain the appropriate result of the subsoiling operation, it should be performed in conditions of adequate (optimum) soil moisture.
In the Kujawy region dry agrometeorological conditions are observed more frequently than wet ones. In conditions of insufficient soil moisture (dry and hard soil) chisels “tear up” the soil and the effect of its proper loosening is not achieved. At the same time performing subsoiling in very dry soil conditions is associated with high soil resistance the tractor must overcome. This results in increase in the tillage cost.
In conditions of excessive soil moisture soil “smearing effect “ occurs and the effect of its proper loosening is also not achieved.
Due to the observed in the region warming of the climate and the unfavourable changes in the distribution of rainfall throughout the year, water deficits in the soils may become more and more frequent. It may cause more rare occurring conditions which are optimal for performing subsoiling. This will be a problem for farmers using this tillage and it will limit possibility of performing subsoiling.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
-
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
-
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
-
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The effects of subsoiling are so noticeable (increased crop yield and quality) that it is worth doing, especially on root crops (e.g. sugar beet). The yield-forming effect of this treatment is also visible throughout the entire crop rotation |
|
It improves air-water relations in the soil. This treatment eliminates the soil layer with excessive density, loosening this layer and the layers located above. It is also recommended for farmers who irrigate their fields. |
| Thanks to the treatment, the plants (i) are better rooted, (ii) give higher yield, especially root crops, (iii) penetrate the soil and reach water more easily, without encountering an obstacle. Other plants also achieve stronger root system, as well as better take up and absorb water and nutrients. |
| This treatment improves biological properties of the soil and reduces root diseases; |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Subsoiling used as a part of reduced tillage lets to reduce magnitude of CO2 emission from soil. |
| Subsoiling enhances water supply of plants by capillary rise. |
| As a loosening treatment, it exposes the soil to water and wind erosion to a lesser extent than ploughing. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Subsoiling is an additional activity, not popular and it is not cheap. | To create the program for subsidies for such activities. |
| Most often it is performed as after harvesting and as pre-winter tillage. In order to be the most economically effective, subsoiling should be performed in optimal conditions of soil moisture due to wearing chisels. | Monitoring of agrometeorological conditions and proper organisation of activities in the farm. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Subsoiling requires very good knowledge of the field (due to risk of drainage system damage). | To possess knowledge of spatial distribution of drainage pipes in the fields, to have maps of the field with such information. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
3
- 与土地使用者的访谈
3
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
09/11/2022
注释:
-
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Influence of agrireclamation measures on water-physical properties of compact soils, changes in roots and plant yields (Wpływ zabiegów agromelioracyjnych na właściwości fizyczno-wodne gleb zwięzłych oraz ukorzenienie i plony roślin), Miatkowski Z., 2001., Bibl. Wiad. IMUZ, no 99, pp 107 (in Polish, summary in English)
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Library of Institute of Technology and Life Sciences, National Research Institute (ITP)
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Subsoiling in conventional and conservation tillage for sugar beet growing (Zastosowanie głęboszowania w tradycyjnej i konserwującej uprawie roli pod buraki cukrowe). Miatkowski Z., Sołtysik A., Banaszak H., 2006, Problemy Inżynierii Rolniczej vol. 2, p. 53-60.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Library of ITP and http://yadda.icm.edu.pl/baztech/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-article-BAR0-0016-0084
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Effects on Soil Water Holding Capacity and Soil Water Retention Resulting from Soil Health Management Practices Implementation
URL:
https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/sites/default/files/2022-10/AWC_Effects_on_Soil_Water_Holding_Capacity_and_Retention.pdf
标题/说明:
Preparation of the beet stand (Przygotowanie stanowiska pod buraki). KWS Agrotechnical Bulletin (Biuletyn Agrotechniczny KWS), no. 3/2003 (4).
URL:
https://docplayer.pl/38709652-Biuletyn-agrotechniczny-kws-biuletyn-agrotechniczny-kws.html
7.4 一般注释
-
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Subsoiling [中国]
Subsoiling with mulching is one of the conservative tillage using subsoiling plough to loose subsoils with surface soil undisturbed.
- 编制者: Zhanguo Bai
模块
无模块