Retention ditches for soil and water conservation [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: William Akwanyi
- 编辑者: Innocent Faith, JARED AYIENA, Noel Templer, George Onyango, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger, Sally Bunning
Mitaro ya kuhifadhi maji (Kiswahili)
technologies_6675 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Odongo Rosemary Ogola
Welthungerhilfe
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Farmers who have implemented the technology have been able to control surface runoff at their farms.
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Community Resource Persons (CRP) in agricultural extension [肯尼亚]
Community Resource Persons (CRP) form a farmer-to-farmer learning approach that bridges the gap in agricultural extension, increases farmers' access to agricultural information (SLM knowledge), and increases the adoption of SLM practices.
- 编制者: William Akwanyi
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
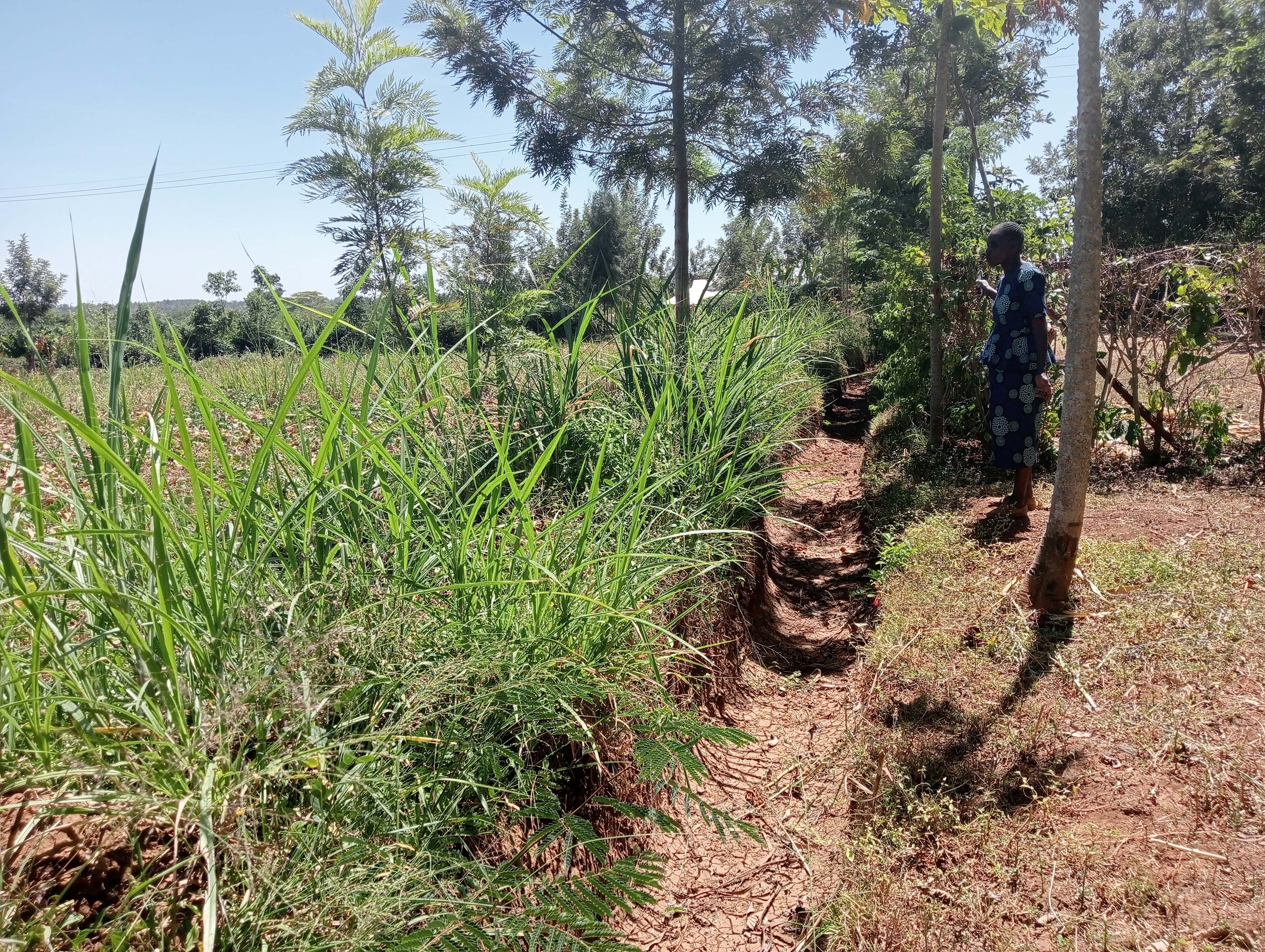
Retention ditches are channels aligned along the contour which are designed for surface runoff management. They improve water infiltration into the ground and prevent soil erosion.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
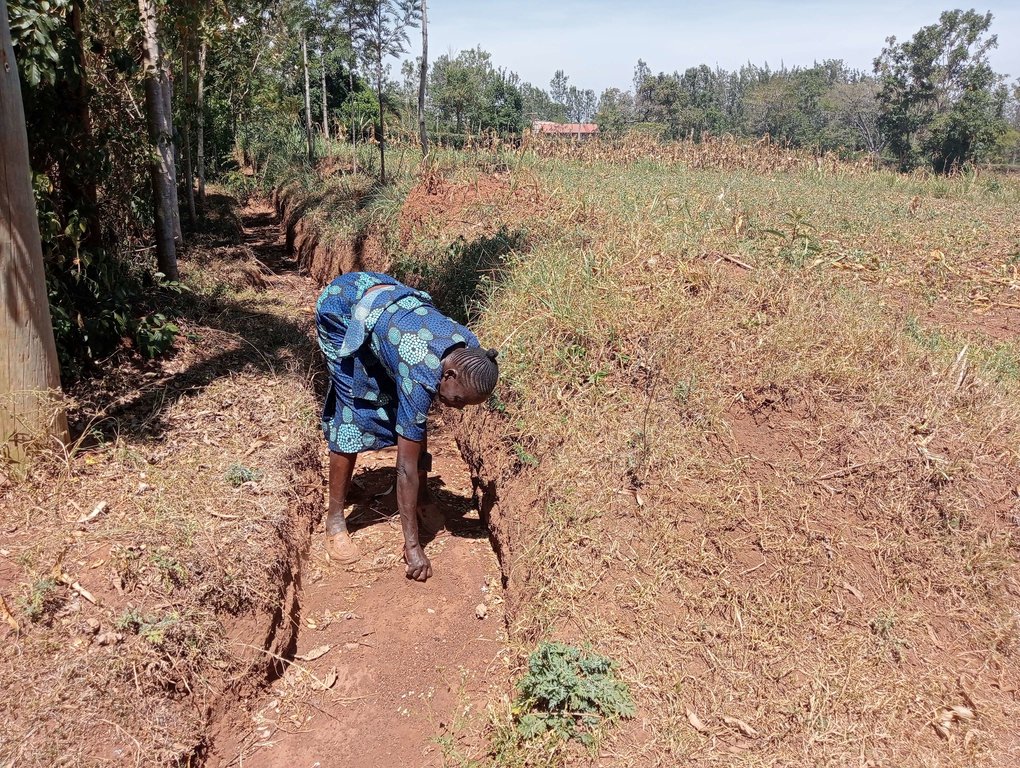
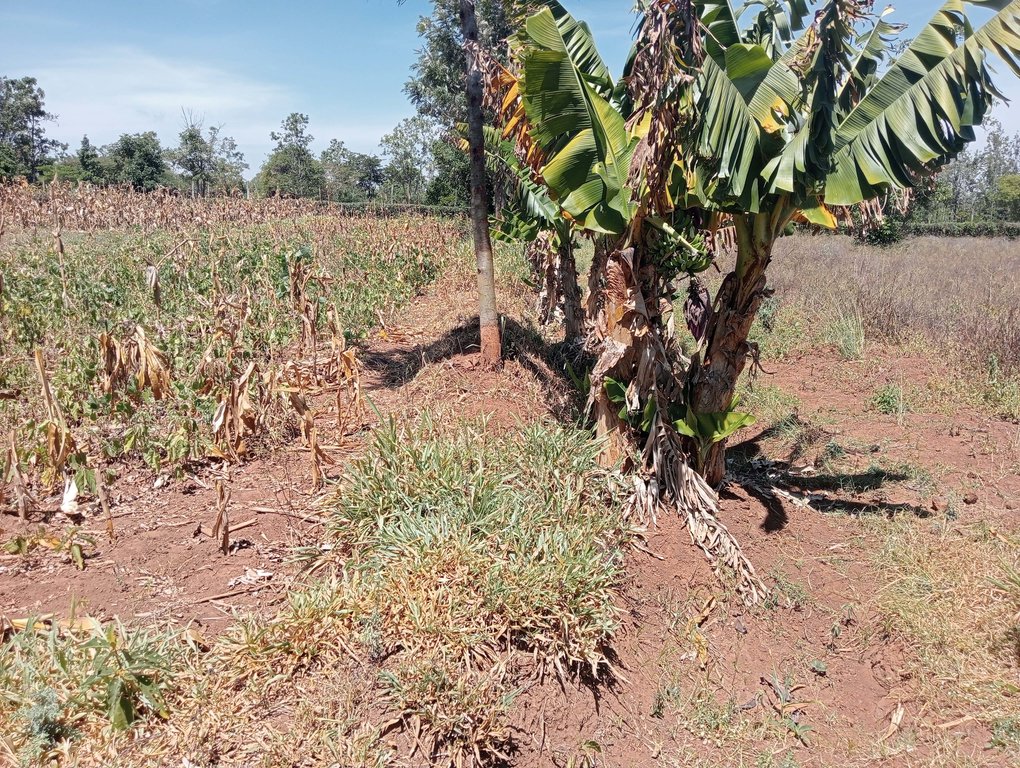
Retention ditches are soil and water conservation practices. They are channels dug along contours (i.e., across the slope), especially at the uppermost part of the farm to retain stormwater/ surface runoff. They typically comprise two components: (a) vegetational-biological and (b) mechanical-structural components which are integrated to collect surface runoff, allowing for sediment carried by runoff to settle as water infiltrates into the ground. The mechanical-structural component consists of channels dug in such a way that they follow the contour and run perpendicular to the flow of water in areas where runoff naturally flows or collects. The soil excavated from the ditch forms a bund below the ditch. Retention ditches prevent surface runoff from outside the farm from flowing into or through the farm. The vegetational-biological component consists of plants grown on the bunds. The plant roots bind the soil thus increasing the slope stability, especially of the bunds; thus, preventing soil from collapsing and falling back into the channel. Retention ditches thus harvest and retain water (especially in low rainfall areas) preventing fertile soil from being washed away by surface runoff and increasing water availability for plants. In high-rainfall areas, they play the role of discharging excessive runoff into waterways.
Retention ditches are dug to about 60 cm deep and about 50 cm wide. To ensure stability, especially in areas with unstable soils, the top width is made wider than the bottom width allowing for slanting walls that are more stable than vertical walls. An understanding of the slope angle is an important factor in the designing and construction of retention ditches. A line-level (a spirit level attached to a string suspended between two poles) can be used to determine the measure slope. The slope angle determines the size of the ditch (depth and width) and the spacing between successive ditches on the same piece of land. In low-rainfall areas (such as Siaya), retention ditches are spaced at about 50 – 70 m while in high-rainfall areas the space between the ditches are closer (about 20 m). Similarly, the size of the retention ditches increases with increasing slope.
Some crops, especially bananas, arrowroot, etc. that demand a lot of water can be established in the ditches. Maintenance of retention ditches involves regular desilting, whenever the ditch is about 1/3 filled with silt. Hoes, shovels/ spades, and a panga (machete) are some of the tools used in digging and maintaining retention ditches. Farmers like retention ditches because they help in controlling soil erosion.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Siaya County, Nyanza Region
有关地点的进一步说明:
Uloma Village, Bondo Municipality, Bondo Sub-county
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
The farm where the technology is implemented is not in a protected area.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2018
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Soil Protection and Rehabilitation of Degraded Soil for Food Security (ProSoil) project
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 饲料作物 - 其他
- 饲料作物 - 草
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 蔬菜 - 其他
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 其他
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
年作制度:
休耕 - 玉米/高粱/谷子与豆类间作
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
- 饲料作物 - 草
- fodder crops - legumes, clover
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 饲料树木(朱缨花属、银合欢、前庭草等)
- 鳄梨
- 水果、其他
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
- 木瓜
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Long and short rain seasons
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Maize and legumes e.g., beans
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Some sections of the farm are left fallow during the short rains to allow for soil regeneration.

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- 家禽
是否实行作物与牲畜的综合管理?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Fodder (nappier grass) planted on the berms is fed to the cattle. The manure from the cattle and droppings from the chicken is used as manure for the crops.
产品和服务:
- 奶类
- 蛋类
- 肉类
品种:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
计数:
3
品种:
家禽
计数:
100
注释:
There are assorted trees on the farm, including fruit trees. Some of the trees are planted on the berm of the retention ditches.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Crops are planted only during the rainy seasons since there is no irrigation.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 引水和排水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑
注释:
Trees and grasses are planted on the berms of the retention ditches.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
注释:
The retention ditches, especially when applied at the top of a plot and the design is to heap the soil below the channel ('fanya chini') has helped control gully erosion. Gullies were common in the farm before the digging of the retention ditches.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
The retention ditches saved the land from gullies, and are still controlling soil erosion.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Ditch dimensions: length = 70m, width = 50cm, depth = 60cm
Slope of the field = 4%
Plants on the berm: nappier grass
作者:
William Akwanyi
日期:
01/07/2023
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
0.4 ha
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
KES
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
122.95
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
300
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slope measurement and determination of position for the retention ditch | During the dry season |
| 2. | Digging the ditches | Before onset of rains |
注释:
The ditches should be constructed during the dry season or before the rains start when the soil is light and easy to remove from the ditches.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Digging the ditches | Man days | 10.0 | 300.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hoe | No. | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Panga (broad blade) | No. | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Wheelbarrow | No. | 1.0 | 800.0 | 800.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Spade | No. | 1.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Planting rope | No. | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Spirit level | No. | 1.0 | 600.0 | 600.0 | |
| 其它 | Slope measurement and determination of position for the retention ditch (professional service) | Professional service | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 6690.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 54.41 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
ProSoil project
注释:
The costs of the implements are KES 400/- for a hoe, KES 4,000/- for a wheelbarrow, KES 300/- for a planting rope and broad blade, KES 3,000/- for a spirit level, and KES 450/- for a spade. It is assumed that the farmer will be able to use the hoe, planting rope, broad blade, and spade over a period of 5 years, and a wheelbarrow over a period of 10 years before these implements will have depreciated to a point where they will not be useable. The cost is thus spread over the years when the farmer will be able to use the implement.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desilting | Whenever the ditch is about 1/3 filled with silt |
注释:
Maintenance activities do not happen at regular intervals but depend on volume of runoff and amount of silt carried by surface runoff for desilting the ditch, rate of growth of weeds for weeding, and factors that lead to lead of plants for plant re-establishment.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
2000.0
注释:
the above cost is based on the farmer's estimate.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Rate of man-days vary from one place to another and also depend on the kind of work.
Exchange rate for January 2023, source: European Commission/ InfoEuro online at https://commission.europa.eu/funding-tenders/procedures-guidelines-tenders/information-contractors-and-beneficiaries/exchange-rate-inforeuro_en
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Rainfall pattern is bimodal. Monthly rainfall variability is high with some months such as January recording less than 5 mm of total rainfall.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Bondo Meteorological Station
农业气候带
- 半干旱
The area is found near Lake Victoria which influences the climate.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凸形情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Retention ditches divert the flow of surface runoff. The slope of the farmer's field is 4%.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
N/A
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
There are several boreholes in the area and according to interviews with some borehole owners, the depts are not more than 50 metres. Lake Victoria is a permanent surface water body in the area.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
The area has high agrobiodiversity as most farms are under crops and trees.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 半游牧的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The farmer uses the land together with his other family members.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
Farmers with more than 2 ha in the area are considered to have large pieces of land since there is high level of land fragmentation in the area.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
具体说明:
Each landowner has full control of the way he/ she wants to use his/ her land.
注释:
The farmer has a title for his piece of land.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
注释:
The above rating varies from one village to the other.
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
2
SLM之后的数量:
4
注释/具体说明:
Quantity refers to the number of 90 Kg bags of maize produced per acre. Based on estimation by the farmer.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Not easy to quantify but according to the farmer, the crops are doing better compared to how they were before the retention ditches were dug.
饲料生产
SLM之前的数量:
1
SLM之后的数量:
3
注释/具体说明:
Quantity refers to harvesting cycles for nappier grass from the same farm. Based on estimation by the farmer.
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Not easy to quantify but according to the farmer, fodder is doing better compared to how it was before the retention ditches were dug.
畜牧生产
SLM之前的数量:
1
SLM之后的数量:
3
注释/具体说明:
Quantity refers to the amount of milk in litres from one cow. Milk production is often at the peak during early lactation months. Based on estimation by the farmer.
生产故障风险
SLM之前的数量:
80
SLM之后的数量:
40
注释/具体说明:
Quantity refers to the percentage probability of the crop failing to do well. Based on estimation by the farmer.
收入和成本
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Refers to the number of hours that the farmer can be free in any working day. During the rainy season, the farmer spends some time desilting the ditches. Based on estimation by the farmer.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
5
SLM之后的数量:
2
注释/具体说明:
Quantity refers to the number of months in a year when there is total lack of food in the house, and the farmer has to buy all the food required in the house. Based on estimation by the farmer.
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
10%
SLM之后的数量:
80%
注释/具体说明:
Quantity refers to the estimated percentage of knowledge in SLM/ land management. This is a farmer's estimate.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
注释/具体说明:
Not easy to quantify. Based on estimation by the farmer.
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Refers to the amount of water that flows through the farm. Not easy to quantify. Based on estimation by the farmer.
土壤
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Not easy to quantify.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Refers to the farmer's estimated percentage vegetation cover at the farm. Based on estimation by the farmer.
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
No recorded data is available for reference. All are estimates based on the farmer's explanation or as given by her.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Not easy to quantify. Retention ditches have reduced the amount of water that flows to the farms in the lower areas. This has reduced soil erosion in these farms.
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
Not easy to quantify. All silt is deposited in the retention ditches and scooped by the farmer for replenishing parts of the farm with low soil levels.
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Not easy to quantify. Retention ditches have reduced the amount of water that flows to the farms in the lower areas. This has reduced soil erosion in these farms.
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
It was not possible for the farmer to quantify the above.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 旱季 | 增加 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The retention ditches have generally improved crop production.
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Controls soil erosion. Silt collected in the ditches is used to replenish other sections of the farm with poor soils. |
| Improved crop yields. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Controls road damage due to runoff as most of the water is collected by the ditches before it destroys the road. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Establishment investment is capital and labour intensive. | The farmer has to be committed. |
| Maintenance is labour intensive. | The farmer has to be committed. Proper planning of farm work. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| If not managed properly by regular removal of silt, the ditch can easily fill up. | The farmer must be committed to remove silt regularly. |
| May overflow and collapse during high rainfall leading to high levels of soil erosion. | Proper designing in consideration of runoff volumes and slope angle. Regular maintenance. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
One visit at one farm
- 与土地使用者的访谈
One farmer interviewed at his farm. Follow-up questions on phone.
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
ProSoil team and project implementers from Welthungerhilfe consulted.
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Siaya County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022 and online sources reviewed.
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
27/01/2023
注释:
One field visit and several follow-up consultations.
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Climate Smart Extension Manual by KCEP - CRAL, 2021
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Download free at https://www.kalro.org/files/kcep/CSA-extension-manual-18-06-21.pdf
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Siaya County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022
URL:
https://repository.kippra.or.ke/bitstream/handle/123456789/1218/2018-2022%20%20Siaya%20County%20CIDP.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
7.4 一般注释
1. Provide a function to be able to link the documented SLM to similar work that has been documented in other databases e.g., LandPortal, UNCCD, etc.
2. Some of the impacts (section 6) cannot be quantified.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Community Resource Persons (CRP) in agricultural extension [肯尼亚]
Community Resource Persons (CRP) form a farmer-to-farmer learning approach that bridges the gap in agricultural extension, increases farmers' access to agricultural information (SLM knowledge), and increases the adoption of SLM practices.
- 编制者: William Akwanyi
模块
无模块